Distributed Firewall Policy Based on Traffic Engineering in Software Defined Network
-
摘要:
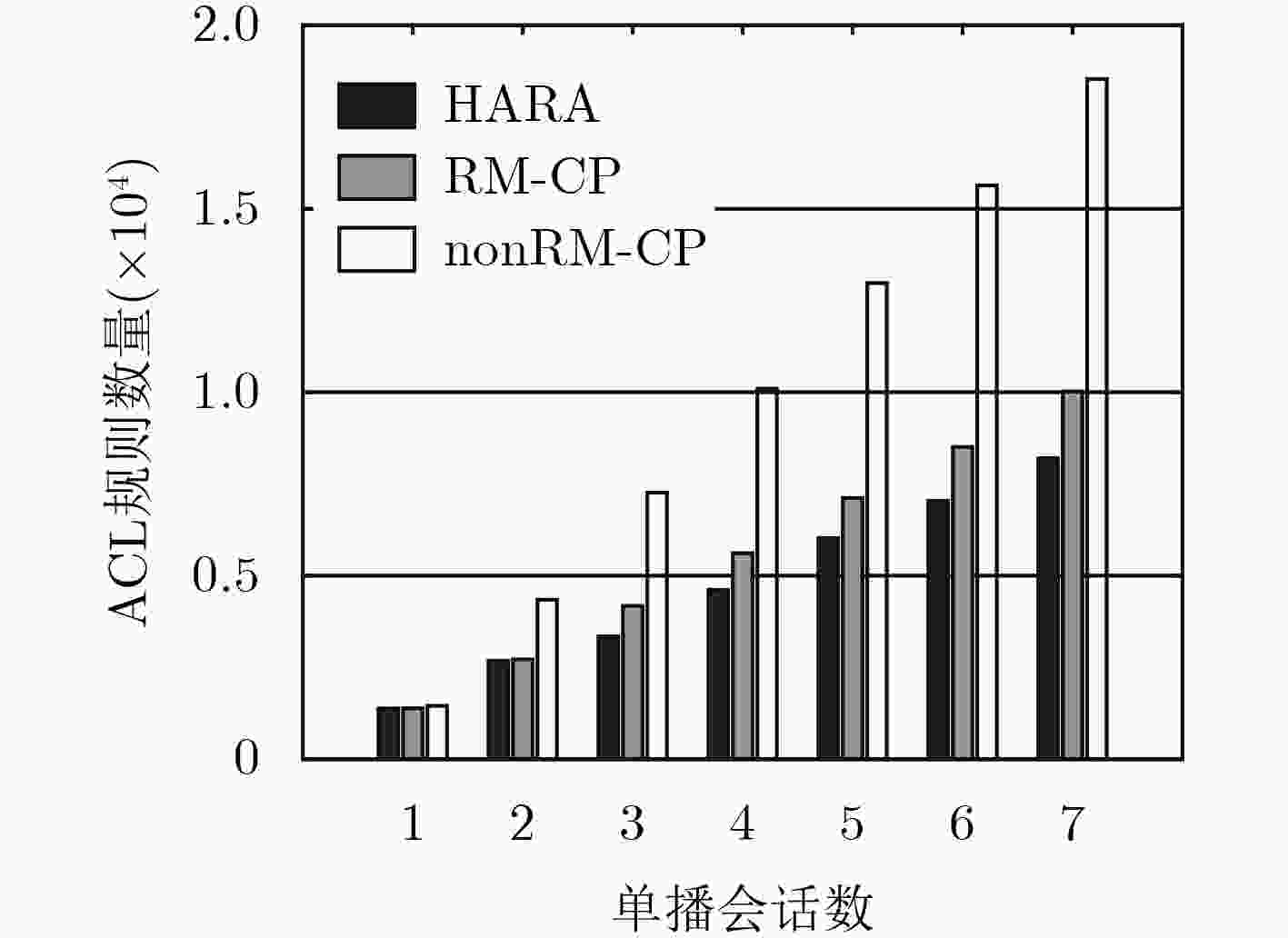
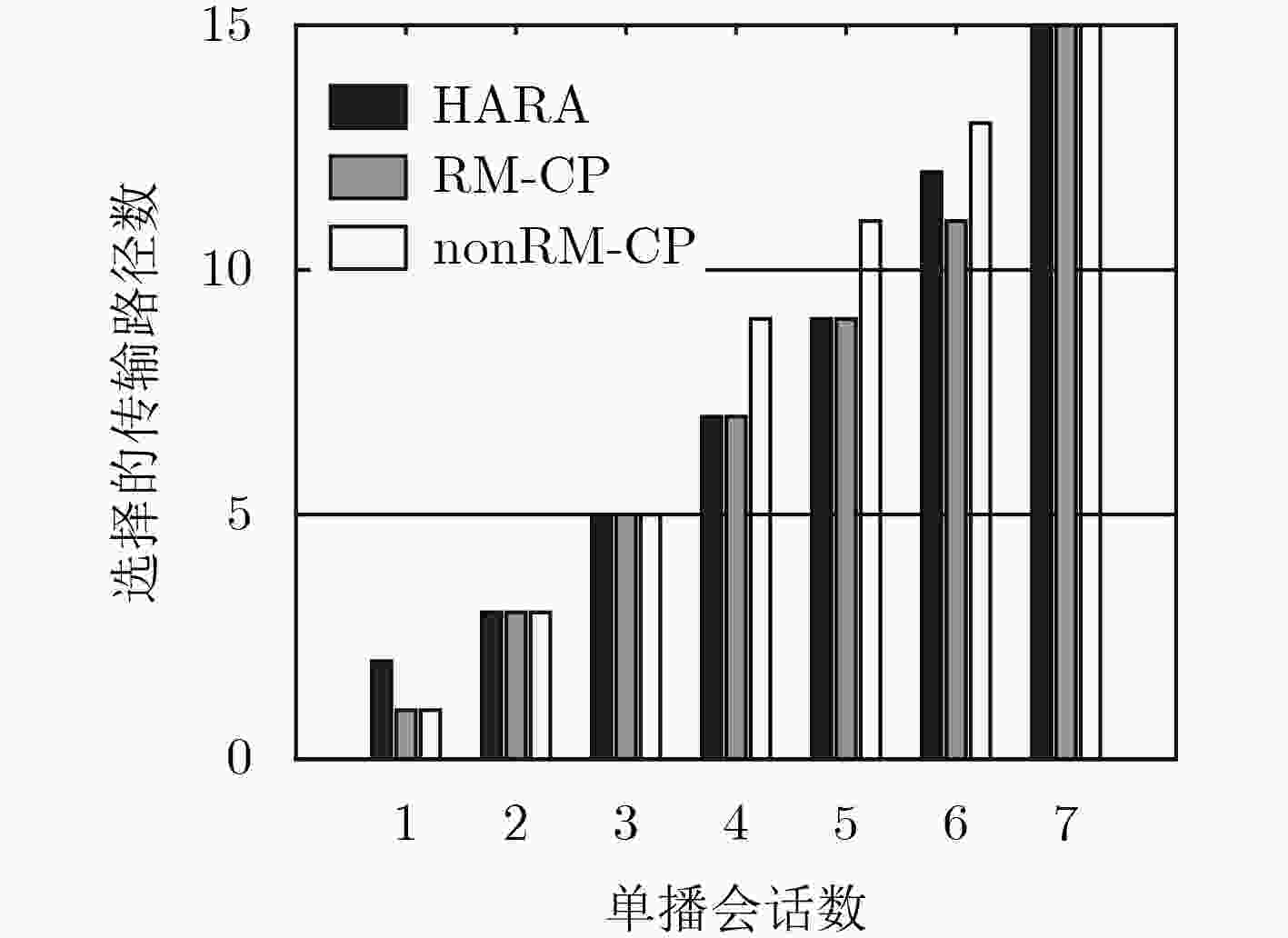
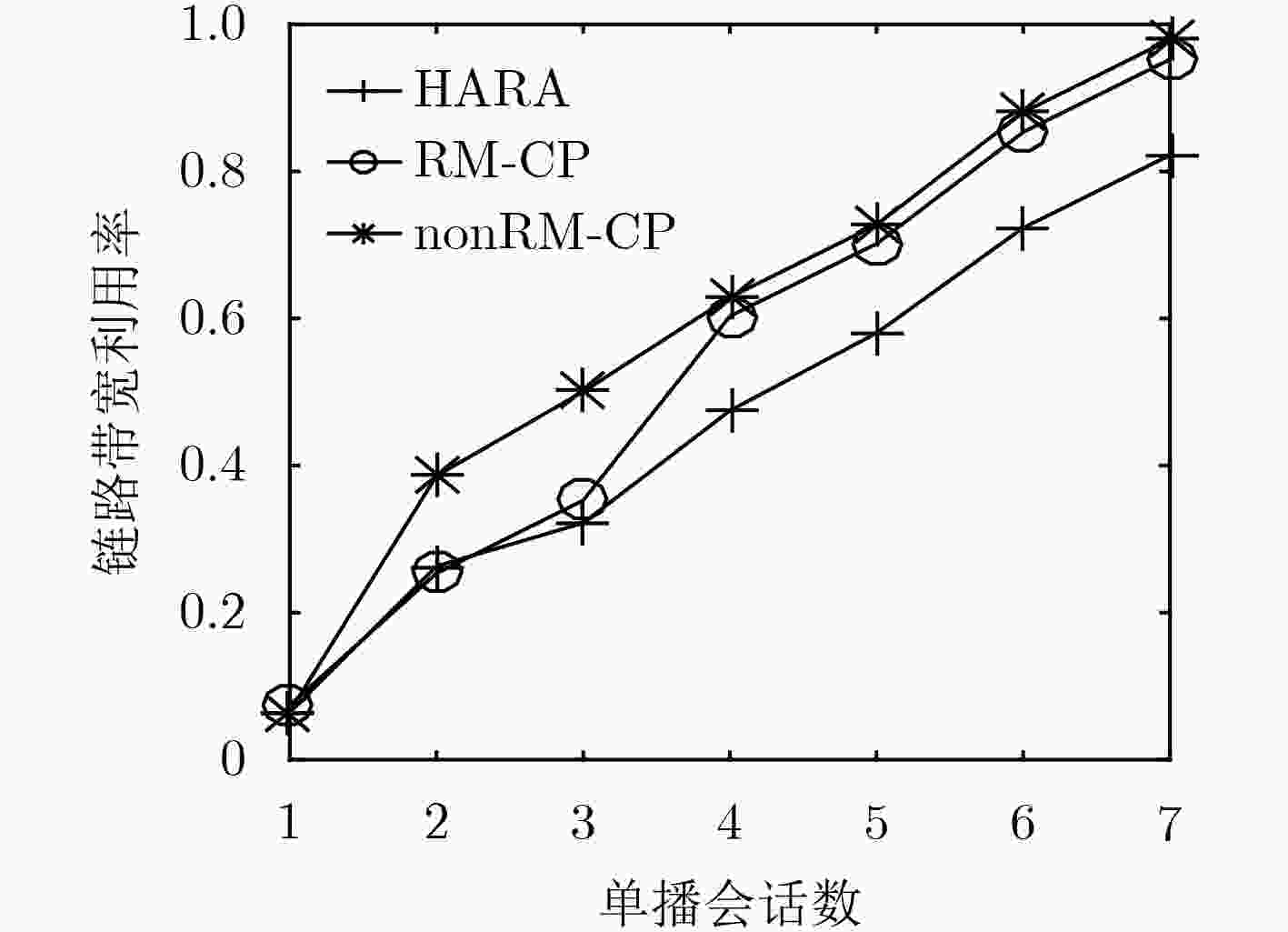
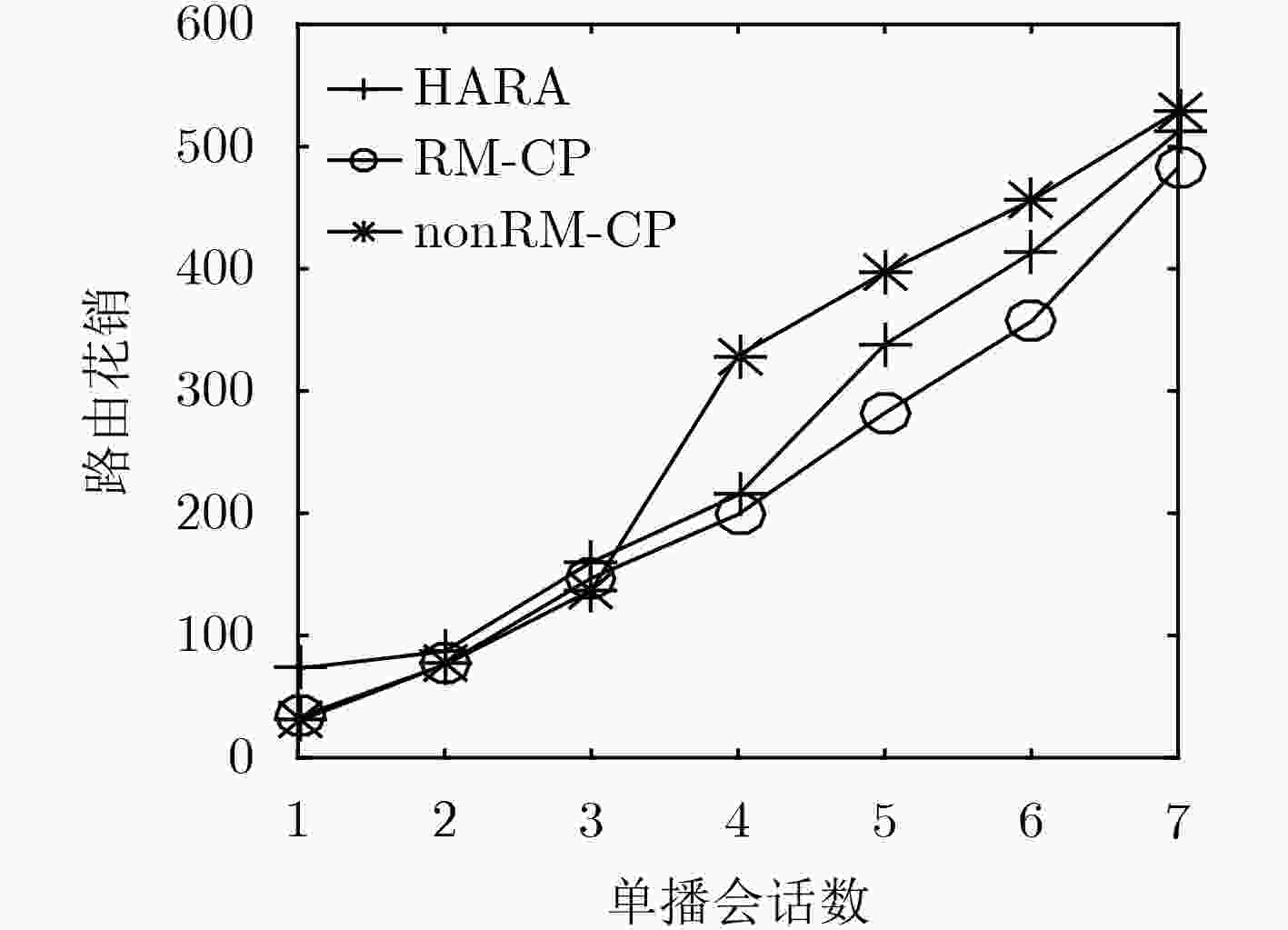
在软件定义网络中将防火墙策略定义为访问控制型规则,并将其分布式地部署在网络中能够提高会话的服务质量。为了减少放置在网络中规则的数量,文中提出多路复用和合并的启发式规则放置算法(HARA)。算法考虑到了商品交换机TCAM存储空间和端点交换机相连链路的流量负载,通过建立以最小化规则放置数量为目标的混合整数线性规划模型,解决不同吞吐量的多路由单播会话的规则放置问题。实验结果表明,与nonRM-CP算法相比,在保证不同会话服务质量的前提下,该算法最多能节省56%的TCAM空间,平均能减少13.1%的带宽资源利用率。
Abstract:Firewall policy is defined as access control rules in Software Definition Network (SDN), and distributing these ACL (Access Control List) rules across the networks, it can improve the quality of service. In order to reduce the number of rules placed in the network, the Heuristic Algorithm of Rules Allocation (HARA) of rule multiplexing and merging is proposed in this paper. Considering TCAM storage space of commodity switches and connected link traffic load of endpoint switches, a mixed integer linear programming model which minimize the number of rules placed in the network is established, and the algorithm solves the rules placement problem of multiple routing unicast sessions of different throughputs. Compared with the nonRM-CP algorithms, simulations show that HARA can save 18% TCAM at most and reduce the bandwidth utilization rate of 13.1% at average.
