Adaptive Affine Propagation Clustering Algorithm for WiFi Indoor Positioning
-
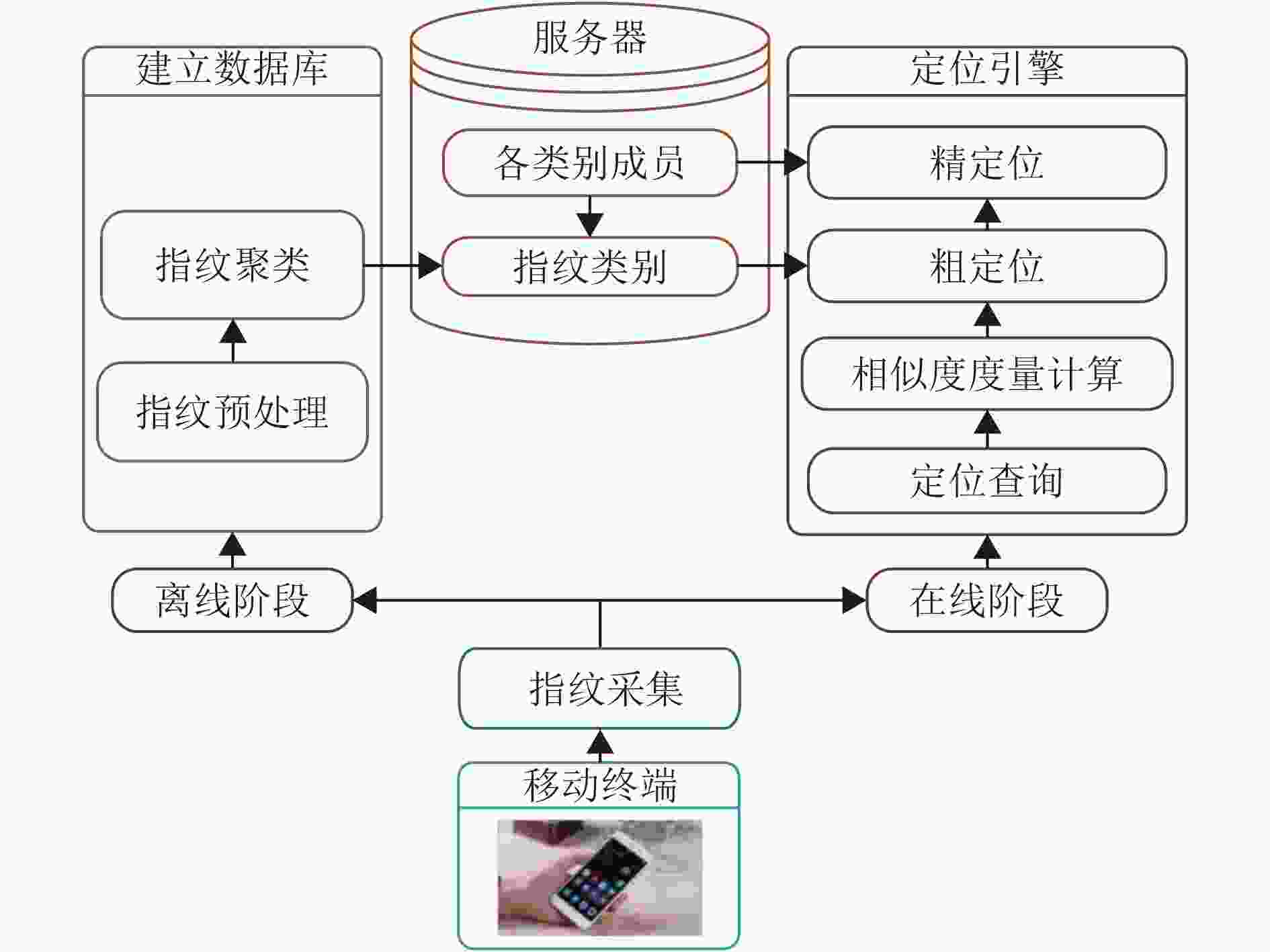
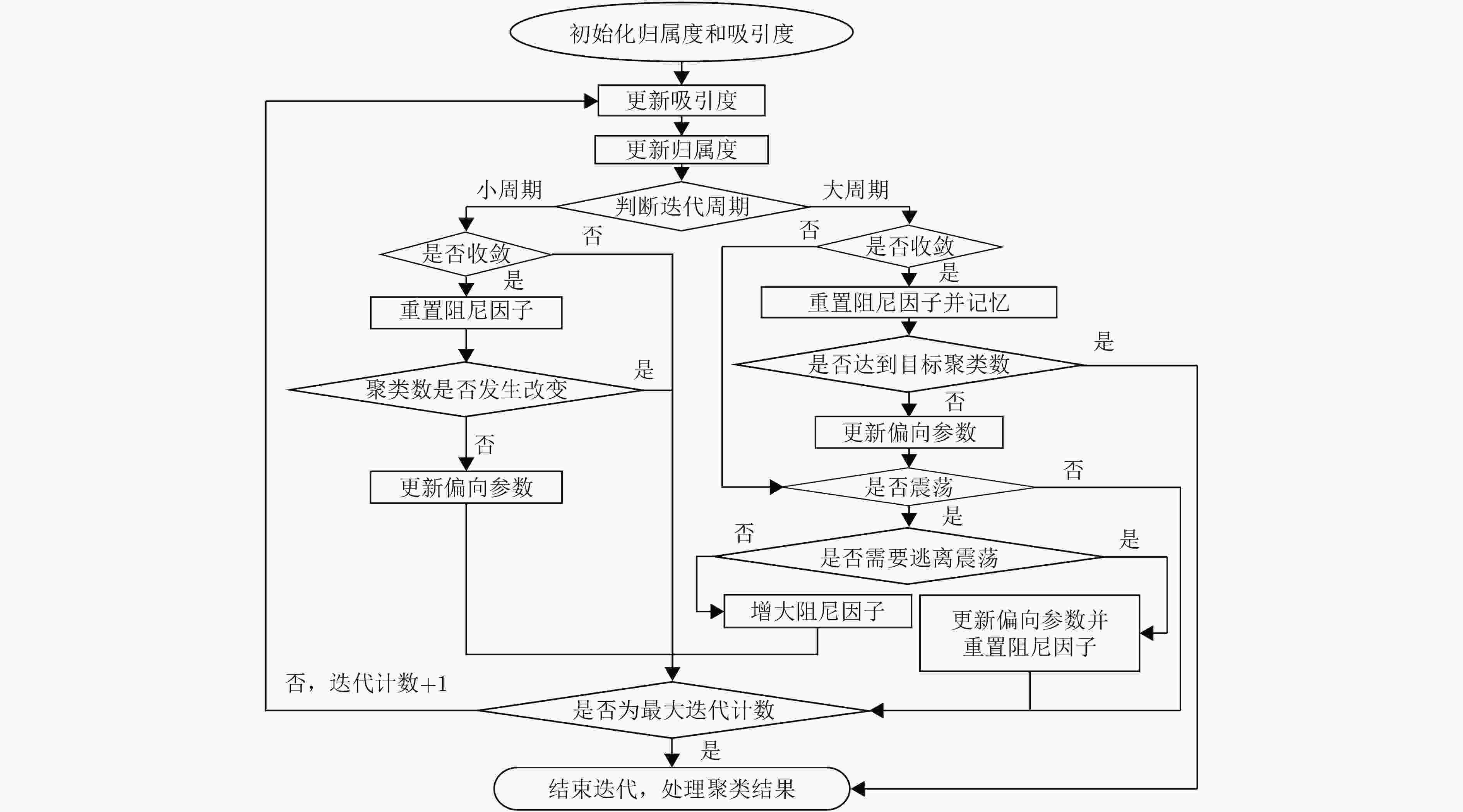
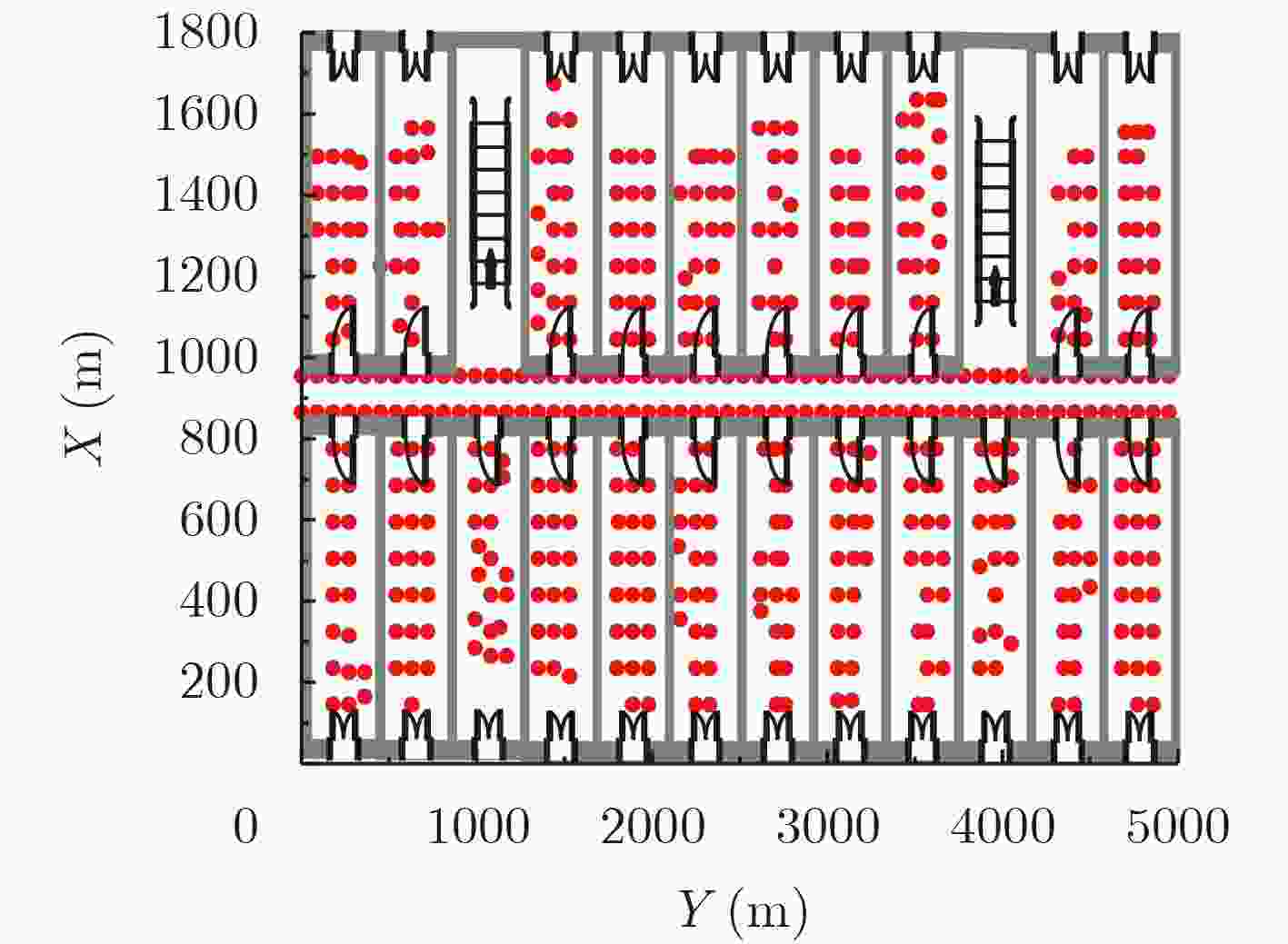
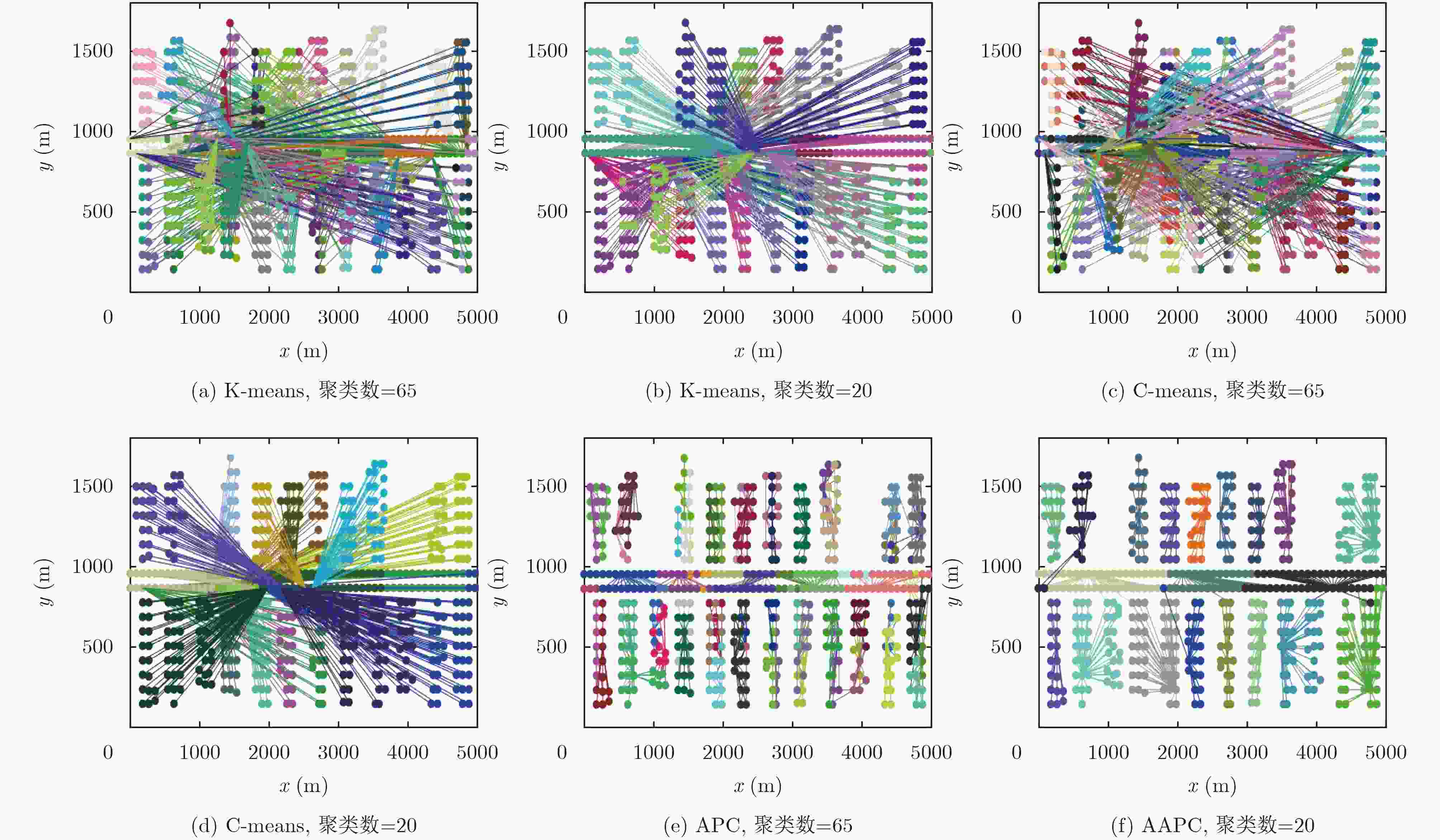
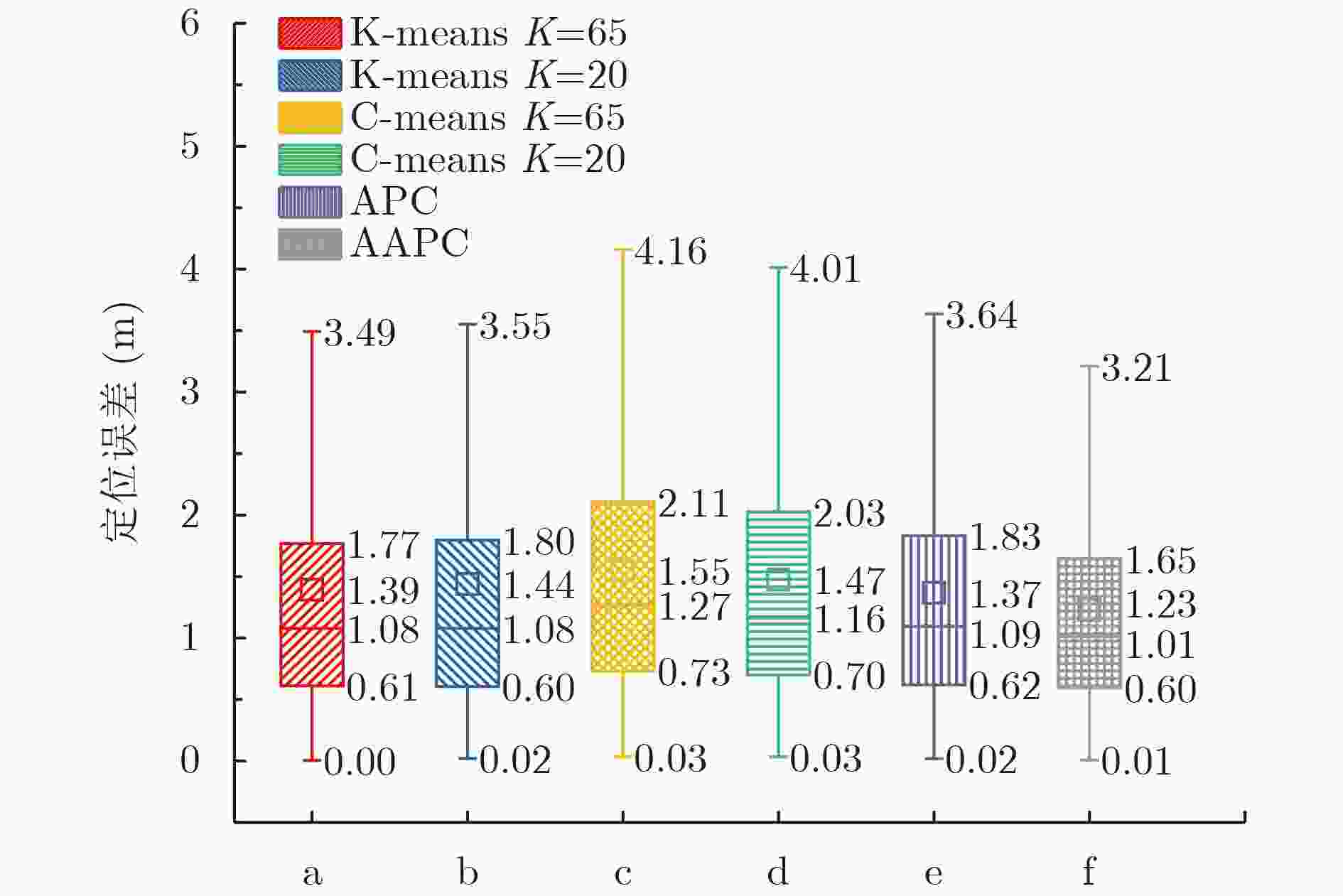
摘要: 在室内覆盖的大量的WiFi信号可以用来室内定位。尽管很多WiFi室内定位技术被提出,但其定位精度仍然未达到实际应用的需求。针对这个问题,该文提出一种自适应仿射传播聚类(AAPC)算法用以提高WiFi指纹的聚类质量,从而提高定位精度。AAPC算法通过动态调整参数生成不同的聚类结果,然后采用聚类有效性指标筛选出其中最佳的。采集大量真实环境数据进行试验,试验结果表明采用AAPC算法产生的聚类结果具有更高的定位精度。Abstract: There are a large number of indoor WiFi signals which can be used for indoor positioning. Although many WiFi indoor positioning technology is proposed, it's positioning accuracy still does not meet the actual application requirements. For this problem, an Adaptive Affinity Propagation Clustering (AAPC) algorithm is proposed to improve the clustering quality of WiFi fingerprint, thus improving the positioning accuracy. The AAPC algorithm generates different clustering results by dynamically adjusting parameters, then cluster validity indices are used to select the best ones. A large number of real environmental data are collected and tested. The experimental results show that the clustering results generated by AAPC algorithm have higher positioning accuracy.
-
表 1 UCI数据集
数据集 类型 样本数 属性个数 类数 iris real 150 4 3 air real 359 64 3 sonar real 208 60 2 glass real 214 9 6 wine real 178 12 3 heart real 270 13 2 zoo artificial 101 16 7 ionosphere real 351 34 2 vote artificial 435 16 2 vowel real 528 10 11 diabetes real 768 8 2 表 2 3种算法的对比结果
数据集 是否收敛 聚类数 真实 时间(s) A B C A B C A B C iris √ √ √ 2 2 2 3 44.6 15.0 1.0 air √ × √ 2 × 2 3 275.6 × 8.4 sonar √ × √ 3 × 3 2 96 × 2.5 glass √ × √ 4 × 5 6 133 × 6.7 wine √ √ √ 2 2 2 3 53.9 32 1.7 heart √ × √ 2 × 3 2 146.6 × 5.3 zoo √ × √ 6 × 4 7 48.1 × 0.9 ionosphere × × √ × × 4 2 × × 0.8 vote √ × √ 2 × 2 2 767.6 × 34.7 vowel √ × √ 22 75 18 11 774.4 576.6 36.9 diabetes √ × √ 2 × 2 2 1670 × 105.5 -
DAVIDSON P and PICHE R. A survey of selected indoor positioning methods for smartphones[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials, 2017, 19(2): 1347–1370 doi: 10.1109/comst.2016.2637663 ZHANG Weile, YIN Qinye, CHEN Hongyang, et al. Distributed angle estimation for localization in wireless sensor networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2013, 12(2): 527–537 doi: 10.1109/TWC.2012.121412.111346 LIU Bin, CHEN Hongyang, ZHONG Ziguo, et al. Asymmetrical round trip based synchronization-free localization in large-scale underwater sensor networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2010, 9(11): 3532–3542 doi: 10.1109/TWC.2010.090210.100146 CHEN Hongyang, LIU Bin, HUANG Pei, et al. Mobility-assisted node localization based on TOA measurements without time synchronization in wireless sensor networks[J]. Mobile Networks&Applications, 2012, 17(1): 90–99 doi: 10.1007/s11036-010-0281-3 HOSSAIN A K M M and SOH W. A survey of calibration-free indoor positioning systems[J]. Computer Communications, 2015, 66: 1–13 doi: 10.1016/j.comcom.2015.03.001 FENG Chen, AU W S A, VALAEE S, et al. Received-signal-strength-based indoor positioning using compressive sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2012, 11(12): 1983–1993 doi: 10.1109/tmc.2011.216 周牧, 唐云霞, 田增山, 等. 基于流形插值数据库构建的WLAN室内定位算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(8): 1826–1834 doi: 10.11999/JEIT161269ZHOU Mu, TANG Yunxia, TIAN Zengshan, et al. WLAN indoor localization algorithm based on manifold interpolation database construction[J]. Journal of Electronics&Information Technology, 2017, 39(8): 1826–1834 doi: 10.11999/JEIT161269 BAI Sidong and WU Tong. Analysis of K-means algorithm on fingerprint based indoor localization system[C]. IEEE International Symposium on Microwave, Antenna, Propagation and EMC Technologies for Wireless Communications. Chengdu, China, 2013: 44–48. ZHANG Liwen, WANG Yunjia, and WANG Xingfeng. Affinity propagation clustering for fingerprinting database in indoor localization[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, 2014(12): 36–39 doi: 10.13474/j.cnki112246.2014.0392 BAHL P and PADMANABHAN V N. RADAR: An in-building RF-based user location and tracking system[C]. Proceedings-IEEE INFOCOM, TelAviv, Israel, 2000, 2: 775–784. YOUSSEF M and AGRAWALA A. The horus WLAN location determination system[C]. Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Mobile Systems, Applications, and Services (MobiSys 2005). Seattle, USA, 2005: 205–218. 李丽娜, 马俊, 龙跃, 等. 基于LANDMARC与压缩感知的双段式室内定位算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(7): 1631–1637 doi: 10.11999/JEIT151050LI Lina, MA Jun, LONG Yue, et al. Double stage indoor localization algorithm based on LANDMARC and compressive sensing[J]. Journal of Electronics&Information Technology, 2016, 38(7): 1631–1637 doi: 10.11999/JEIT151050 CASO G, NARDIS L D, and BENEDETTO M G D. A mixed approach to similarity metric selection in affinity propagation-based WiFi fingerprinting indoor positioning[J]. Sensors, 2015, 15(11): 27692–27720 doi: 10.3390/s151127692 AU A W S, FENG Chen, VALAEE S, et al. Indoor tracking and navigation using received signal strength and compressive sensing on a mobile device[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2013, 12(10): 2050–2062 doi: 10.1109/TMC.2012.175 FREY B J and DUECK D. Clustering by passing messages between data points[J]. Science, 2007, 315(5814): 972–976 doi: 10.1126/science.1136800 FREY L P and STATISTICAL I G. Affinity propagation (University of Toronto) [OL]. avail-able: https://www.psi.toronto.edu/affinitypropagation/software/, 2018. YU Jian and JIA Caiyan. Convergence analysis of affinity propagation[C]. International Conference on Knowledge Science, Engineering and Management. Berlin, Germany, 2009: 54–65. 王开军, 张军英, 李丹, 等. 自适应仿射传播聚类[J]. 自动化学报, 2008, 33(12): 1242–1246 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2007.12.017WANG Kaijun, ZHANG Junying, LI Dan, et al. Adaptive affinity propagation clustering[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2008, 33(12): 1242–1246 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2007.12.017 YU Jian and CHENG Qiansheng. The upper bound of the optimal number of clusters in fuzzy clustering[J]. Science in China Series:Information Sciences, 2001, 44(2): 119–125 doi: 10.1007/bf02713970 ARBELAITZ O, GURRUTXAGA I, MUGUERZA J, et al. An extensive comparative study of cluster validity indices[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2013, 46(1): 243–256 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2012.07.021 SUROSO D J, CHERNTANOMWONG P, SOORAKSA P, et al. Location fingerprint technique using fuzzy C-means clustering algorithm for indoor localization[C]. TENCON 2011–2011 IEEE Region 10 Conference. IEEE, Bali, Indonesia, 2012: 88–92. BLAKE C L and MERZ C J. UCI repository of machine learning databases (University of California) [OL], available: http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/, 2018. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
