Plane-wave Compounding with Short-lag Coherence Factor Weighting
-
摘要: 相干平面波复合(CPWC)成像算法采用多个角度平面波成像结果直接叠加的方式进行成像,具有速度快,质量高等优点,CPWC成像直接叠加的成像方式,忽略了平面波成像结果之间的相干性。相干系数(CF)加权算法可以有效提高成像的分辨率和对比度,降低了背景成像质量。该文提出了短阶相干系数(SLCF)加权算法,该算法采用角度差异参数来确定相干系数的阶数,根据角度差异较小的平面波输出计算相干系数,对CPWC成像结果进行加权成像。仿真和实验结果表明SLCF加权算法相对于传统的CPWC成像算法,可以改善成像的横向分辨率和对比度。相对CF和广义相干系数(GCF)算法,SLCF可以提高对比度和背景成像质量,而且运算量更低。Abstract: The Coherent Plane-Wave Compounding (CPWC) algorithm is based on the recombination of several plane-waves with different steering angles, which can achieve high-quality images with high frame rate. However, CPWC ignores the coherence between the plane-wave imaging results. Coherence Factor (CF) weighted algorithm can effectively improve the imaging contrast and resolution, while it degrades the background speckle quality. A Short-Lag Coherence Factor (SLCF) algorithm for CPWC is proposed. SLCF uses the angular difference parameter to ascertain the order of the coherence factor and calculates the coherence factor for the plane-waves with small angular difference. Then, SLCF is utilized to weight CPWC to obtain the final images. Simulated and experimental results show that SLCF-weighted algorithm can improve the imaging quality in terms of lateral resolution and Contrast Ratio (CR), compared with CPWC. In addition, in comparison with CF and Generalized Coherence Factor (GCF) weighted algorithm, SLCF can achieve better background speckle quality and it has lower computational complexity.
-
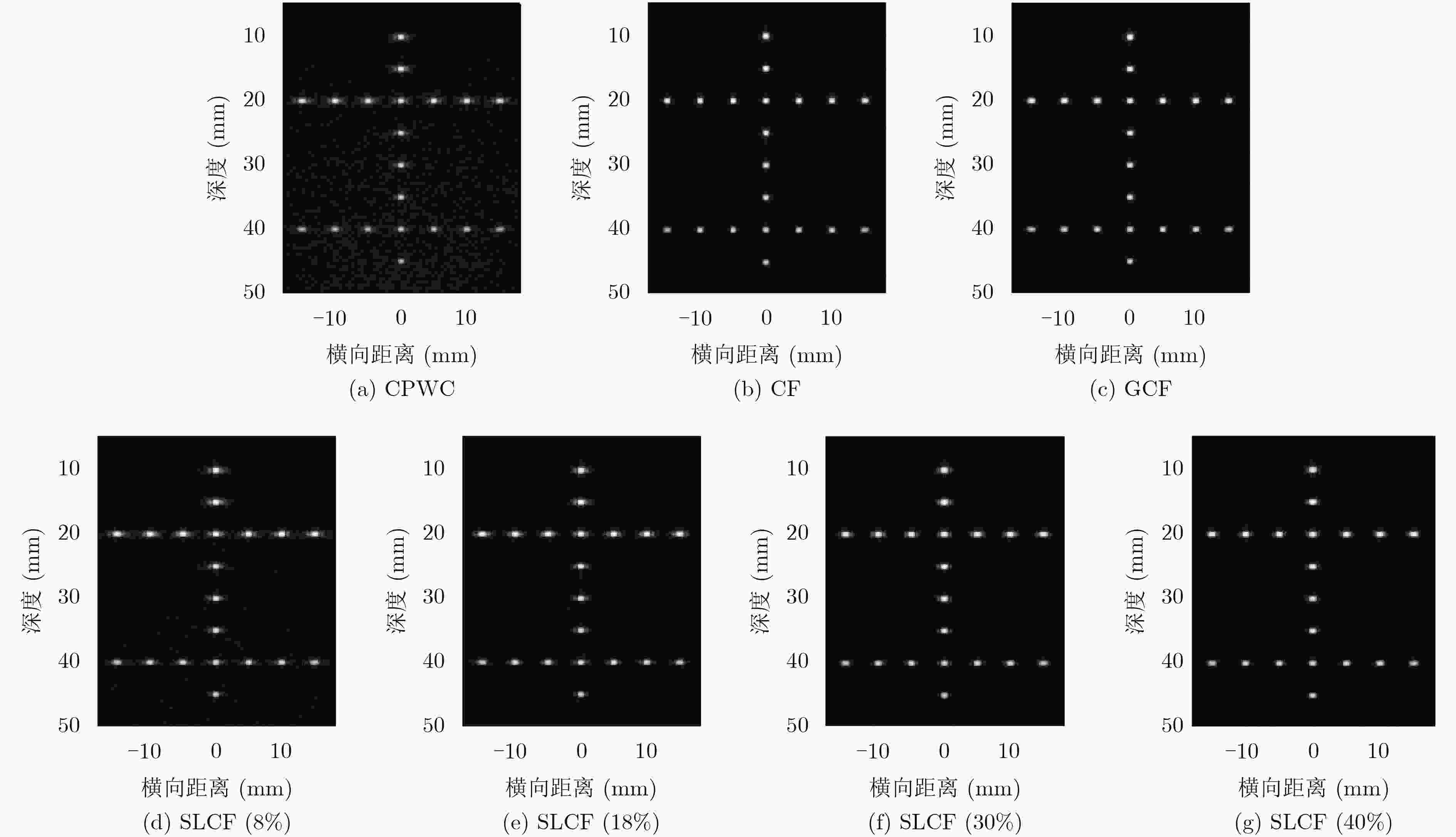
表 1 不同算法仿真点的横向与纵向FWHM及仿真斑的CR, CNR和背景SNR
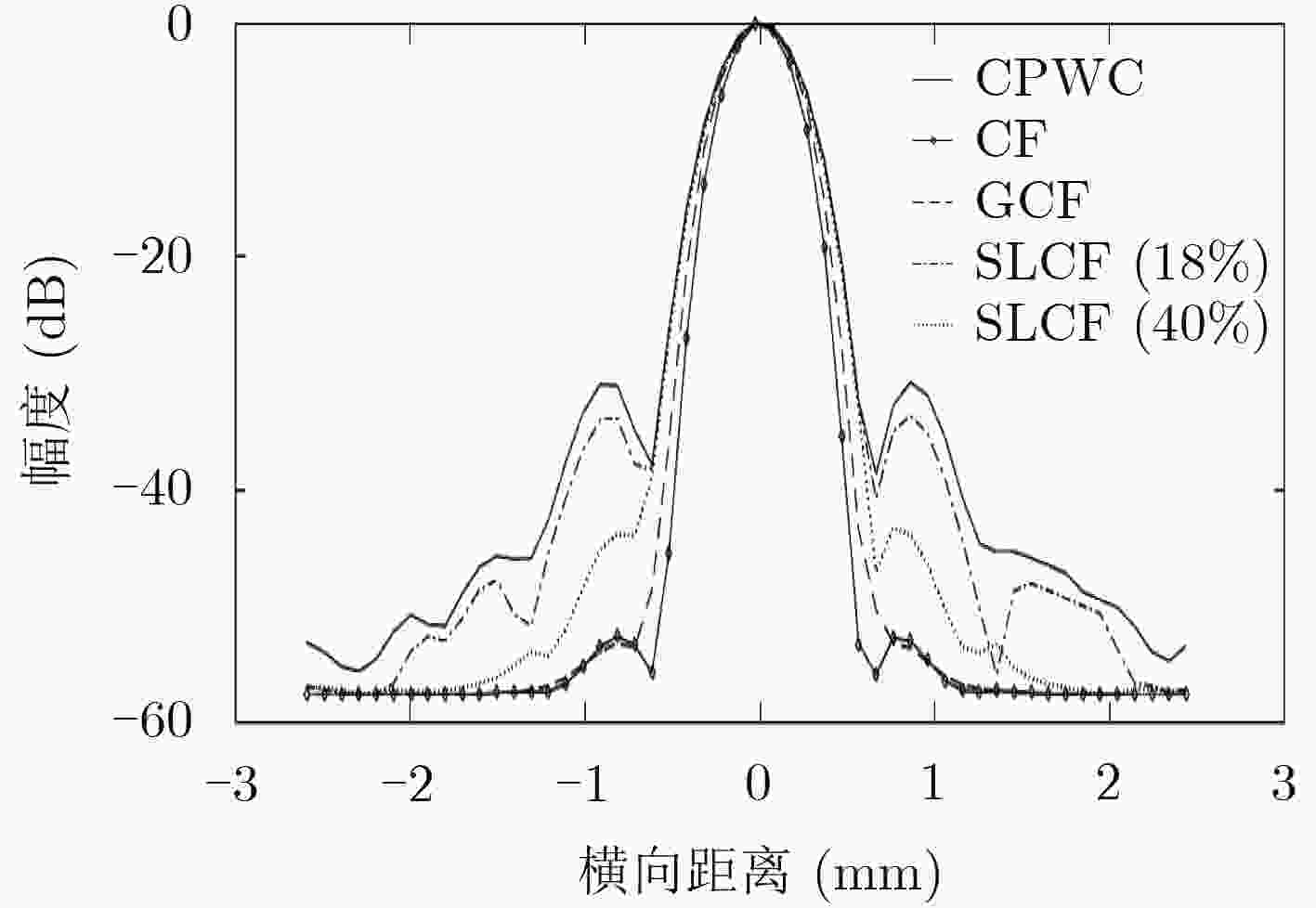
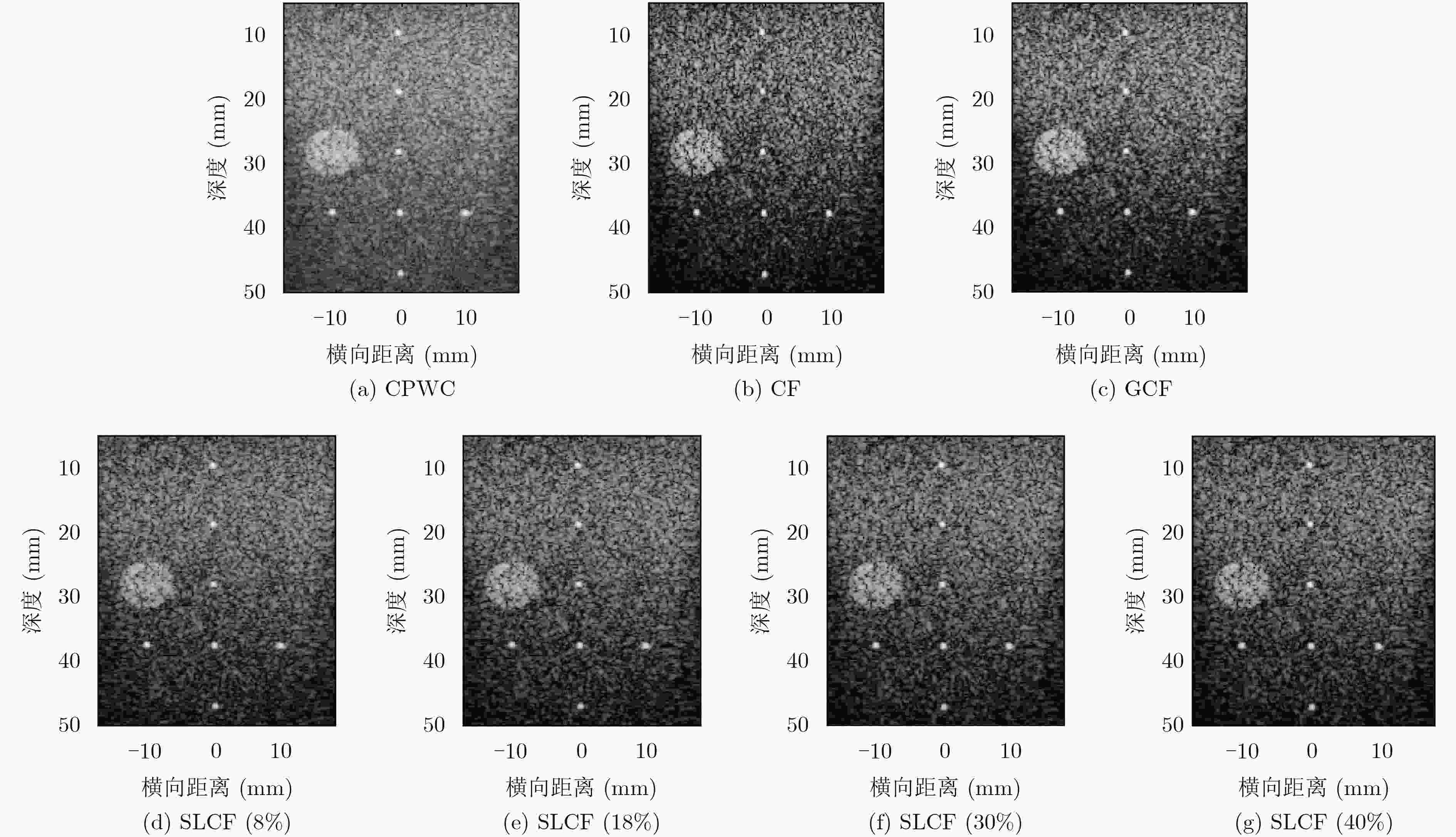
算法 横向FWHM(mm) 纵向FWHM(mm) CR(dB) CNR SSNR CPWC 0.540 0.415 30.22\15.96 4.68\2.45 8.52\6.36 CF 0.443 0.414 38.69\23.02 4.02\2.25 4.37\2.56 GCF 0.495 0.413 40.64\24.28 5.15\2.60 5.57\2.96 SLCF(8%) 0.537 0.415 38.00\21.62 5.22\2.31 6.86\3.40 SLCF(18%) 0.530 0.415 39.86\23.45 5.31\2.46 6.25\3.15 SLCF(30%) 0.524 0.415 40.48\24.14 5.17\2.48 5.83\3.01 SLCF(40%) 0.516 0.415 40.29\24.46 4.89\2.50 5.45\2.93 表 2 不同算法实验点的横向与纵向FWHM及实验斑的CR, CNR和背景SNR
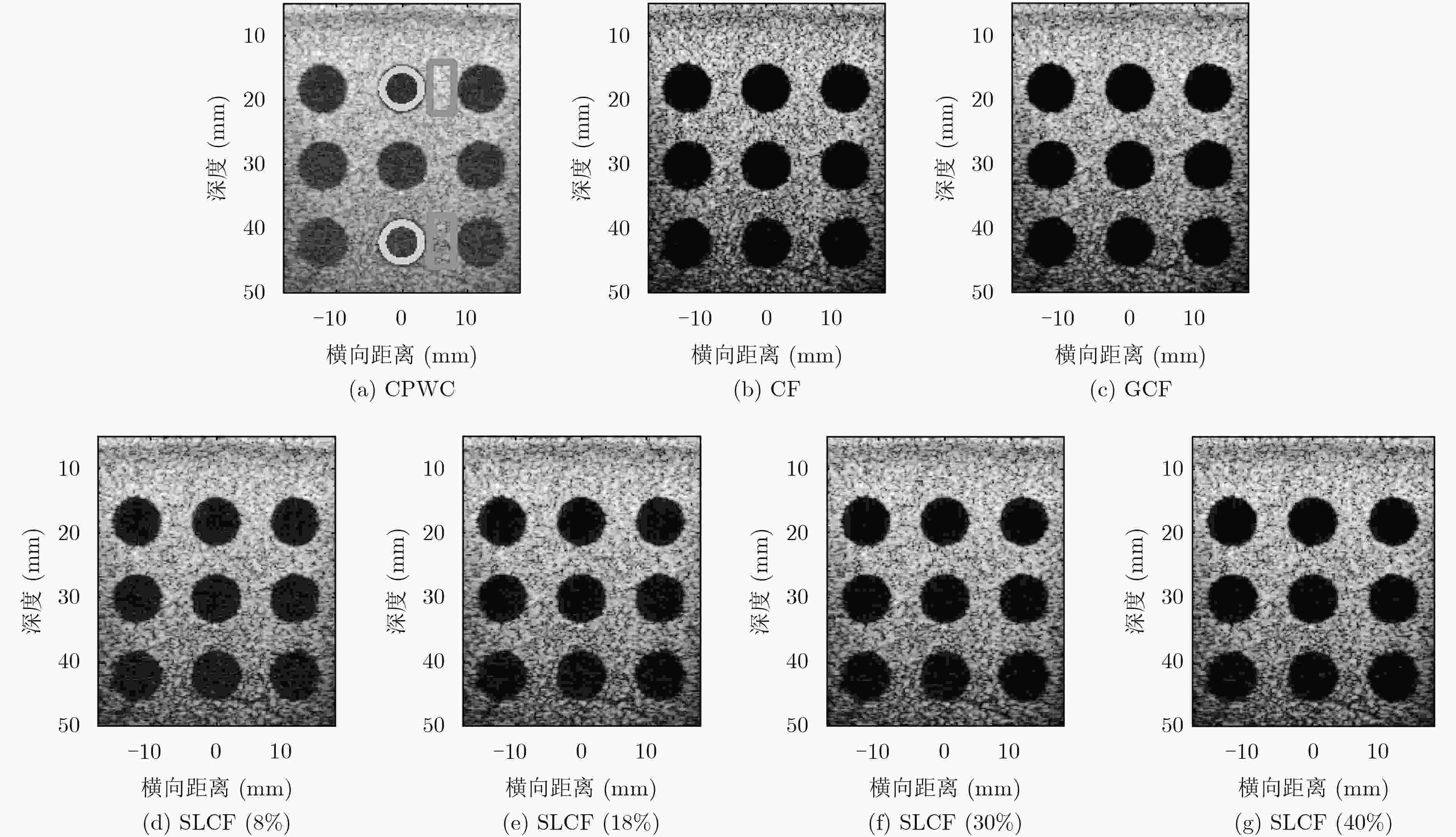
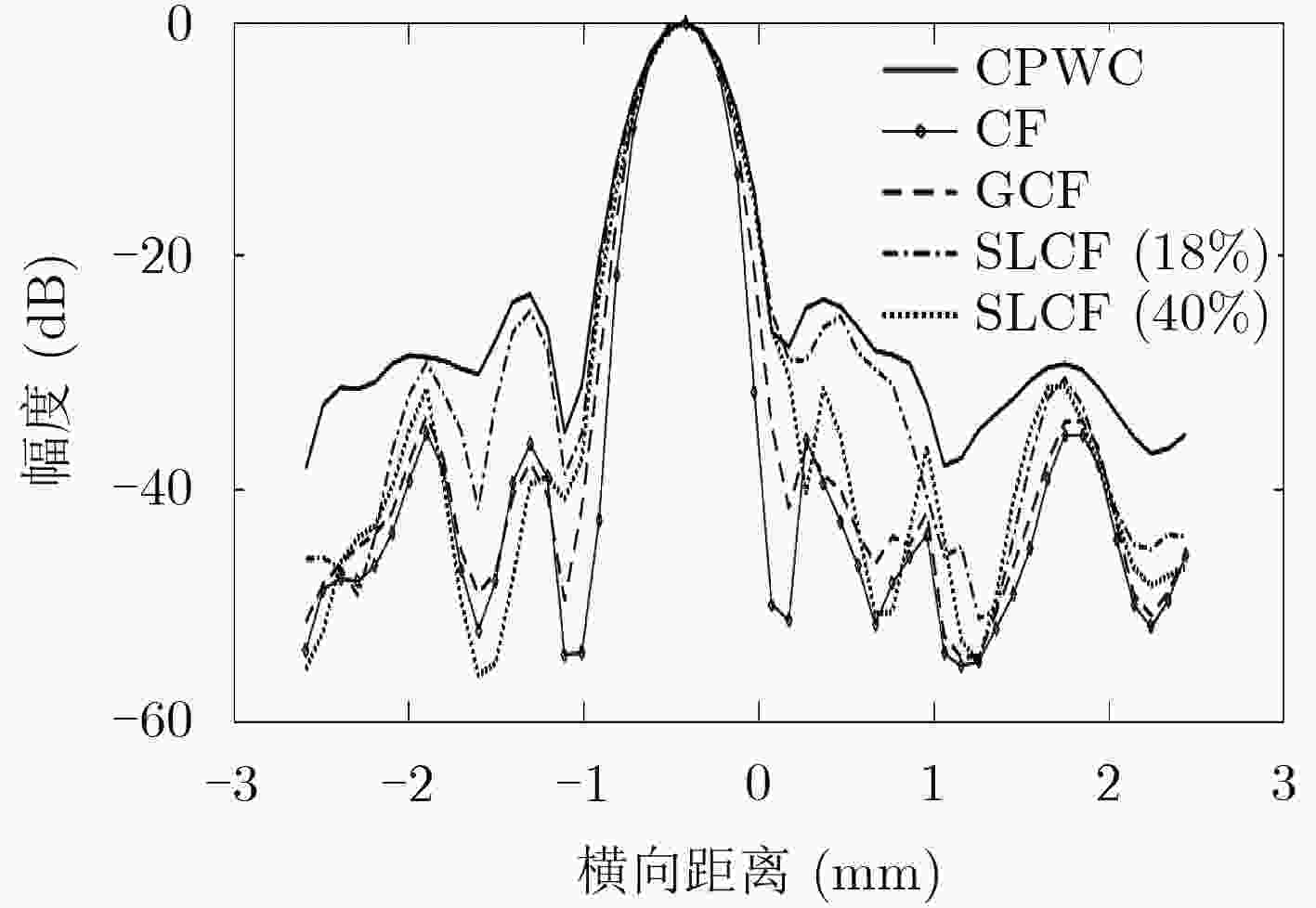
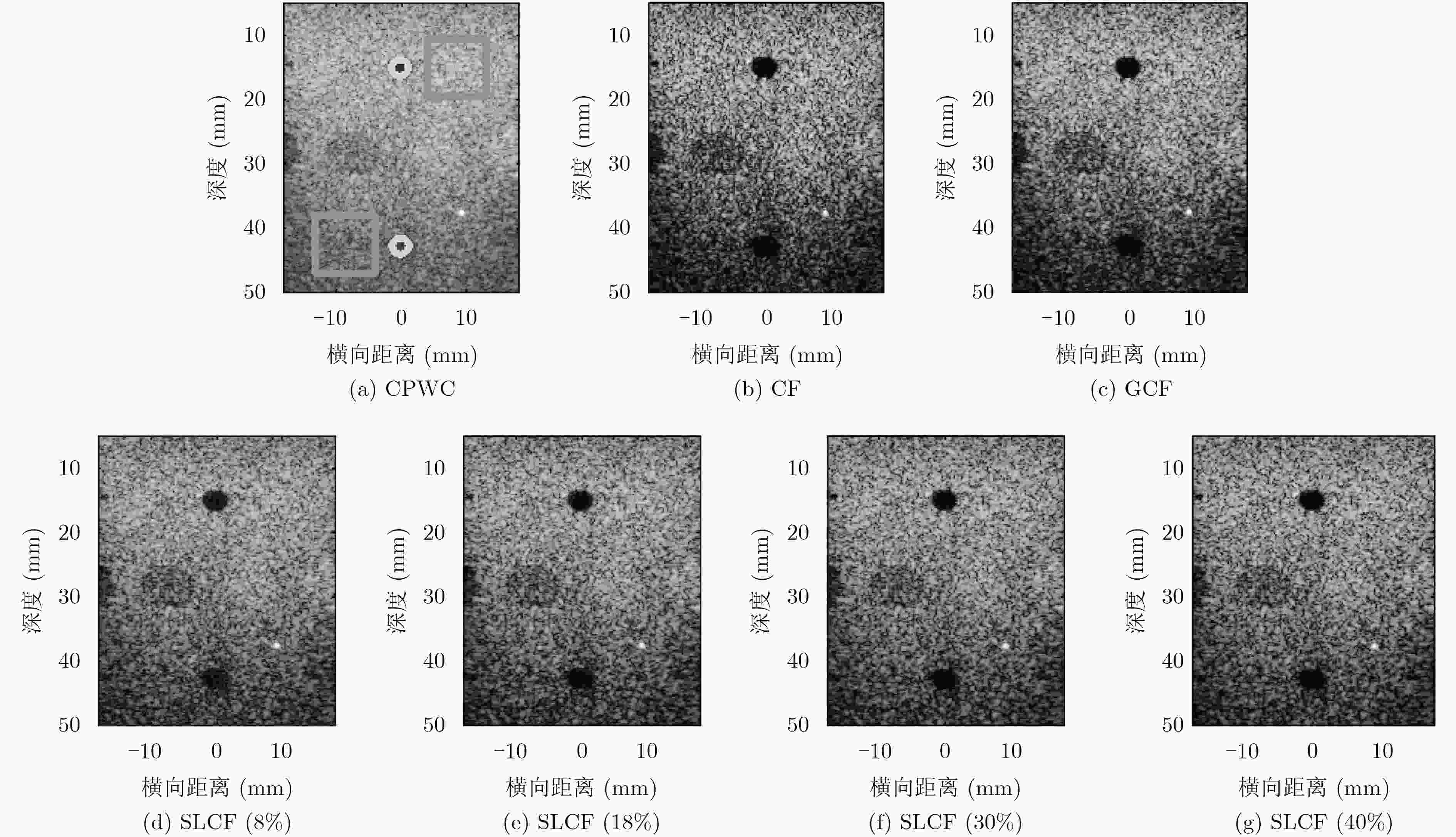
算法 横向宽度(mm) 纵向宽度(mm) CR(dB) CNR SSNR CPWC 0.550 0.554 24.39\10.16 3.76\1.61 7.50\5.38 CF 0.477 0.542 31.73\12.64 3.25\1.49 3.56\1.82 GCF 0.513 0.553 33.38\13.66 4.10\1.64 4.49\1.97 SLCF(8%) 0.546 0.550 30.20\15.82 3.84\1.89 5.57\2.96 SLCF(18%) 0.536 0.554 32.71\17.85 4.08\2.10 5.05\2.71 SLCF(30%) 0.522 0.555 33.63\18.54 4.06\2.17 4.71\2.61 SLCF(40%) 0.501 0.557 33.72\18.64 3.90\2.14 4.42\2.51 表 3 人体成像数据的CR, CNR和背景SNR
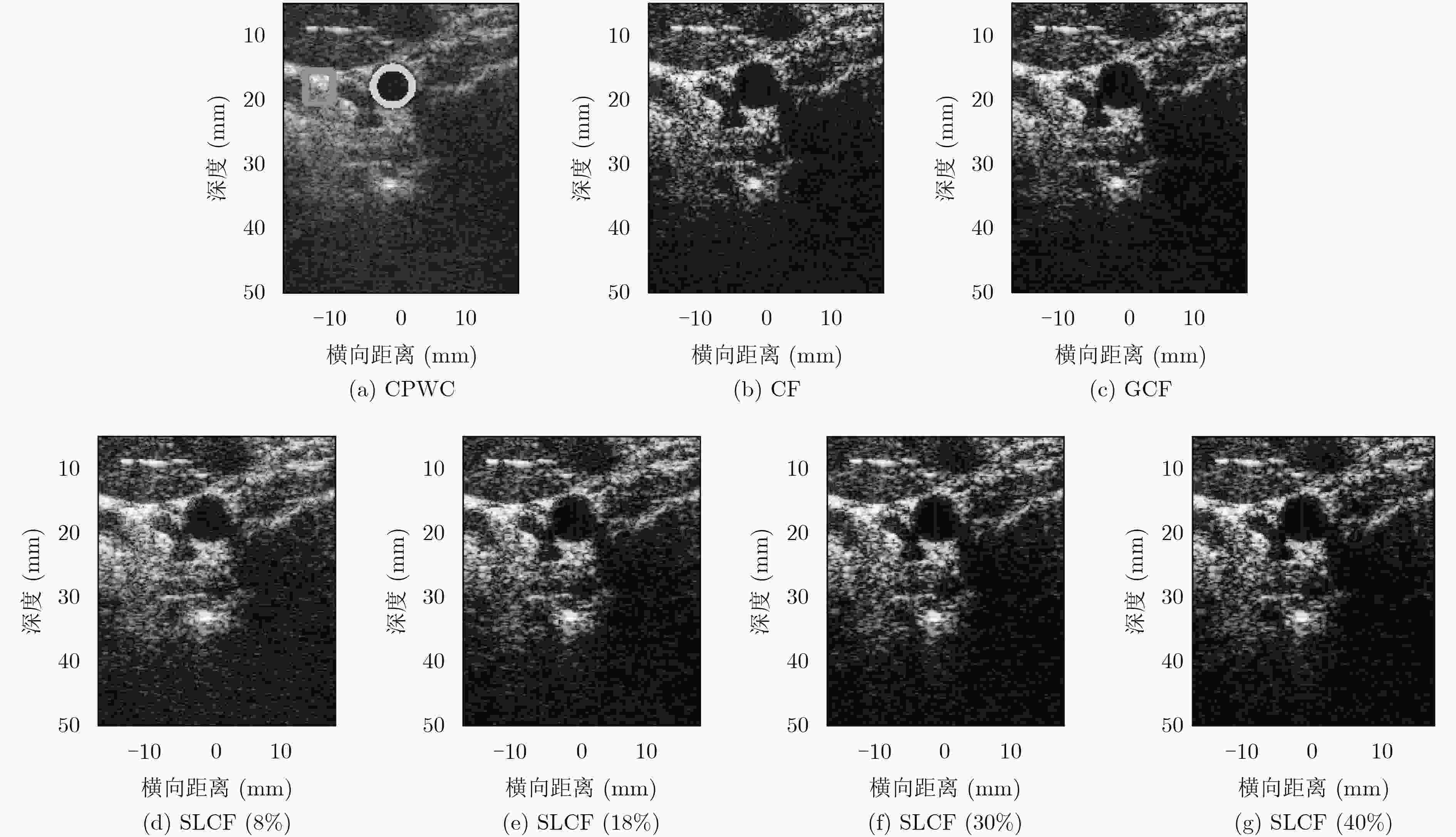
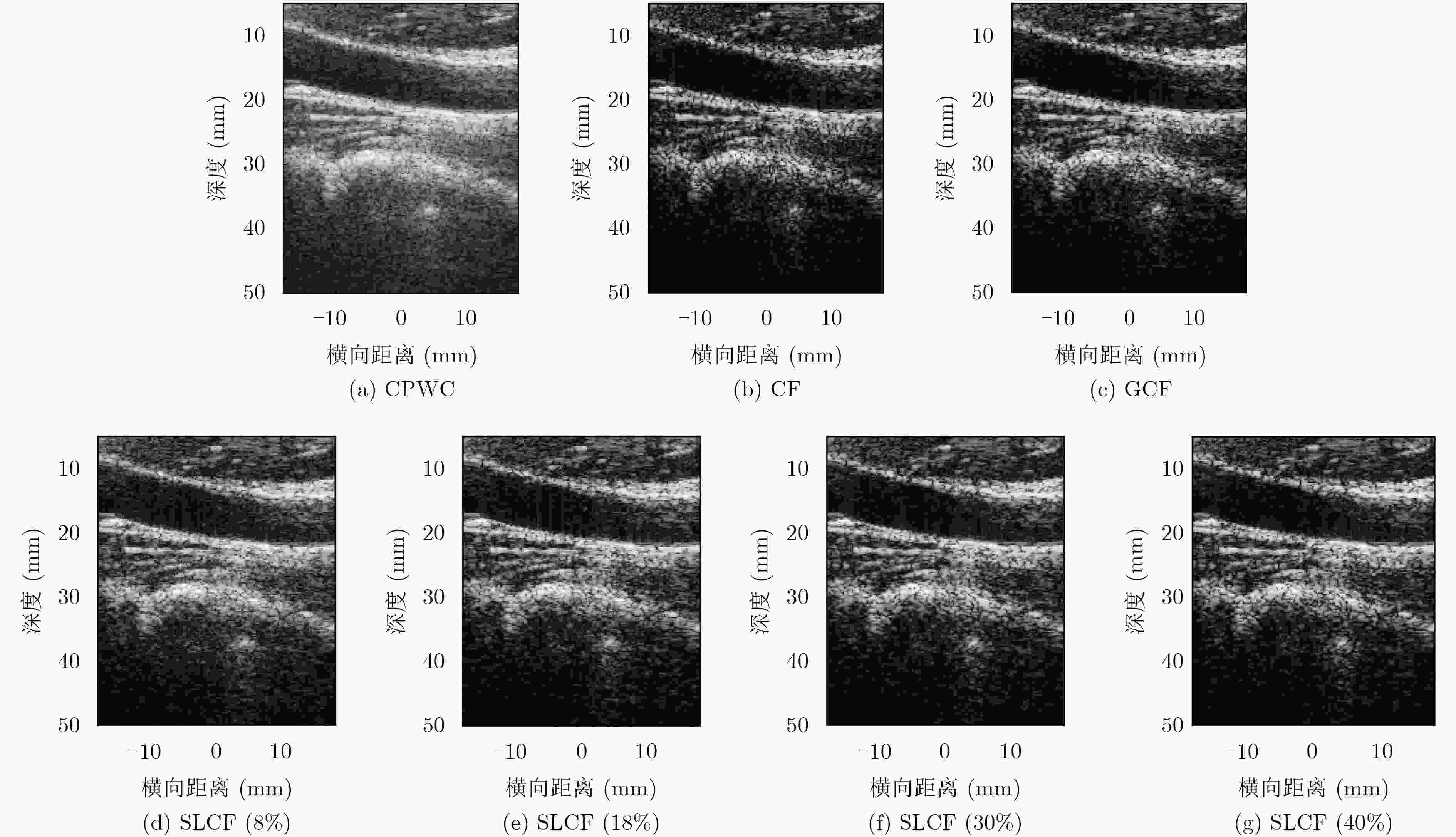
算法 CR(dB) CNR SSNR CPWC 26.33 2.45 3.68 CF 26.96 1.85 1.99 GCF 28.28 1.98 2.10 SLCF(8%) 29.84 2.39 2.79 SLCF(18%) 28.84 2.10 2.32 SLCF(30%) 28.23 1.94 2.11 SLCF(40%) 27.86 1.86 2.01 -
MONTALDO G, TANTER M, BERCOFF J, et al. Coherent plane-wave compounding for very high frame rate ultrasonography and transient elastography[J]. IEEE Transactions on Ultrasonics Ferroelectrics&Frequency Control, 2009, 56(3): 489–506 doi: 10.1109/TUFFC.2009.1067 BERCOFF J, MONTALDO G, LOUPAS T, et al. Ultrafast compound Doppler imaging: Providing full blood flow characterization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Ultrasonics Ferroelectrics&Frequency Control, 2011, 58(1): 134–147 doi: 10.1109/TUFFC.2011.1780 VITI J, VOS H J, DE JONG N, et al. Contrast detection efficacy for plane vs. focused wave transmission[C]. 2014 IEEE International on Ultrasonics Symposium (IUS), Chicago, USA, 2014: 1750–1753. SEBASTIEN S, HERVé L, OLIVIER B, et al. Experimental evaluation of spectral-based quantitative ultrasound imaging using plane wave compounding[J]. IEEE Transactions on Ultrasonics Ferroelectrics&Frequency Control, 2014, 61(11): 1824–1834 doi: 10.1109/TUFFC.2014.006543 POREE J, GARCIA D, CHAYER B, et al. Non-invasive vascular elastography with plane strain incompressibility assumption using ultrafast coherent compound plane wave imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2015, 34(12): 2618–2631 doi: 10.1109/TMI.2015.2450992 DENARIE B, TANGEN T A, EKROLL I K, et al. Coherent plane wave compounding for very high frame rate ultrasonography of rapidly moving targets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2013, 32(7): 1265–1276 doi: 10.1109/TMI.2013.2255310 ZHAO Jinxin, WANG Yuanyuan, ZENG Xing, et al. Plane wave compounding based on a joint transmitting-receiving adaptive beamformer[J]. IEEE Transactions on Ultrasonics Ferroelectrics&Frequency Control, 2015, 62(8): 1440–1452 doi: 10.1109/TUFFC.2014.006934 TOULEMONDE M, BASSET O, TORTOLI P, et al. Thomson’s multitaper approach combined with coherent plane-wave compounding to reduce speckle in ultrasound imaging[J]. Ultrasonics, 2015, 56: 390–398 doi: 10.1016/j.ultras.2014.09.006 GASSE M, MILLIOZ F, ROUX E, et al. High-quality plane wave compounding using convolutional neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Ultrasonics Ferroelectrics&Frequency Control, 2017, 64(10): 1637–1639 doi: 10.1109/TUFFC.2017.2736890 HOLLMAN K W, RIGBY K W, and O'DONNELL M. Coherence factor of speckle from a multi-row probe[C]. IEEE, Ultrasonics Symposium, Caesars Tahoe, USA, 1999: 1257–1260. NILSEN C C and HOLM S. Wiener beamforming and the coherence factor in ultrasound imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Ultrasonics Ferroelectrics&Frequency Control, 2010, 57(6): 1329–1346 doi: 10.1109/TUFFC.2010.1553 YU Mingyue, LI Yang, MA Teng, et al. Intravascular ultrasound imaging with virtual source synthetic aperture (VSSA) focusing and coherence factor weighting[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2017, 36(10): 2171–2178 doi: 10.1109/TMI.2017.2723479 ZHAO Jinxin, WANG Jin, and WANG Yuanyuan. Synthetic aperture ultrasound imaging with classified aperture coherence factors[J]. Journal of Medical Imaging&Health Informatics, 2017, 7(5): 1013–1020 doi: 10.1166/jmihi.2017.21301013 LI Paichi and LI Menglin. Adaptive imaging using the generalized coherence factor[J]. IEEE Transactions on Ultrasonics Ferroelectrics&Frequency Control, 2003, 50(2): 128–141. WEI G, WANG Y, and YU J. Ultrasound harmonic enhanced imaging using eigenspace-based coherence factor[J]. Ultrasonics, 2016, 72: 106–116 doi: 10.1016/j.ultras.2016.07.017 WANG Y H and LI P C. SNR-dependent coherence-based adaptive imaging for high-frame-rate ultrasonic and photoacoustic imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Ultrasonics Ferroelectrics&Frequency Control, 2014, 61(8): 1419–1432 doi: 10.1109/TUFFC.2014.3051 LI Y L and DAHL J J. Angular coherence in ultrasound imaging: Theory and applications[J]. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2017, 141(3): 1582–1594 doi: 10.1121/1.4976960 Plane-wave Imaging challenge in medical ultraSound[OL]. https://www.creatis.insa-lyon.fr/Challenge/IEEE_IUS_2016/, 2016. JENSEN J A. Field: A program for simulating ultrasound systems[J]. Medical&Biological Engineering&Computing, 1996, 34(1): 351–353. ZHAO Jinxin, WANG Yuanyuan, YU Jinhua, et al. Short-lag spatial coherence ultrasound imaging with adaptive synthetic transmit aperture focusing[J]. Ultrason Imaging, 2017, 39(4): 224–239 doi: 10.1177/0161734616688328 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