-
表 1 多路由选取算法
算法1 多路由选取算法(MRSA) 输入:网络拓扑$G = (V,E)$,路由花销$w(i,j)$ ,单播会话集$K$ 输出:$\widetilde {{P}}_k$ (1) $\widetilde {{P}}_k,A,B \leftarrow \varnothing $, $\varOmega _{ab}^k \leftarrow \{ a,b\} $, ${\rm{inf}} \leftarrow \infty $, $n,m \leftarrow 0$ (2) for each single session $k \in K$ in $G(V,E)$ do (3) $A \leftarrow $ the nodes of connecting to $a$ (4) $B \leftarrow $ the nodes of connecting to $b$ (5) $\deg _a^{\rm{ + }},\deg _b^ - \leftarrow $ compute the degree of $a$ and $b$ in $G(V,E)$ (6) while $n \ne \deg _a^{\rm{ + }}$ in $G(V,E)$ do (7) $\widetilde {{P}}_k \leftarrow $ Dijkstra $(a,b)$ (8) $n \leftarrow $ count the number of node $a$ in $\widetilde {{P}}_k$ (9) the first link routing cost of previous candidate path in $G(V,E) \leftarrow {\rm{inf}}$ (10) end while (11) while $n \ne \deg _b^ - $ in $G(V,E)$ do (12) $n \leftarrow $ count the number of different nodes connecting to $b$ in $\widetilde {{P}}_k$ (13) $\widetilde {{P}}_k \leftarrow $ Dijkstra $(a,B) \cup \{ b\} $ (14) end while (15) $\deg_i^{\rm{ + }} \leftarrow $ compute the degree of $i$ from $A$ in $G(V,E)$ (16) while $m \ne \deg _i^{\rm{ + }}$ in $G(V,E)$ do (17) $m \leftarrow $ count the number of different nodes connecting $i$ in $\widetilde {{P}}_k$ (18) the second link routing cost of previous candidate path in$G(V,E)$ (19) $\widetilde {{P}}_k \leftarrow $ Dijkstra $(A,b) \cup \{ a\} $ (20) end while (21) end for (22) return $\widetilde {{P}}_k$ 表 2 分布式防火墙部署算法
