Stackelberg Game-based Resource Allocation Strategy in Virtualized Wireless Sensor Network
-
摘要:
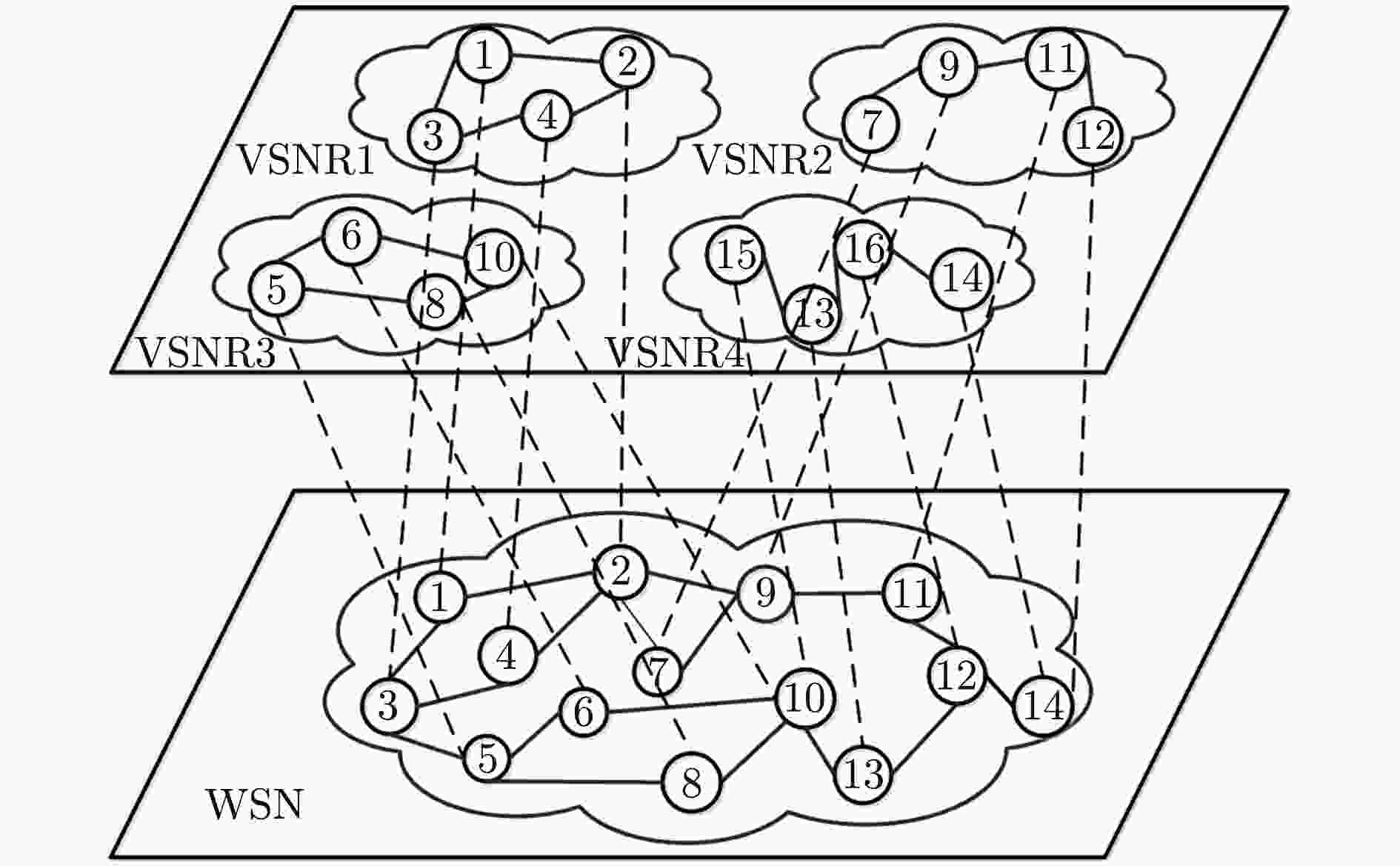
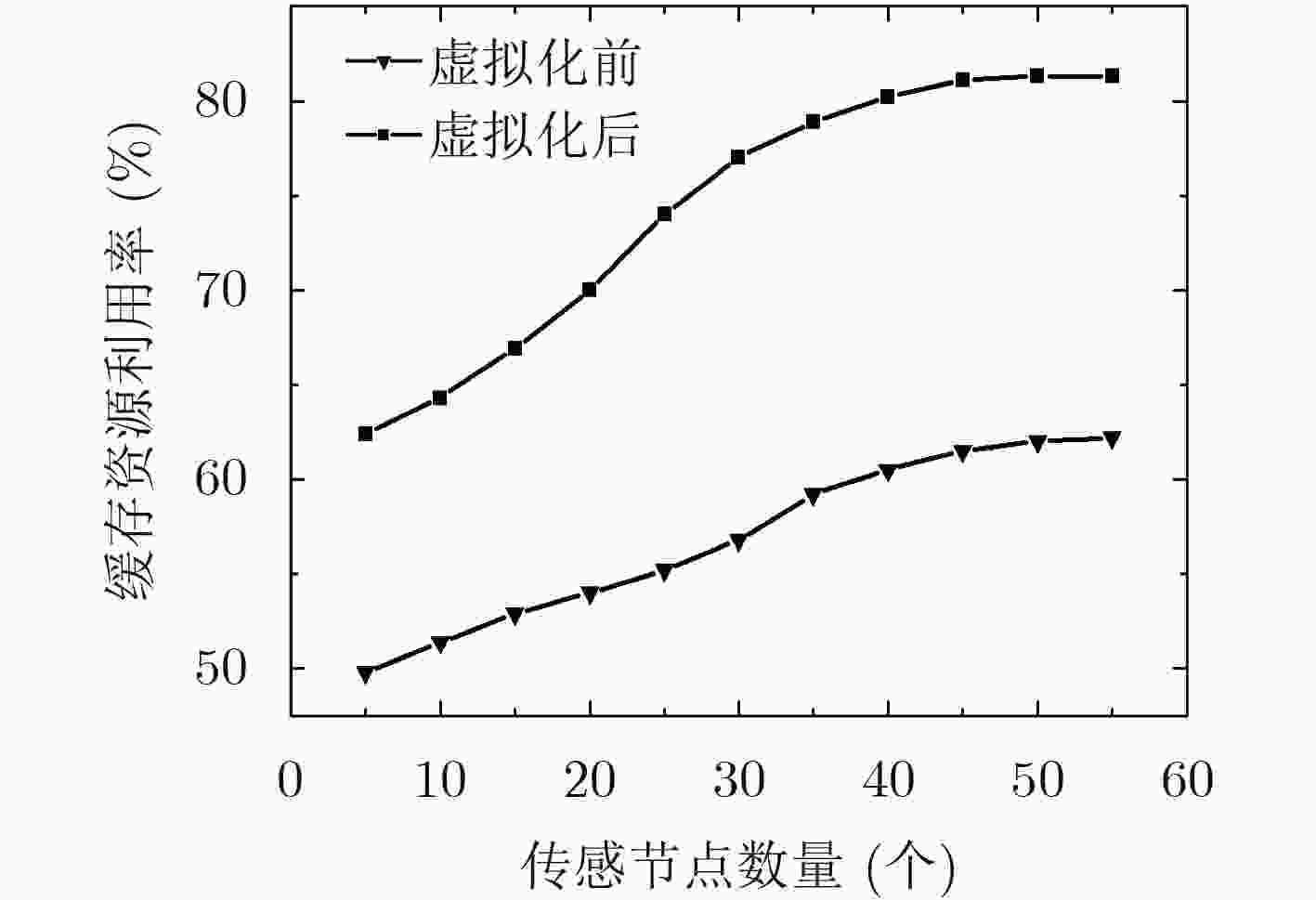
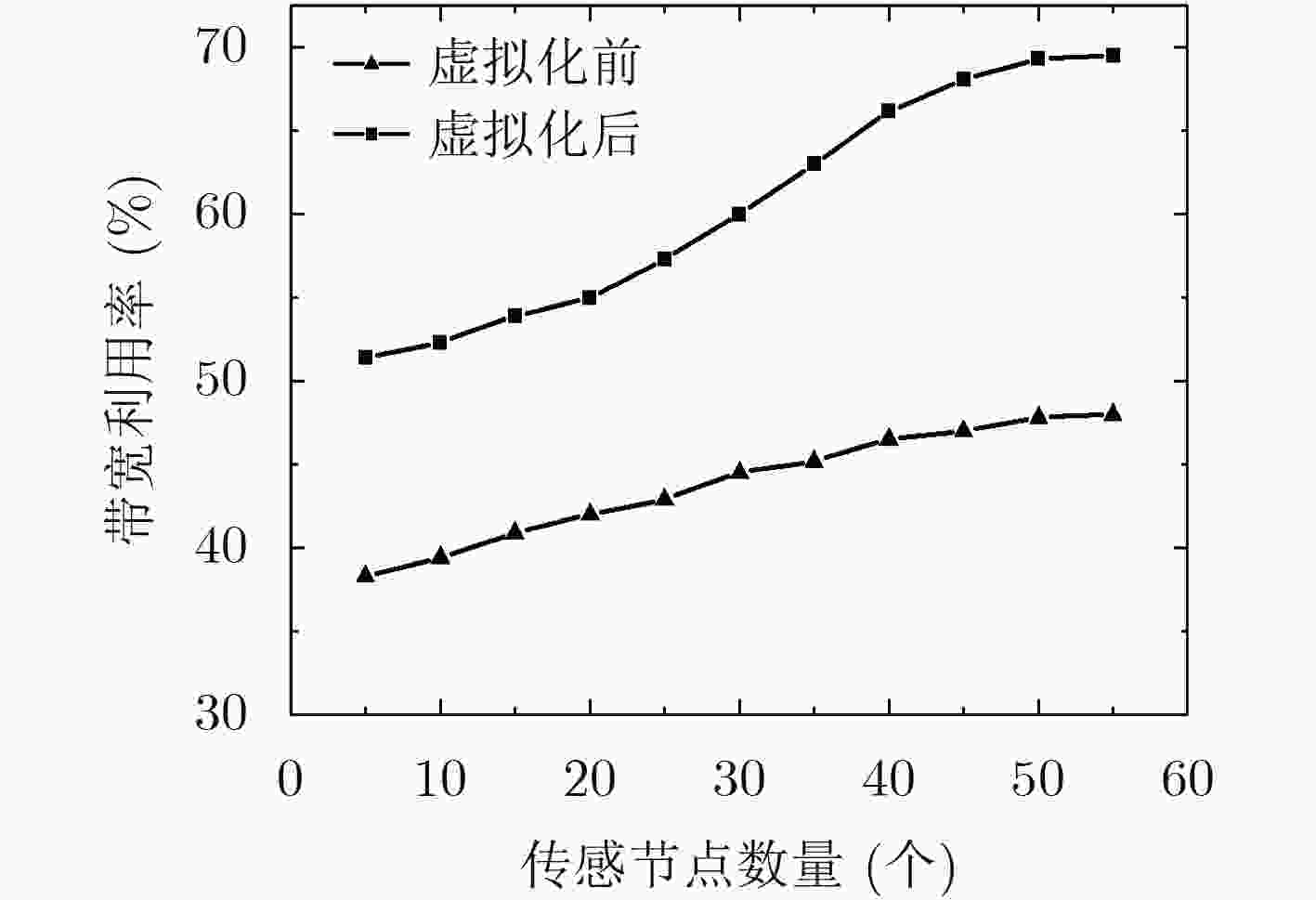
