Impossible Differential Cryptanalysis of the Digital Video Broadcasting-common Scrambling Algorithm
-
摘要:
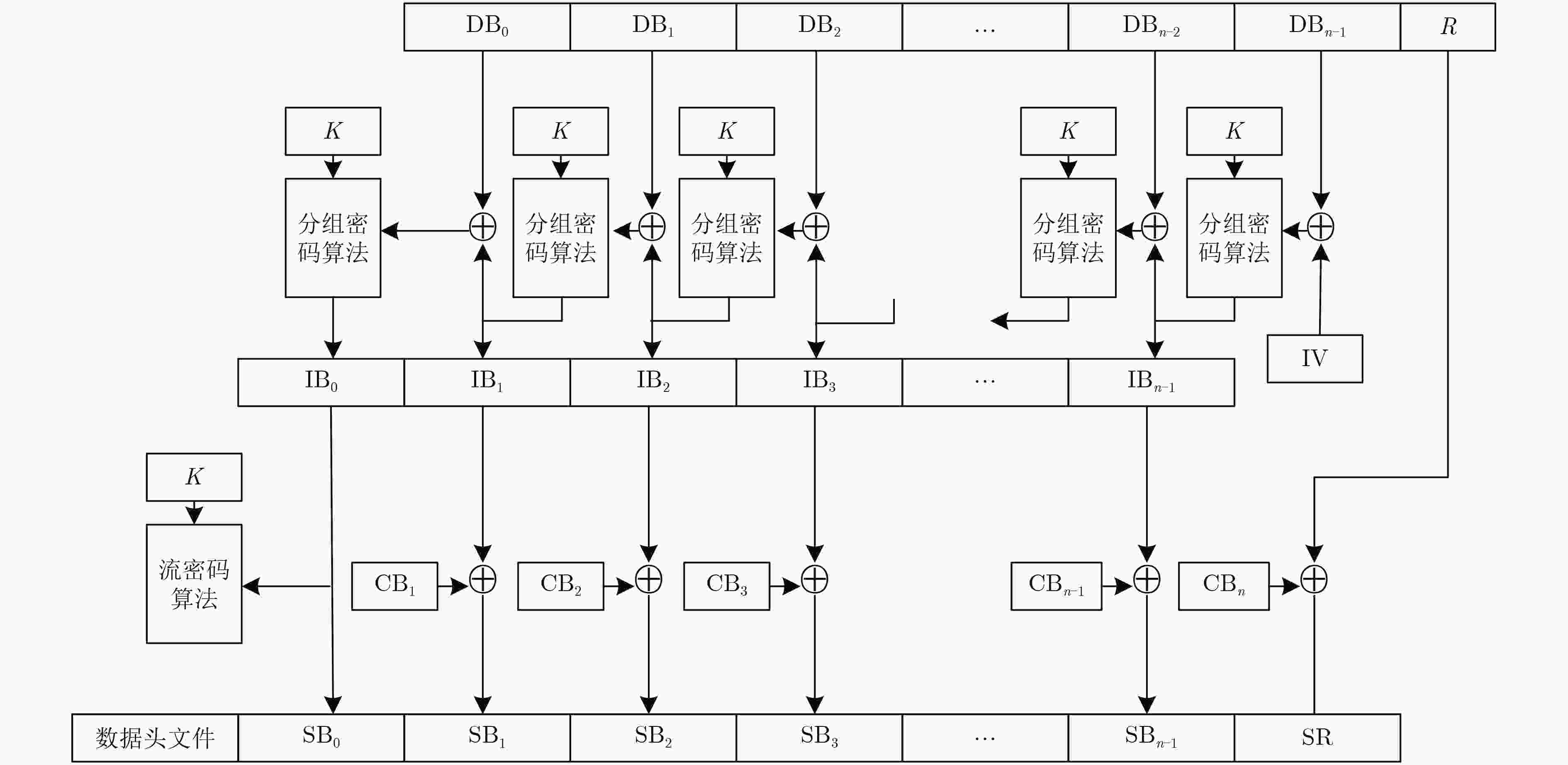
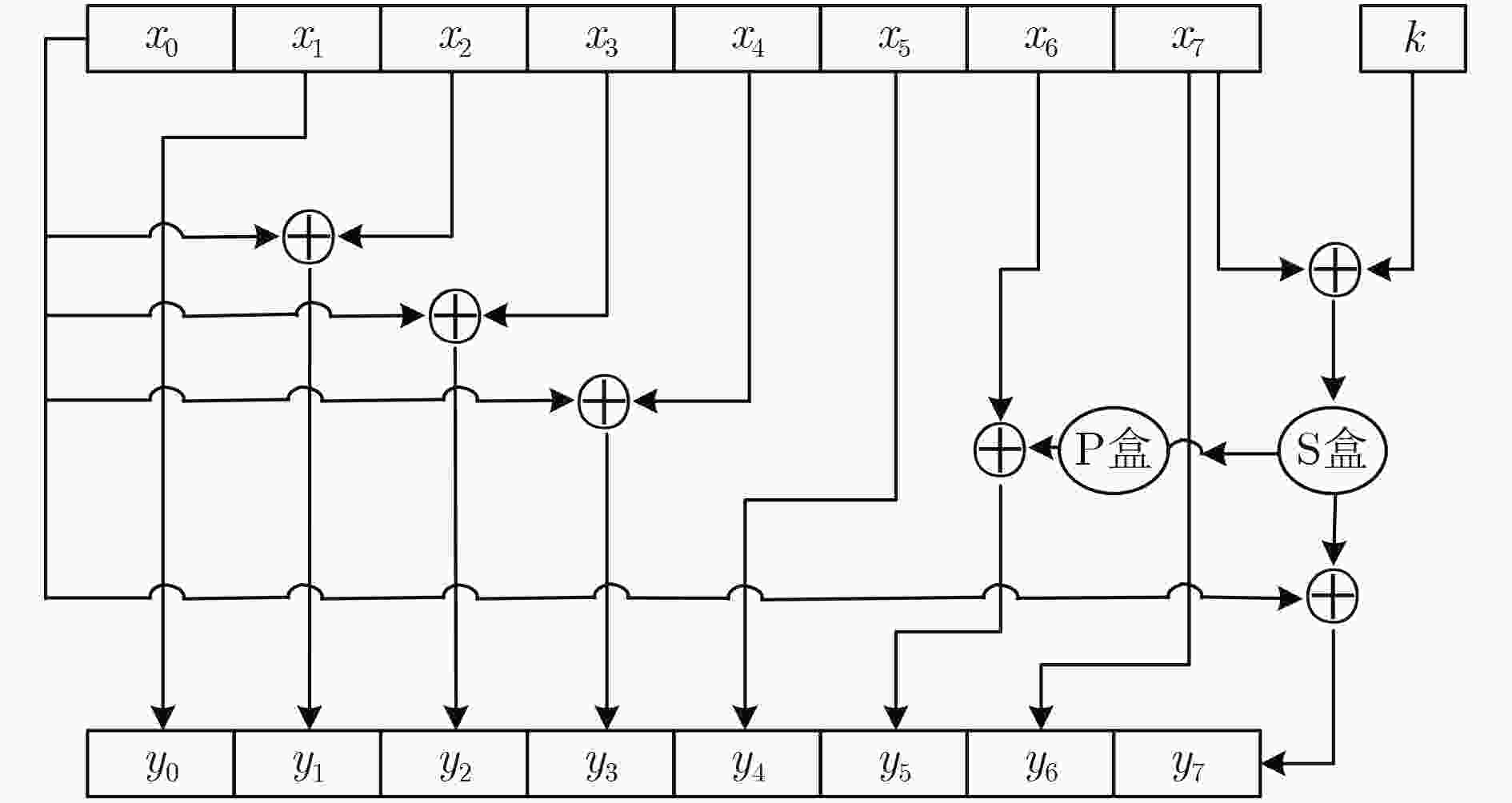
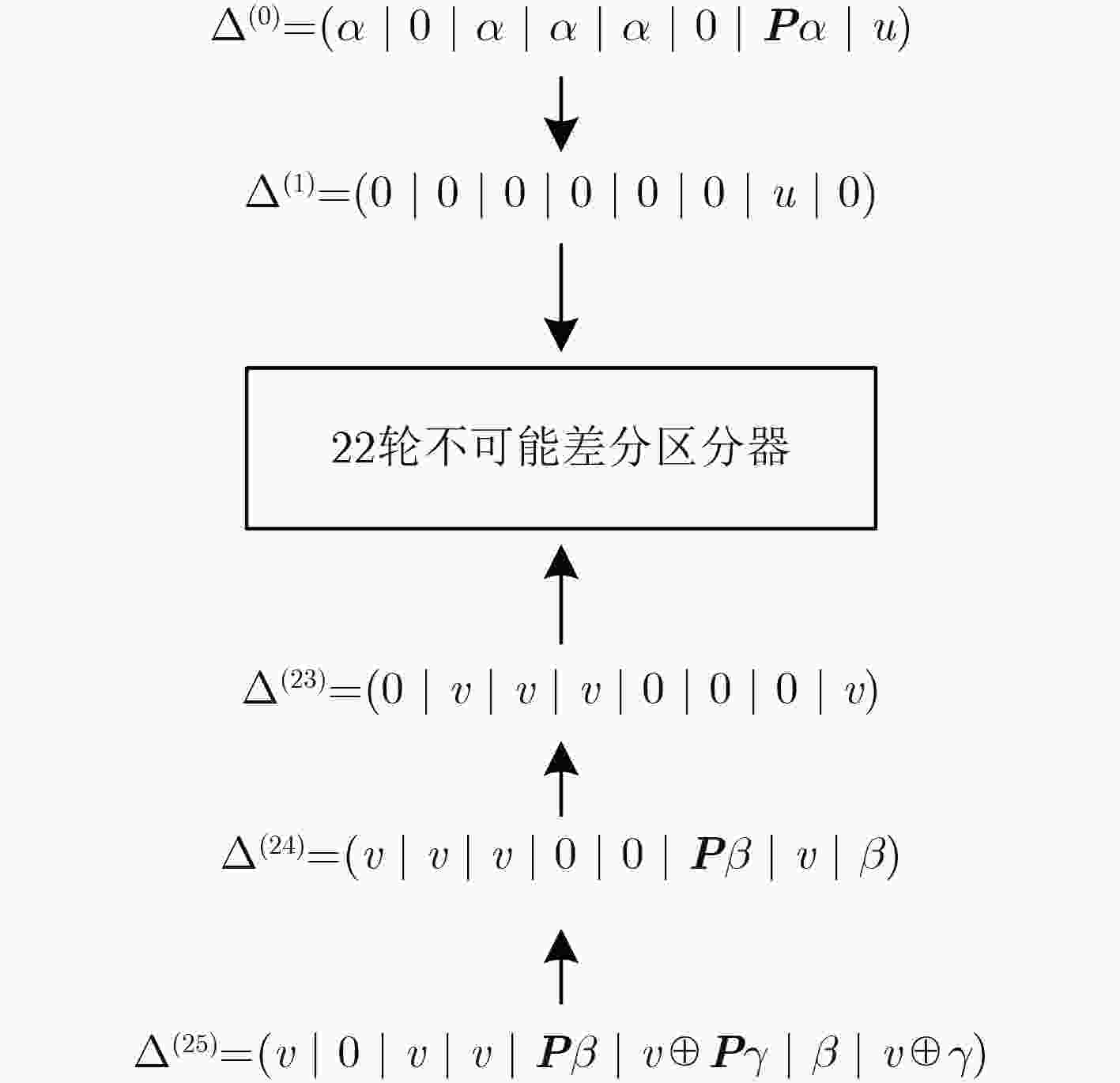
数字视频广播通用加扰算法(DVB-CSA)是一种混合对称加密算法,由分组密码加密和流密码加密两部分组成。该算法通常用于保护视讯压缩标准(MPEG-2)中的信号流。主要研究DVB-CSA分组加密算法(DVB-CSA-Block Cipher, CSA-BC)的不可能差分性质。通过利用S盒的具体信息,该文构造了CSA-BC的22轮不可能差分区分器,该区分器的长度比已有最好结果长2轮。进一步,利用构造的22轮不可能差分区分器,攻击了缩减的25轮CSA-BC,该攻击可以恢复24 bit种子密钥。攻击的数据复杂度、时间复杂度和存储复杂度分别为253.3个选择明文、232.5次加密和224个存储单元。对于CSA-BC的不可能差分分析,目前已知最好结果能够攻击21轮的CSA-BC并恢复16 bit的种子密钥量。就攻击的长度和恢复的密钥量而言,该文的攻击结果大大改进了已有最好结果。
-
关键词:
- 混合对称密码 /
- 分组密码 /
- 数字视频广播通用加扰算法 /
- 不可能差分分析
Abstract:The Digital Video Broadcasting-Common Scrambling Algorithm (DVB-CSA) is a hybrid symmetric cipher. It is made up of the block cipher encryption and the stream cipher encryption. DVB-CSA is often used to protect MPEG-2 signal streams. This paper focuses on impossible differential cryptanalysis of the block cipher in DVB-CSA called CSA-BC. By exploiting the details of the S-box, a 22-round impossible differential is constructed, which is two rounds more than the previous best result. Furthermore, a 25-round impossible differential attack on CSA-BC is presented, which can recover 24 bit key. For the attack, the data complexity, the computational complexity and the memory complexity are 253.3 chosen plaintexts, 232.5 encryptions and 224 units, respectively. For impossible differential cryptanalysis of CSA-BC, the previous best result can attack 21-round CSA-BC and recover 16 bit key. In terms of the round number and the recovered key, the result significantly improves the previous best result.
-
表 1 算法1:CSA-BC的加密流程
输入:明文${{M}} = ({M_0},{M_1},{M_2},{M_3},{M_4},{M_5},{M_6},{M_7})$ 输出:密文${{C}} = ({C_0},{C_1},{C_2},{C_3},{C_4},{C_5},{C_6},{C_7})$ (1) ${{{S}}^0} = {{M}}$; (2) for r=0 to 55 (3) ${{{S}}^{r + 1}} = f({{{S}}^r},(k_{8r}^E,k_{8r + 1}^E, \cdots ,k_{8r + 7}^E))$; (4) end for (5) ${{C}} = {{{S}}^{56}}$. 表 2 加密方向的差分传播规律
轮数 差分传播 约束条件 0 $(0|0|0|0|0|0|u|0)$ 1 $(0|0|0|0|0|u|0|0)$ 2 $(0|0|0|0|u|0|0|0)$ 3 $(0|0|0|u|0|0|0|0)$ 4 $(0|0|u|0|0|0|0|0)$ 5 $(0|u|0|0|0|0|0|0)$ 6 $(u|0|0|0|0|0|0|0)$ 7 $(0|u|u|u|0|0|0|u)$ 8 $(u|u|u|0|0|{{P}}{u_1}|u|{u_1})$ ${u_1} \in \Delta S(u)$ 9 $(u|0|u|u|{{P}}{u_1}|u \oplus {{P}}{u_2}|{u_1}|u \oplus {u_2})$ ${u_2} \in \Delta S({u_1})$ 10 $(0|0|0|u \oplus {{P}}{u_1}|u \oplus {{P}}{u_2}|{u_1} \oplus {{P}}{u_3}|u \oplus {u_2}|u \oplus {u_3})$ ${u_3} \in \Delta S(u \oplus {u_2})$ 11 $(0|0|u \oplus {{P}}{u_1}|u \oplus {{P}}{u_2}|{u_1} \oplus {{P}}{u_3}|u \oplus {u_2} \oplus {{P}}{u_4}|u \oplus {u_3}|{u_4})$ ${u_4} \in \Delta S(u \oplus {u_3})$ 12 $(0|u \oplus {{P}}{u_1}|u \oplus {{P}}{u_2}|{u_1} \oplus {{P}}{u_3}|u \oplus {u_2} \oplus {{P}}{u_4}|u \oplus {u_3} \oplus {{P}}{u_5}|{u_4}|{u_5})$ ${u_5} \in \Delta S({u_4})$ 13 $(u \oplus {{P}}{u_1}|u \oplus {{P}}{u_2}|{u_1} \oplus {{P}}{u_3}|u \oplus {u_2} \oplus {{P}}{u_4}|u \oplus {u_3} \oplus {{P}}{u_5}|{u_4} \oplus {{P}}{u_6}|{u_5}|{u_6})$ ${u_6} \in \Delta S({u_5})$ 14 $\begin{aligned} (u \oplus {{P}}{u_2}|{u_1} \oplus {{P}}{u_3} \oplus u \oplus {{P}}{u_1}|{u_2} \oplus {{P}}{u_4} \oplus {{P}}{u_1}|\\ {u_3} \oplus {{P}}{u_5} \oplus {{P}}{u_1}|{u_4} \oplus {{P}}{u_6}|{u_5} \oplus {{P}}{u_7}|{u_6}|u \oplus {{P}}{u_1} \oplus {u_7}) \end{aligned} $ ${u_7} \in \Delta S({u_6})$ 表 3 解密方向的差分传播规律
轮数 差分传播 约束条件 22 $(0|v|v|v|0|0|0|v)$ 21 $(v|0|0|0|0|0|0|0)$ 20 $(0|v|0|0|0|0|0|0)$ 19 $(0|0|v|0|0|0|0|0)$ 18 $(0|0|0|v|0|0|0|0)$ 17 $(0|0|0|0|v|0|0|0)$ 16 $(0|0|0|0|0|v|0|0)$ 15 $(0|0|0|0|0|0|v|0)$ 14 $({v_1}|0|{v_1}|{v_1}|{v_1}|0|{{P}}{v_1}|v)$ ${v_1} \in \Delta S(v)$ 表 4 本文结果与已有最好结果比较
区分器
长度攻击
长度恢复密钥量 数据复杂度 时间复杂度 存储复杂度 来源 20轮 21轮 16 bit ${2^{44.5}}$ ${2^{22.7}}$ ${2^{10.5}}$ 文献[6] 22轮 25轮 24 bit ${2^{53.3}}$ ${2^{32.5}}$ ${2^{24}}$ 本文 -
WEINMANN R P and WIRT K. Analysis of the DVB common scrambling algorithm[C]. International Federation for Information Processing, Boston, USA, 2005: 195–207. WIRT K. Fault attack on the DVB common scrambling algorithm[C]. Computational Science and Its Applications, Singapore, 2005: 511–517. SIMPSON L, HENRICKSEN M, and YAP W S. Improved cryptanalysis of the common scrambling algorithm stream cipher[C]. The 14th Australasian Conference on Information Security and Privacy, Brisbane, Australia, 2009: 108–121. TEWS E, WALDE J, and WEINER M. Breaking DVB-CSA[C]. West European Workshop on Research in Cryptography, Weimar, Germany, 2011: 41–45. ZHANG Kai and GUAN Jie. Distinguishing attack on common scrambling algorithm[J]. The International Arab Journal of Information Technology, 2015, 12(4): 410–414. ZHANG Kai, GUAN Jie, and HU Bin. Impossible differential cryptanalysis on DVB-CSA[J]. KSII Transactions on Internet and Information Systems, 2016, 10(3): 1944–1956. doi: 10.3837/tiis.2016.04.027 SUN Siwei, HU Lei, WANG Peng, et al. Automatic security evaluation and (related-key) differential characteristic search: Application to SIMON, PRESENT, LBlock, DES(L) and other bit-oriented block ciphers[C]. International Conference on the Theory and Application of Cryptology and Information Security, Kaoshiung, China, 2014: 158–178. 李俊志, 关杰. 一种基于完全性的不可能差分区分器构造方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(2): 430–437. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170422LI Junzhi and GUAN Jie. A method of constructing impossible differential distinguishers based on completeness[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(2): 430–437. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170422 徐洪, 苏鹏晖, 戚文峰. 减轮SPECK算法的不可能差分分析[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(10): 2479–2486. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170049XU Hong, SU Penghui, and QI Wenfeng. Impossible differential cryptanalysis of reduced-round SPECK[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2017, 39(10): 2479–2486. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170049 付立仕, 崔霆, 金晨辉. 嵌套SP网络的New-Structure系列结构的零相关线性逼近与不可能差分性质研究[J]. 电子学报, 2017, 45(6): 1367–1374. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2017.06.013FU Lishi, CUI Ting, and JIN Chenhui. Zero correlation linear approximations and impossible differentials of New-Structure series with SP networks[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2017, 45(6): 1367–1374. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2017.06.013 SUN Bing, LIU Meicheng, GUO Jian, et al. Provable security evaluation of structures against impossible differential and zero correlation linear cryptanalysis[C]. Advances in Cryptology – EUROCRYPT 2016, Vienna, Austrian, 2016: 196–213. SHEN Xuan, LI Ruilin, SUN Bing, et al. Dual relationship between impossible differentials and zero correlation linear hulls of SIMON-like ciphers[C]. Information Security Practice and Experience, Melbourne, Australia, 2017: 237–255. BOURA C, LALLEMAND V, PLASENCIA M N, et al. Making the impossible possible[J]. Journal of Cryptology, 2018, 31(1): 101–133. doi: 10.1007/s00145-016-9251-7 KNUDSEN L. DEAL-A 128-bit block cipher[R]. Department of Informatics, University of Bergen, Norway, 1998. BIHAM E, BIRYUKOV A, and SHAMIR A. Cryptanalysis of Skipjack reduced to 31 rounds using impossible differentials[C]. Advances in Cryptology – EUROCRYPT 1999, Prague, Czech, 1999: 12–23. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
