PolSAR Image Classification Based on Discriminative Clustering
-
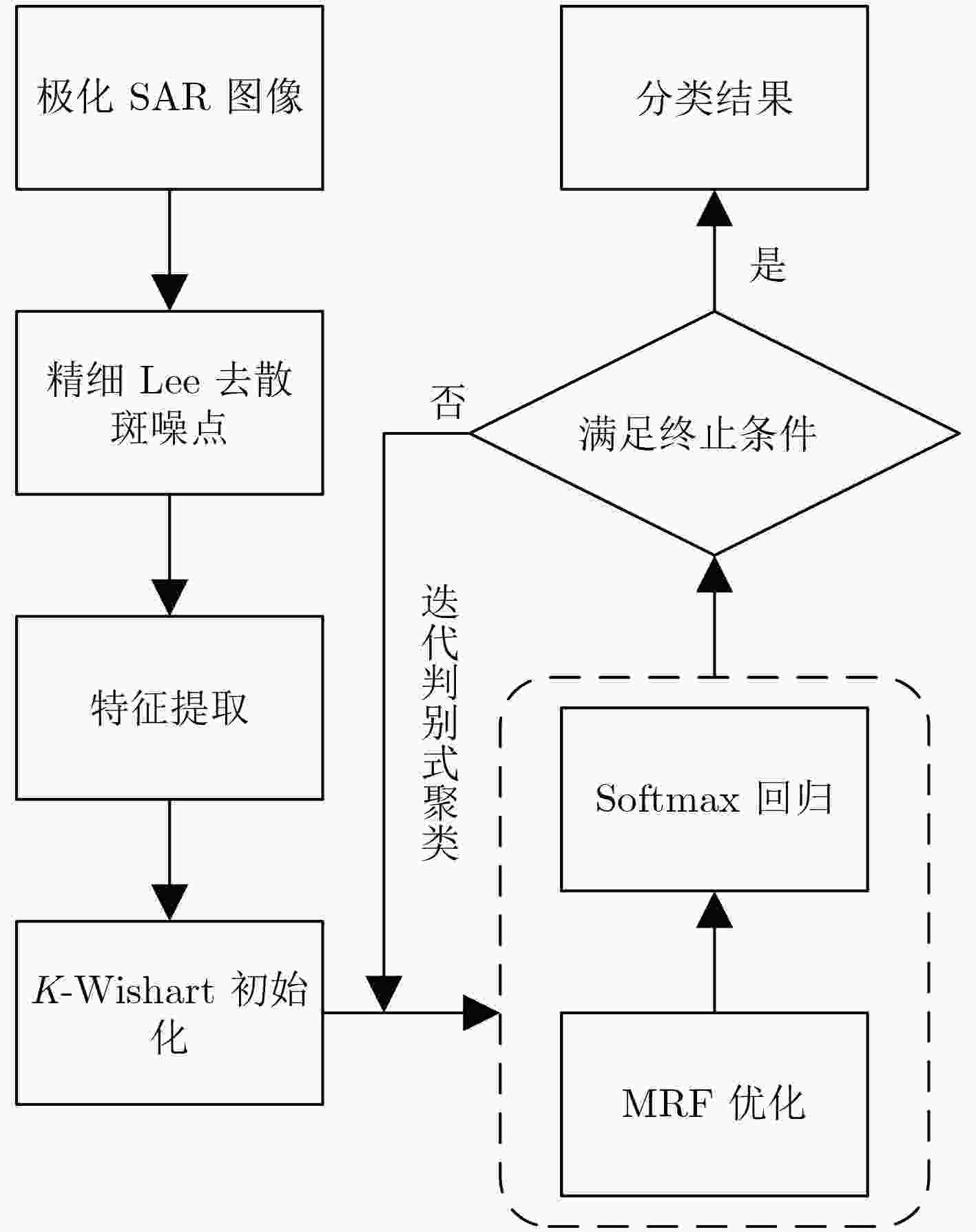
摘要: 该文提出一种基于判别式聚类框架的非监督极化SAR图像分类算法,利用判别式监督分类技术实现非监督聚类。为实现该算法,定义了一个结合softmax回归模型和马尔科夫随机场光滑性约束的能量函数。该模型中,像素类标和分类器均为需要优化的未知变量。该算法从基于
${H / {\bar \alpha }}$ 目标极化分解和K-Wishart极化统计分布而产生的初始化类标开始,交替迭代优化分类器和类标的能量函数,从而实现对分类器和类标的求解。真实极化SAR数据上的实验结果证明了该算法的有效性和先进性。-
关键词:
- 极化SAR图像分类 /
- 判别式聚类 /
- 马尔科夫随机场 /
- softmax回归模型
Abstract: This paper presents a novel unsupervised image classification method for Polarimetric Synthetic Aperture Radar (PolSAR) data. The proposed method is based on a discriminative clustering framework that explicitly relies on a discriminative supervised classification technique to perform unsupervised clustering. To implement this idea, an energy function is designed for unsupervised PolSAR image classification by combining a supervised Softmax Regression (SR) model with a Markov Random Field (MRF) smoothness constraint. In this model, both the pixelwise class labels and classifiers are taken as unknown variables to be optimized. Starting from the initialized class labels generated by Cloude-Pottier decomposition and K-Wishart distribution hypothesis, the classifiers and class labels are iteratively optimized by alternately minimizing the energy function with respect to them. Finally, the optimized class labels are taken as the classification result, and the classifiers for different classes are also derived as a side effect. This approach is applied to real PolSAR benchmark data. Extensive experiments justify that the proposed approach can effectively classify the PolSAR image in an unsupervised way and produce higher accuracies than the compared state-of-the-art methods. -
表 1 本文算法所使用的特征
极化特征分类 标识 物理描述 极化矩阵及其数学变换 ${{{T}}_{ij}}(i,j = 1,2,3,i \le j)$ 水平垂直线极化方式下的相干矩阵元素(模值与幅角) ${\rm{Lin}}45{{{T}}_{ij}}(i,j = 1,2,3,i \le j)$ +45°/–45°线极化方式下的相干矩阵元素(模值与幅角) ${\rm{Cir}}45{{{T}}_{ij}}(i,j = 1,2,3,i \le j)$ 左右旋圆极化方式下的相干矩阵元素(模值与幅角) $\frac{{{I_{{\rm{hv}}}}}}{{{I_{{\rm{hh}}}}}},\frac{{{I_{{\rm{hv}}}}}}{{{I_{{\rm{vv}}}}}},\frac{{{I_{{\rm{hh}}}}}}{{{I_{{\rm{vv}}}}}},\frac{{{I_{{\rm{rr}}}}}}{{{I_{{\rm{lr}}}}}},\frac{{{I_{{\rm{ll}}}}}}{{{I_{{\rm{lr}}}}}},\frac{{{I_{{\rm{ll}}}}}}{{{I_{{\rm{rr}}}}}},\frac{{{I_{{\rm{mn}}}}}}{{{I_{{\rm{mm}}}}}},\frac{{{I_{{\rm{mn}}}}}}{{{I_{{\rm{nn}}}}}},\frac{{{I_{{\rm{mm}}}}}}{{{I_{{\rm{nn}}}}}}$ 水平垂直线极化,+45°/–45°线极化以及
左右旋圆极化方式下的强度比值SPAN 极化总功率 目标分解特征 Pauli矩阵分解 Pauli分解参数 ${P_{\rm{s}}},{P_{\rm{d}}},{P_{\rm{v}}},{\alpha _{\rm{L}}}$ Freeman分解参数 $\bar \alpha ,H,A,\beta ,(1 - H)(1 - A),(1 - H)A,H(1 - A),HA$ ${H / {\bar \alpha }}$分解参数 表 2 不同方法在Flevoland地区数据上的分类准确率(%)
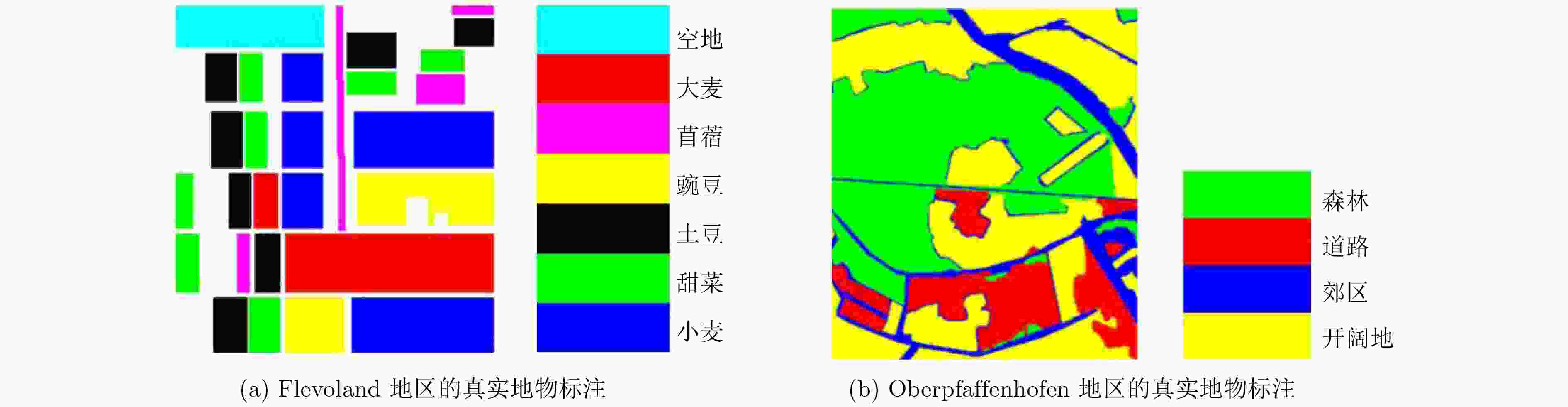
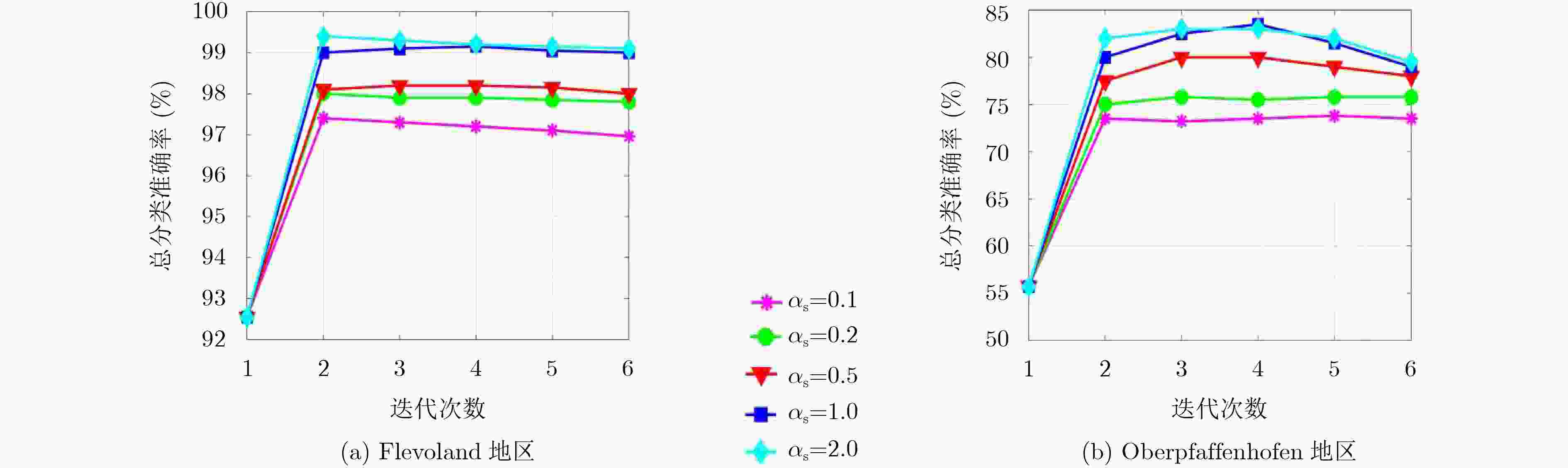
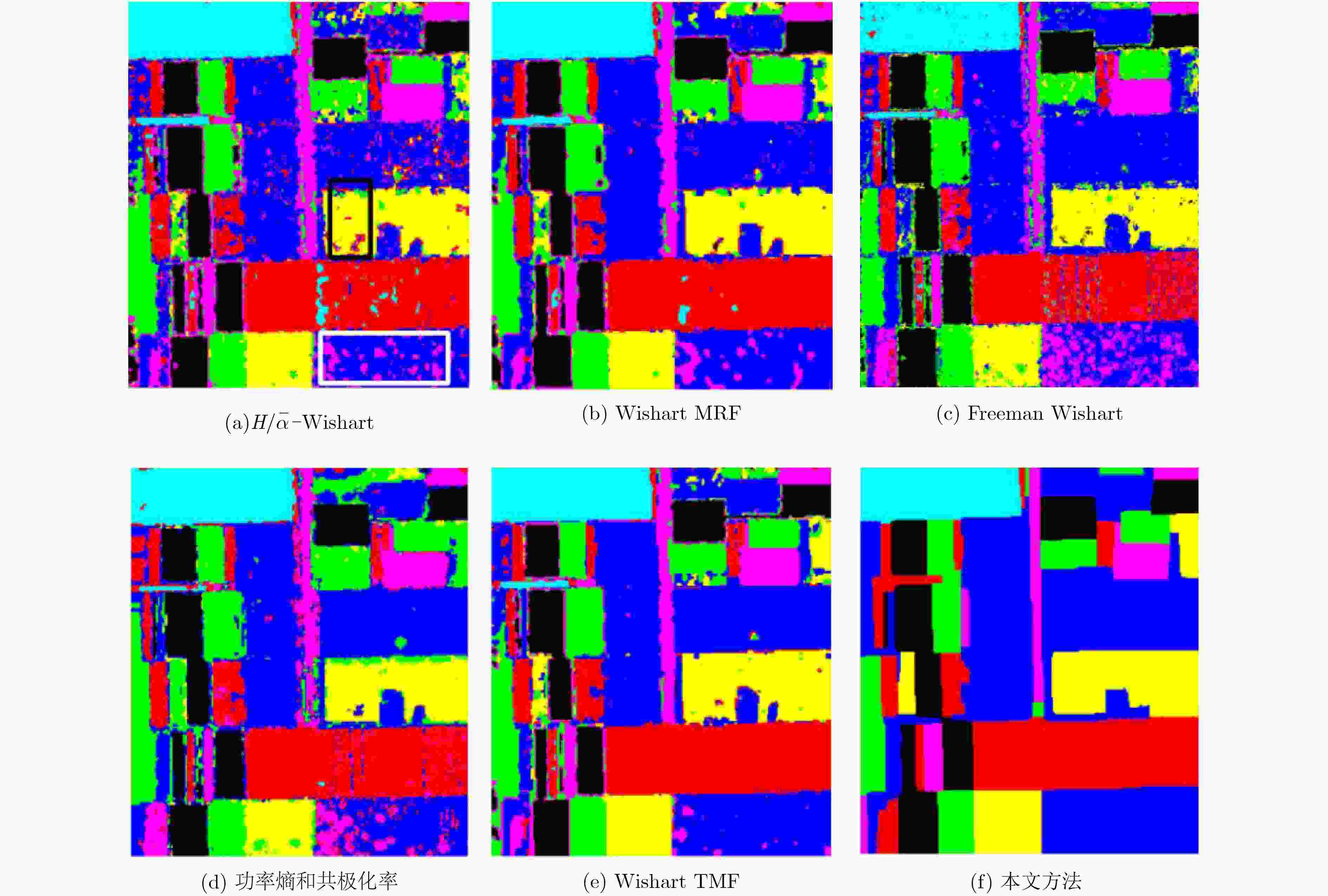
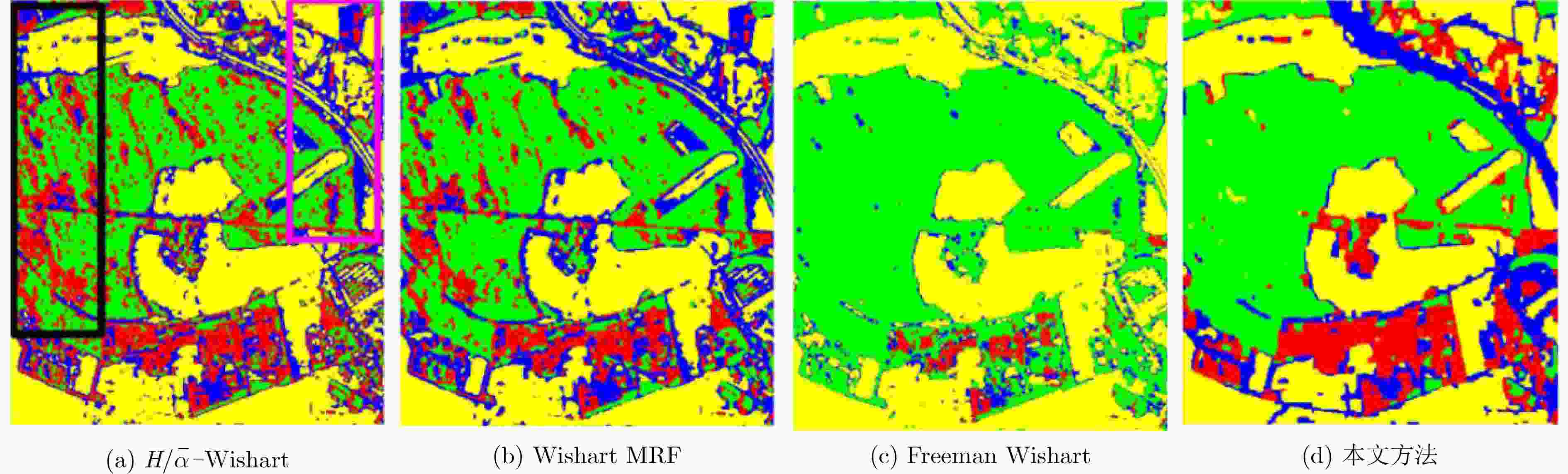
方法/类别 空地 大麦 苜蓿 豌豆 土豆 甜菜 小麦 总分类准确率 $H/\bar \alpha {\scriptsize{-}} {\rm{Wishart}}$ 99.94 86.60 84.63 88.50 81.44 84.00 82.48 85.59 Wishart MRF 100.00 86.21 93.27 94.24 85.55 89.54 92.55 91.82 Freeman Wishart 98.26 87.97 83.38 93.22 98.13 92.20 84.53 90.16 功率熵和共极化率 99.44 89.85 75.22 85.92 85.79 91.01 87.89 88.30 Wishart TMF 99.81 97.60 86.10 98.27 90.00 95.86 97.33 95.86 本文算法 100.00 100.00 95.07 98.21 98.57 98.63 99.93 99.05 表 3 本文方法在Oberpfaffenhofen地区数据上的分类准确率(%)
对象/类别 森林 道路 郊区 开阔地 总分类准确率 ${H / {\bar \alpha }} {\scriptsize{-}} {\rm{Wishart}}$ 65.21 41.80 51.51 76.01 64.43 Wishart MRF 74.43 55.52 42.28 72.93 67.26 Freeman Wishart 97.71 18.13 16.80 87.85 73.35 本文算法 93.65 64.70 60.78 84.41 82.25 -
KONG J A, SWARTZ A A, YUEH H A, et al. Identification of terrain cover using the optimum polarimetric classifier[J]. Journal of Electromagnetic Waves and Applications, 1988, 2(2): 171–194. POTTIER E and SAILLARD J. On radar polarization target decomposition theorems with application to target classification by using network method[C]. Proceedings of the International Conference on Antennas and Propagation, York, UK, 1991, 1: 265–268. FUKUDA S and HIROSAWA H. Support vector machine classification of land cover: Application to polarimetric SAR data[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Sydney, NSW, Australia, 2001, 1: 187–189. JIAO Licheng and LIU Fang. Wishart deep stacking network for fast PolSAR image classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2016, 25(7): 3273–3286 