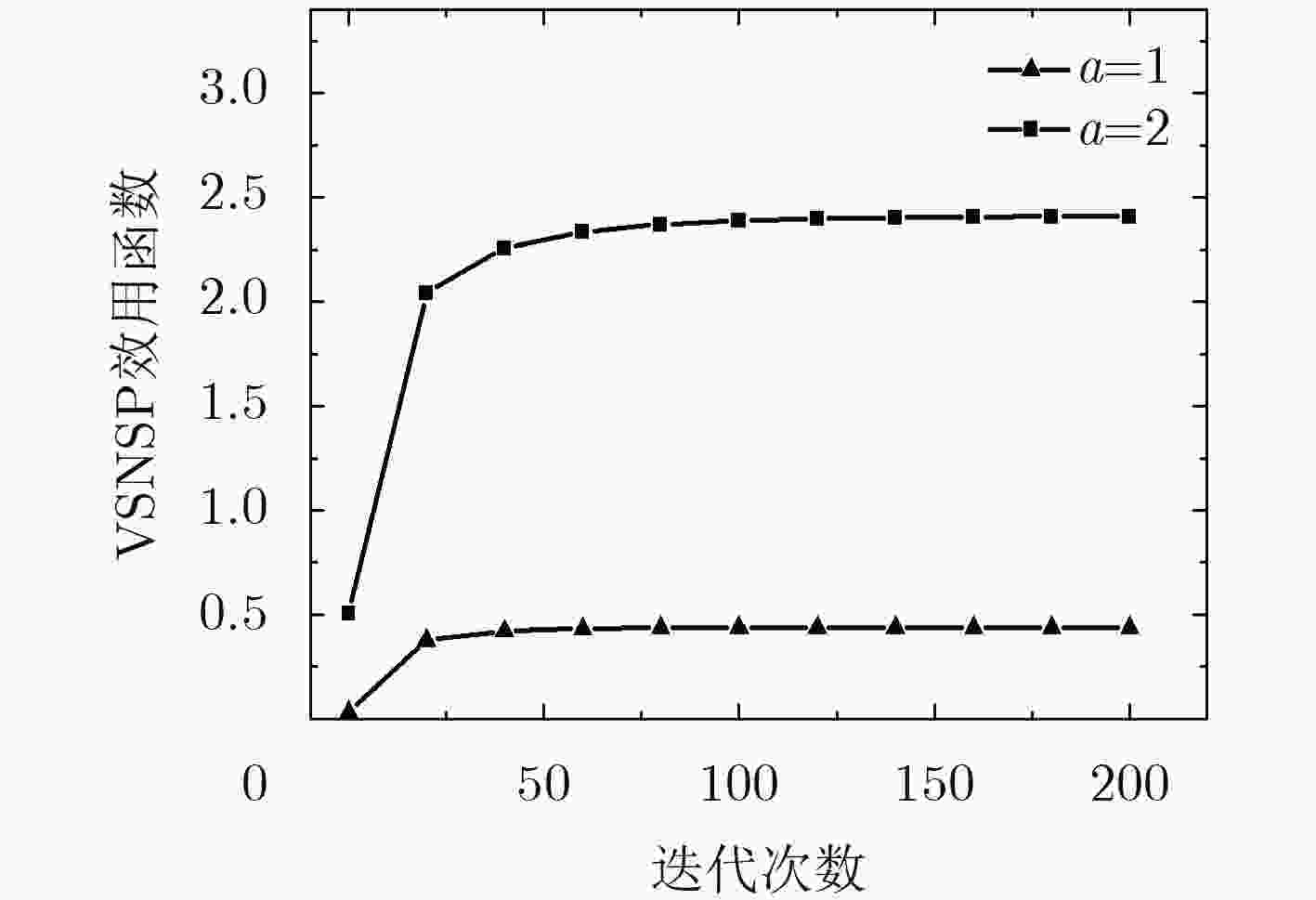
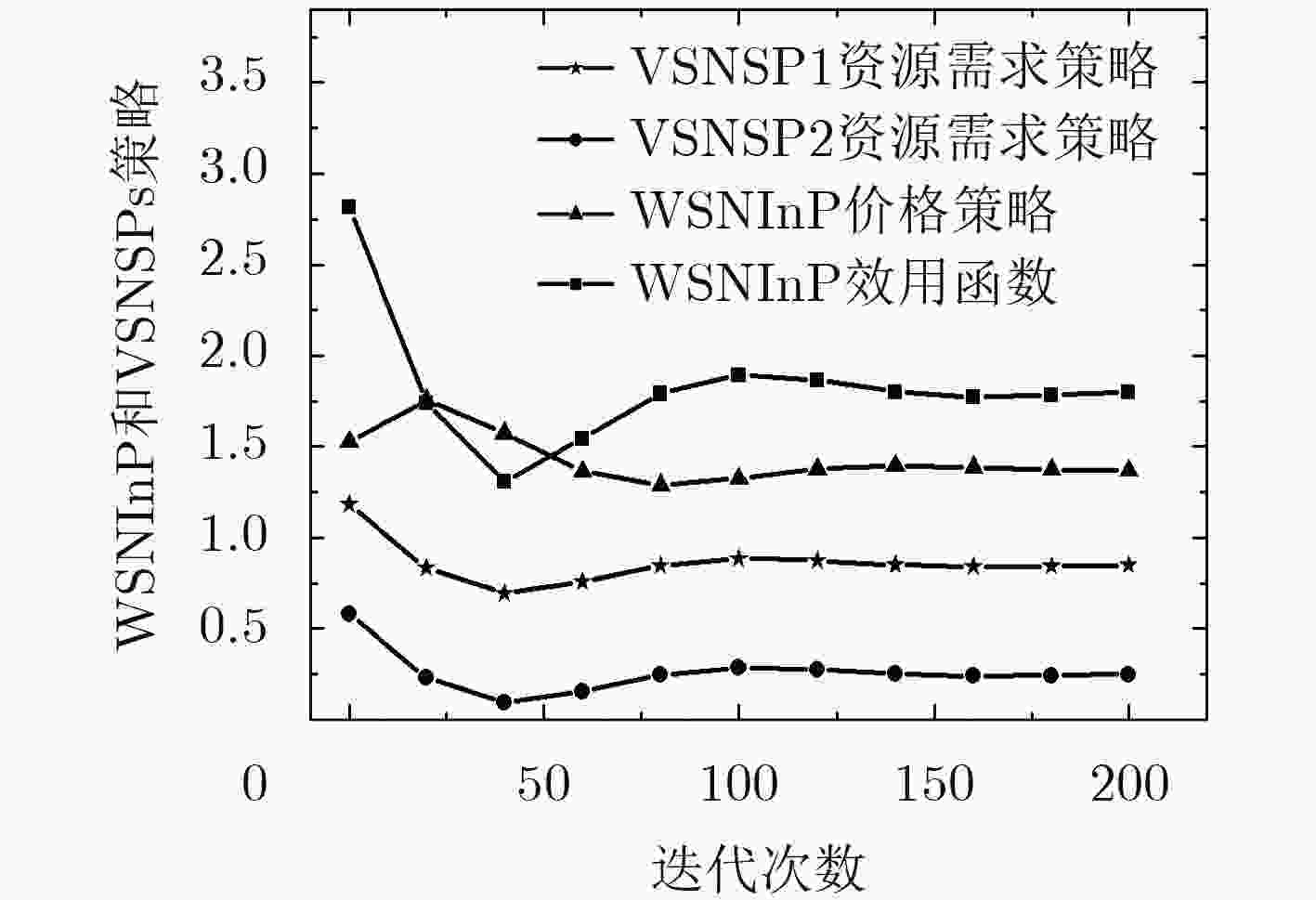
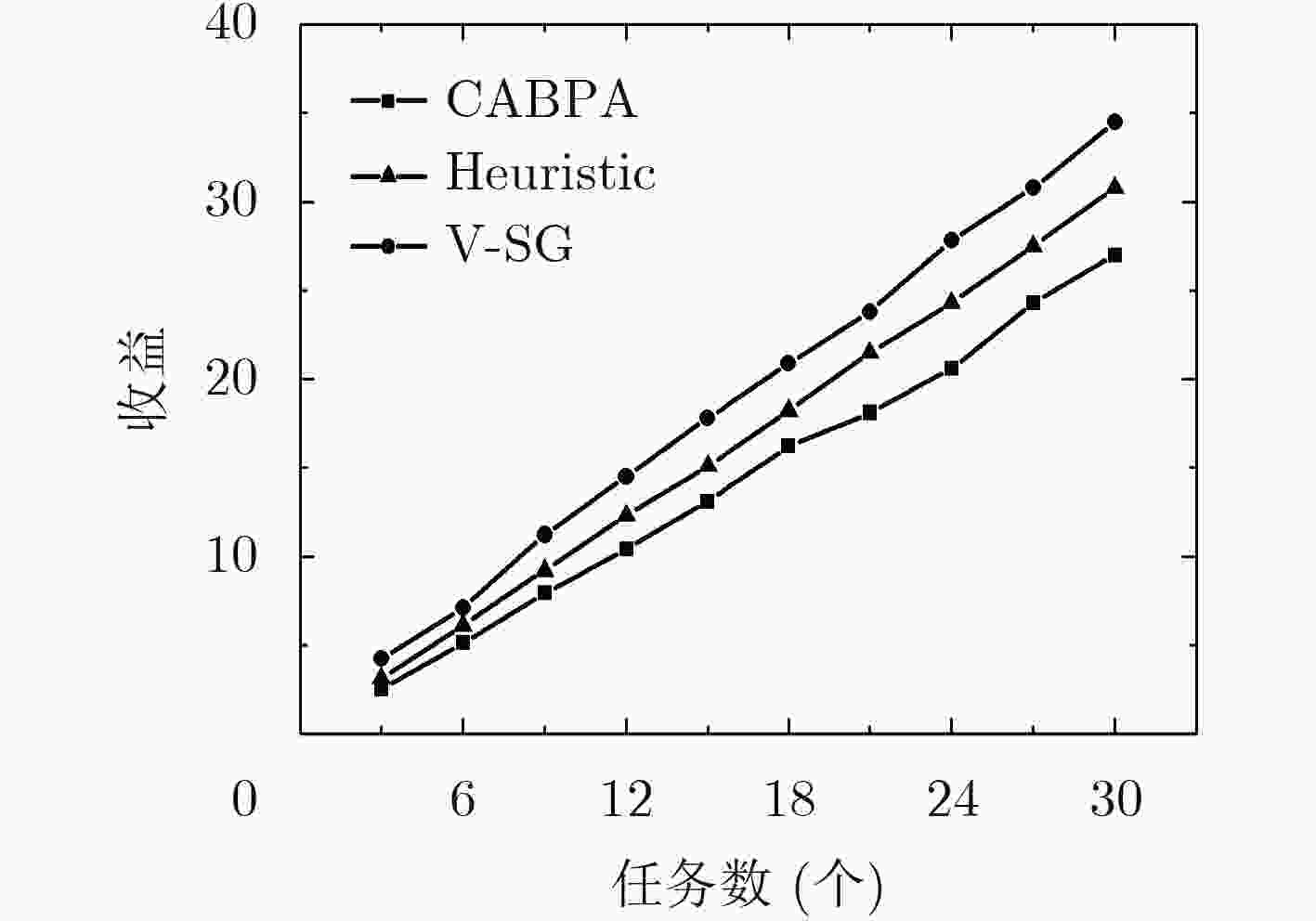
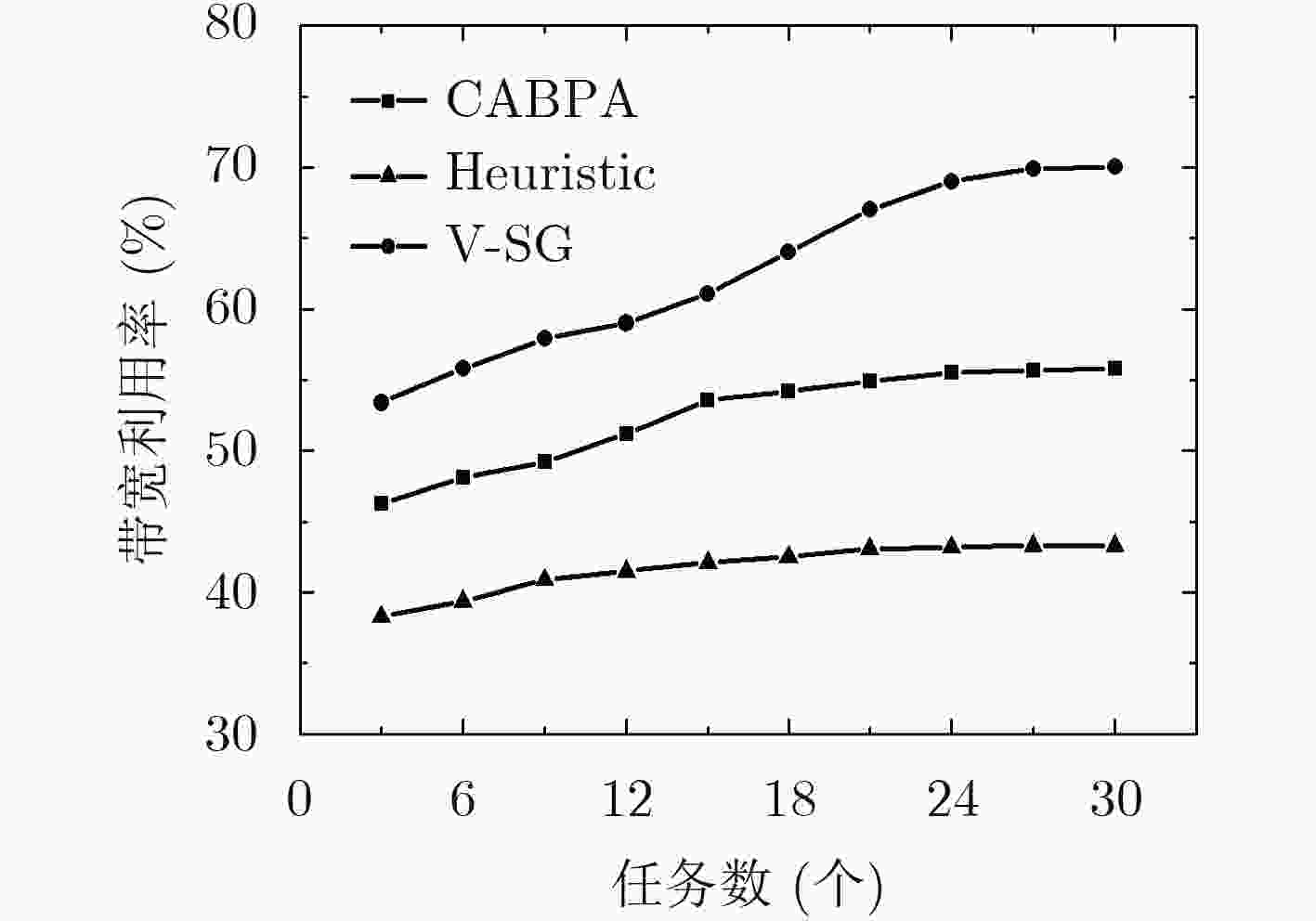
虚拟化技术可有效缓解当前无线传感网络(WSN)中资源利用率较低、服务不灵活的问题。针对虚拟化WSN中的资源竞争问题,该文提出一种基于Stackelberg博弈的多任务资源分配策略。依据所承载业务的不同服务质量(QoS)需求,量化多个虚拟传感网络请求(VSNRs)的重要程度,进而,利用分布式迭代方法,获取WSN的最优价格策略和VSNRs的最优资源需求量,最后,根据纳什均衡所确定的最优价格、最优资源分配量,对多个VSNRs分配资源。仿真结果表明,所提策略不仅能满足用户的多样化需求,而且提升了节点和链路资源利用率。
Abstract:Virtualization is a new technology that can effectively solve the low resource utilization and service inflexibility problem in the current Wireless Sensor Network (WSN). For the resource competition problem in virtualized WSN, a multi-task resource allocation strategy based on Stackelberg game is proposed. According to the different Quality of Service (QoS) requirements of the business carried by Virtual Sensor Network Request (VSNR), the importance of multiple VSNRs is quantified. Then, the optimal price of WSN and the optimal resource requirements of VSNRs are obtained by using distributed iteration method. Finally, the resource corresponding to multiple VSNRs is acquired according to optimal price and optimal resource allocation determined by Nash equilibrium. The simulation results show that the proposed strategy can not only meet the diversified needs of users, but also improve the resource utilization of nodes and links.
-
Key words:
- Wireless Sensor Network (WSN) /
- Virtualization /
- Resource allocation /
- Game theory
-
表 1 仿真参数设置
参数设定 参考数值 仿真区域(m2) 50×50 节点数量(个) 55 节点处理速度(bit/s) 16~32 节点存储能力(kb) 4~15 节点能量(J) 2~4 链路带宽(kb/s) 5~30 用户体验常量 1或2 VSNR资源需求策略调节步长 0.1 WSN价格策略调节步长 0.1 最大迭代次数/次 200 -
EZDIANI S, ACHARYYA I S, SIVAKUMAR S, et al. Wireless sensor network softwarization: Towards WSN adaptive QoS[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2017, 4(5): 1517–1527. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2017.2740423 LIAO Yizheng, MOLLINEAUX M, HSU R, et al. SnowFort: An open source wireless sensor network for data analytics in infrastructure and environmental monitoring[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2014, 14(12): 4253–4263. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2014.2358253 HU Xiaoya, YANG Liuqing, and XIONG Wei. A novel wireless sensor network frame for urban transportation[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2015, 2(6): 586–595. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2015.2475639 ALAIAD A and ZHOU Lina. Patients’ adoption of WSN-Based smart home healthcare systems: an integrated model of facilitators and barriers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Professional Communication, 2017, 60(1): 4–23. doi: 10.1109/TPC.2016.2632822 PARK P, MARCO P D, and JOHANSSON K H. Cross-layer optimization for industrial control applications using wireless sensor and actuator mesh networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2017, 64(4): 3250–3259. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2016.2631530 KHAN I, BELQASMI F, GLITHO R, et al. Wireless sensor network virtualization: Early architecture research perspectives[J]. IEEE Network, 2015, 29(3): 104–112. doi: 10.1109/MNET.2015.7113233 KHAN I, BELQASMI F, GLITHO R, et al. Wireless sensor network virtualization: A survey[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2016, 18(1): 553–576. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2015.2412971 GUO Lei, NING Zhaolong, SONG Qingyang, et al. A QoS-oriented high-efficiency resource allocation scheme in wireless multimedia sensor networks[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2017, 17(5): 1538–1548. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2016.2645709 DELGADO C, BOUSNINA S, CESANA M, et al. On optimal resource allocation in virtual sensor networks[J]. Ad Hoc Networks, 2016, 50(C): 23–40. doi: 10.1016/j.adhoc.2016.04.004 DELGADO C, CANALES M, ORTIN J, et al. Joint application admission control and network slicing in virtual sensor networks[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2017, 5(1): 28–43. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2017.2769446 OBELE B O, IFTIKHAR M, MANIPORNSUT S, et al. Analysis of the behavior of self-similar traffic in a QoS-aware architecture for integrating WiMAX and GEPON[J]. Journal of Optical Communication and Network, 2009, 1(4): 259–273. doi: 10.1364/JOCN.1.000259 MILAN G, JUAN E S, and JAMETT M. A simple estimator of the Hurst exponent for self-similar traffic flows[J]. IEEE Latin America Transactions, 2015, 12(8): 1349–1354. doi: 10.1109/TLA.2014.7014500 TRAN T D and LE L B. Stackelberg game approach for wireless virtualization design in wireless networks[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Paris, France, 2017: 1–6. WANG Cong, WANG Cuirong, and YUAN Ying. Game based dynamical bandwidth allocation model for virtual networks[C]. 2009 First International Conference on Information Science and Engineering, Nanjing, China, 2009: 1745–1747. LUONG N C, HOANG D T, WANG Ping, et al. Data collection and wireless communication in Internet of Things (IoT) using economic analysis and pricing models: A survey[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2016, 18(4): 2546–2590. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2016.2582841 AL-ZAHRANI A Y and YU F R. An energy-efficient resource allocation and interference management scheme in green heterogeneous networks using game theory[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2016, 65(7): 5384–5396. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2015.2464322 XU Qichao, SU Zhou, and GUO Song. A game theoretical incentive scheme for relay selection services in mobile social networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2016, 65(8): 6692–6702. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2015.2472289 GHOSH A, COTTATELLUCCI L, and ALTMAN E. Normalized Nash equilibrium for power allocation in cognitive radio Networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 2015, 1(1): 86–99. doi: 10.1109/TCCN.2015.2496578 RAO M S S and SOMAN S A. Marginal pricing of transmission services using min-max fairness policy[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2015, 30(2): 573–584. doi: 10.1109/TPWRS.2014.2331424 ZHANG Yueyue, ZHU Yaping, YAN Feng, et al. Energy-efficient radio resource allocation in software-defined wireless sensor networks[J]. IET Communications, 2018, 12(3): 349–358. doi: 10.1049/iet-com.2017.0937 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
