Research on SDN-based Load Balancing Technology of Server Cluster
-
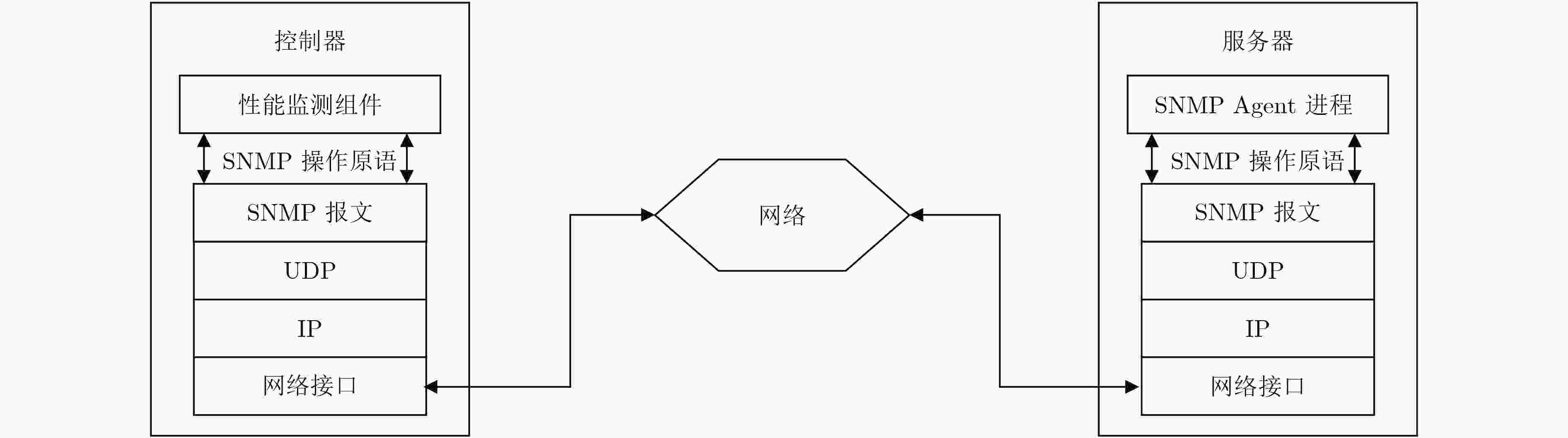
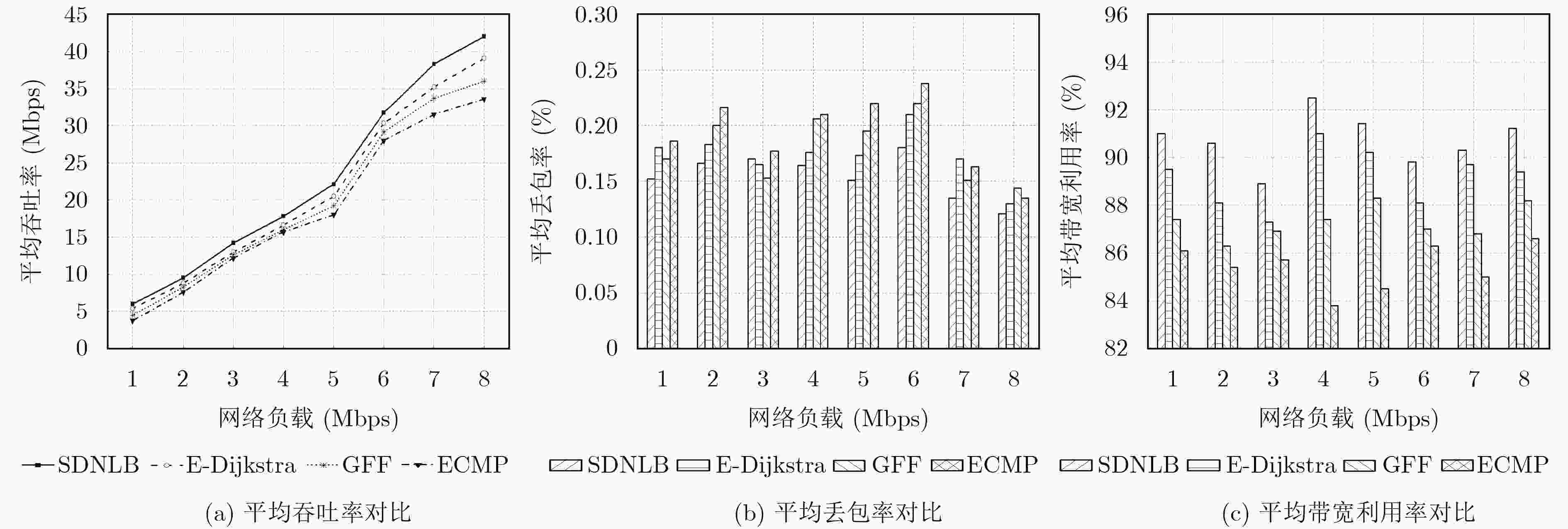
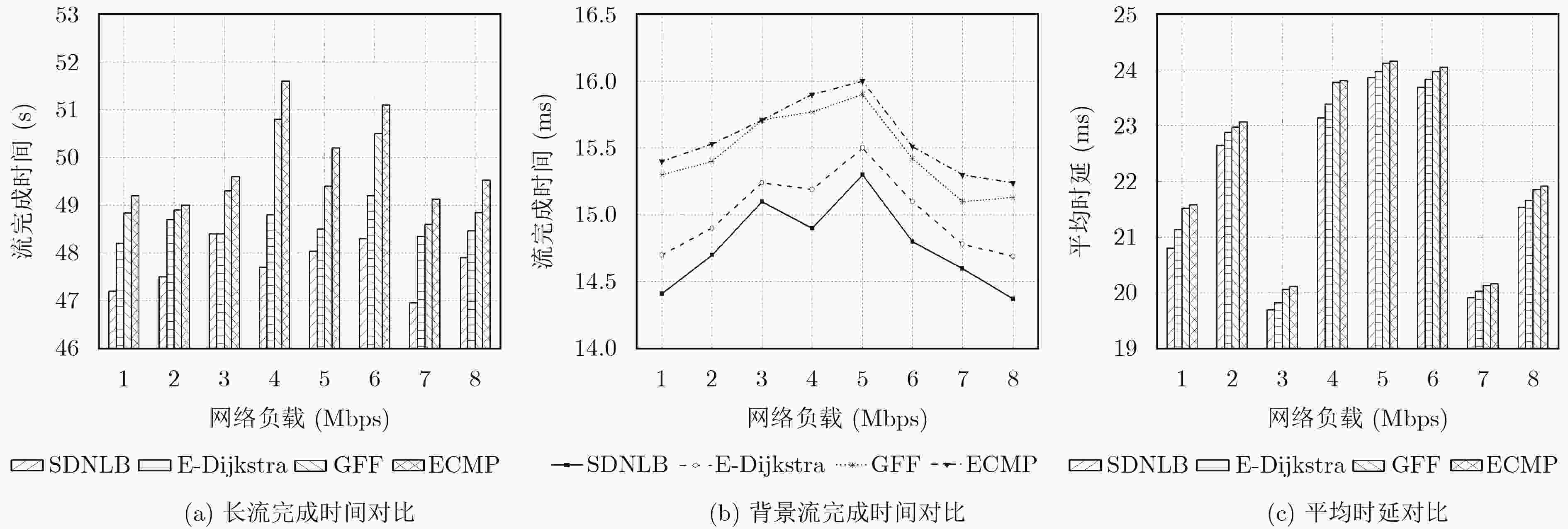
摘要: 在当前的网络体系结构下,采用硬件系统实现服务器集群负载均衡存在着获取负载节点状态困难、流量导向方式复杂等制约因素,不利于提升服务器集群的伸缩性和服务性能。针对此问题,该文提出一种基于软件定义网络(SDN)的负载均衡机制(SDNLB)。该机制借助SDN具有的集中式控制和流量灵活调度优势,利用SNMP协议和OpenFlow协议对服务器的运行状态和全局网络负载信息进行实时监测,并通过权值计算的方式选择出权重最高的服务器作为流处理的目标服务器,在此基础上,采用最优转发路径算法进行流量调度,从而达到提高服务器集群的利用率与处理性能的目的。搭建了实验平台对SDNLB的性能进行仿真测试,实验结果表明:在相同的网络负载条件下,SDNLB与其他负载均衡算法相比,能够有效地降低服务器集群的负载,并能够显著提高网络吞吐量和带宽利用率,缩短流的完成时间和平均时延。Abstract: Under the present network architecture, it is disadvantageous for scalability and service performance of server cluster to adopt hardware systems to realize load balancing of server cluster, because there are some restriction factors in such a method, including the difficulty of acquiring load nodes status and the complexity of redirecting traffic, etc. To solve the problem, a Load Balancing mechanism based on Software-Defined Networking (SDNLB) is proposed. With superiorities of SDN such as centralized control and flexible traffic scheduling, SDNLB monitors run states of servers and overall network load information by means of SNMP protocol and OpenFlow protocol in real time, and chooses the highest weight server as target server aiming for processing coming flows through the way of weight value calculation. On this basis, SDNLB takes full advantage of the optimal forwarding path algorithm to carry on traffic scheduling, and achieves the goal that raises utilization rate and processing performance of server cluster. An experiment platform is built to carry out simulation tests for overall performance of SDNLB, and the experiment results show that under the same network load conditions, SDNLB lowers effectively loads of server cluster, noticeably raises network throughput and bandwidth utilization, and reduces finish time and average latency of flows, compared with other load balancing algorithms.
-
Key words:
- Software-Defined Networking (SDN) /
- OpenFlow /
- Server cluster /
- Load balancing /
- Traffic engineering
-
表 1 服务器主要性能指标
指标类型 指标值 状态 CPU利用率 非空闲任务占用比小于70% 良好 70%~85% 过高 90%以上 很差 内存访问 没有页交换 良好 每个CPU每秒10个页交换 过高 更多的页交换 很差 磁盘I/O 活动时间百分比小于30% 良好 30%~45% 过高 50%以上 很差 表 2 流转发过程
算法1 SDNLB最优转发路径算法 输入:Topology_View /*当前网络拓扑视图*/ Link_Load /*网络链路负载信息*/ Target-Server /*目标服务器*/ Flow /*新到达的流*/ 输出:R /*最优转发路径*/ (1) implement logical loopless processing (2) destination=target-server (3) create a graph that meets bandwidth demand of flow (4) A=[ ] (5) A[0]= Dijkstra(graph, source, destination) (6) B=[ ] (7) for i: 1 to K do (8) for j: 0 to size(A[i –1])–1 do (9) spur=A[i –1].node( j) (10) root=A[i –1].nodes(0, j) (11) for path in A do (12) if root==path.nodes(0, j) do (13) remove path.nodes(j, j+1) (14) end if (15) end for (16) spurpath=Dijkstra(graph, spur, destination) (17) entirepath=root+spurpath (18) if entirepath not in B do (19) B.add(entirepath) (20) end if (21) recover those removed edges (22) end for (23) if B.length==0 do (24) break (25) else do (26) B.sort() (27) A[i]=B[0] (28) B.delete(B[0]) (29) end if (30) end for (31) if A.length==1 do (32) R=A[0] (33) else do (34) determine R by choosing a path from list A.Bandwidth utilization of the path should be minimum (35) end if (36) return R 表 4 服务器平均负载
服务器编号 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 SDNLB 0.71 0.71 0.70 0.71 0.68 0.69 0.73 0.72 E-Dijkstra 0.75 0.74 0.75 0.76 0.74 0.74 0.76 0.77 GFF 0.74 0.75 0.78 0.78 0.77 0.74 0.77 0.78 ECMP 0.86 0.86 0.87 0.89 0.87 0.87 0.85 0.87 表 3 CPU平均利用率(%)
服务器编号 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 SDNLB 22.65 22.53 22.43 22.31 22.20 22.58 22.48 22.11 E-Dijkstra 23.39 23.34 23.32 23.29 23.26 23.50 23.36 23.29 GFF 23.40 23.46 23.45 23.48 23.46 23.37 23.34 23.54 ECMP 23.79 23.70 23.66 23.60 23.59 23.75 23.68 23.56 -
