Fast Cross-range Scaling for ISAR Imaging Based on Pseudo Polar Fourier Transform
-
摘要:
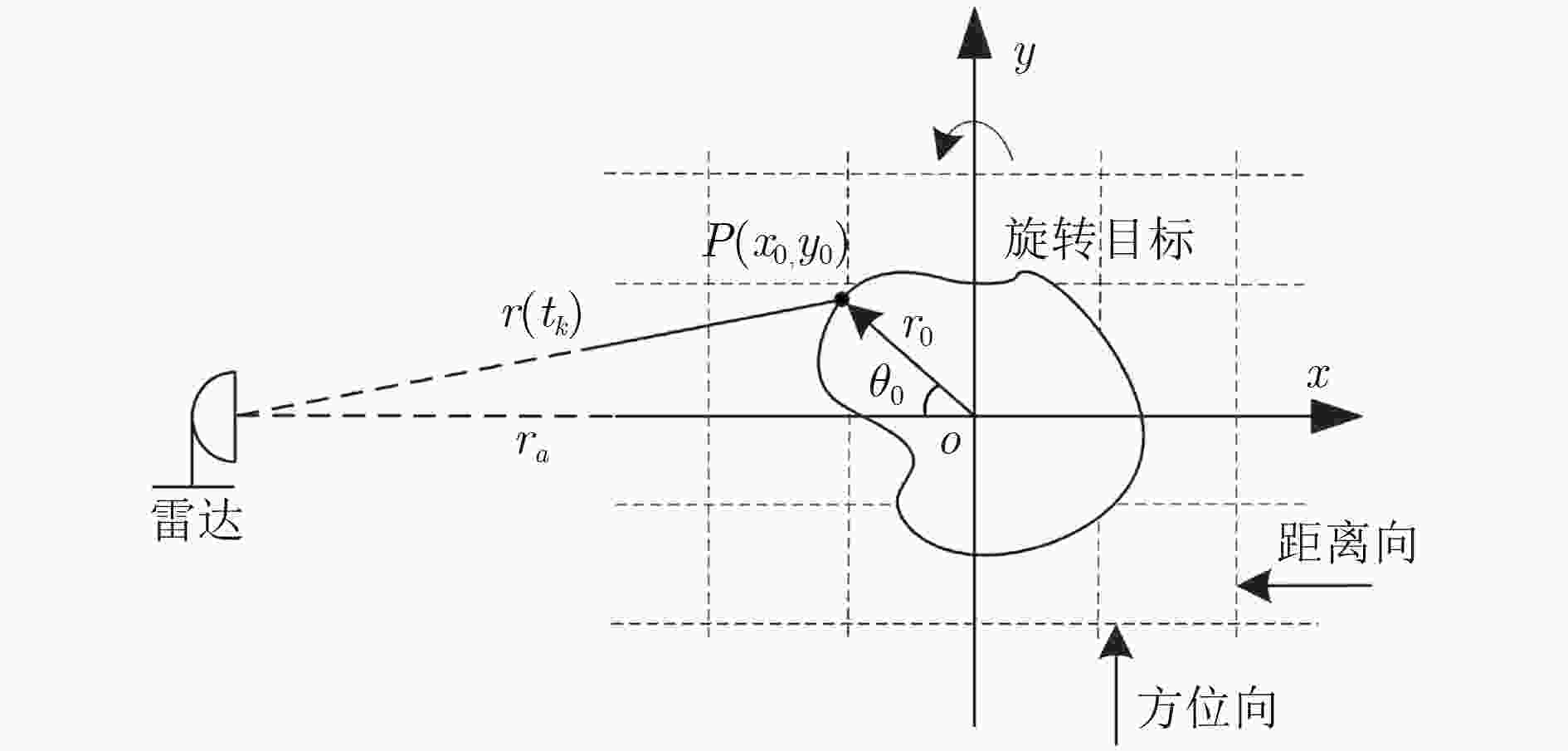
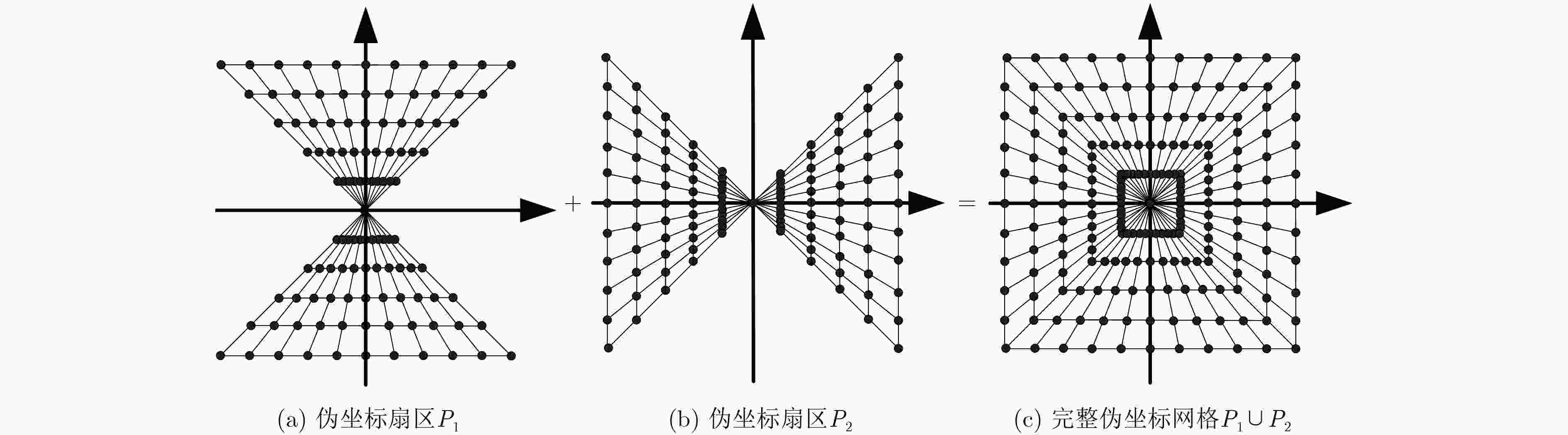
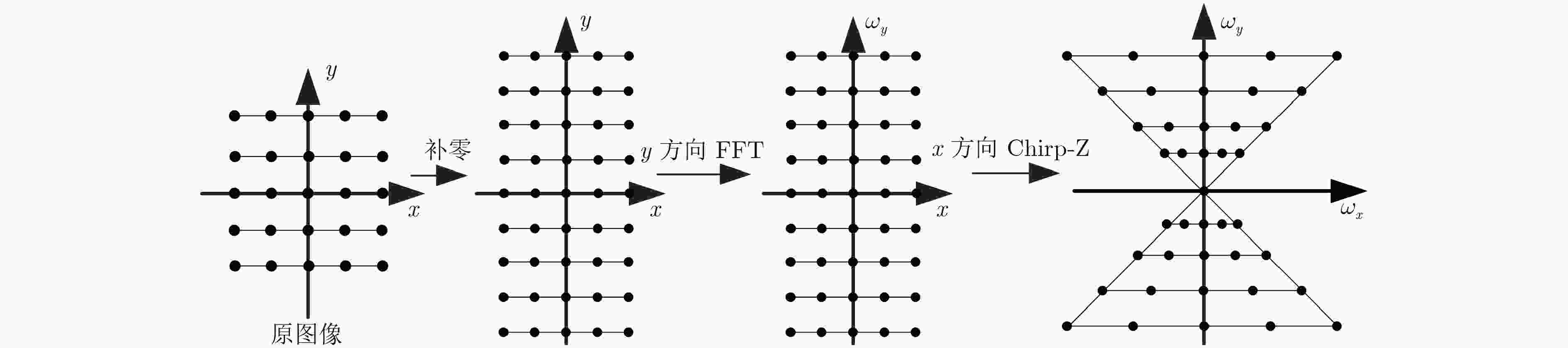
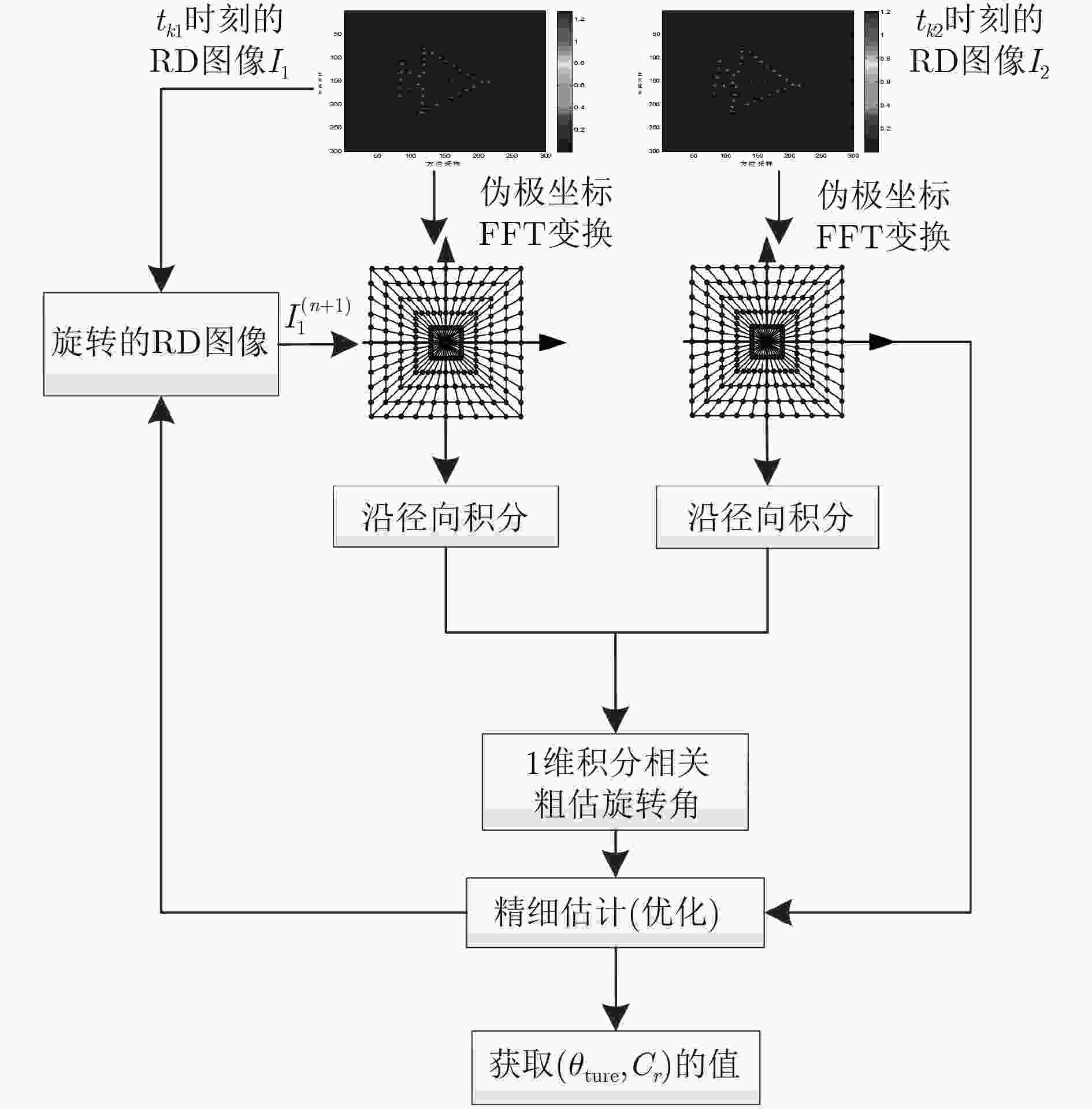
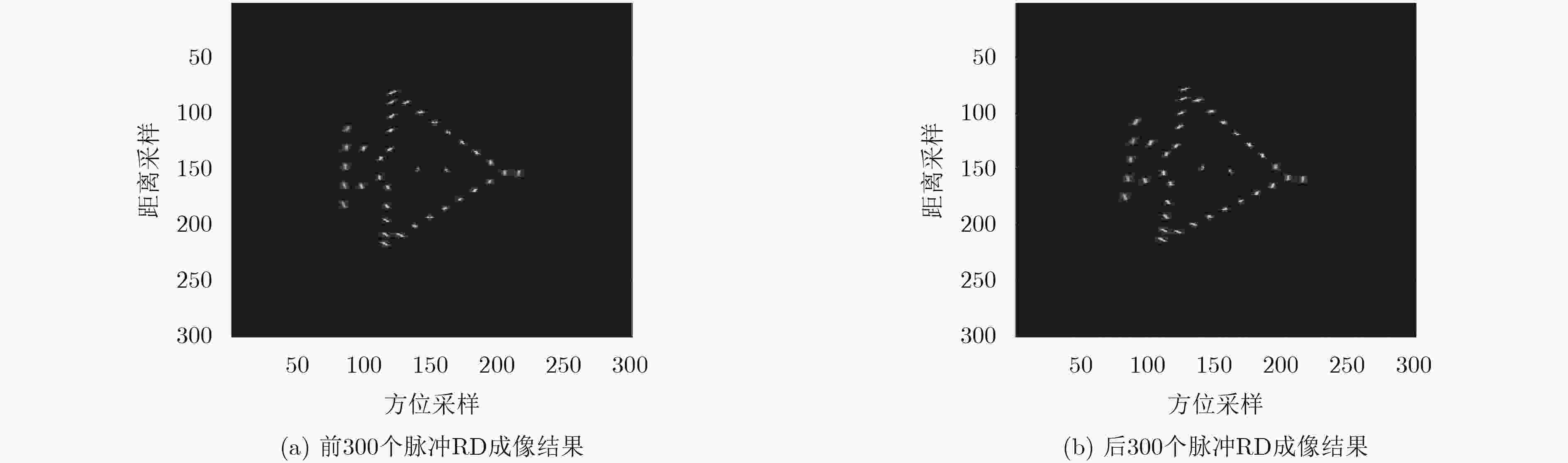
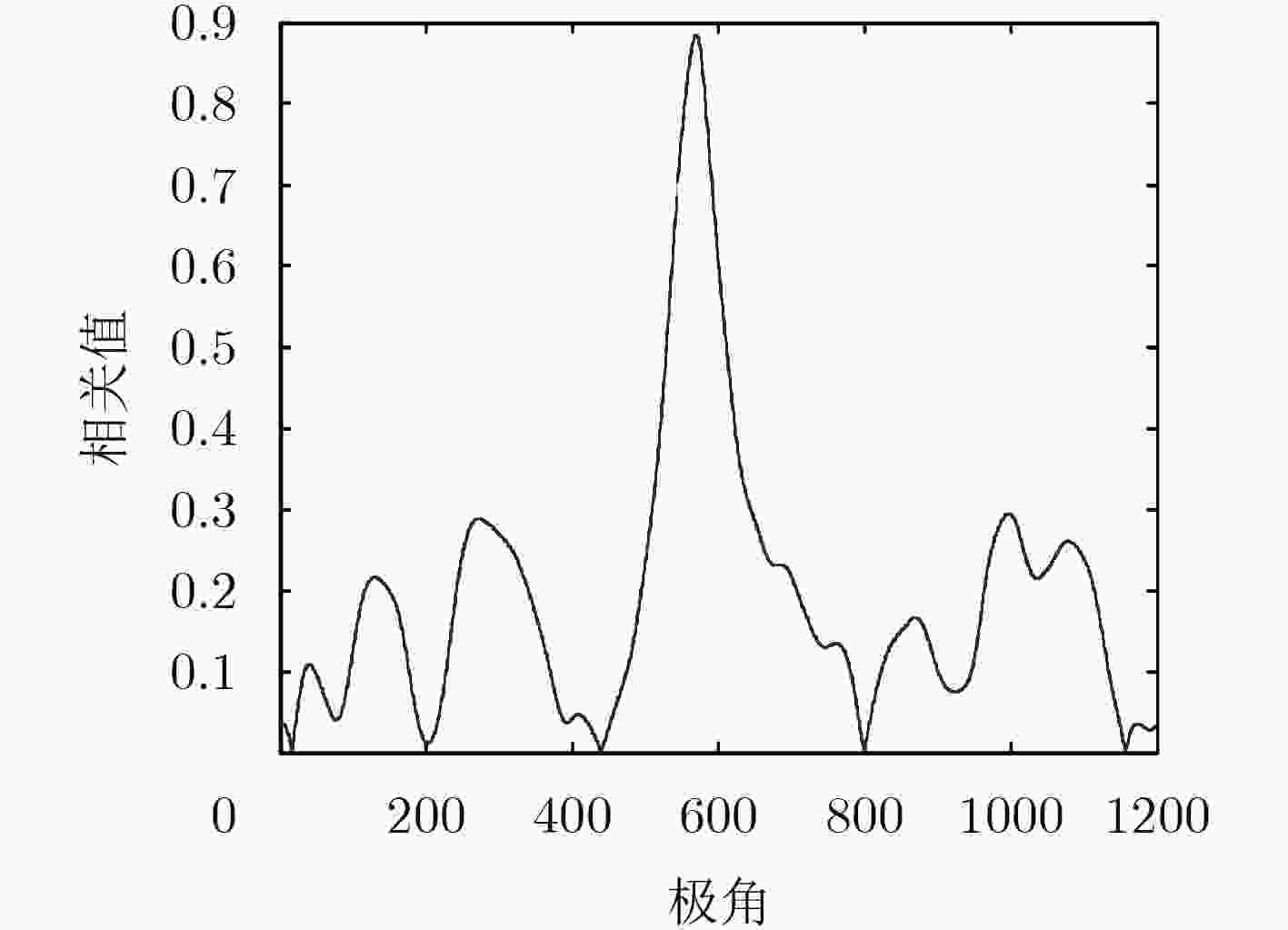
