Medium-earth-orbit SAR Data Focusing Method Based on Two-step Azimuth Resampling
-
摘要:
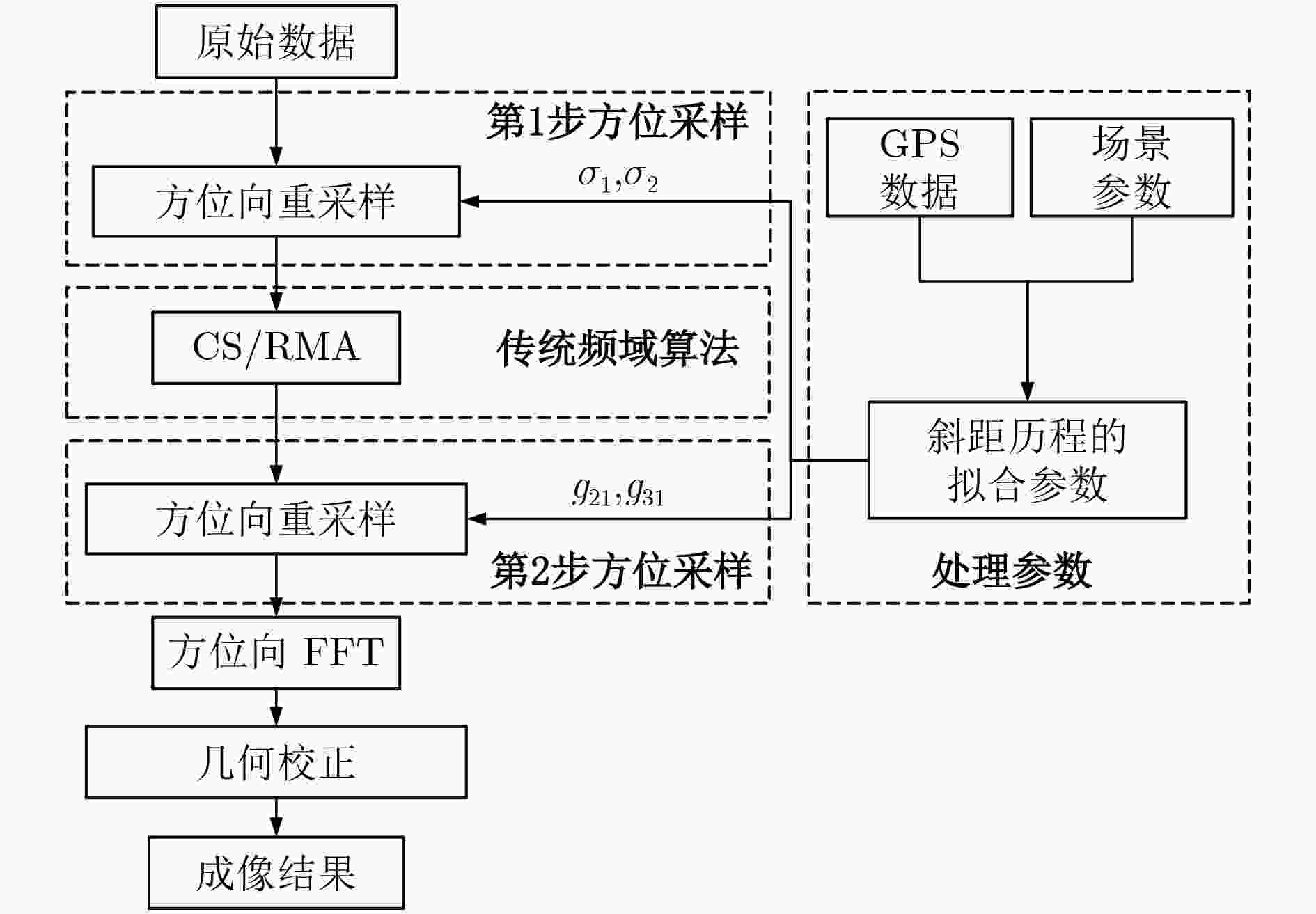
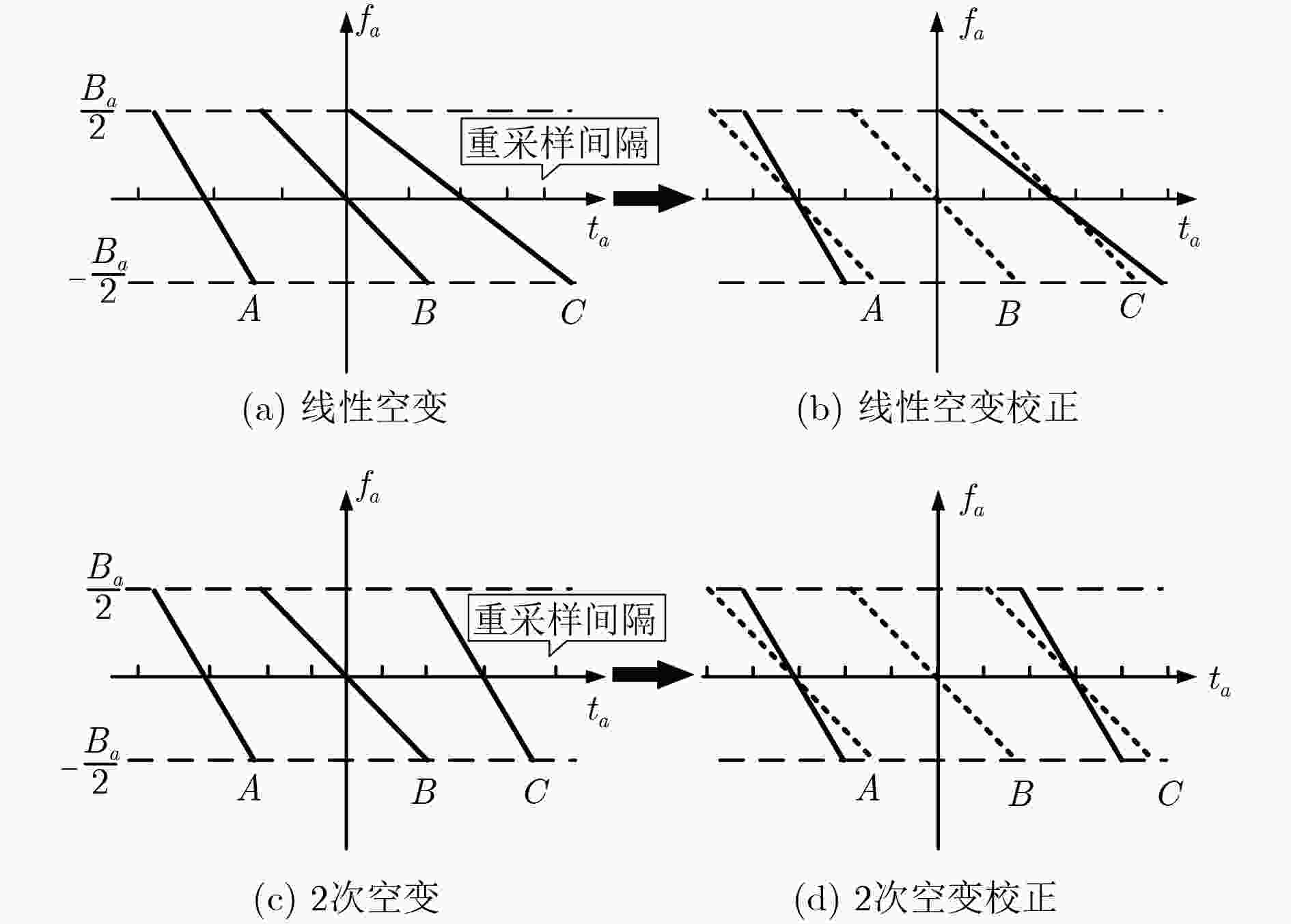
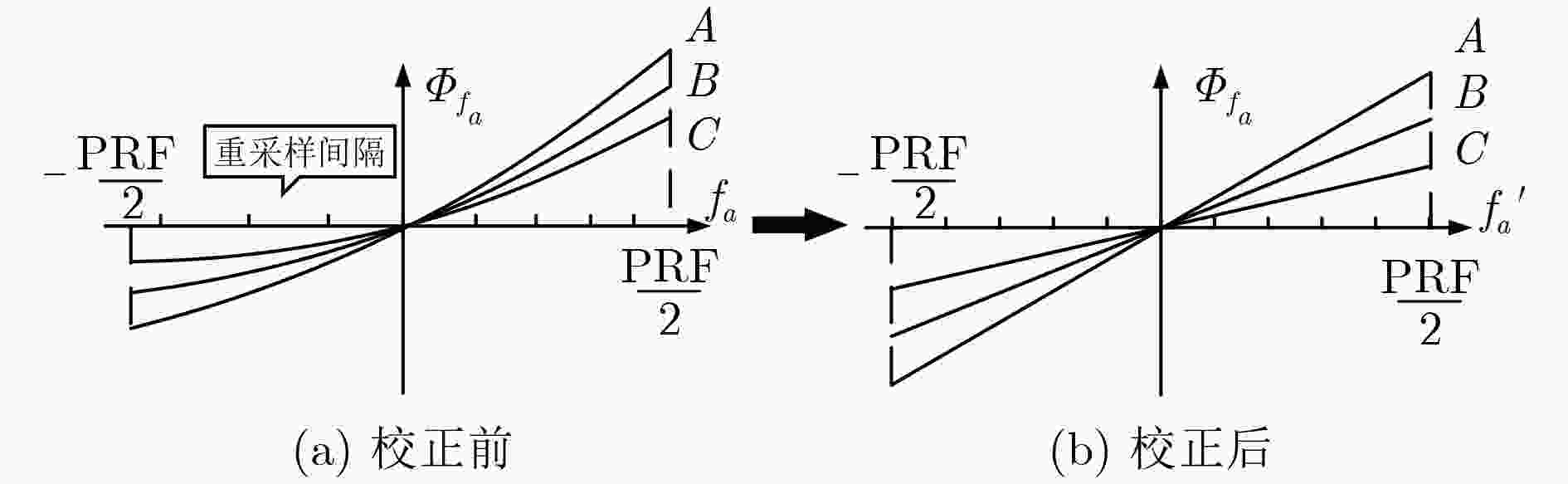
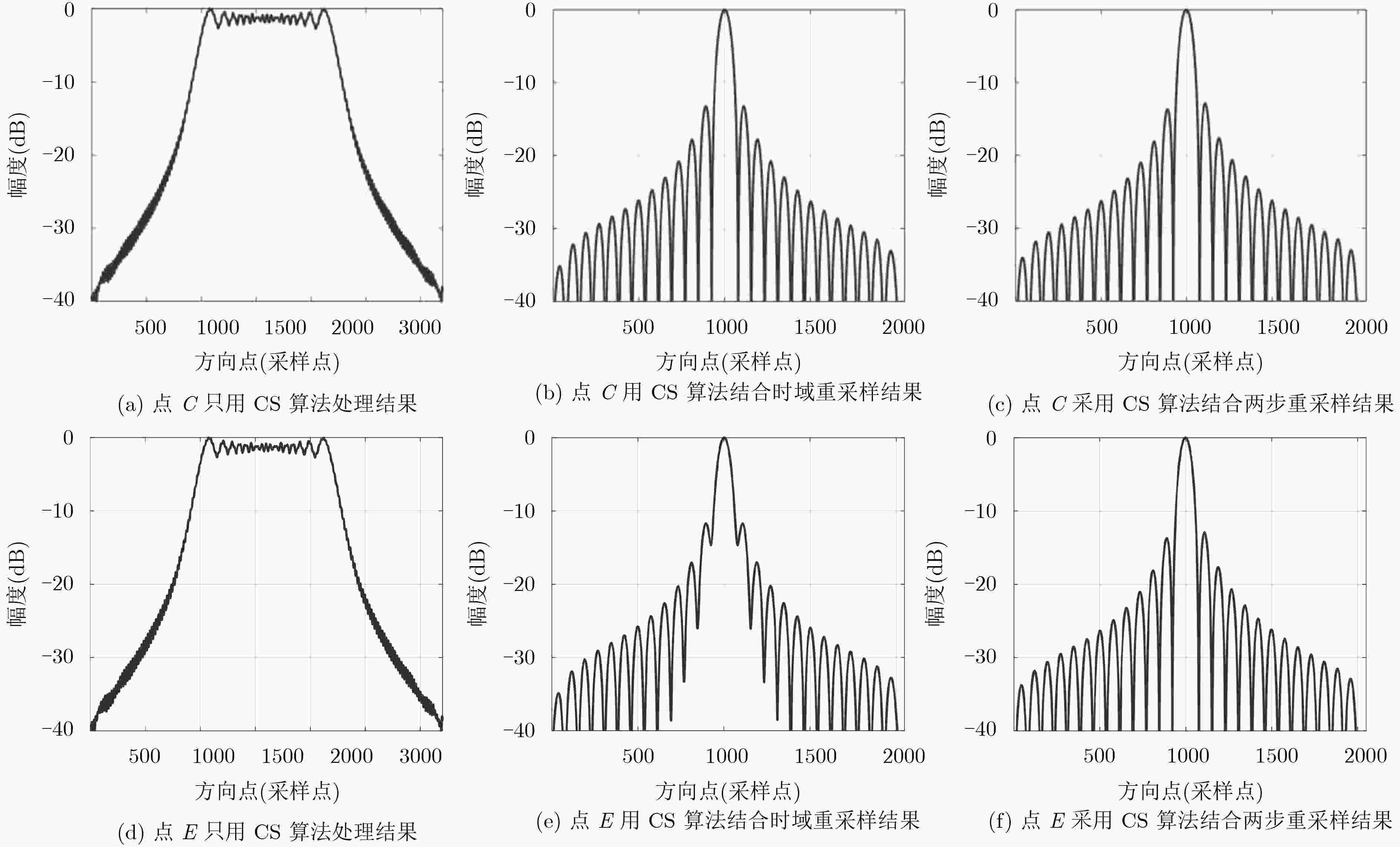
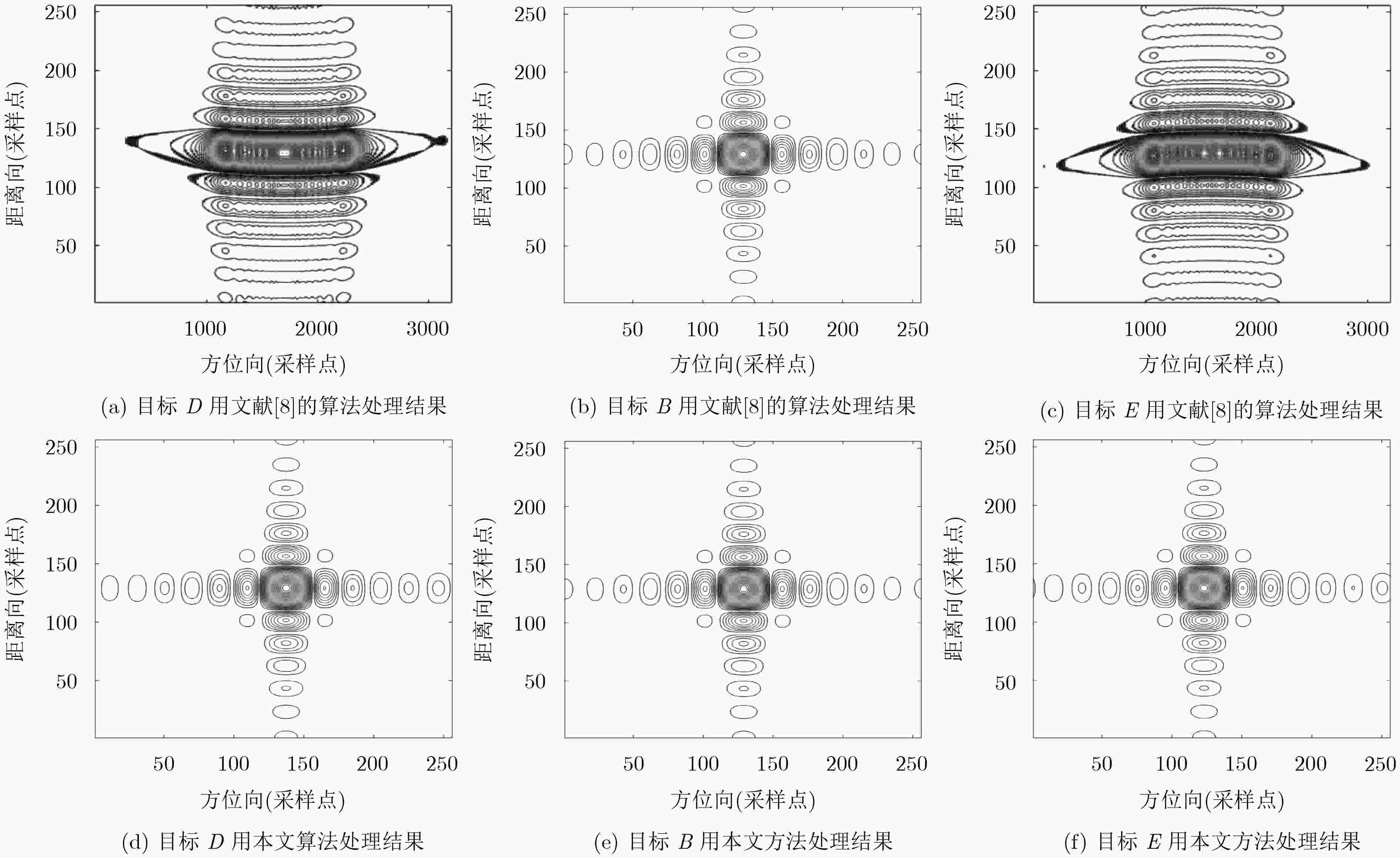