GHOMI E, RAHMANI A, and QADER N. Load-balancing algorithms in cloud computing: A survey[J]. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 2017, 88(12): 50–71 doi: 10.1016/j.jnca.2017.04.007 SHARMA G and BUSCH C. A load balanced directory for distributed shared memory objects[J]. Journal of Parallel and Distributed Computing, 2015, 78(4): 6–24 doi: 10.1016/j.jpdc.2015.02.002 ILCHOL P, QIAO Baiyou, SHEN Muchuan, et al. An efficient load balancing approach for N-hierarchical web server cluster[J]. Wuhan University Journal of Natural Sciences, 2015, 20(6): 537–542 doi: 10.1007/s11859-015-1130-9 YANG Juipin. Elastic load balancing using self-adaptive replication management[J]. IEEE Access, 2017, 5(99): 7495–7504 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2016.2631490 SHEIKHI S and BABAMIR S. A predictive framework for load balancing clustered web servers[J]. The Journal of Supercomputing, 2016, 72(2): 588–611 doi: 10.1007/s11227-015-1584-8 MAO Qilin and SHEN Weikang. A load balancing method based on SDN[C]. The 7th International Conference on Measuring Technology and Mechatronics Automation, Nanchang, China, 2015: 18–21. TRESTIAN R, KATRINIS K, and MUNTEAN G. OFLoad: An OpenFlow-based dynamic load balancing strategy for datacenter networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management, 2017, 14(4): 792–803 doi: 10.1109/TNSM.2017.2758402 李龙, 付斌章, 陈明宇, 等. Nimble: 一种适用于OpenFlow网络的快速流调度策略[J]. 计算机学报, 2015, 38(5): 1056–1068 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1016.2015.01056LI Long, FU Binzhang, CHEN Mingyu, et al. Nimble: A fast flow scheduling strategy for OpenFlow networks[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2015, 38(5): 1056–1068 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1016.2015.01056 AL-FARES M, RADHAKRISHNAN S, RAGHAVAN B, et al. Hedera: Dynamic flow scheduling for data center networks[C]. NSDI’10 Proceedings of the 7th USENIX conference on networked systems design and implementation, San Jose, USA, 2010: 281–296. 