A Hyperspectral Imagery Anomaly Detection Algorithm Based on Cokurtosis Tensor
-
摘要:
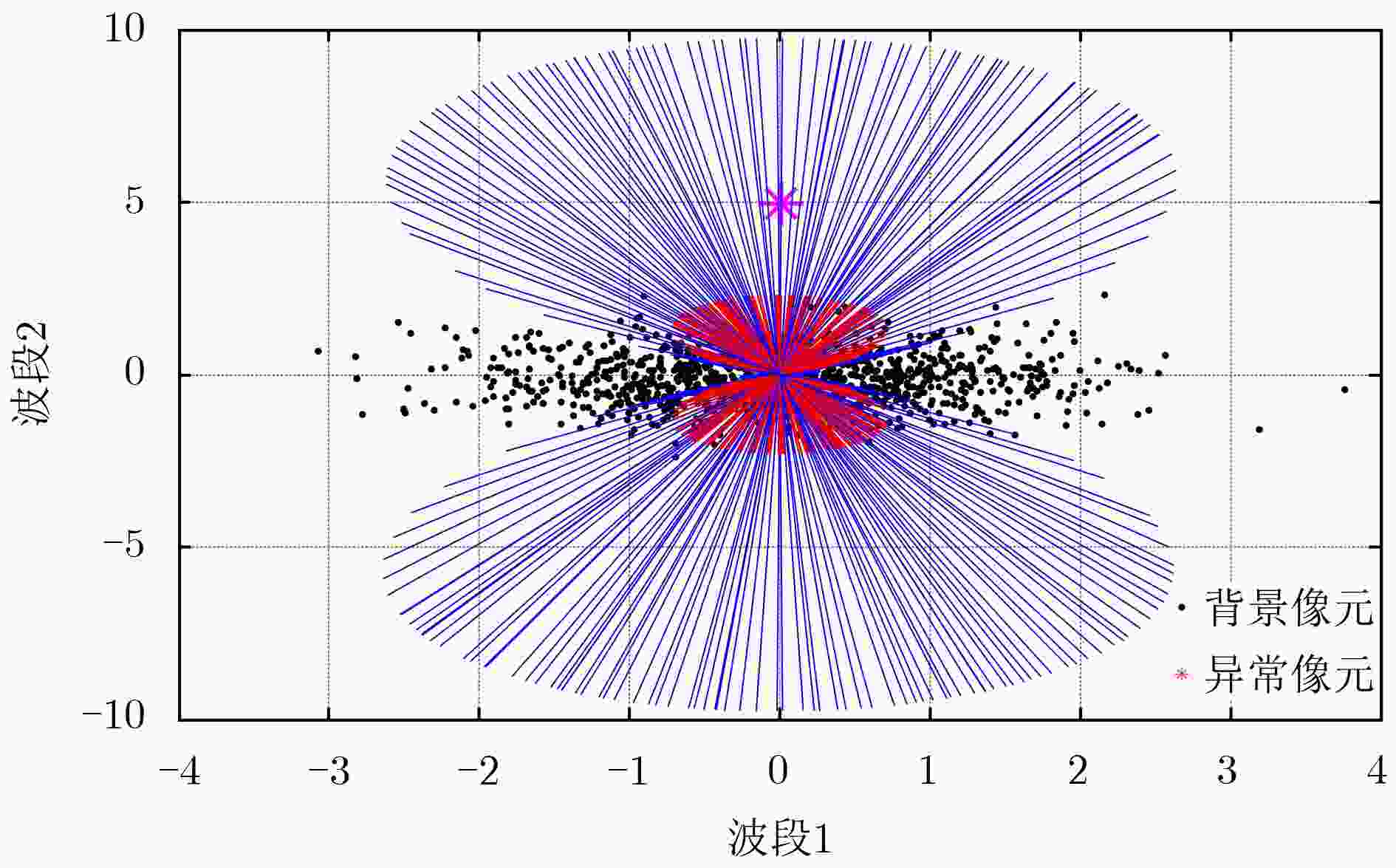
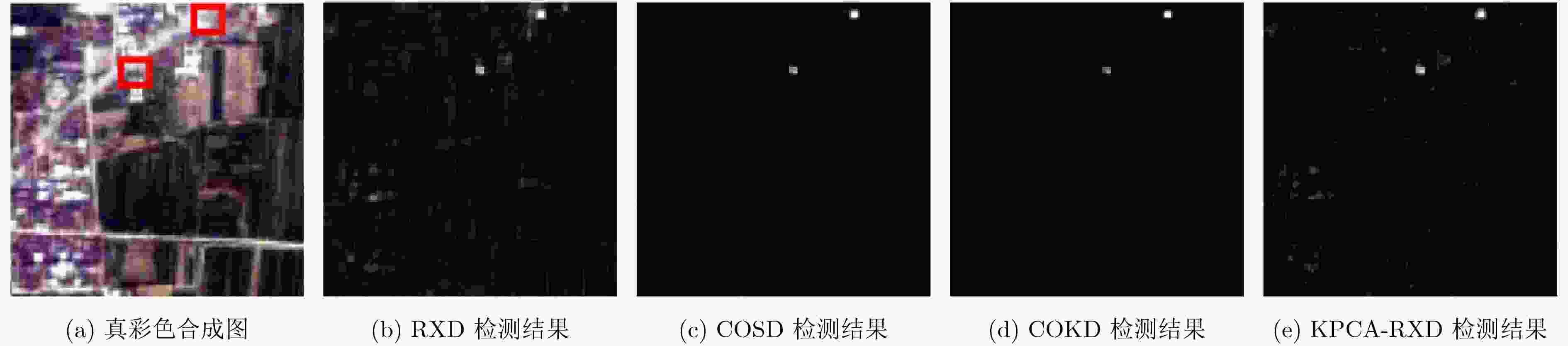
高光谱图像中的异常像元往往具有在图像中出现的概率低和游离于背景数据云团之外的特点,如何“自动”确定这些异常像元是高光谱遥感图像处理中的一个重要研究方向。经典的高光谱异常检测方法一般从图像的统计特性入手,广泛应用的RXD异常检测算法通过计算图像的2阶统计特征,可以直接给出异常点的分布情况,算法复杂度低,但缺点是没有考虑到图像的高阶统计信息。基于独立成分分析的异常检测算法虽然考虑了高阶统计量对异常点的敏感性,但需要反复迭代提取异常成分后,再对提取后的成分进行异常检测。该文提出一种基于协峭度张量的异常检测算法,该算法不需要事先提取异常成分,可以直接对观测像元进行逐一检测,从而给出异常点的分布情况。基于模拟数据和真实数据的实验结果表明,该方法能够在检测出异常像元的同时更好地压制背景信息、减小虚警率,从而提高异常检测精度。
Abstract:The abnormal pixels in hyperspectral images are often have the characteristics of low probability and scattered outside the background data cloud. How to automatically detect these abnormal pixels is an important research direction in hyperspectral imagery processing. Classical hyperspectral anomaly detection methods are usually based on statistical perspective. The RXD algorithm which is widely used can give the anomalies distribution directly through the second order statistical feature of the image, but the disadvantage is that it does not take into account the higher order statistics of the image. Anomaly detection algorithm based on Independent Component Analysis (ICA) considers the sensitivity of higher order statistics to outliers, but it needs iteration process to extract abnormal components first. And then the extracted components is used for anomaly detection. A method based on cokurtosis tensor for anomaly detection is proposed. This method does not need to extract anomaly components first. It can directly detect the observed pixels and give the distribution of abnormal pixels. Experiments results on both simulated and real data show that it can detect abnormal pixels while suppressing the background information better. Therefore, it can reduce false alarm rate and improve detection accuracy.