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2016.2567069 ZHOU Yu, WANG Haipeng, XU Feng, et al. Polarimetric SAR image classification using deep convolutional neural networks[J]. IEEE Geoscience Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 13(12): 1935–1939 doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2016.2618840 GAO Wei, YANG Jian, and MA Wenting. Land cover classification for polarimetric SAR images based on mixture models[J]. Remote Sensing, 2014, 6(5): 3770–3790 doi: 10.3390/rs6053770 CLOUDE S R and POTTIER E. An entropy based classification scheme for land application of polarimetric SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1997, 35(1): 68–78 doi: 10.1109/36.551935 FREEMAN A and DURDEN S L. A three-component scattering model for polarimetric SAR data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1998, 36(3): 963–973 doi: 10.1109/36.673687 YAMAGUCHI Y, MORIYAMA T, ISHIDO M, et al. Four-component scattering model for polarimetric SAR image decomposition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2005, 43(8): 1699–1706 doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2005.852084 XU Feng and JIN Yaqiu. Deorientation theory of polarimetric scattering targets and application to terrain surface classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2005, 43(10): 2351–2364 doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2005.855064 DOULEGERIS A P, ANFINSEN S N, and ELROFT T. Classification with a non-Gaussian model for PolSAR data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2008, 46(10): 2999–3009 doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2008.923025 徐丰, 王海鹏, 金亚秋. 