算法2:分布式防火墙部署算法(DPAA) 输入:单播会话集$K$,会话集的吞吐量${d_k}$,候选路径集$\widetilde {{P}}_k$,规则子 集${R_k}$ 输出:规则数量${R_{\rm{all}}}$,带宽利用率${B_{\rm{use}}}$,路由花销${L_{\rm{cost}}}$ (1) ${R_{\rm{all}}},{B_{\rm{use}}},{L_{\rm{cost}}} \leftarrow {\rm{0}}$ (2) ${P_k} \leftarrow $ sort $\widetilde {{P}}_k$ from algorithm 1 into a two-dimension array (3) for each single session $k \in K$ in $G(V,E)$ do (4) for $p \in {P_k}$ do (5) ${B_{\min }} \leftarrow $ sort the minimum bandwidth of all paths (6) if $\sum\nolimits_{i \in V} {{r_u}} \le {C_i}$ and ${R_k} \subseteq {\forall _{i \in V}}\left\{ i \right\}$ do (7) if ${d_k} < {B_{{\rm{min}}}}$ do (8) ${l^p} \leftarrow 1$, $x_i^{up} \leftarrow 1$ (9) else (10) ${l^p} \leftarrow 1$, $l_{(i,j)}^p \leftarrow 1$, $x_i^u \leftarrow 1$, $x_i^{up} \leftarrow 1$ (11) end if (12) end if (13) end for (14) end for (15) for all nodes do (16) if each node satisfy $(12)$ do (17) $x_{ui}^m \leftarrow 1$ (18) end if (19) end for (20) return ${R_{\rm{all}}}$, ${B_{\rm{use}}}$, ${L_{\rm{cost}}}$ 表 3 不同场景下规则放置的节点及数量
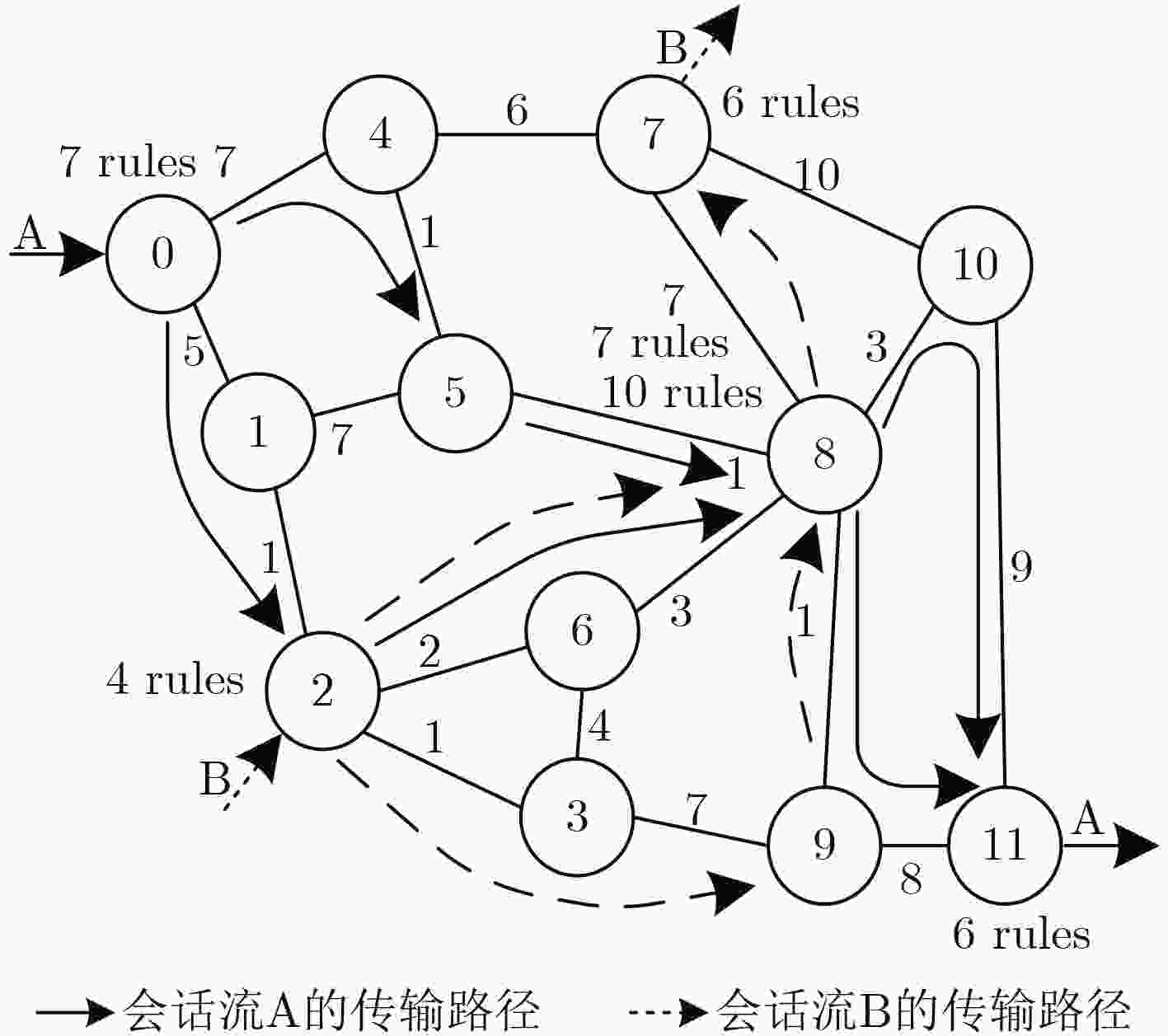
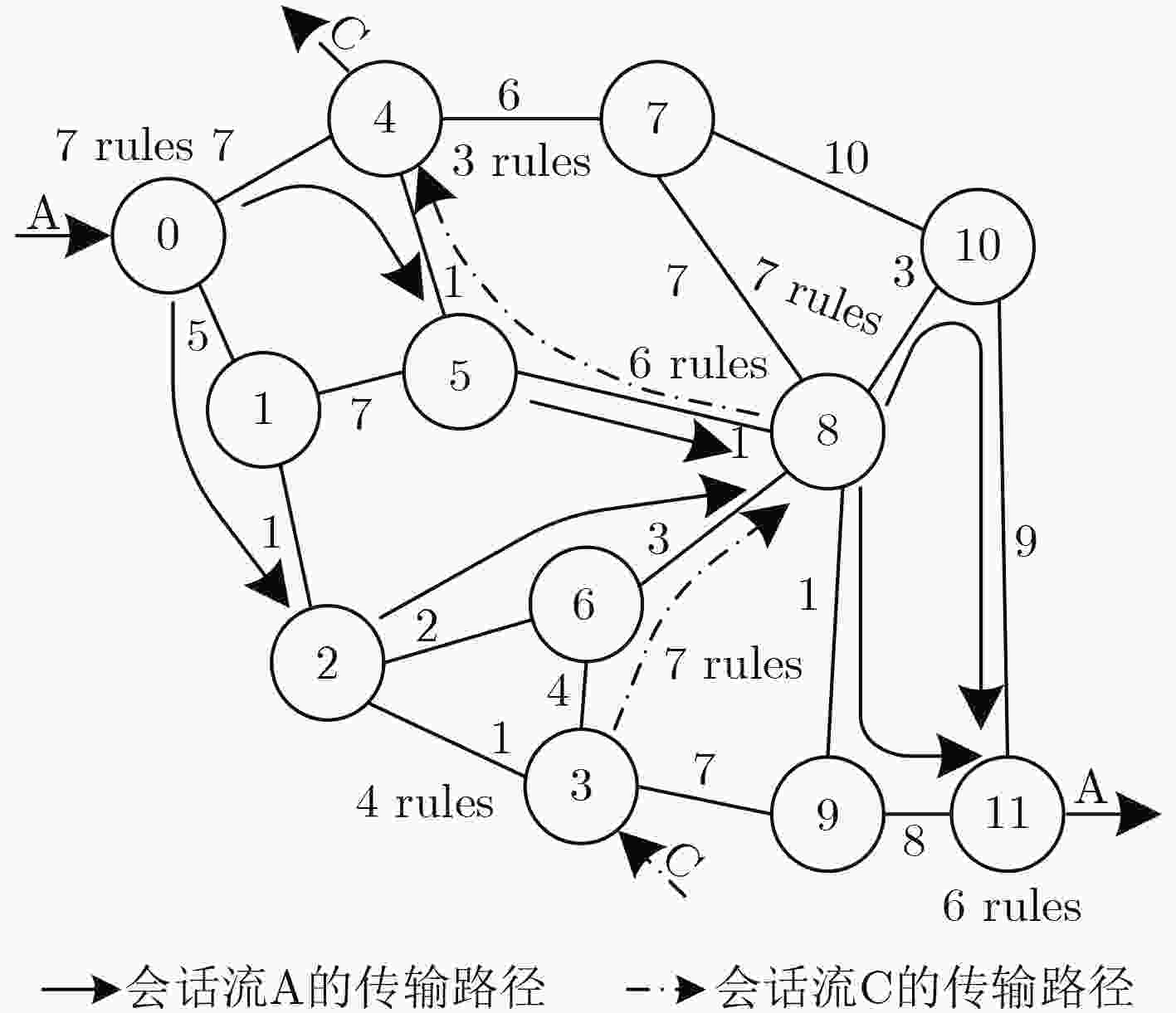
典型会话
场景选择的节点:规则数量 规则总
数量场景1 会话流A: 0: 7, 8: 7, 11: 6
会话流B: 2: 4, 7: 6, 8: 10[33, 40] 场景2 会话流A: 0: 7, 8: 7, 11: 6
会话流C: 3: 4, 4: 3, 6: 7, 8: 6[34, 40] -
MCKEOWN N, ANDERSON T, BALAKRISHNAN H, et al. OpenFlow: Enabling innovation in campus networks[J]. ACM SIGCOMM Computer Communication Review, 2008, 38(2): 69–74. doi: 10.1145/1355734.1355746 NGUYEN X N, SAUCEZ D, BARAKAT C, et al. Rules placement problem in openflow networks: A survey[J]. IEEE Communications Survey & Tutorials, 2016, 18(2): 1273–1286. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2015.2506984 KANG Nanxi, LIU Zhenming, REXFORD Jennifer, et al. Optimizing the " one big switch” abstraction in software-defined networks[C]. Proceedings of the Ninth ACM Conference on Emerging Networking Experiments and Technologies, Santa Barbara, California, USA, 2013: 13–24. KANIZO Y, HAY D, and KESLASSY I. Palette: distributing tables in software-defined networks[C]. 