Spatial Smoothing Regularization for Bi-direction Long Short-term Memory Model
-
摘要:
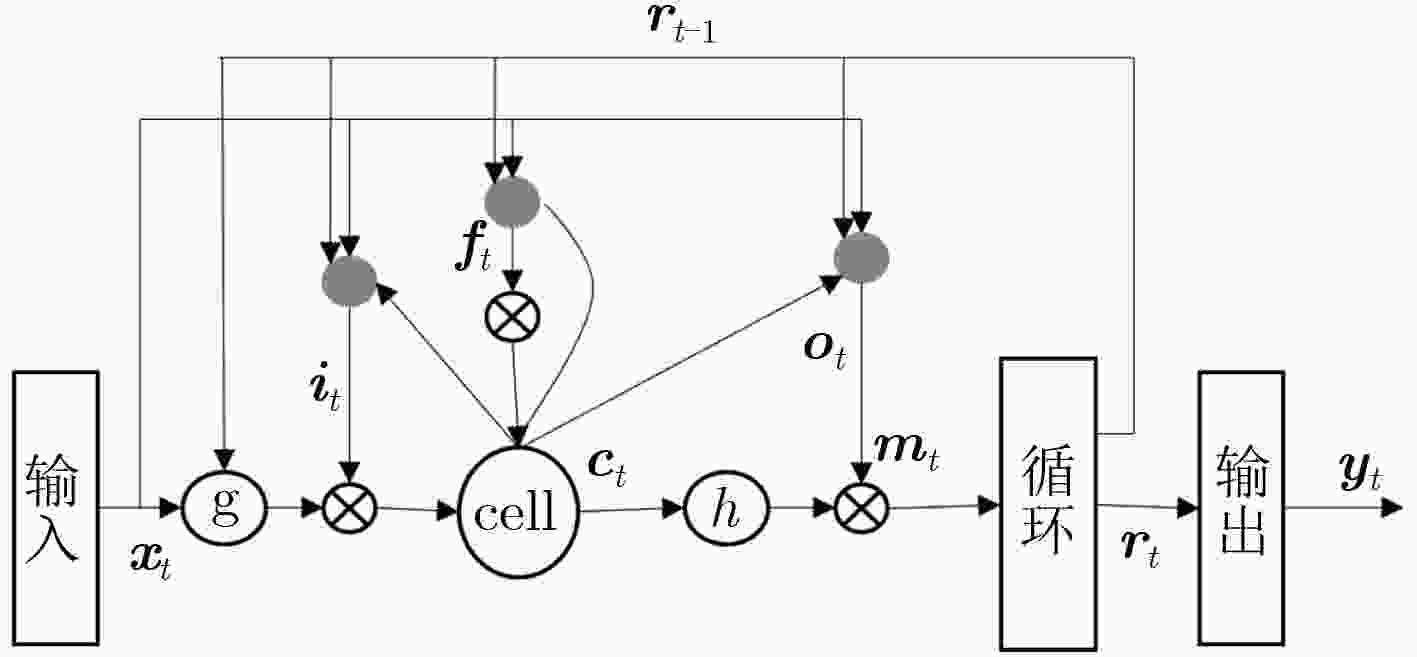
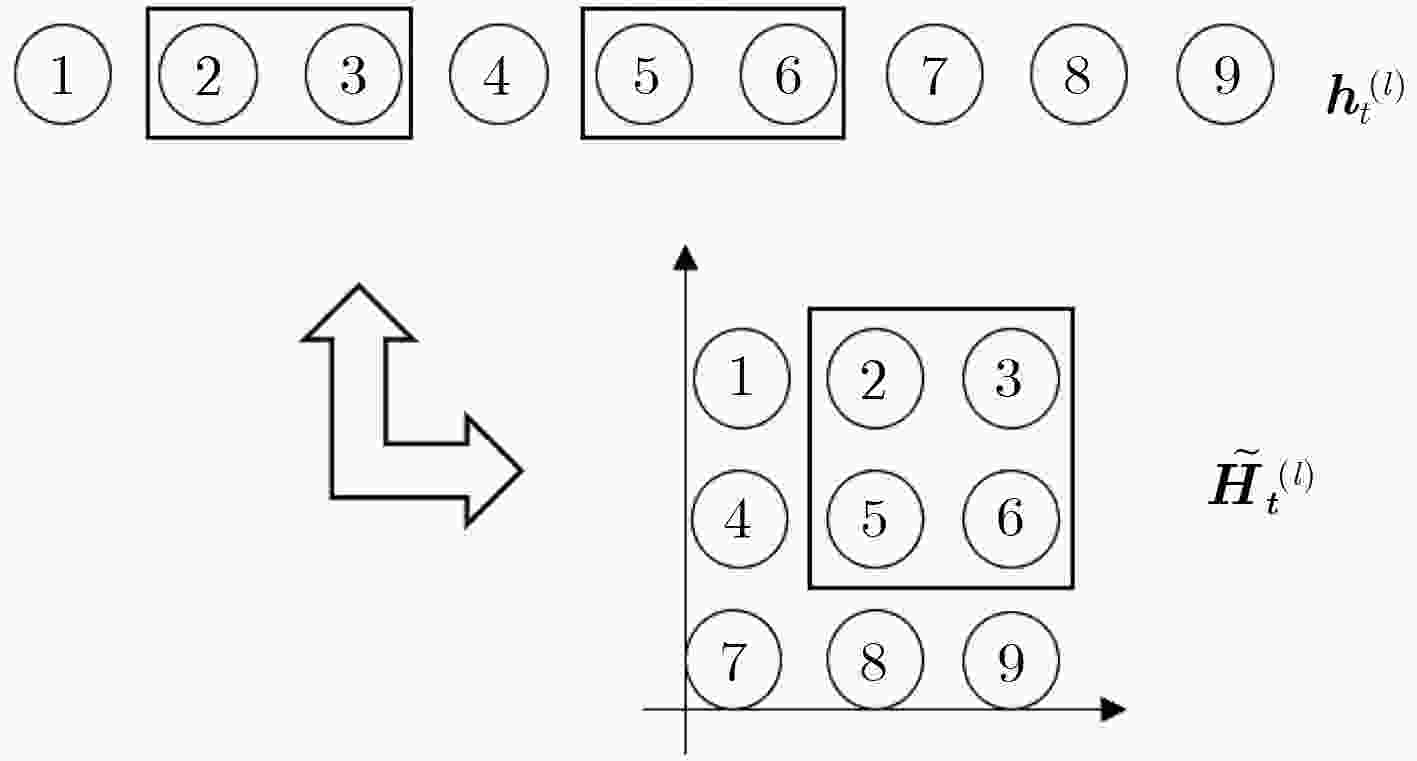
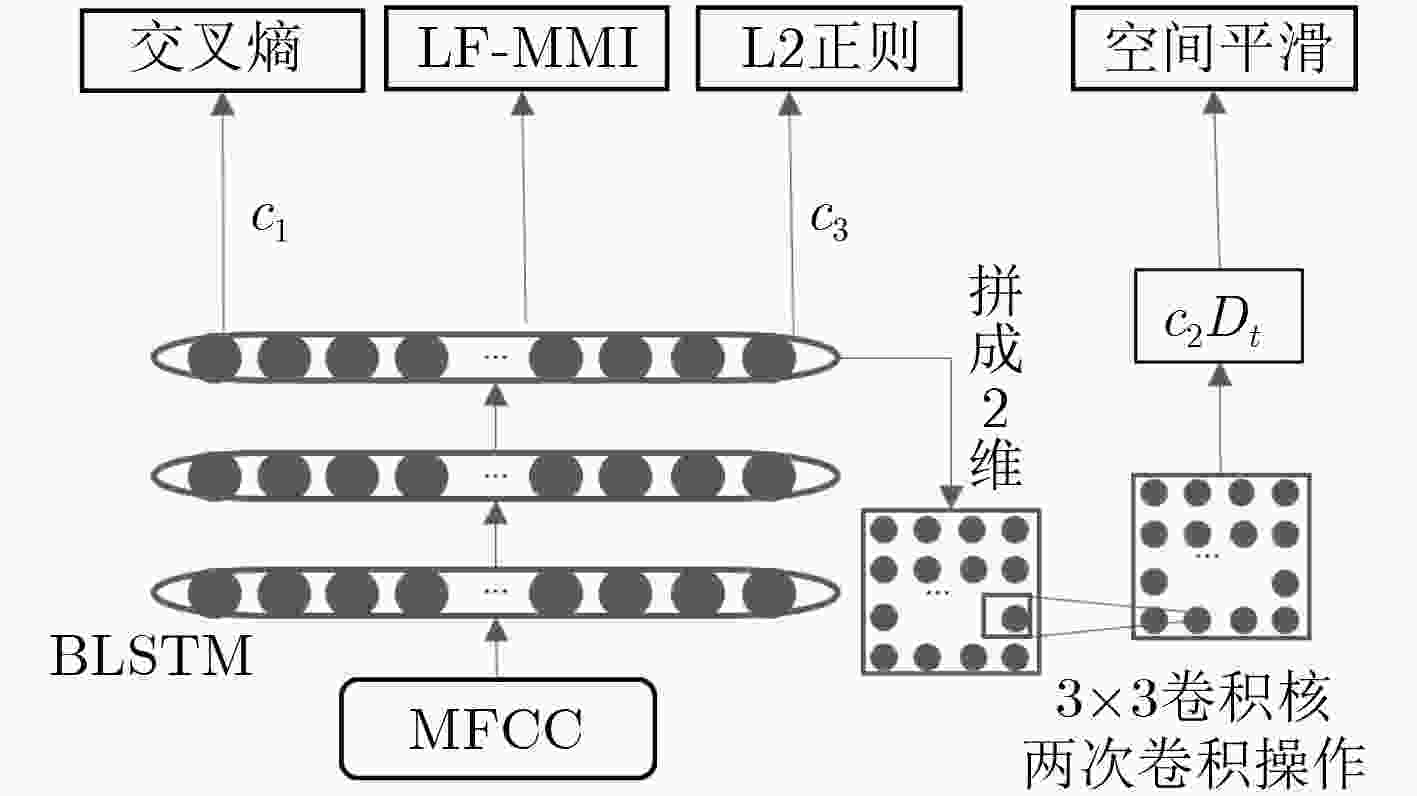
双向长短时记忆模型(BLSTM)由于其强大的时间序列建模能力,以及良好的训练稳定性,已经成为语音识别领域主流的声学模型结构。但是该模型结构拥有更大计算量以及参数数量,因此在神经网络训练的过程当中很容易过拟合,进而无法获得理想的识别效果。在实际应用中,通常会使用一些技巧来缓解过拟合问题,例如在待优化的目标函数中加入L2正则项就是常用的方法之一。该文提出一种空间平滑的方法,把BLSTM模型激活值的向量重组成一个2维图,通过滤波变换得到它的空间信息,并将平滑该空间信息作为辅助优化目标,与传统的损失函数一起,作为优化神经网络参数的学习准则。实验表明,在电话交谈语音识别任务上,这种方法相比于基线模型取得了相对4%的词错误率(WER)下降。进一步探索了L2范数正则技术和空间平滑方法的互补性,实验结果表明,同时应用这2种算法,能够取得相对8.6%的WER下降。
-
关键词:
- 语音信号处理 /
- 空间平滑 /
- 双向长短时记忆模型(LSTM) /
- 正则化 /
- 过拟合
Abstract:Bi-direction Long Short-Term Memory (BLSTM) model is widely used in large scale acoustic modeling recently. It is superior to many other neural networks on performance and stability. The reason may be that the BLSTM model gets complicated structure and computation with cell and gates, taking more context and time dependence into account during training. However, one of the biggest problem of BLSTM is overfitting, there are some common ways to get over it, for example, multitask learning, L2 model regularization. A method of spatial smoothing is proposed on BLSTM model to relieve the overfitting problem. First, the activations on the hidden layer are reorganized to a 2-D grid, then a filter transform is used to induce smoothness over the grid, finally adding the smooth information to the objective function, to train a BLSTM network. Experiment results show that the proposed spatial smoothing way achieves 4% relative reduction on Word Error Ratio (WER), when adding the L2 norm to model, which can lower the relative WER by 8.6% jointly.
-
表 1 不同位置空间平滑的结果
空间平滑
位置空间平滑
权重(c)CallHm WER (%) Swbd WER (%) 总计WER (%) 无 无 20.0 10.3 15.2 P1 0.0020 19.9 10.4 15.2 P1 0.0010 19.9 10.0 15.0 P1 0.0007 20.0 10.3 15.2 P2 0.0020 19.7 10.0 14.9 P2 0.0010 19.7 9.8 14.8 P2 0.0007 19.9 9.8 15.0 P3 0.0020 20.1 10.3 15.2 P3 0.0010 20.0 9.8 15.0 P3 0.0007 20.0 10.1 15.1 P4 0.0010 20.9 10.6 15.8 P4 0.0007 20.6 10.3 15.5 P4 0.0006 20.5 10.6 15.6 表 2 不同权重下的细胞状态值
${{{c}}_t}$ 的空间平滑结果空间平滑权重
(c)CallHm WER
(%)Swbd WER
(%)总计WER
(%)无 20.0 10.3 15.2 0.0100 20.3 10.4 15.4 0.0010 19.7 9.8 14.8 0.0009 19.3 9.8 14.6 0.0008 19.6 9.7 14.7 0.0007 19.9 9.8 15.0 表 3 网络中添加L2正则后的结果
L2正则
有/无空间平滑
有/无CallHm WER (%) Swbd WER (%) 总计WER (%) 无 无 20.0 10.3 15.2 无 有 19.3 9.8 14.6 有 无 19.0 9.5 14.3 有 有 18.5 9.3 13.9 -
LI X, and WU X. Constructing long short-term memory based deep recurrent neural networks for large vocabulary speech recognition[C]. IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Brisbane, Australia, 2015: 4520–4524. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP.2015.7178826. CHEN K and HUO Q. Training deep bidirectional LSTM acoustic model for LVCSR by a context-sensitive-chunk BPTT approach[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech and Language Processing (TASLP) , 2016, 24(7): 1185–1193. doi: 10.1109/TASLP.2016.2539499 AXELROD S, GOEL V, Gopinath R, et al. Discriminative estimation of subspace constrained gaussian mixture models for speech recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2007, 15(1): 172–189. doi: 10.1109/TASL.2006.872617 POVEY D, KANEVSKY D, KINGSBURY B, et al. Boosted MMI for model and feature-space discriminative training[C]. IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Las Vegas, USA, 2008: 4057–4060. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP.2008.4518545. POVEY D and KINGSBURY B. Evaluation of proposed modifications to MPE for large scale discriminative training[C]. IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Honolulu, USA, 2007: 321–324. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP.2007.366914. HUANG Z, SINISCALCHI S M, and LEE C H. Hierarchical Bayesian combination of plug-in maximum a posteriori decoders in deep neural networks-based speech recognition and speaker adaptation[J]. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2017, 98(15): 1–7. doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2017.08.001 POVEY D. Discriminative training for large vocabulary speech recognition[D].[Ph.D. dissertation], University of Cambridge, 2003. ZHOU P, JIANG H, DAI L R, et al. State-clustering based multiple deep neural networks modeling approach for speech recognition[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech and Language Processing (TASLP) , 2015, 23(4): 631–642. doi: 10.1109/TASLP.2015.2392944 SRIVASTAVA N, HINTON G, KRIZHEYSKY A, et al. Dropout: A simple way to prevent neural networks from overfitting[J]. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2014, 15(1): 1929–1958. GOODFELLOW I, BENGIO Y, and COURVILLE A, Deep Learning[M], Cambridge, MA: MIT Press, 2016: 228–230. POVEY D, PEDDINTI V, GALVEZ D, et al. Purely sequence-trained neural networks for ASR based on lattice-free MMI[C]. International Speech Communication Association (INTERSPEECH), San Francisco, USA, 2016: 2751–2755. doi: 10.21437/Interspeech.2016-595. SAHRAEIAN R, and VAN D. Cross-entropy training of DNN ensemble acoustic models for low-resource ASR[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2018, 26(11): 1991–2001. doi: 10.1109/TASLP.2018.2851145 LIU P, LIU C, JIANG H, et al. A constrained line search optimization method for discriminative training of HMMs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2008, 16(5): 900–909. doi: 10.1109/TASL.2008.925882 WU C, KARANASOU P, GALES M J, et al. Stimulated deep neural network for speech recognition[C]. International Speech Communication Association (INTERSPEECH), San Francisco, USA, 2016: 400–404. doi: 10.21437/Interspeech.2016-580. Wu C, CALES M J F, RAGNI A, et al. Improving interpretability and regularization in deep learning[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech and Language Processing (TASLP) , 2018, 26(2): 256–265. doi: 10.1109/TASLP.2017.2774919 KO T, PEDDINTI V, POVEY D, et al. Audio augmentation for speech recognition[C]. International Speech Communication Association (INTERSPEECH), Dresden, Germany, 2015: 3586–3589. doi: 10.21437/Interspeech.2015-571. LAURENT C, PEREYRA G, BRAKEL P, et al. Batch normalized recurrent neural networks[C]. IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Shanghai, China, 2016: 2657–2661. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP.2016.7472159. -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