蔡岳平, 王昌平. 软件定义数据中心网络混合路由机制[J]. 通信学报, 2016, 37(4): 44–52 doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2016071CAI Yueping and WANG Changping. Software defined data center network with hybrid routing[J]. Journal on Communications, 2016, 37(4): 44–52 doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2016071 覃匡宇, 黄传河, 刘柯威, 等. 基于多路广播树的SDN多路径路由算法[J]. 计算机科学, 2018, 45(1): 211–215 doi: 10.11896/j.issn.1002-137X.2018.01.037TAN Kuangyu, HUANG Chuanhe, LIU Kewei, et al. Multipath routing algorithm in software defined networking based on multipath broadcast tree[J]. Computer Science, 2018, 45(1): 211–215 doi: 10.11896/j.issn.1002-137X.2018.01.037 LIAO Lingxia and LEUNG VC. LLDP based link latency monitoring in software defined networks[C]. The 12th International Conference on Network and Service Management, Montreal, Canada, 2016: 330–335. RUBIN I and ZHANG Runhe. Max-min utility fair flow management for networks with route diversity[J]. International Journal of Network Management, 2010, 20(6): 361–381 doi: 10.1002/nem.740 YEN J Y. Finding the K shortest loopless paths in a network[J]. Management Science, 1971, 17(11): 712–716 doi: 10.1287/mnsc.17.11.712 JIANG J R, HUANG H W, LIAO J H, et al. Extending Dijkstra’s shortest path algorithm for software defined networking[C]. The 16th Asia-Pacific Network Operations and Management Symposium, Hsinchu, China, 2014: 1–4. ZHANG Zhe, BOCKELMAN B, CARDER D, et al. Lark: An effective approach for software-defined networking in high throughput computing clusters[J]. Future Generation Computer Systems, 2017, 72(7): 105–117 doi: 10.1016/j.future.2016.03.010 CHEN Yingying, JAIN S, ADHIKARI V, et al. A first look at inter-data center traffic characteristics via Yahoo! datasets[C]. IEEE INFOCOM, Shanghai, China, 2011: 1620–1628. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