中轨轨道显著的弯曲特性导致中轨SAR信号存在2维空变,因此大场景成像对于中轨SAR仍然是个难题。该文使用参数2维空变的4阶多项式模型对信号进行建模。同时提出一种基于两步方位插值的信号方位空变校正方法,通过方位时域重采样可以校正参考距离上不同方位目标点的多普勒调频率的线性和2次空变,距离向利用CS/RMA算法即可校正场景中所有点目标的距离徙动,而第2步多普勒重采样则能够校正剩余的多普勒参数的空变特性,包括剩余的距离方位耦合空变,以及高阶多普勒参数空变。通过两步插值法能够完全校正整个场景目标信号的方位空变特性,使得传统频域成像算法可以应用于中轨SAR的大场景聚焦。最后通过所提方法与参考方法的仿真结果对比,验证了所提方法的有效性。
Abstract:The obvious orbit curvature of Medium Earth Orbit (MEO) results in severe two-dimensional space variance in the received signals. Thus, the focusing of MEO SAR data is still a problem to be solved. Fourth-order polynomial is used to model the range history. Also, an azimuth two-step resampling method is proposed to address the azimuth variance. The azimuth resampling in the time domain can adjust the azimuth chirp rate to be the same, then CS/RMA algorithm can be used to handle the space variance of the RCM. The second-step azimuth resampling can correct the left space variance of the Doppler parameters, including range-azimuth coupled space variance of the azimuth chirp rate, and the higher-order focusing parameters. The proposed method can well address the azimuth space variance of the whole scene, make the conventional frequency-domain focusing algorithms applicable to large scene focusing. Finally, the comparison results obtained by the proposed method and the reference method, validate the effectiveness of the proposed method.
-
Key words:
- Medium Earth Orbit (MEO) SAR /
- Space variance /
- Two-step resampling
-
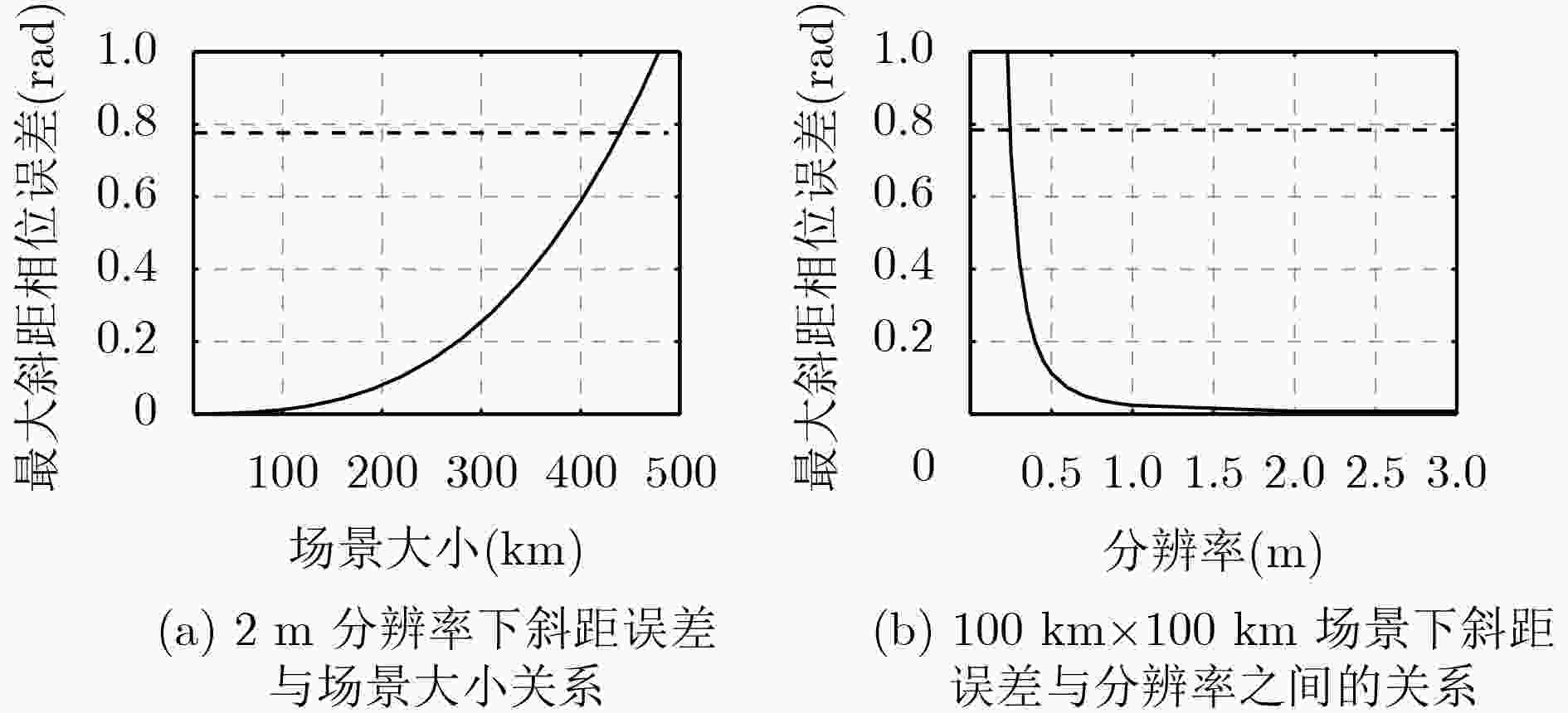
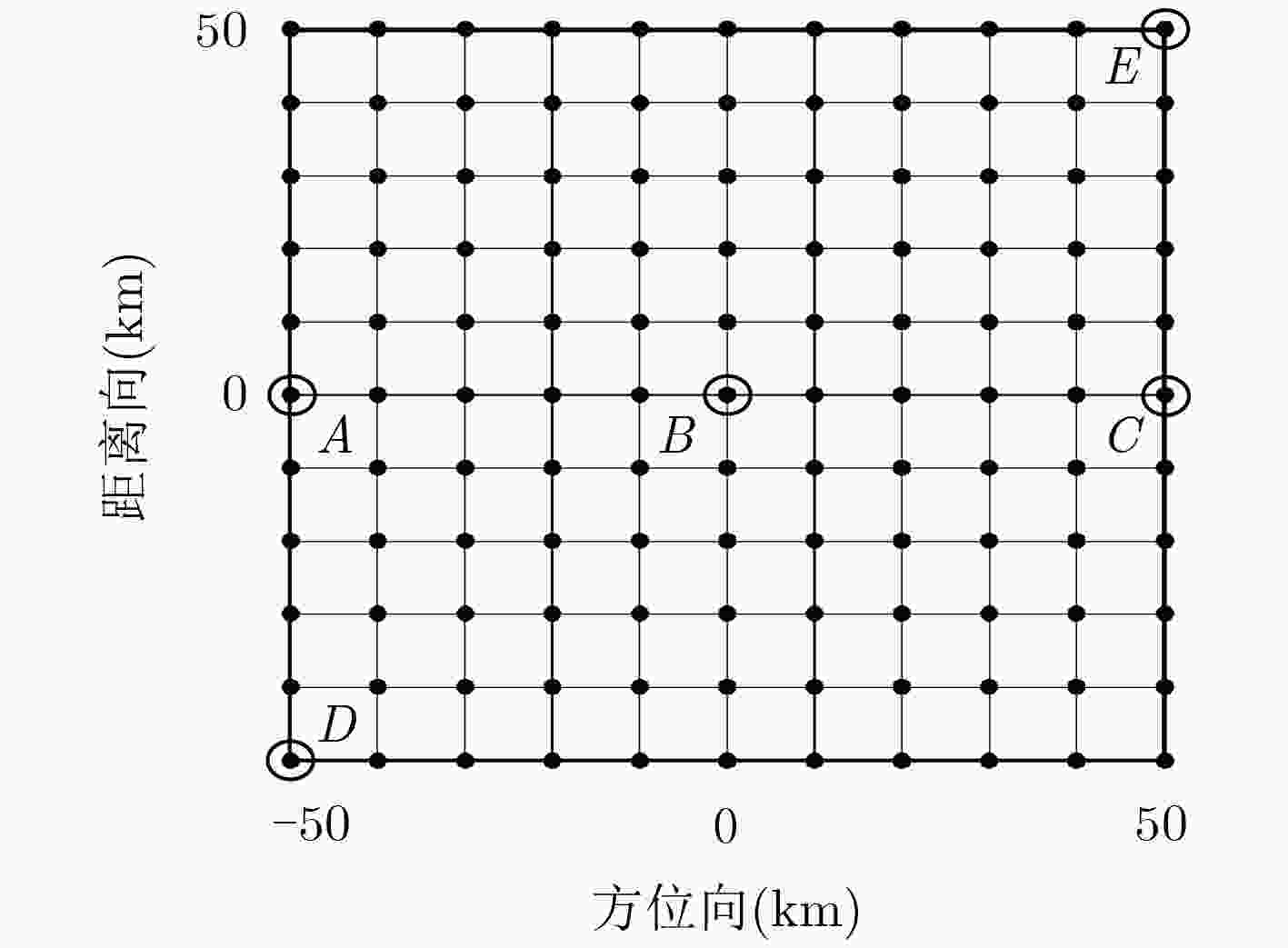
表 1 仿真参数
参数类型 参数名称 数值 轨道参数 轨道高度(km) 15000 离心率 0 倾角(°) 90 近地点幅角(°) 0 雷达参数 频率(GHz) 5.4 带宽(MHz) 103.4 PRF(Hz) 4000 入射角(°) 40 合成孔径时间(s) 43.1 地表距离分辨率(m) 2 地表方位分辨率(m) 2 场景参数 场景方位宽度(km) 100 场景距离宽度(km) 100 表 2 成像质量评估(dB)
目标(行,列) PSLR ISLR 距离向 方位向 距离向 方位向 D(11,1) –13.27 –13.27 –10.06 –10.06 B(6,6) –13.24 –13.26 –10.04 –10.06 E(1,11) –13.27 –13.27 –10.06 –10.05 -
ROLF W and STEFAN B. The TerraSAR-X mission and system design[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(2): 606–615. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2009.2031062 ZHANG Tianyi, DING Zegang, TIAN Weiming, et al. A 2-D nonlinear chirp scaling algorithm for high squint GEO SAR imaging based on optimal azimuth polynomial compensation[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations And Remote Sensing, 2017, 10(12): 5724–5735. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2017.2765353 STEPHEN H. System design for geosynchronous synthetic aperture radar missions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(12): 7750–7763. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2014.2318171 JALAL M, PACO L D, and GERHARD K. Potentials and limitations of MEO SAR[C]. European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Hamburg, Germany, 2016: 1–5. TIAN Ye, HU Cheng, DONG Xichao, et al. Theoretical analysis and verification of time variation of background ionosphere on geosynchronous SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(4): 721–725. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2014.2360235 LI Liang, HONG Jun, and MING Feng. Study about ionospheric effects on medium-earth-orbit SAR imaging[C]. 2014 IEEE Radar Conference, Cincinnati, USA, 2014: 27–31. 温雪娇, 仇晓兰, 尤红建, 等. 高分辨率星载SAR起伏运动目标精聚焦与参数估计方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(2): 213–220. doi: 10.12000/JR17005WEN Xuejiao, QIU Xiaolan, YOU Hongjian, et al. Focusing and parameter estimation of fluctuating targets in high resolution space-borne SAR[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(2): 213–220. doi: 10.12000/JR17005 HUANG Lijia, QIU Xiaolan, HU Donghui, et al. Focusing of medium-earth-orbit SAR with advanced nonlinear chirp scaling algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(1): 500–508. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2053211 BAO Ming, XING Mengdao, LI Yachao, et al. Two-dimensional spectrum for MEO SAR processing using a modified advanced hyperbolic range equation[J]. Electronics Letters, 2011, 47(18): 1043–1045. doi: 10.1049/el.2011.1322 TANG Shiyang, LIN Chunhui, ZHOU Yu, et al. Processing of long integration time spaceborne SAR data with curved orbit[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 52(2): 888–904. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2756109 CHEN Jie, KUANG Hui, YANG Wei, et al. A novel imaging algorithm for focusing high-resolution spaceborne SAR data in squinted sliding-spotlight mode[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(10): 1577–1581. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2016.2598066 RICHARD B. A comparison of range-Doppler and wavenumber domain SAR focusing algorithms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1992, 30(4): 706–713. doi: 10.1109/36.158864 HUANG Lijia, QIU Xiaolan, HU Donghui, et al. Medium-Earth-Orbit SAR focusing using range Doppler algorithm with integrated two-step azimuth perturbation[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(3): 626–630. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2014.2353674 WANG Yan, LI Jingwen, XU Feng, et al. A new nonlinear chirp scaling algorithm for high-squint high-resolution SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 14(12): 2225–2229. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2017.2758386 LI Zhenyu, XING Mengdao, LIANG Yi, et al. A frequency-domain imaging algorithm for highly squinted SAR mounted on maneuvering platforms with nonlinear trajectory[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(7): 4023–4038. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2535391 LI Zhenyu, LIANG Yi, XING Mengdao, et al. An improved range model and omega-k-based imaging algorithm for high-squint SAR with curved trajectory and constant acceleration[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(5): 656–660. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2016.2533631 LI Dexin, WU Manqing, SUN Zaoyu, et al. Modeling and processing of two-dimensional spatial-variant geosynchronous SAR data[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2015, 8(8): 3999–4009. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2015.2418814 DAVIDE D and ANDREA M G. High-resolution spaceborne SAR focusing by SVD-Stolt[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2007, 4(4): 639–643. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2007.903081 CHEN Jianlai, SUN Guangcai, YANG Jun, et al. A TSVD-NCS algorithm in range-Doppler domain for geosynchronous synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(11): 1631–1635. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2016.2599224 HAUKE F, ELKE B, and JOSEF M. Total zero Doppler steering—A new method for minimizing the Doppler centroid[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2005, 2(2): 141–145. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2005.844591 DANIEL P S. Analytic yaw-pitch steering for side-looking SAR with numerical roll algorithm for incidence angle[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2012, 50(9): 3587–3594. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2183375 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