2013 Proceedings IEEE INFOCOM, Turin, Italy, 2013: 545–549. HUANG Jenfeng, CHANG Gueyyun, WANG Chunfeng, et al. Heterogeneous flow table distribution in software-defined networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Emerging Topics in Computing, 2016, 4(2): 252–261. doi: 10.1109/TETC.2015.2457333 NGUYEN X, SAUCEZ D, BARAKAT C, et al. OFFICER: A general optimization framework for openflow rule allocation and endpoint policy enforcement[C]. 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Communications (INFCOM), Kowloon, China, 2015: 478–486. HUANG Huawei, GUO Song, LI Peng, et al. Joint optimization of rule placement and traffic engineering for QoS provisioning in Software Defined Network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 2015, 64(12): 3488–3499. doi: 10.1109/TC.2015.2401031 ASHRAF U. Rule minimization for traffic evolution in software-defined networks[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2017, 21(4): 793–796. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2016.2636212 GIROIRE F, MOULIERAC J, and PHAN T K. Optimizing rule placement in software-defined networks for energy-aware routing[C]. 2014 IEEE Global Communications Conference, Austin, USA, 2014: 2523–2529. ZHANG Shuyuan, IVANCIC F, LUMEZANU C, et al. An adaptable rule placement for software-defined networks[C]. 