-
Key words:
- Hyperspectral imagery /
- Anomaly detection /
- Higher-order statistical /
- Cokurtosis tensor
-
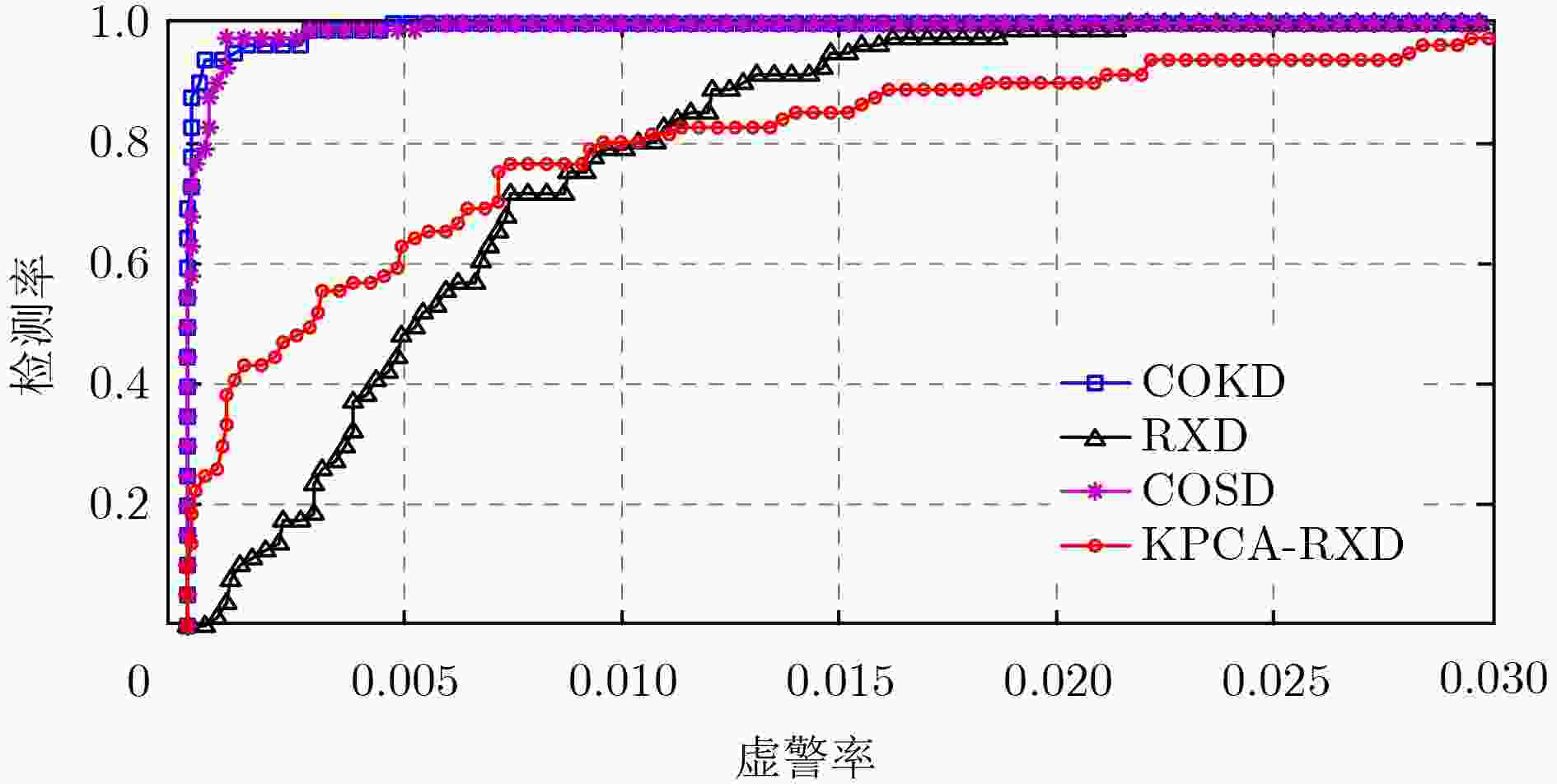
表 1 4种异常检测算法的AUC
算法 AUC COKD 0.9997 RXD 0.9934 COSD 0.9996 KPCA-RXD 0.9936 表 2 4种异常检测算法的AUC
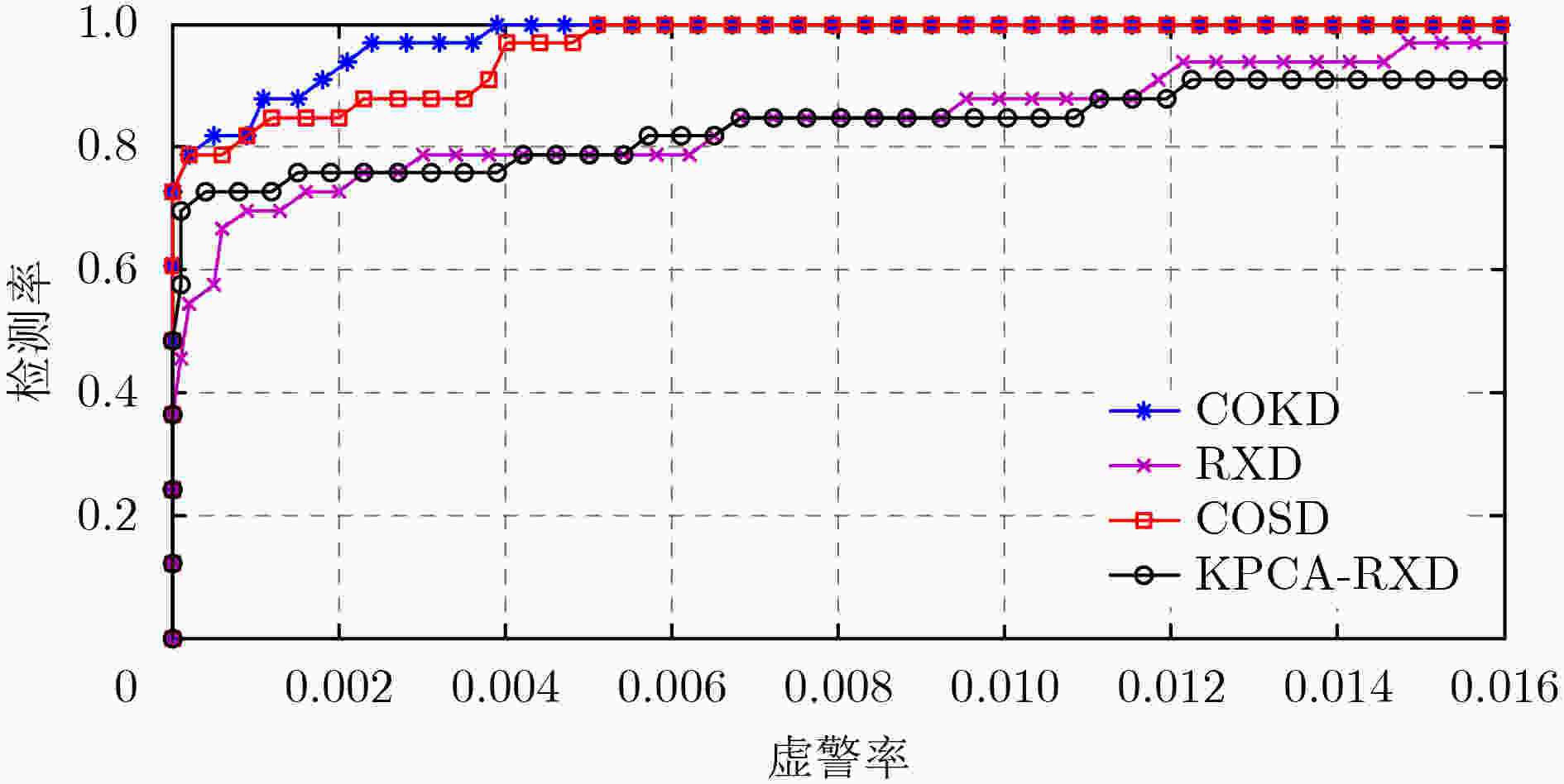
算法 AUC COKD 0.9832 RXD 0.9779 COSD 0.9830 KPCA-RXD 0.9778 -
LÜ Qi, NIU Xin, DOU Yong, et al. Classification of hyperspectral remote sensing image using hierarchical local-receptive-field-based extreme learning machine[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(3): 434–438. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2016.2517178 HEIDEN U, IWASAKI A, MULLER A, et al. Foreword to the special issue on hyperspectral remote sensing and imaging spectroscopy[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2016, 9(9): 3904–3908. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2016.2610199 LI Wei and DU Qian. A survey on representation-based classification and detection in hyperspectral remote sensing imagery[J]. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2016, 83: 115–123. doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2015.09.010 VERACINI T, MATTEOLI S, DIANI M, et al. Fully unsupervised learning of Gaussian mixtures for anomaly detection in hyperspectral imagery[C]. Ninth International Conference on Intelligent Systems Design and