深度学习在SAR目标识别与地物分类中的应用[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(2): 136–148 doi: 10.12000/JR16130XU Feng, WANG Haipeng and JIN Yaqiu. Deep Learning as Applied in SAR Target Recognition and Terrain Classification[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(2): 136–148 doi: 10.12000/JR16130 钟能, 杨文, 杨祥立, 等. 基于混合Wishart模型的极化SAR图像非监督分类[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(2): 136–148 doi: 10.12000/JR16133ZHONG Neng, YANG Wen, YANG Xiangli, et al. Unsupervised Classification for Polarimetric Synthetic Aperture RadarImages Based on Wishart Mixture Models[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(2): 136–148 doi: 10.12000/JR16133 BACH F and HARCHAOUI Z. DIFFRAC: A discriminative and flexible framework for clustering[C]. Proceedings of Conference and Workshop on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada, 2007: 49–56. SUN Jian and PONECE J. Learning discriminative part detectors for image classification and cosegmentation[C]. Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Sydney, NSW, Australia, 2013: 3400–3407. ZHU Ciyou, BYRD R H, LU Peihuang, et al. L-BFGS-B: Fortran subroutines for large-scale bound-constrained optimization[J]. ACM Transaction Mathematical Software, 1997, 23(4): 550–560 doi: 10.1145/279232.279236 WU Yonghui, JI Kefeng, YU Wenxian, et al. Region-based classification of polarimetric SAR images using Wishart MRF[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2008, 5(4): 668–672 doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2008.2002263 LEE J S, GRUNES M R, Ainsworth T L, et al. Unsupervised classification using polarimetric decomposition and the complex Wishart classifier[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1999, 37(5): 2249–2258 doi: 10.1109/36.789621 WANG Shuang, LIU Kun, PEI Jingjing, et al. Unsupervised classification of fully polarimetric SAR images based on scattering power entropy and copolarized ratio[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2013, 10(3): 622–626 doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2012.2216249 LIU Gaofeng, LI Ming, WU Yan, et al. PolSAR image classification based on Wishart TMF with specific auxiliary field[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2014, 11(7): 1230–1234 doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2013.2290066 LEE J S, GRUMES M R, POTTIER E, et al. Unsupervised terrain classification preserving polarimetric scattering characteristics[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2004, 42(4): 722–731 doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2003.819883 -






 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