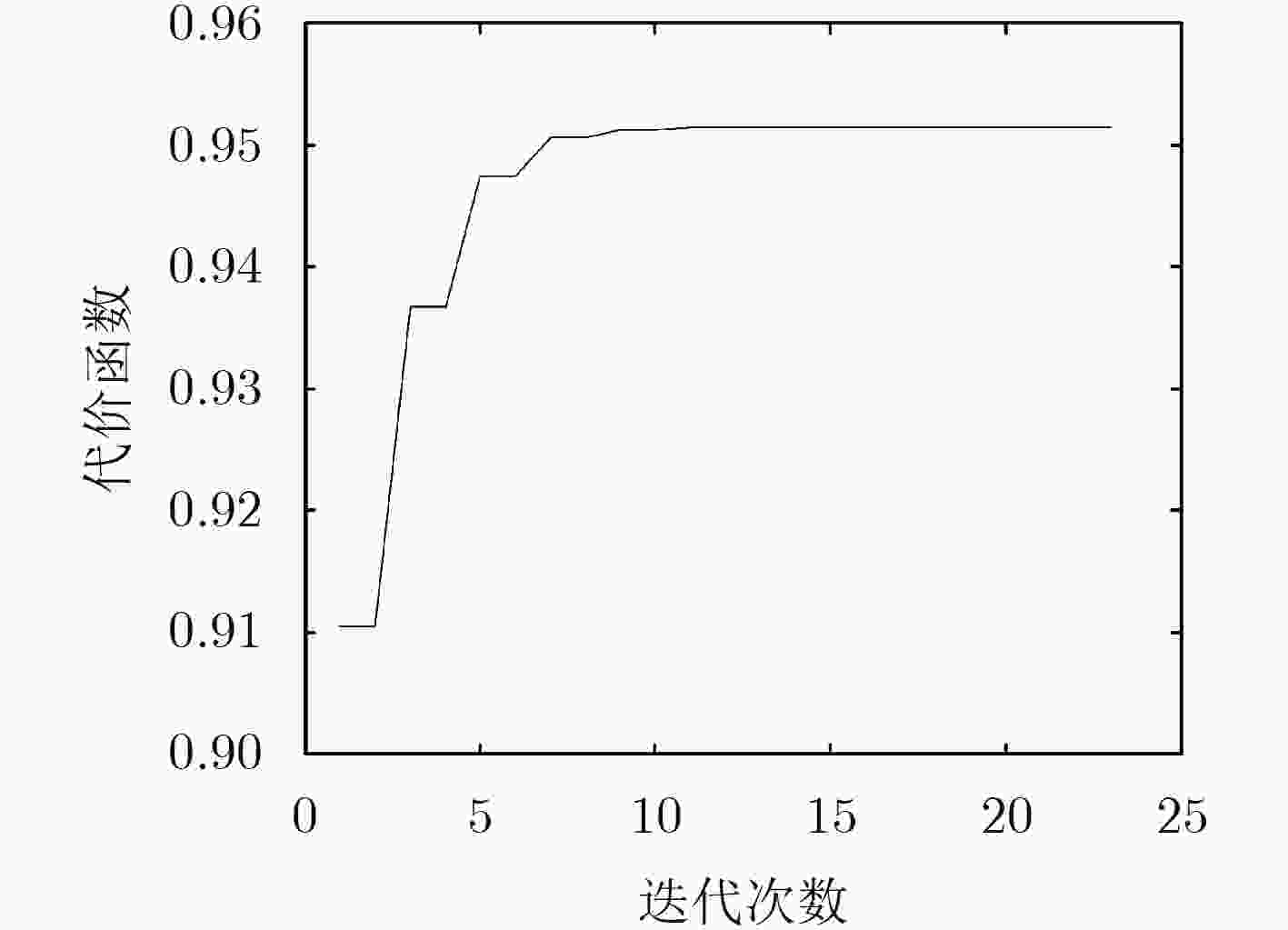
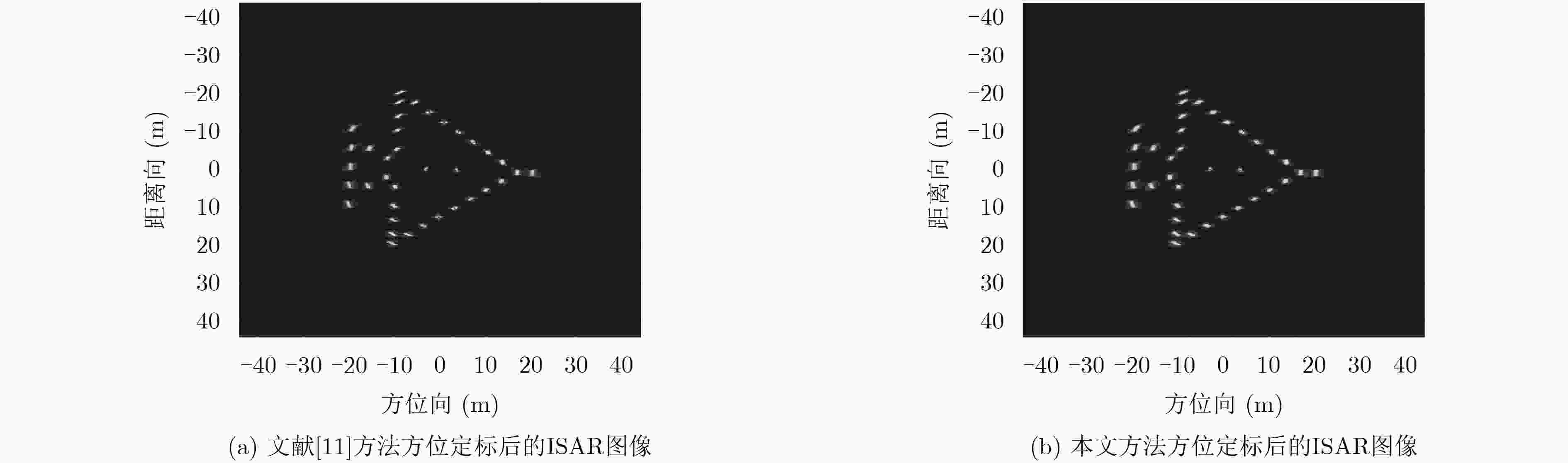
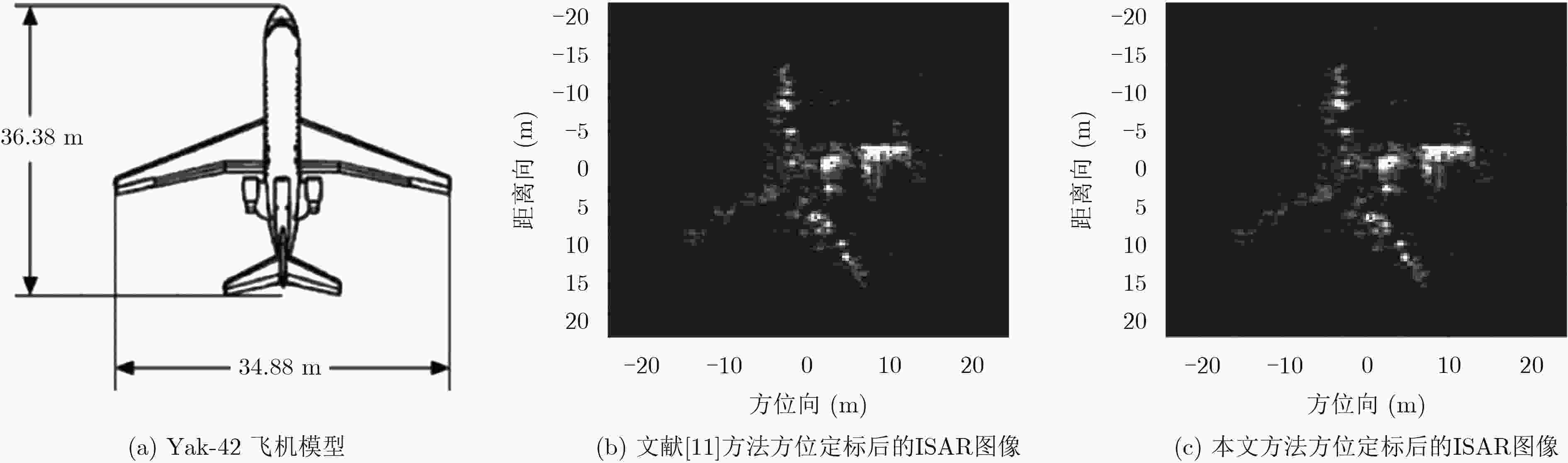
在逆合成孔径雷达(ISAR)成像中,由距离多普勒或时频分析方法得到的ISAR图像方位向仅是目标的多普勒频率分布,不能反映目标的真实形状,需对ISAR图像进行方位定标。该文提出一种快速的ISAR方位定标方法来估计目标的旋转角速度(RAV)。首先,该方法利用高效的伪逆极坐标快速傅里叶变换把两幅不同时刻ISAR图像的旋转运动转化为沿极角的平移运动。然后,在极坐标域定义了一种新的积分相关代价函数来粗估目标的RAV。最后,通过采用二分法估计得到最优的RAV,进而实现ISAR方位定标。相比于现有方位定标算法,所提方法避免了插值操作带来的精度损失和高计算复杂度问题。计算机仿真和实测数据实验结果证明了所提方法的有效性。
-
关键词:
- 逆合成孔径雷达 /
- 旋转角速度 /
- 伪逆极坐标快速傅里叶变换 /
- 二分法
Abstract:For the Inverse Synthetic Aperture Radar (ISAR) imaging, the ISAR image obtained by the Range-Doppler (RD) or time-frequency analysis methods can not display the target's real shape due to its azimuth relating to the target Doppler frequency, thus the cross-range scaling is required for ISAR image. In this paper, a fast cross-range scaling method for ISAR is proposed to estimate the Rotational Angular Velocity (RAV). Firstly, the proposed method utilizes efficient Pseudo Polar Fast Fourier Transform (PPFFT) to transform the rotational motion of two ISAR images from two different instant time into translation in the polar angle direction. Then, a new cost function called integrated correction is defined to obtain the RAV coarse estimation. Finally, the optimal RAV can be estimated using the Bisection method to realize the cross-range scaling. Compared with the available algorithms, the proposed method avoids the problems of precision loss and high computational complexity caused by interpolation operation. The results of computer simulation and real data experiments are provided to demonstrate the validity of the proposed method.
-
表 1 雷达参数和目标运动模型
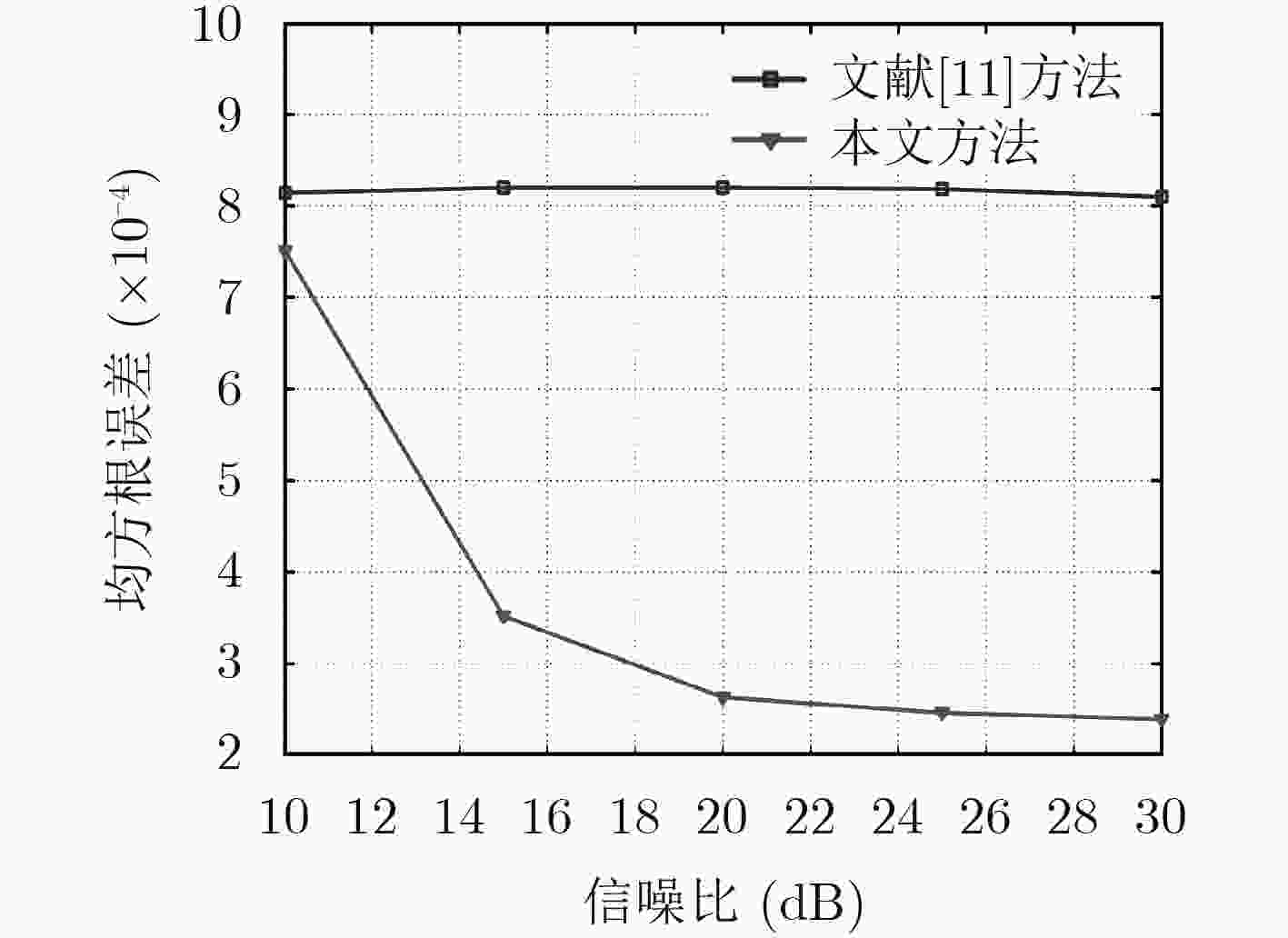
参数 数值 载波频率 5.6 GHz 波长 0.0536 m 传输信号带宽 400 MHz 距离采样频率 512 MHz 脉冲重复频率 150 Hz 有效回波脉冲 600 旋转角速度 0.0436 rad/s 表 2 两种方法运行时间对比(s)
方法名称 粗估所用时间 定标总时间 文献[11]方法 107.224 958.659 本文方法 12.203 96.712 -
XU Gang, XING Mengdao, XIA Xianggen, et al. 3D geometry and motion estimations of maneuvering targets for interferometric ISAR with sparse aperture[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience & Remote Sensing, 2017, 25(5): 2005–2020. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2016.2535362 LI Dong, ZHAN Muyang, ZHANG Xinzheng, et al. ISAR imaging of nonuniformly rotating target based on the multicomponent CPS model under low SNR environment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace & Electronic Systems, 2017, 53(3): 1119–1135. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2017.2667538 李玺, 顾红, 刘国岁. ISAR成像中转角估计的新方法[J]. 电子学报, 2000, 28(6): 44–47. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2000.06.012LI Xi, GU Hong, and LIU Guosui. A method estimating the rotation angle in ISAR imaging[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2000, 28(6): 44–47. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2000.06.012 WANG Yong and JIANG Yicheng. A novel algorithm for estimating the rotation angle in ISAR imaging[J]. IEEE Geoscience & Remote Sensing Letters, 2008, 5(4): 608–609. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2008.2000955 MARTORELLA M. Novel approach for ISAR image cross-range scaling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace & Electronic Systems, 2008, 44(1): 281–294. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2008.4517004 WANG Xin, ZHANG Min, and ZHAO Jia. Efficient cross-range scaling method via two-dimensional unitary ESPRIT scattering center extraction algorithm[J]. IEEE Geoscience & Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 12(5): 928–932. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2014.2367521 XU Zhiwei, ZHANG Lei, and XING Mengdao. Precise cross-range scaling for ISAR images using feature registration[J]. IEEE Geoscience & Remote Sensing Letters, 2014, 11(10): 1792–1796. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2014.2309604 SHENG Jialian, XING Mengdao, ZHANG Lei, et al. ISAR cross-range scaling by using sharpness maximization[J]. IEEE Geoscience & Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(1): 165–169. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2014.2330625 陈倩倩, 徐刚, 李亚超, 等. 短孔径ISAR方位定标[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2013, 35(8): 1854–1861. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2012.01252CHEN Qianqian, XU Gang, LI Yachao, et al. Cross-range scaling of short aperture ISAR[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2013, 35(8): 1854–1861. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2012.01252 YEH Chunmao, XU Jia, PENG Yingning, et al. Cross-range scaling for ISAR based on image rotation correlation[J]. IEEE Geoscience & Remote Sensing Letters, 2009, 6(3): 597–601. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2009.2021990 PARK S H, KIM H T, and KIM K T. Cross-range scaling algorithm for ISAR images using 2-D fourier transform and polar mapping[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience & Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(2): 868–877. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2060731 AVERBUCH A, COIFMAN R R, DONOHO D L, et al. A framework for discrete integral transformations I-the pseudopolar fourier transform[J]. SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing, 2014, 30(2): 764–784. KELLER Y, SHKOLNISKY Y, and AVERBUCH A. The angular difference function and its application to image registration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis & Machine Intelligence, 2005, 27(6): 969–976. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2005.128 XING Hao, MOU Yuting, FU Minyue, et al. Distributed bisection method for economic power dispatch in smart grid[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2016, 30(6): 3024–3035. doi: 10.1109/TPWRS.2014.2376935 LI Dong, LIU Hongqing, LIAO Yong, et al. A novel helicopter-borne rotating SAR imaging model and algorithm based on inverse Chirp-Z transform using frequency-modulated continuous wave[J]. IEEE Geoscience & Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 12(8): 1625–1629. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2015.2416437 -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