Applications, Pisa, Italy, 2009: 596–601. doi: 10.1109/ISDA2009220. SALEM M B, ETTABAA K S, and BOUHLEL M S. Anomaly detection in hyperspectral images based spatial spectral classification[C]. International Conference on Sciences of Electronics, Technologies of Information and Telecommunications, Hammamet, Tunisia, 2017: 166–170. doi: 10.1109/SETIT.2016.7939860. ZHANG Lili and ZHAO Chunhui. Hyperspectral anomaly detection based on spectral-spatial background joint sparse representation[J]. European Journal of Remote Sensing, 2017, 50(1): 362–376. doi: 10.1080/22797254.2017.1331697 THEILER J and ZIEMANN A K. Right spectrum in the wrong place: A framework for local hyperspectral anomaly detection[J]. Electronic Imaging, 2016, 2016(19): 1–9. doi: 10.2352/ISSN.2470-1173.2016.19.COIMG-160 CHIANG S S, CHANG C I, and GINSBERG I W. Unsupervised target detection in hyperspectral images using projection pursuit[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2001, 39(7): 1380–1391. doi: 10.1109/36.934071 WANG Lijing, GAO Kun, CHENG Xinman, et al. A hyperspectral imagery anomaly detection algorithm based on Gauss-Markov model[C]. Fourth International Conference on Computational and Information Sciences (ICCIS), Chongqing, China, 2012: 135–138. doi: 10.1109/ICCIS.2012.21. 耿修瑞. 