2014 44th Annual IEEE/IFIP International Conference on Dependable Systems and Networks, Atlanta, USA, 2014: 88–99. NGUYEN X, SAUCEZ D, BARAKAT C, et al. Optimizing rules placement in openflow networks: Trading routing for better efficiency[C]. Proceedings of the Third Workshop on Hot Topics in Software Defined Networking, 2014: 127–132. GARG N and KONEMANN J. Faster and simpler algorithms for multicommodity flow and other fractional packing problems[C]. Proceedings 39th Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science, Palo Alto, USA, 2007: 630–652. OPTIMIZATION G. Gurobi Optimizer Reference Manual[M]. 2013. Sndlib: Library of test instance for survivable fixed telecommunication network design[OL]. http://sndlib.zib.de/home.action, 2006. 史久根, 许辉亮, 陆立鹏. 软件定义网络中数据中心虚拟机迁移序列问题的研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(5): 1193–1199. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160792SHI Jiugen, XU Huiliang, and LU Lipeng. Research on the migration queue of data center’s virtual machine in software defined networks[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2017, 39(5): 1193–1199. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160792 伊鹏, 刘洪, 胡宇翔. 一种可扩展的软件定义数据中心网络流调度策略[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(4): 825–831. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160623YI Peng, LIU Hong, and HU Yuxiang. A scalable traffic scheduling policy for software defined data center network[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2017, 39(4): 825–831. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160623 KATTA N, ALIPOURFARD O, REXFORD J, et al. CacheFlow: Dependency-aware rule-caching for software-defined networks[C]. Proceedings of the Symposium on SDN Research, Santa Clara, USA 2016: 1–12. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
