An Improved SSD Model for Saliency Object Detection
-
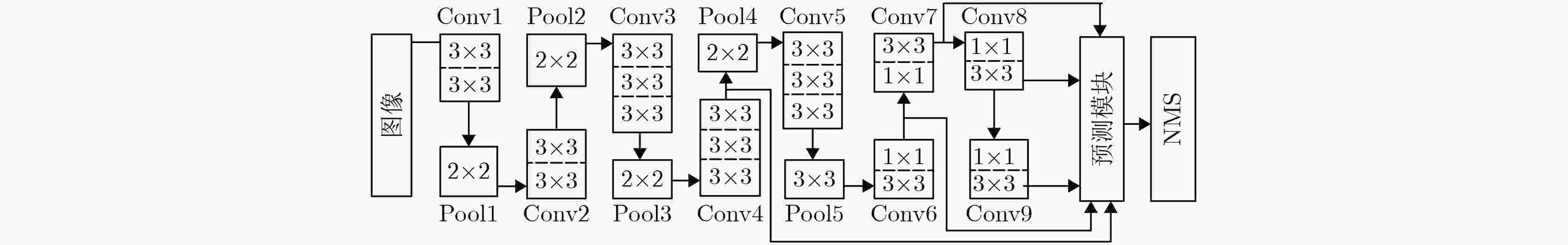
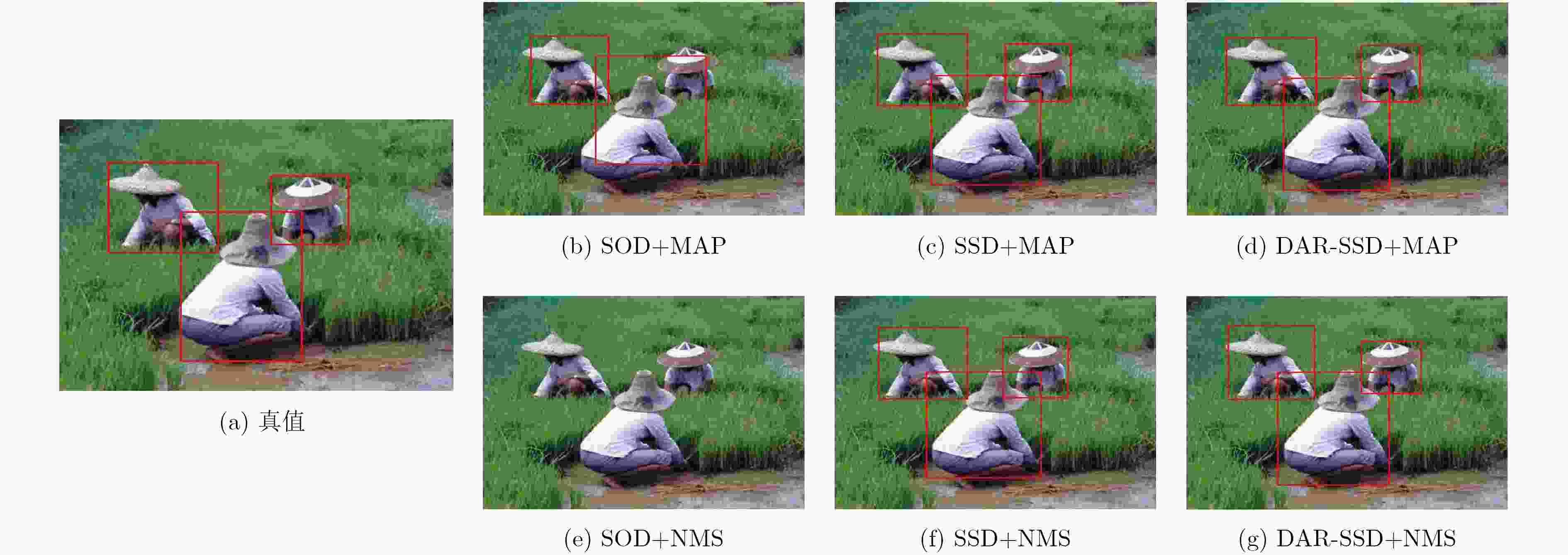
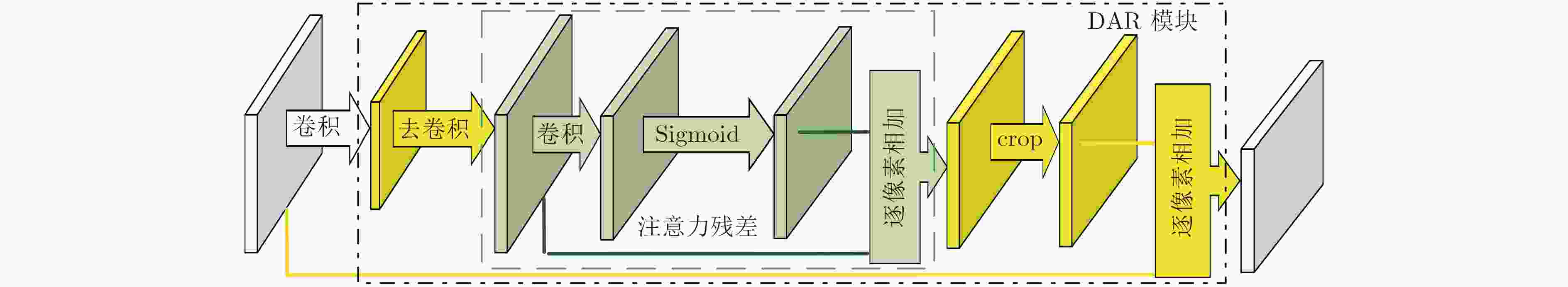
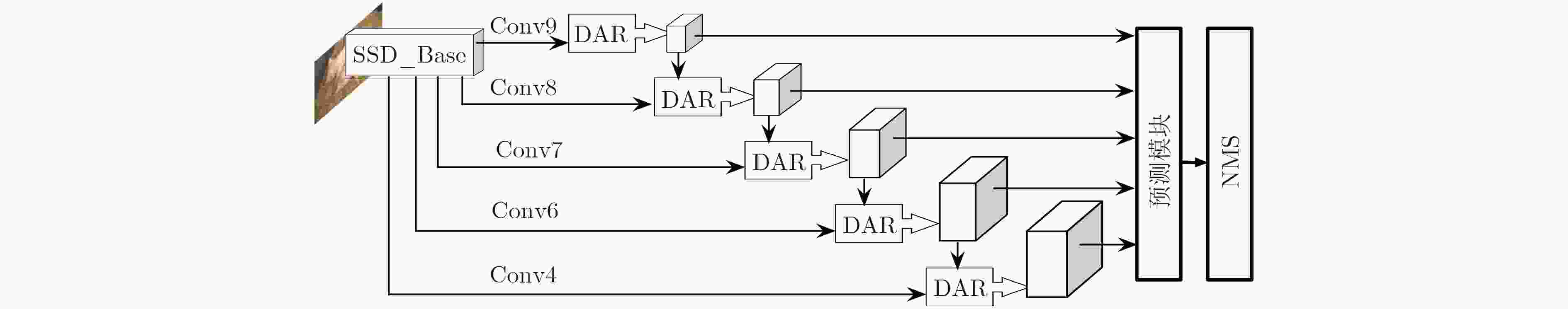
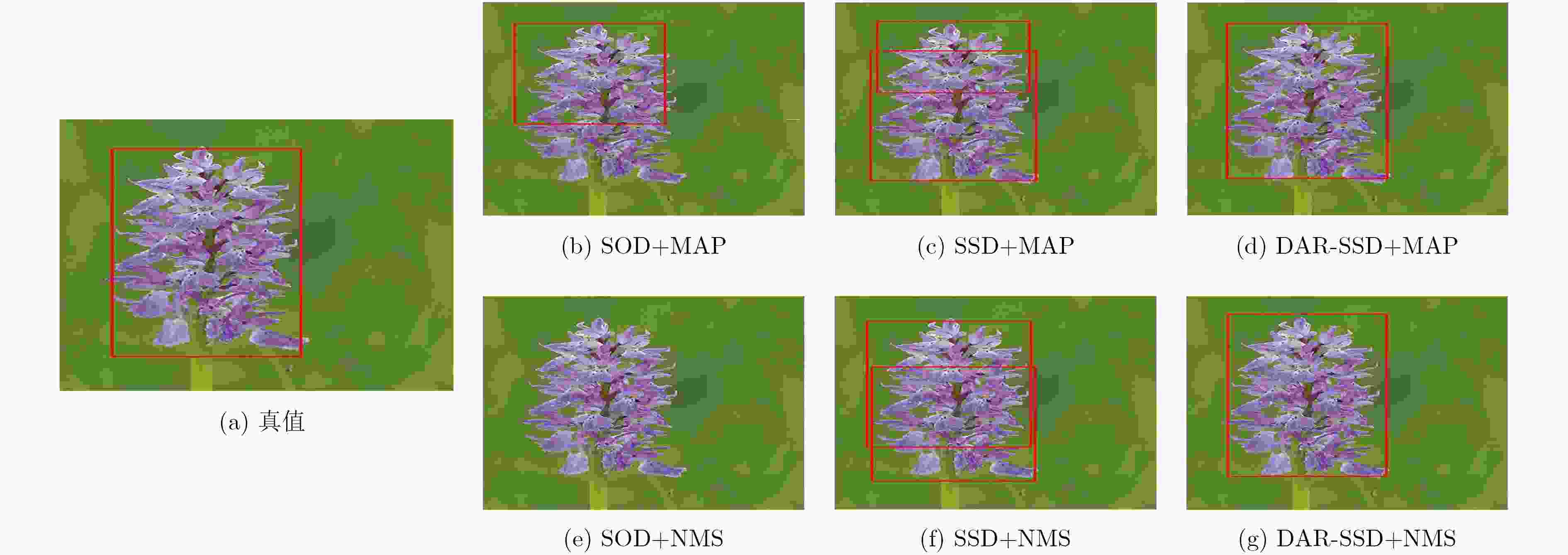
摘要: 传统显著性目标检测方法常假设只有单个显著性目标,其效果依赖显著性阈值的选取,并不符合实际应用需求。近来利用目标检测方法得到显著性目标检测框成为一种新的解决思路。SSD模型可同时精确检测多个不同尺度的目标对象,但小尺寸目标检测精度不佳。为此,该文引入去卷积模块与注意力残差模块,构建了面向多显著性目标检测的DAR-SSD模型。实验结果表明,DAR-SSD检测精度显著高于SOD模型;相比原始SSD模型,在小尺度和多显著性目标情形下性能提升明显;相比MDF和DCL等深度学习框架下的方法,也体现了复杂背景情形下的良好检测性能。Abstract: Traditional saliency object detection methods, assuming that there is only one salient object, is not conductive to practical application. Their effects are dependent on saliency threshold. Object detection model provides a kind of new solutions. SSD can accurately detect multi-objects with different scales simultaneously, except for small objects. To overcome this drawback, this paper presents a new multi- saliency objects detection model, DAR-SSD, appending a deconvolution module embedded with an attention residual module. Experiments show that DAR-SSD achieves a higher detection accuracy than SOD. Also, it improves detection performance for multi- saliency objects on small scales, compared with original SSD, and it has an advantage over complicated background, compared with MDF and DCL, which also are deep model based methods.