高光谱遥感图像目标探测与分类技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 中国科学院遥感与数字地球研究所, 2005: 81–91.GENG Xiurui. Target detection and classification for hyperspectral imagery[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Institute of Remote Sensing and Digital Earth, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2015: 81–91. TAGHIPOUR A and GHASSEMIAN H. Hyperspectral anomaly detection using attribute profiles[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 14(7): 1136–1140. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2017.2700329 ZHANG Xing, WEN Gongjian, and DAI Wei. A tensor decomposition-based anomaly detection algorithm for hyperspectral image[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(10): 5801–5820. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2572400 TERREAUX E, OVARLEZ J P, and PASCAL F. Anomaly detection and estimation in hyperspectral imaging using random matrix theory tools[C]. IEEE International Workshop on Computational Advances in Multi-Sensor Adaptive Processing, Cancun, Mexico, 2016: 169–172. doi: 10.1109/CAMSAP.2015.7383763. XUN Lina and FANG Yonghua. Anomaly detection based on high-order statistics in hyperspectral imagery[C]. The Sixth World Congress on IEEE Intelligent Control and Automation, Dalian, China, 2006: 10416–10419. doi: 10.1109/WCICA.2006.1714044. REN Hsuan and CHANG Yang Lang. A parallel approach for initialization of high-order statistics anomaly detection in hyperspectral imagery[C]. IEEE International Geosciences and Remote Sensing Symposium, Boston, USA, 2008: 1017–1020. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2008.4779170. CARDOSO J F. Eigen-structure of the fourth-order cumulate tensor with application to the blind source separation problem[C]. International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Albuquerque, USA, 1990: 2655–2658. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP.1990.116165. OSAKO K, MORI Y, TAKAHASHI Y, et al. Fast convergence blind source separation based on frequency subband interpolation by null beamforming[C]. IEEE Workshop on Applications of Signal Processing to Audio and Acoustics, New Paltz, USA, 2007. doi: 10.1109/ASPAA.2007.4392999. GU Yanfeng, LIU Ying, and ZHANG Ye. A selective KPCA algorithm based on high-order statistics for anomaly detection in hyperspectral imagery[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2008, 5(1): 43–47. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2007.907304 成宝芝, 赵春晖, 王玉磊. 基于四阶累积量的波段子集高光谱图像异常检测[J]. 光电子·激光, 2012, 23(8): 1582–1588.CHENG Baozhi, ZHAO Chunhui, and WANG Yulei. Abnormal detection of hyperspectral images for band subsets based on fourth order cumulant[J]. Journal of Optoelectronics·Laser, 2012, 23(8): 1582–1588. 成宝芝. 基于光谱特性的高光谱图像异常目标检测算法研究[D]. [博士论文], 哈尔滨工程大学, 2014.CHENG Baozhi. Abnormal target detection algorithm for hyperspectral images based on spectral characteristics[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Harbin Engineering University, 2014. GENG Xiurui, SUN Kang, JI Luyan, et al. A high-order statistical tensor based algorithm for anomaly detection in hyperspectral imagery[J]. Scientific Reports, 2014, 4: 6869–6869. doi: 10.1038/srep06869 GENG Xiurui, JI Luyan, and SUN Kang. Principal skewness analysis: Algorithm and its application for multispectral/hyperspectral images indexing[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2014, 11(10): 1821–1825. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2014.2311168 GENG Xiurui, JI Luyan, ZHAO Yongchao, et al. A small target detection method for the hyperspectral image based on Higher Order Singular Value Decomposition (HOSVD)[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2013, 10(6): 1305–1308. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2013.2238504 孙康. 高光谱图像波段选择技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 中国科学院电子学研究所, 2015: 123–160.SUN Kang. Research on band selection method for hyperspectral imagery[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Institute of Electrics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2015: 123–160. -





 下载:
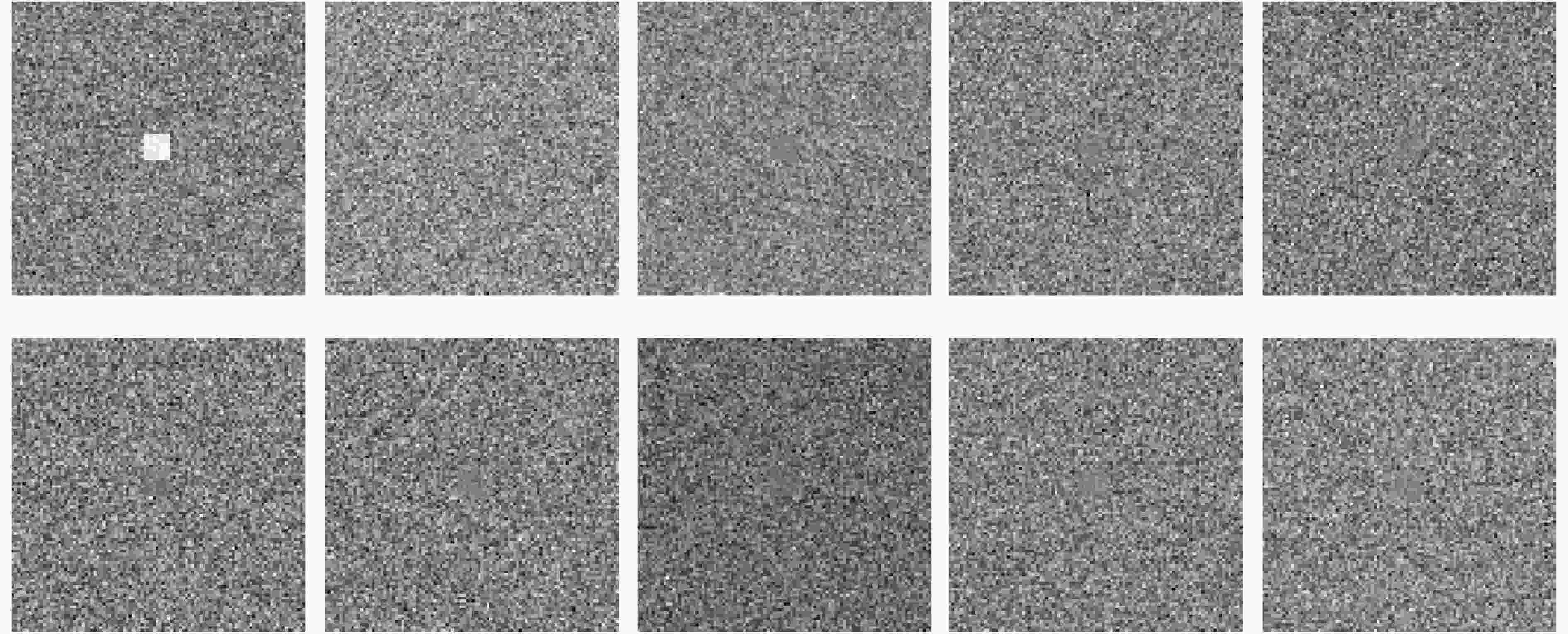
下载:
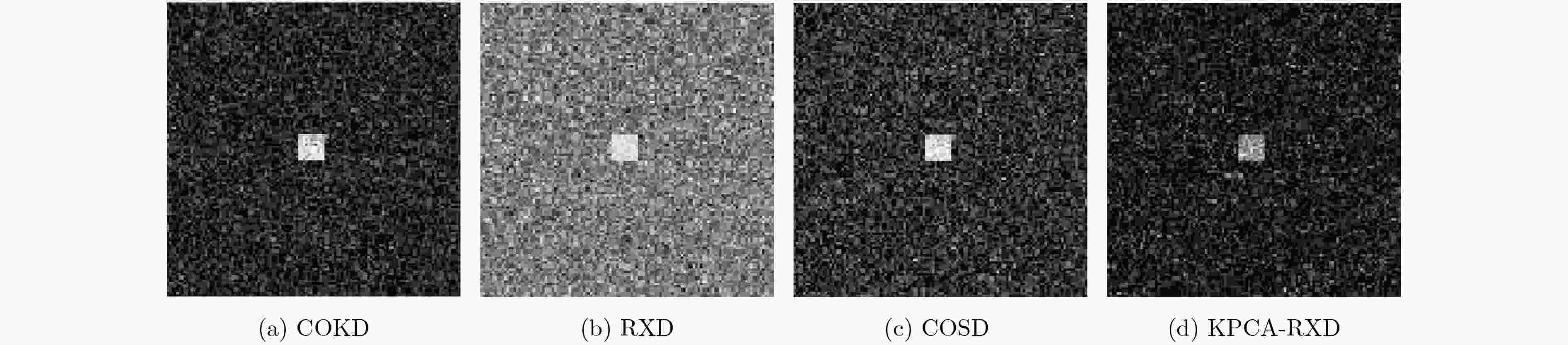




 下载:
下载:
