Detection of Sound Event under Low SNR Using Multi-band Power Distribution
-
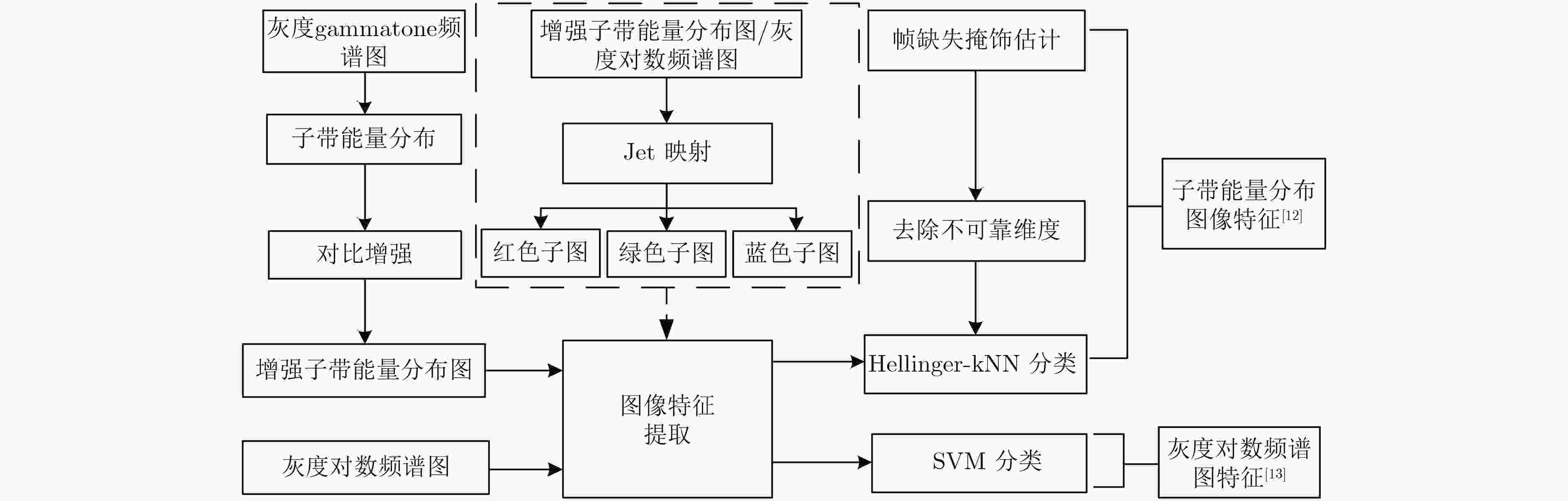
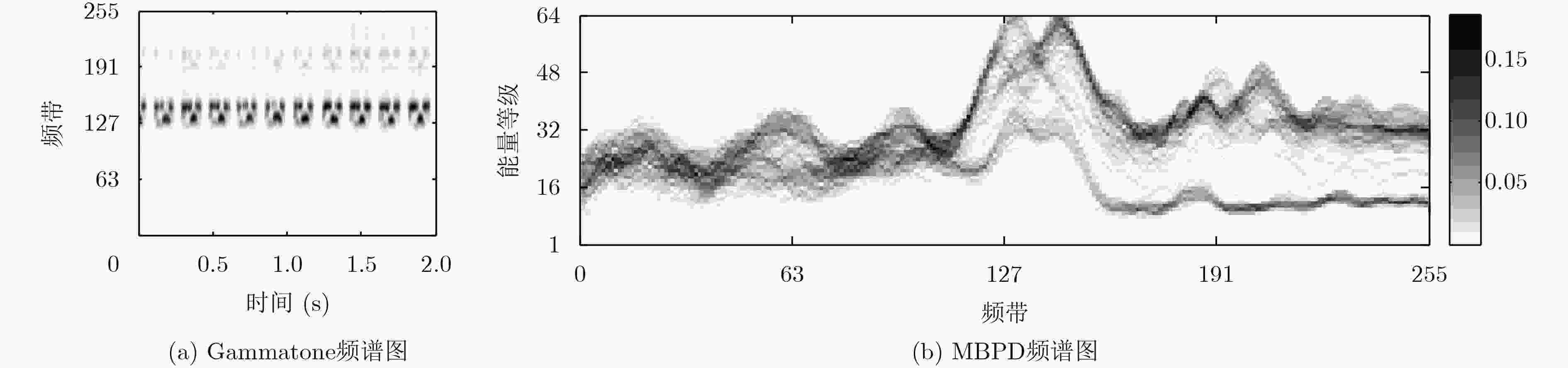
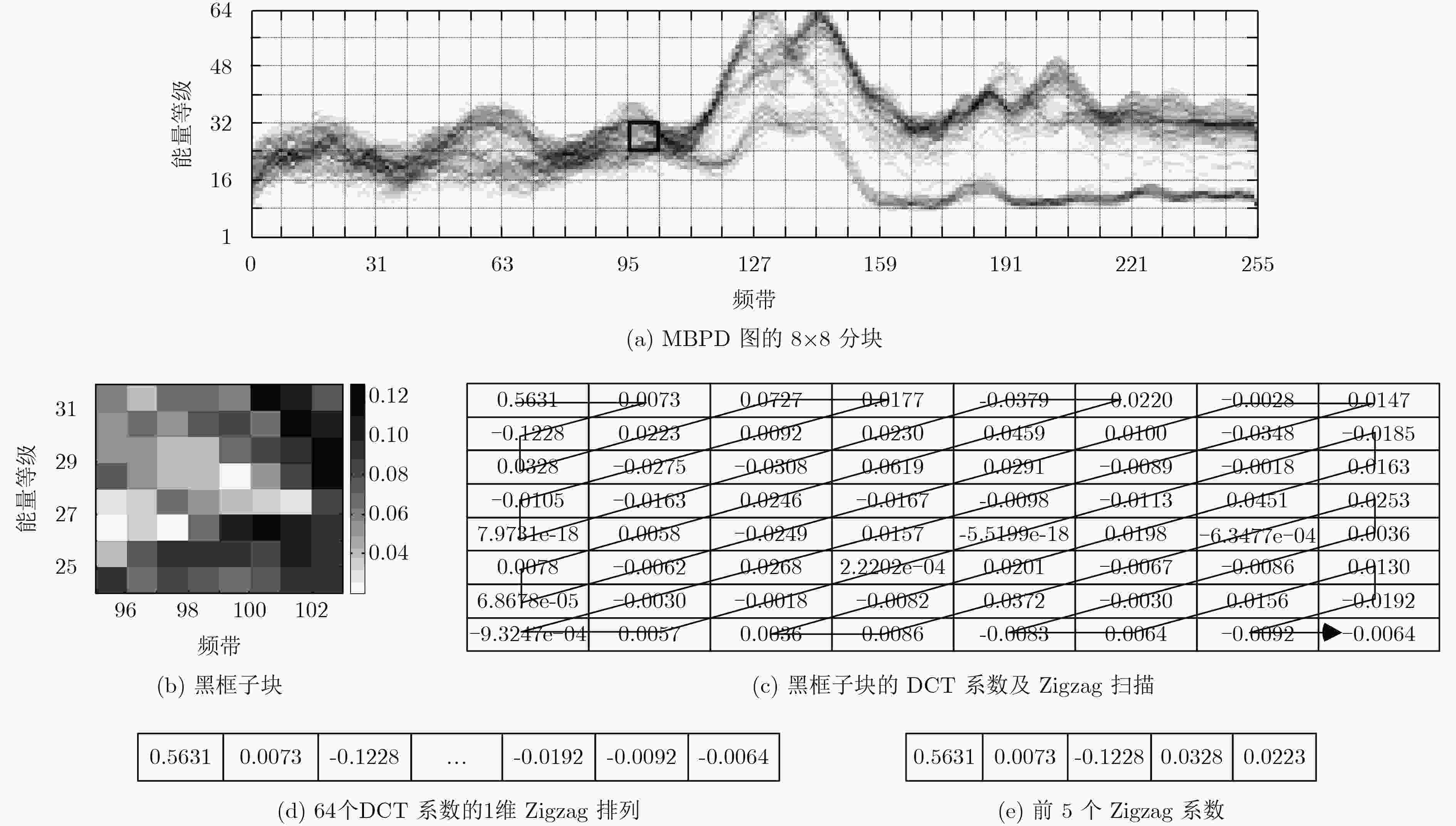
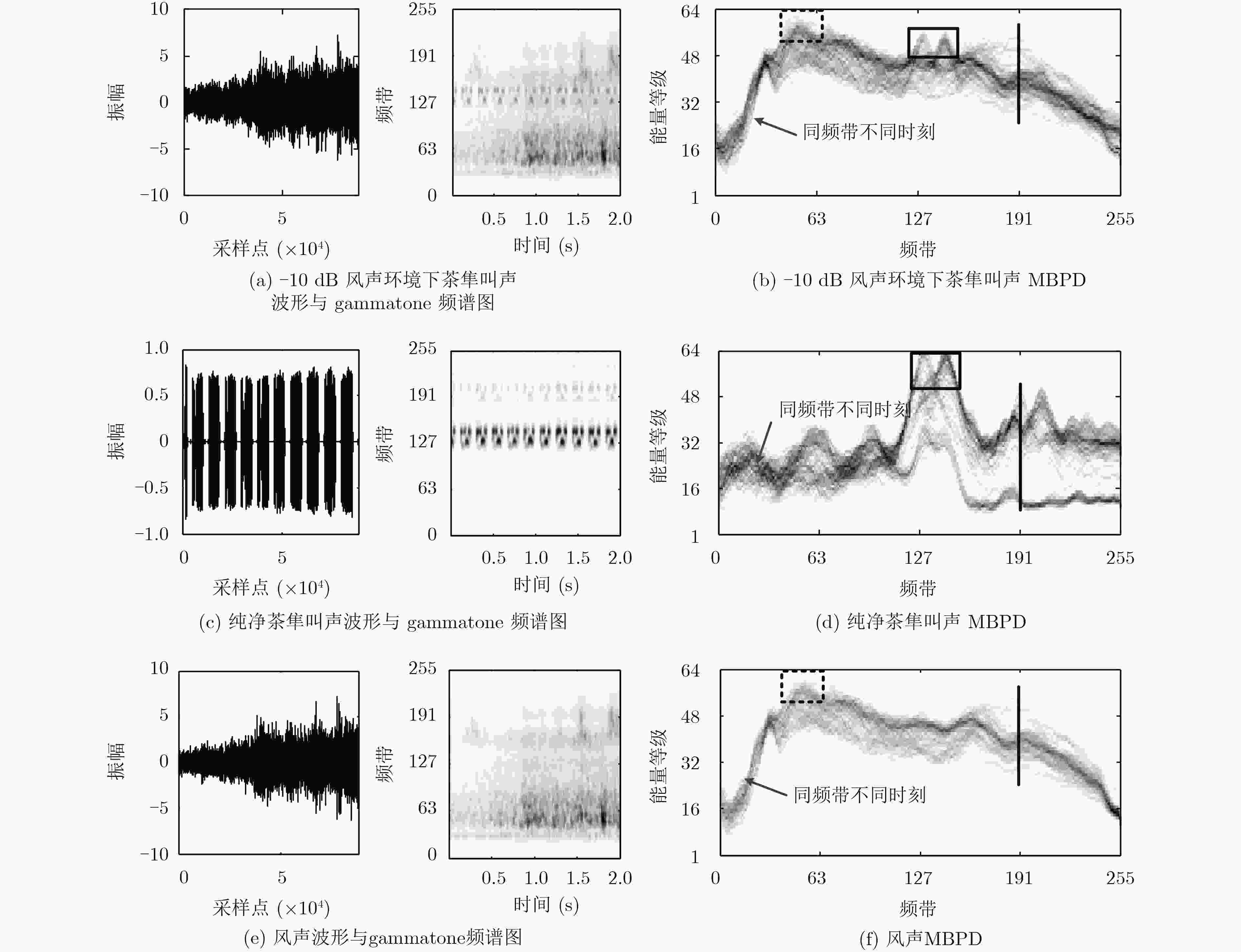
摘要: 该文针对低信噪比噪声环境下的声音事件检测问题,提出基于多频带能量分布图离散余弦变换的声音事件检测的方法。首先,将声音数据转化为gammatone频谱,并计算其多频带能量分布;接着,对多频带能量分布图进行8×8分块与离散余弦变换;然后,对8×8的离散余弦变换系数进行Zigzag扫描,抽取离散余弦变换系数的主要系数作为声音事件的特征;最后,利用随机森林分类器对特征建模与检测。实验结果表明,在低信噪比及各种噪声环境下,该文提出的方法具有良好的检测效果。Abstract: As to the problem of sound event detection in low Signal-Noise-Ratio (SNR) noise environments, a method is proposed based on discrete cosine transform coefficients extracted from multi-band power distribution image. First, by using gammatone spectrogram analysis, sound signal is transformed into multi-band power distribution image. Next, 8×8 size blocking and discrete cosine transform are applied to analyze the multi-band power distribution image. Based on the main Zigzag coefficients which are scanned from the discrete cosine transform coefficients, features of sound event are constructed. Finally, features are modeled and detected through random forests classifier. The results show that the proposed method achieves a better detection performance in low SNR comparing to other methods.
-
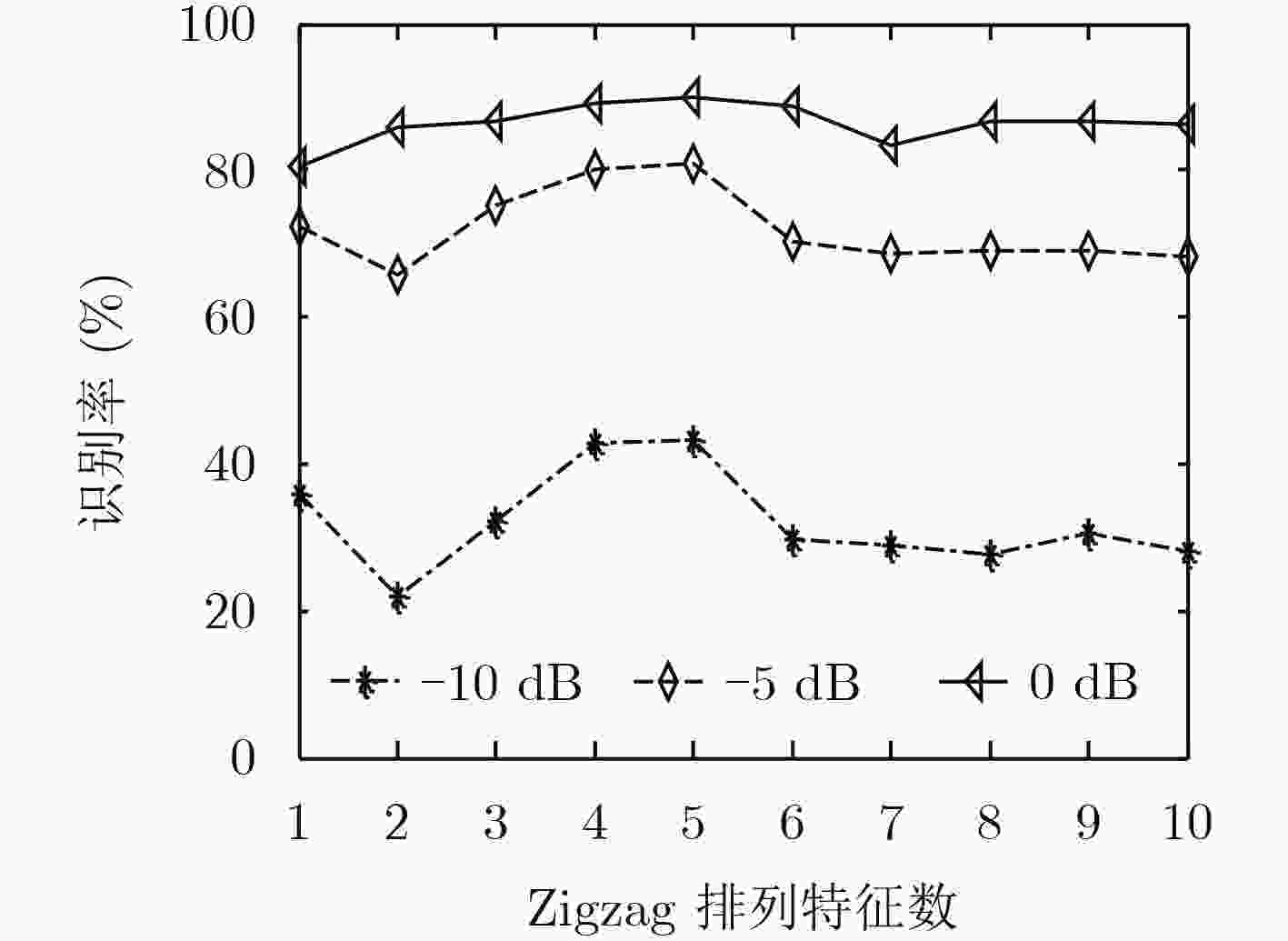
表 1 MBPD-DCTZ特征的交叉验证结果(%)
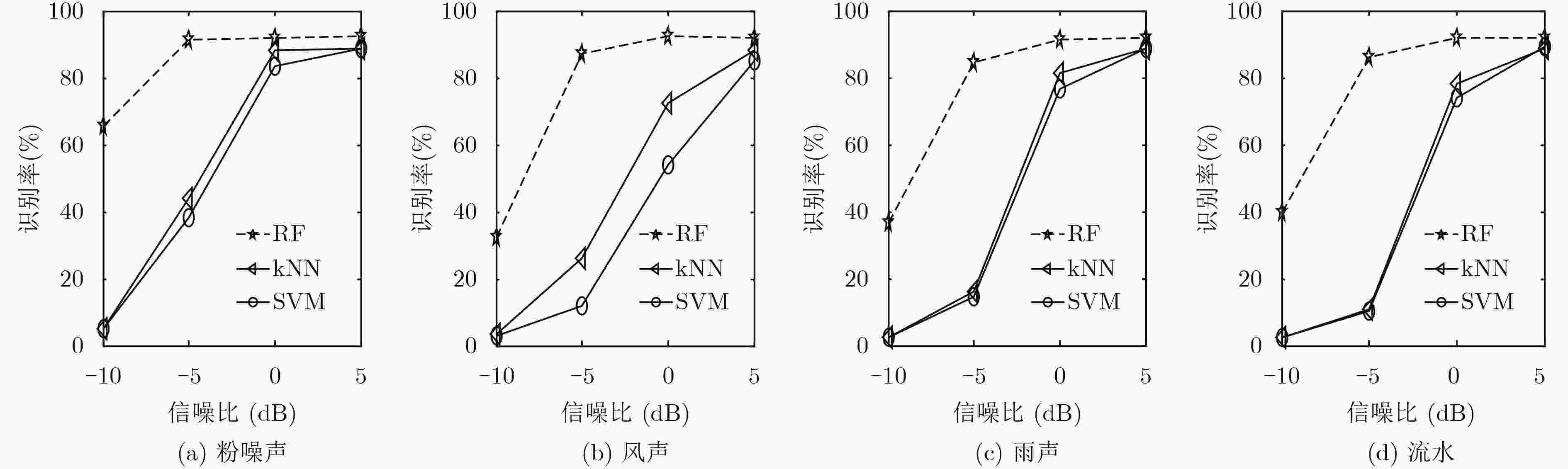
信噪比(dB) 噪声环境 流水 粉噪声 风声 海浪 公路 雨声 平均 –10 40.0±0.7 65.7±5.1 32.5±3.8 44.7±0.9 52.6±3.8 36.5±3.2 45.3±11.1 –5 86.1±3.4 91.1±1.7 87.0±3.2 82.9±1.9 91.2±2.1 84.7±2.5 87.2±3.1 0 91.7±1.9 91.8±1.9 92.3±1.9 91.6±1.4 92.01±2.2 91.5±1.9 91.8±0.3 5 91.9±1.9 92.2±1.9 92.1±2.3 92.2±1.8 92.3±2.1 92.0±1.9 92.1±0.1 表 3 不同特征对办公室声音事件的检测率(%)
特征 办公室声音事件 粉噪声信噪比(dB) 5 0 –5 LBP 69.7±2.3 70.9±5.1 35.2±0.9 16.4±2.6 GLCM-SDH 47.3±5.4 44.2±7.5 45.5±5.4 38.8±4.8 HOG 70.3±5.2 40.6±4.8 33.9±3.1 32.1±2.3 MFCC 43.7±0.7 27.2±4.7 22.1±4.5 17.6±3.4 PNCC 47.2±1.9 34.3±2.0 28.1±2.3 22.1±1.8 MBPD-DCTZ 75.2±0.6 75.2±1.7 75.8±4.3 54.6±5.4 表 2 6种噪声环境下不同特征对动物声音事件的平均检测率(%)
特征 信噪比(dB) 5 0 –5 –10 LBP 64.3±14.3 16.6±10.5 2.8±0.8 2.4±0.9 GLCM-SDH 41.4±3.5 36.0±4.3 14.6±9.5 4.2±1.7 HOG 68.9±5.4 28.8±10.5 7.4±5.2 4.1±1.8 MFCC 17.5±4.8 9.5±2.5 4.7±0.7 3.0±0.8 PNCC 28.0±0.9 20.0±0.9 9.1±2.0 2.5±0.8 MBPD-DCTZ 92.1±0.1 91.8±0.3 87.2±3.1 45.3±11.1 表 4 6种噪声环境下不同方法对动物声音事件的平均检测率(%)
-
米建伟, 方晓莉, 仇原鹰. 非平稳背景噪声下声音信号增强技术[J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2017, 38(1): 17–22 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-3087.2017.01.003MI Jianwei, FANG Xiaoli, and QIU Yuanying. Enhancement technology for the audio signal with nonstationary background noise[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2017, 38(1): 17–22 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-3087.2017.01.003 汪家冬, 邹采荣, 蒋本聪, 等. 基于数字助听器声音场景分类的噪声抑制算法[J]. 数据采集与处理, 2017, 32(4): 825–830 doi: 10.16337/j.1004-9037.2017.04.021WANG Jiadong, ZOU Cairong, JIANG Bencong, et al. Noise reduction algorithm based on acoustic scene classification in digital hearing aids[J]. Journal of Data Acquisition and Processing, 2017, 32(4): 825–830 doi: 10.16337/j.1004-9037.2017.04.021 FENG Zuren, ZHOU Qing, ZHANG Jun, et al. A target guided subband filter for acoustic event detection in noisy environments using wavelet packets[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio,Speech,and Language Processing, 2015, 23(2): 361–372 doi: 10.1109/TASLP.2014.2381871 GRZESZICK R, PLINGE A, and FINK G A. Bag-of-features methods for acoustic event detection and classification[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio,Speech,and Language Processing, 2017, 25(6): 1242–1252 doi: 10.1109/TASLP.2017.2690574 REN Jianfeng, JIANG Xudong, YUAN Junsong, et al. Sound-event classification using robust texture features for robot hearing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2017, 19(3): 447–458 doi: 10.1109/TMM.2016.2618218 YE Jiaxing, KOBAYASHI T, and MURAKAWA M. Urban sound event classification based on local and global features aggregation[J]. Applied Acoustics, 2017, 117: 246–256 doi: 10.1016/j.apacoust.2016.08.002 CAKIR E, PARASCANDOLO G, HEITTOLA T, et al. Convolutional recurrent neural networks for polyphonic sound event detection[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio,Speech,and Language Processing, 2017, 25(6): 1291–1303 doi: 10.1109/TASLP.2017.2690575 SHARAN R V and MOIR T J. Robust acoustic event classification using deep neural networks[J]. Information Sciences, 2017, 396: 24–32 doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2017.02.013 OZER I, OZER Z, and FINDIK O. Noise robust sound event classification with convolutional neural network[J]. Neurocomputing, 2018, 272: 505–512 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2017.07.021 WANG Jiaching, LIN Changhong, and CHEN Bowei. Gabor-based nonuniform scale-frequency map for environmental sound classification in home automation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2014, 11(2): 607–613 doi: 10.1109/TASE.2013.2285131 SHARMA A and KAUL S. Two-stage supervised learning-based method to detect screams and cries in urban environments[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio,Speech,and Language Processing, 2016, 24(2): 290–299 doi: 10.1109/TASLP.2015.2506264 DENNIS J, TRAN H D, and CHNG E S. Image feature representation of the subband power distribution for robust sound event classification[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio,Speech,and Language Processing, 2013, 21(2): 367–377 doi: 10.1109/TASL.2012.2226160 DENNIS J, TRAN H D, and LI Haizhou. Spectrogram image feature for sound event classification in mismatched conditions[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2011, 18(2): 130–133 doi: 10.1109/LSP.2010.2100380 SLANEY M. An efficient implementation of the Patterson-Holdsworth auditory filter bank[R]. Apple Computer Technical Report, 1993. PAPAKOSTAS G A, KOULOURIOTIS D E, and KARAKASIS E G. Efficient 2-D DCT Computation from An Image Representation Point of View[M]. London, UK, Intch Open, 2009: 21–34. LAY J A and GUAN Ling. Image retrieval based on energy histograms of the low frequency DCT coefficients[C]. IEEE International Conference on Acoustic, Speech and Signal Processing, Arizona, USA, 1999: 3009–3012. BREIMAN L. Random forests[J]. Machine Learning, 2001, 45(1): 5–32 doi: 10.1023/A:1010933404324 Universitat Pompeu Fabra. Repository of sound under the creative commons license, Freesound. org[OL]. http://www.freesound.org, 2012.5.14. IEEE Signal Processing Society, Tampere University of Technology, Queen Mary University of London, et al. IEEE DCASE 2016 Challenge[OL]. http://www.cs.tut.fi/sgn/arg/dcase2016/, 2016. CHANG Chihchung and LIN Chihjen. LIBSVM: A library for support vector machines[J]. ACM Transactions on Intelligent Systems and Technology, 2011, 2(3): 1–27 doi: 10.1145/1961189.1961199 COVER T and HART P. Nearest neighbor pattern classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 1967, 13(1): 21–27 doi: 10.1109/TIT.1967.1053964 ZHENG Fang, ZHANG Guoliang, and SONG Zhanjiang. Comparison of different implementations of MFCC[J]. Journal of Computer Science and Technology, 2001, 16(6): 582–589 doi: 10.1007/BF02943243 KIM C and STERN R M. Feature extraction for robust speech recognition based on maximizing the sharpness of the power distribution and on power flooring[C]. IEEE International Conference on Acoustic, Speech and Signal Processing, Dallas, USA, 2010: 4574–4577. 魏静明, 李应. 利用抗噪纹理特征的快速鸟鸣声识别[J]. 电子学报, 2015, 43(1): 185–190 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2015.01.029WEI Jingming and LI Ying. Rapid bird sound recognition using anti-noise texture features[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2015, 43(1): 185–190 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2015.01.029 KOBAYASHI T and YE J. Acoustic feature extraction by statictics based local binary pattern for environmental sound classification[C]. IEEE International Conference on Acoustic, Speech and Signal Processing, Florence, Italy, 2014: 3052–3056. RAKOTOMAMONJY A and GASSO G. Histogram of gradients of time-frequency representations for audio scene classification[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio,Speech,and Language Processing, 2015, 23(1): 142–153 doi: 10.1109/TASLP.2014.2375575 -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