-
Key words:
- Object detection /
- Saliency object detection /
- Deconvolutional /
- Attention residual
-
表 1 数据集构成(张)
数据集 MSO ECSSD DUT-OMRON HKU-IS 含显著性目标图像数 886 945 4893 3938 含单显著性目标图像数 611 807 4121 1276 含多显著性目标图像数 275 138 772 2662 含小尺度显著性目标图像数 446 323 3067 3020 含大尺度显著性目标图像数 440 622 1826 918 表 2 MAP方法下AP对照
AP-MAP MSO ECSSD DUT-OMRON HKU-IS 平均 SOD 0.7338 0.8152 0.5476 0.6938 0.6976 SSD 0.8229 0.8645 0.6698 0.8164 0.7934 DAR-SSD 0.8361 0.8766 0.6774 0.8317 0.8054 表 3 NMS方法下AP对照
AP-NMS MSO ECSSD DUT-OMRON HKU-IS 平均 SOD 0.6104 0.7157 0.4409 0.5822 0.5873 SSD 0.8120 0.8619 0.6585 0.7974 0.7824 DAR-SSD 0.8387 0.8665 0.6737 0.8256 0.8011 表 4 单显著性目标情形下AP对照
AP-one MSO ECSSD DUT-OMRON HKU-IS SSD+NMS 0.8823 0.8841 0.6908 0.8147 DAR-SSD+NMS 0.8844 0.8803 0.7052 0.8323 SSD+MAP 0.8881 0.8870 0.7076 0.8483 DAR-SSD+MAP 0.8877 0.8921 0.7127 0.8571 表 7 大尺度显著性目标情形下AP对照
AP-large MSO ECSSD DUT-OMRON HKU-IS SSD+NMS 0.9016 0.8936 0.8190 0.8680 DAR-SSD+NMS 0.9017 0.8888 0.8253 0.8723 SSD+MAP 0.9019 0.8978 0.8330 0.8807 DAR-SSD+MAP 0.9019 0.8997 0.8306 0.8860 表 5 多显著性目标情形下AP对照
AP-multi MSO ECSSD DUT-OMRON HKU-IS SSD+NMS 0.8207 0.7684 0.5920 0.8122 DAR-SSD+NMS 0.8583 0.8055 0.6071 0.8305 SSD+MAP 0.8453 0.7882 0.6073 0.8198 DAR-SSD+MAP 0.8616 0.8149 0.6137 0.8331 表 6 小尺度显著性目标情形下AP对照
AP-small MSO ECSSD DUT-OMRON HKU-IS SSD+NMS 0.7984 0.7719 0.5734 0.7886 DAR-SSD+NMS 0.8288 0.7951 0.5980 0.8142 SSD+MAP 0.8044 0.7877 0.5786 0.8056 DAR-SSD+MAP 0.8310 0.8067 0.5948 0.8128 表 8 多种显著性目标检测方法AP对照
数据集 RC GLGOV MDF DCL DAR-SSD+NMS DAR-SSD+MAP ECSSD 0.733 0.773 0.829 0.897 0.8665 0.8766 DUT-OMRON 0.503 0.539 0.649 0.675 0.6737 0.6774 -
LIU Feng and GLEICHER M. Automatic image retargeting with fisheye-view warping[C]. Annual ACM Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology, Seattle, USA, 2005: 153–162. VALENTI R, SEBE N, and GEVERS T. Image saliency by isocentric curvedness and color[C]. IEEE 12th International Conference on Computer Vision, Kyoto, Japan, 2009: 2185–2192. LUO Ye, YUAN Junsong, XUE Ping, et al. Saliency density maximization for efficient visual objects discovery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2011, 21(12): 1822–1834 doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2011.2147230 FENG Jie, WEI Yichen, TAO Litian, et al. Salient object detection by composition[C]. IEEE International Conference on IEEE Computer Vision. Barcelona, Spain, 2011: 1028–1035. YILDIRIM G and SUSSTRU S. FASA: Fast, accurate, and size-aware salient object detection[C]. Asian Conference on Computer Vision, Singapore, 2014: 514–528. REN Shaoqing, HE Kaiming, GIRSHICK R, et al. Object detection networks on convolutional feature maps[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(7): 1476–1481 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2601099 REDMON J, DIVVAL S, GIRSHICK R, et al. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection[C]. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 779–788. REN Shaoqing, HE Kaiming, GIRSHICK R, et al. Faster r-cnn: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(6): 1137–1149 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2577031 ZHANG Jianming, SCLAROFF S, LIN Zhe, et al. Unconstrained salient object detection via proposal subset optimization[C]. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 5733–5742. ERHAN D, SZEGEDY C, TOSHEV A, et al. Scalable object detection using deep neural networks[C]. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, USA, 2014: 2155–2162. LIU Wei, ANGULEVO D, ERHAN D, et al. SSD: Single shot multibox detector[C]. European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2016: 21–37. LONG J, SHELHAMER E, DARRELL T, et al. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(4): 640–651 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2572683 CAI Zhaowei, FAN Quanfu, FEIRS R S, et al. A unified multi-scale deep convolutional neural network for fast object detection[C]. European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2016: 354–370. HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Spatial pyramid pooling in deep convolutional networks for visual recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 37(9): 1904–1916 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2015.2389824 ZHANG Jianming, MA Shugao, SAMEKI M, et al. Salient object subitizing[C]. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA, 2015: 4045–4054. CHENG Mingming, MITRA N J, HUANG Xiaolei, et al. Global contrast based salient region detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 37(3): 569–582 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2014.2345401 YAN Yijun, REN Jinchang, SUN Genyun, et al. Unsupervised image saliency detection with gestalt-laws guided optimization and visual attention based refinement[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2018, 7, 9(7): 65–78 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2018.02.004 LI Guanbin and YU Yizhou. Visual saliency detection based on multiscale deep CNN features[J]. IEEE Transaction on Image Processing, 2016, 25(11): 5012–5024 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2016.2602079 LI Guanbin and YU Yizhou. Deep contrast learning for salient object detection[C]. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 478–487. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.58. -





 下载:
下载:

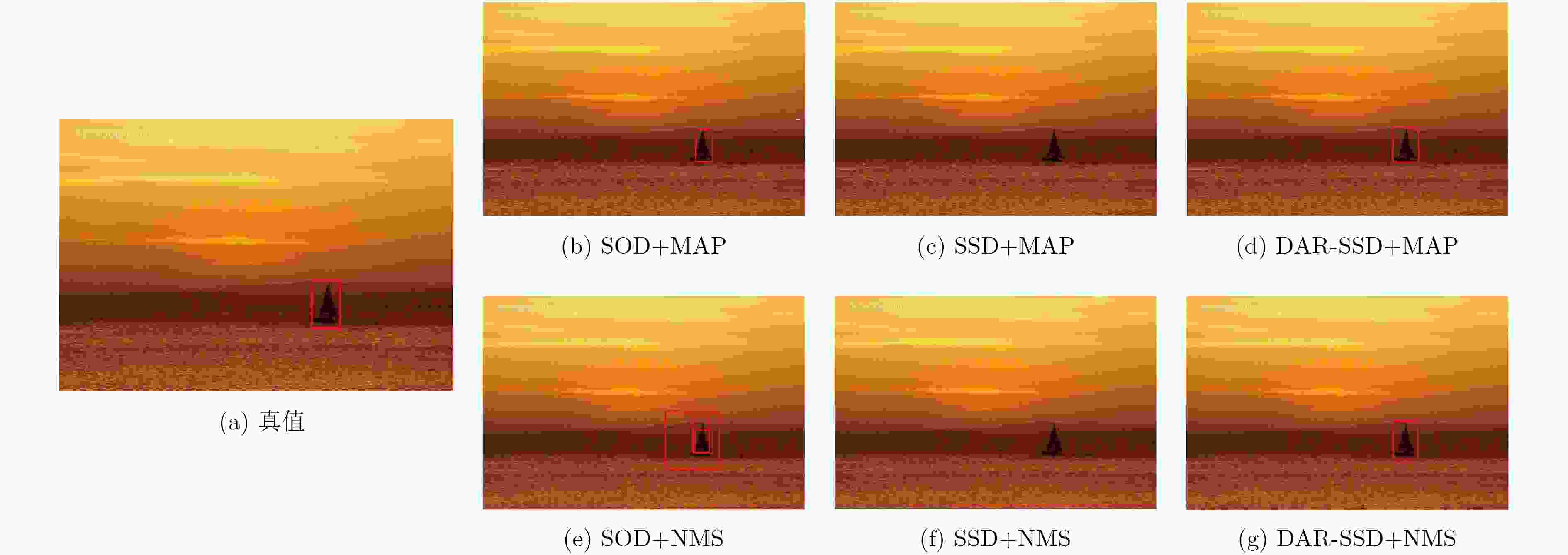
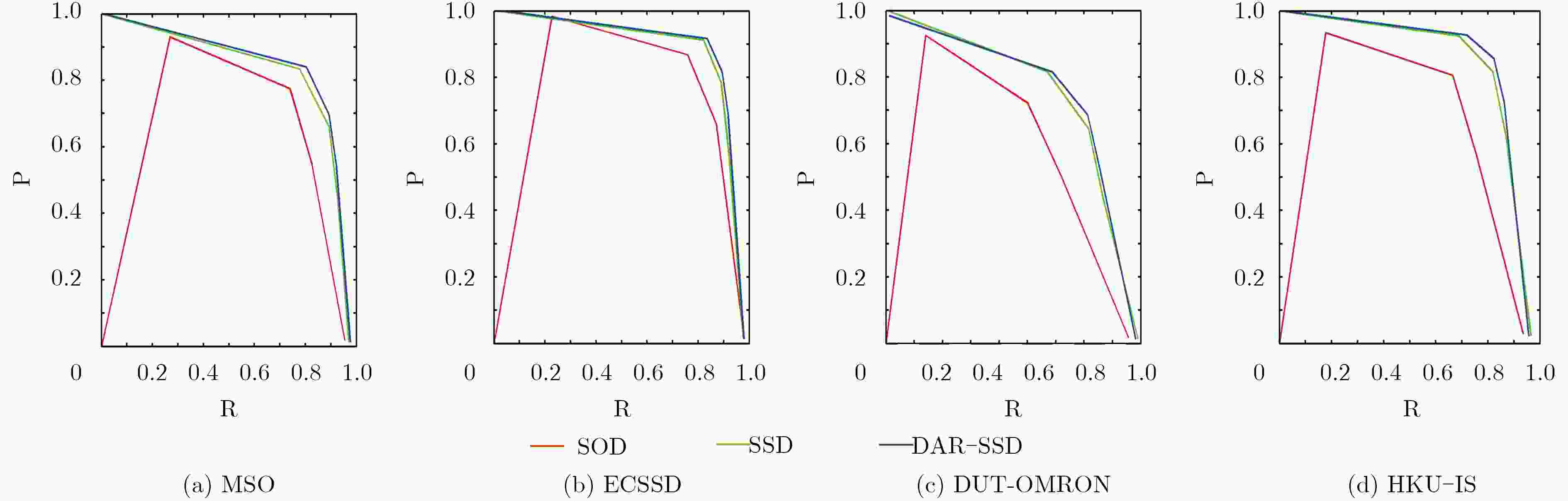
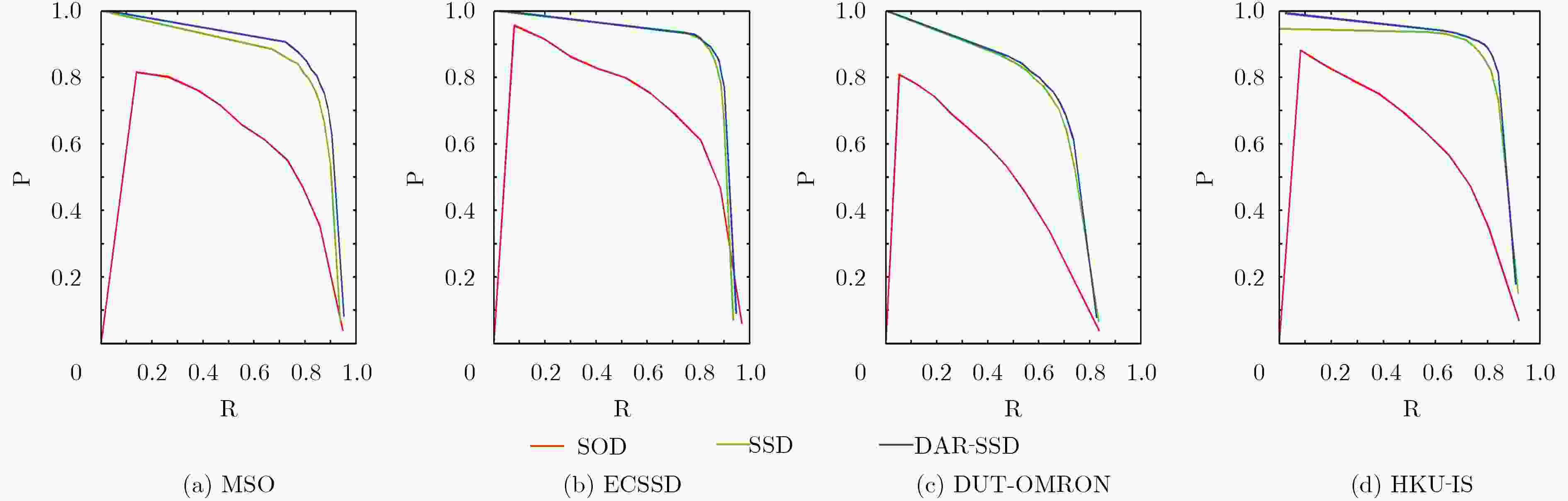


 下载:
下载:
