Low Complexity Iterative Parallel Interference Cancellation Detection Algorithms for Massive MIMO Systems
-
摘要: 基于干扰消除思想该文提出一种适用于大规模MIMO系统上行链路的低复杂度迭代并行干扰消除算法,在算法实现中避免了线性检测算法所需的高复杂度
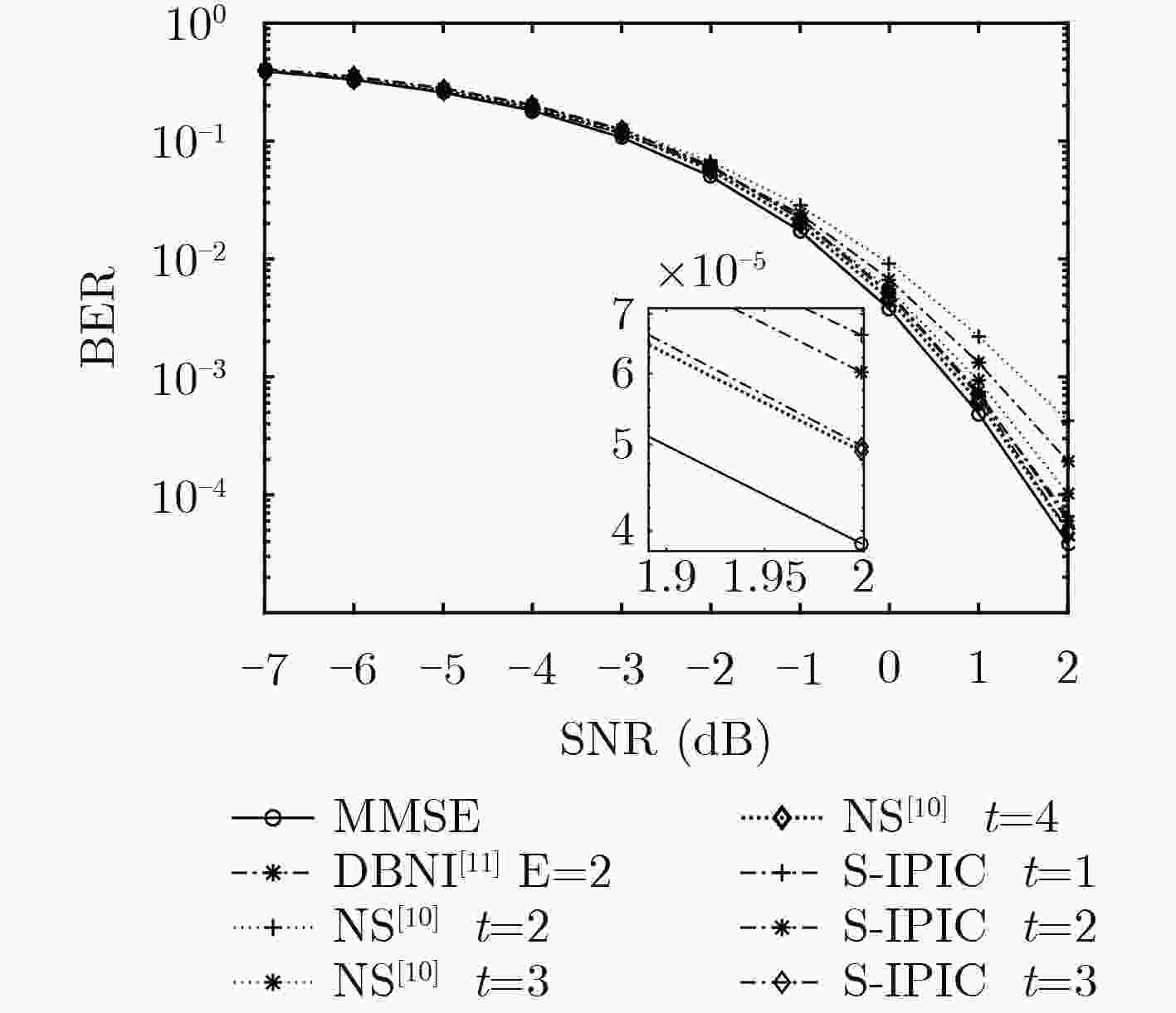
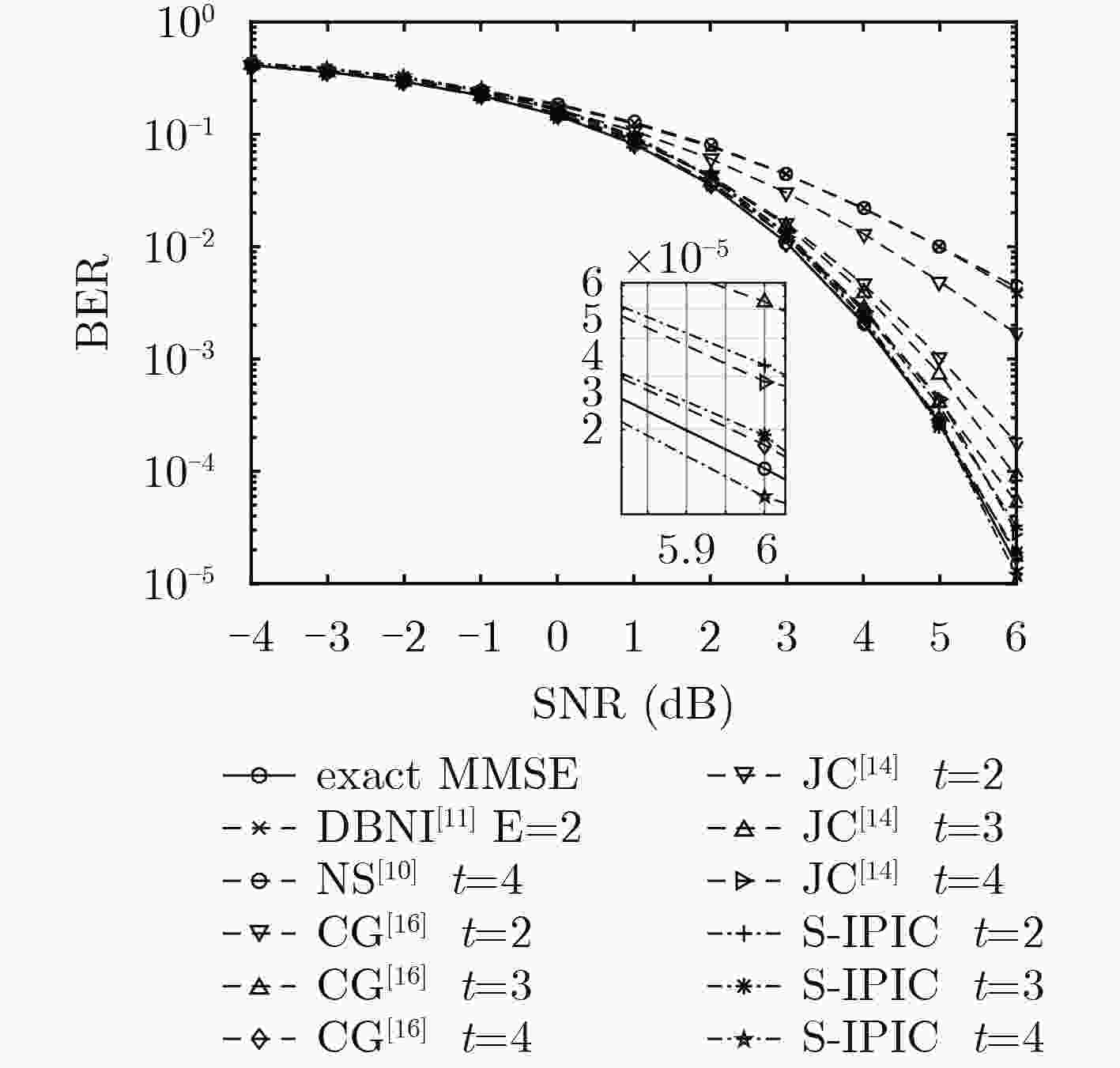
$({\cal O}({K^3}))$ 矩阵求逆运算,将复杂度保持在$({\cal O}({K^2}))$ 。在此基础上,引入噪声预测机制,提出一种基于噪声预测的迭代并行干扰消除算法,进一步提高了硬判决检测性能。考虑天线间残留干扰,将干扰消除思想运用到软判决中,最后提出一种基于迭代并行干扰消除的低复杂度软输出信号检测算法。仿真结果表明:提出的信号检测方法的复杂度优于MMSE检测算法,经过几次简单的迭代,算法即快速收敛并获得接近甚至优于MMSE检测算法的误码率性能。Abstract: Based on interference cancellation method, a low complexity Iterative Parallel Interference Cancellation (IPIC) algorithm is proposed for the uplink of massive MIMO systems. The proposed algorithm avoids the high complexity matrix inversion required by the linear detection algorithm, and hence the complexity is maintained only at$({\cal O}({K^2}))$ . Meanwhile, the noise prediction mechanism is introduced and the noise-prediction aided iterative parallel interference cancellation algorithm is proposed to improve further the detection performance. Considering the residual inter-antenna interference, a low-complexity soft output signal detection algorithm is proposed as well. The simulation results show that the complexity of all the proposed signal detection methods are better than that of the MMSE detection algorithm. With only a small number of iterations, the proposed algorithm achieves its performance quite close to or even surpassing that of the MMSE algorithm. -
表 1 基于迭代并行干扰消除算法(IPIC)
算法1 基于迭代并行干扰消除算法(IPIC) 输入: ${{H}},{{y}},{\sigma ^2},K,{T_{{\rm{iter}}}};$ 初始化: (1) ${{G}} = {{{H}}^{\rm{H}}}{{H}},{{b}} = {{{H}}^{\rm{H}}}{{y}},{{\hat{ s}}^{(0)}} = {{{D}}^{ - 1}}{{{H}}^{\rm{H}}}$ ${{y}} = \{ \hat s_1^{(0)},\hat s_2^{(0)}, ·\!·\!· ,\hat s_K^{(0)}\} $ For $t = 1:{T_{{\rm{iter}}}};$ For $i = 1:K$;
(2) 更新 $\hat s_i^{(t)} = \hat s_i^{(t - 1)} + \frac{{{b_i} - \displaystyle\sum\nolimits_{j = 1}^{i - 1} {{G_{ij}}} \hat s_j^{(t)} - \displaystyle\sum\nolimits_{j = i}^K {{G_{ij}}} \hat s_j^{(t - 1)}}}{{{G_{ii}}}}$(3) 更新 ${{\hat{ s}}^{(t)}} = {\left[ {\hat s_1^{(t)},\hat s_2^{(t)}, ·\!·\!· ,\hat s_{i - 1}^{(t)}}, {Q(\hat s_i^{(t)})}, {\hat s_{i + 1}^{(t - 1)},\hat s_{i + 2}^{(t - 1)}, ·\!·\!· ,\hat s_K^{(t - 1)}}\right]^{\rm{T}}}$ (4) $i = i + 1$ end for (5) $t = t + 1$ end for 输出 ${\hat{ s}} = {{\hat{ s}}^{({T_{{\rm{iter}}}})}}$ 表 2 基于噪声预测的迭代并行干扰消除算法(NP-IPIC)
算法2 基于噪声预测的迭代并行干扰消除算法(NP-IPIC) 输入: ${{H}},{{y}},{\sigma ^2},K,{T_{{\rm{iter}}}};$ 初始化: (1) ${{G}} = {{{H}}^{\rm{H}}}{{H}},{{b}} = {{{H}}^{\rm{H}}}{{y}}$, ${{D}} = {\rm{diag}}({{G}} + {\sigma ^2}{{{I}}_K})$ ${{\hat{ s}}^{(0)}} = Q({{{D}}^{ - 1}}{{{H}}^{\rm{H}}}{{y}}) = \{ \hat s_1^{(0)},\hat s_2^{(0)}, ·\!·\!· ,\hat s_K^{(0)}\}$ (2) 对 ${{H}}$列范数进行降序排序,
$o = \arg {\rm{sort}}({\tau _1},{\tau _2}, ·\!·\!· ,{\tau _K}),\ {\tau _k} = \left\| {{{{h}}_k}} \right\|_2^2,\ \forall k = 1,2, ·\!·\!· ,K$For $t = 1:{T_{{\rm{iter}}}}$; For $i = 1:K$; (3) 更新
$\hat s_{o(i)}^{(t)} = \hat s_{o(i)}^{(t - 1)} + \frac{{{b_{o(i)}} - \displaystyle\sum\limits_{j = 1}^{i - 1} {{G_{o(i)o(j)}}} \hat s_{o(j)}^{(t)} - \displaystyle\sum\limits_{j = i}^K {{G_{o(i)o(j)}}} \hat s_{o(j)}^{(t - 1)}}}{{{G_{o(i)o(i)}}}}$(4) 判断 $i$是否等于1,如果为1,则计算 $\bar s_{o(1)}^{(t)} = Q\left(\hat s_{o(1)}^{(t)}\right)$, 噪声
采样 $\hat n_{o(1)}^{(t)} = \hat s_{o(1)}^{(t)} - \bar s_{o(1)}^{(t)} = \hat s_{o(1)}^{(t)} - \mathbb{Q}\left(\bar s_{o(1)}^{(t)}\right)$, 如果 $i > 1$,跳过
本步骤,执行下一步;
(5) 更新 ${\hat{ n}} = \frac{{{{a}}_{o(i - 1)}^{\rm{H}}}}{{{{\left\| {{{{a}}_{o(i - 1)}}} \right\|}^2}}}\hat n_{o(i - 1)}^{(t)}$(6) $\hat n_{o(i)}^{(t)} = {{{a}}_{o(i)}}{\hat{ n}}$, $\bar s_{o(i)}^{(t)} = Q\left(\hat s_{o(i)}^{(t)} - \hat n_{o(i)}^{(t)}\right)$ (7) 更新
${{\hat{ s}}^{(t)}} = {[ {\hat s_{o(1)}^{(t)},\hat s_{o(2)}^{(t)}, ·\!·\!· ,\hat s_{o(i - 1)}^{(t)}}, {\bar s_{o(i)}^{(t)}}, {\hat s_{o(i + 1)}^{(t - 1)},\hat s_{o(i + 2)}^{(t - 1)}, ·\!·\!· ,\hat s_{o(K)}^{(t - 1)}}]^{\rm{T}}}$(8) $i = i + 1$ end for (9) $t = t + 1$ end for (10) 根据 ${{\hat{ s}}^{({T_{{\rm{iter}}}})}}$中下标进行重新排序得到 ${{\hat{ s}}^{{\rm{final}}}}$ 输出 ${\hat{ s}} = {{\hat{ s}}^{{\rm{final}}}}$ 表 3 基于迭代并行干扰消除的软输出算法(S-IPIC)
算法3 基于迭代并行干扰消除的软输出算法(S-IPIC) 输入: ${{H}},{{y}},{\sigma ^2},K,{T_{{\rm{iter}}}};$ 初始化: (1) ${G}={H}^{\rm H}{H}, {b}={H}^{\rm H}{y}$, ${{D}} = {\rm{diag}}({{G}} + {\sigma ^2}{{{I}}_K}) {{\hat{ s}}^{(0)}} = {{{D}}^{ - 1}}{{{H}}^{\rm{H}}}{{y}} = \{ \hat s_1^{(0)},\hat s_2^{(0)}, ·\!·\!· ,\hat s_K^{(0)}\} $ (2) 估计方差 For $i = 1:K;$
(3) $V_i^{(0)} = \sum\limits_{{\alpha _n} \in {\cal{Q}}} \Bigr| {\alpha _n} - \hat s_i^{(0)}{\Bigr|^2}P({s_i} = {\alpha _n})$end for 估计发送信号并计算NPI方差 For $t = 1:{T_{{\rm{iter}}}};$ For $i = 1:K;$
(4) 更新
$\hat s_i^{(t)} = {\rm{ }}\hat s_i^{(t - 1)} + \frac{{{b_i} - \displaystyle\sum\limits_{j = 1}^{i - 1} {{G_{ij}}} \hat s_j^{(t)} - \displaystyle\sum\limits_{j = i}^K {{G_{ij}}} \hat s_j^{(t - 1)}}}{{{G_{ii}}}}$(5) 更新 ${{\hat{ s}}^{(t)}} = {\left[ {\hat s_1^{(t)},\hat s_2^{(t)}, ·\!·\!· ,\hat s_{i - 1}^{(t)}}, {\hat s_i^{(t)}}, {\hat s_{i + 1}^{(t - 1)},\hat s_{i + 2}^{(t - 1)}, ·\!·\!· ,\hat s_K^{(t - 1)}}\right]^{\rm T}}$ (6) 更新
$V_i^{(t)} = \sum\limits_{{\alpha _n} \in {\cal{O}}} | {\alpha _n} - \hat s_i^{(t)}{|^2}P({s_i} = {\alpha _n})$(7) 计算等效信道增益和NPI方差 ${\mu _i} = 1$,
${(\nu _i^{(t)})^2}{\rm{ }} = \frac{1}{{G_{ii}^2}}\left( {\sum\limits_{j = 1}^{i - 1} | {G_{ij}}{|^2}V_j^{(t)} + \sum\limits_{j = i + 1}^K | {G_{ij}}{|^2}V_j^{(t - 1)}} \right) + \frac{{{\sigma ^2}}}{{{G_{ii}}}}$(8) 计算SINR ${{\rm Y}_i} = {{\mu _i^2} / {{{(\nu _i^{(t)})}^2}}}$ (9) $i = i + 1$ end for (10) $t = t + 1$ end for 输出
${L_{i,b}} = {{\rm Y} _i}\left( {\mathop {\min }\limits_{a \in {\cal{O}}_b^0} {{\left| {\frac{{\hat s_i^{(t)}}}{{{\mu _i}}} - a} \right|}^2} - \mathop {\min }\limits_{a' \in {\cal{O}}_b^1} {{\left| {\frac{{\hat s_i^{(t)}}}{{{\mu _i}}} - a'} \right|}^2}} \right)$ -
MARZETTA T L. Noncooperative cellular wireless with unlimited numbers of base station antennas[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2010, 9(11): 3590–3600 doi: 10.1109/TWC.2010.092810.091092 LU Lu, LI G Y, SWINDLEHURST A L, et al. An overview of massive MIMO: benefits and challenges[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2014, 8(5): 742–758 doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2014.2317671 MUMTAZ S, MORGADO A, HUQ K M S, et al. A survey of 5G technologies: regulatory, standardization and industrial perspectives[J]. Digital Communications&Networks, 2017, 4(2): 87–97 doi: 10.1016/j.dcan.2017.09.010 ARAÚJO D C, MAKSYMYUK T, ALMEIDA A L F D, et al. Massive MIMO: Survey and future research topics[J]. IET Communications, 2016, 10(15): 1938–1946 doi: 10.1049/iet-com.2015.1091 NGO H Q, LARSSON E G, and MARZETTA T L. Energy and spectral efficiency of very large multiuser MIMO systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2013, 61(4): 1436–1449 doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2013.020413.110848 曹海燕, 杨敬畏, 方昕, 等. 大规模MIMO系统中基于二对角矩阵分解的低复杂度检测算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(2): 416–420 doi: 10.11999/JEIT170399CAO Haiyan, YANG Jingwei, FANG Xin, et al. Low complexity detection algorithm based on two-diagonal matrix decomposition in massive MIMO systems[J]. Journal of Electronics&Information Technology, 2018, 40(2): 416–420 doi: 10.11999/JEIT170399 WU M, YIN B, VOSOUGHI A, et al. Approximate matrix inversion for high-throughput data detection in the large-scale MIMO uplink[C]. IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, Beijing, China 2013: 2155–2158. DATTA T, SRINIDHI N, CHOCKALINGAM A, et al. Random-restart reactive tabu search algorithm for detection in large-MIMO systems[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2010, 14(12): 1107–1109 doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2010.101210.101587 PEREIRA AA J and SAMPAIO-NETO R. A random-list based LAS algorithm for near-optimal detection in large-scale uplink multiuser MIMO systems[C]. WSA 2015; 19th International ITG Workshop on Smart Antennas, Ilmenau, Germany, 2015: 1–5. WU M, YIN B, WANG G, et al. Large-scale MIMO detection for 3GPP LTE: algorithms and FPGA implementations[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2014, 8(5): 916–929 doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2014.2313021 TANG C, LIU C, YUAN L, et al. High precision low complexity matrix inversion based on Newton iteration for data detection in the massive MIMO[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2016, 20(3): 490–493 doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2015.2514281 GAO Xinyu, DAI Linglong, YUEN C, et al. Low-complexity MMSE signal detection based on Richardson method for large-scale MIMO systems[C]. Vehicular Technology Conference, Vancouver, Canada, 2014: 1–5. DAI Linglong, GAO Xinyu, SU Xin, et al. Low-complexity soft-output signal detection based on gauss–seidel method for uplink multiuser large-scale MIMO systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2015, 64(10): 4839–4845 doi: 10.1109/TVT.2014.2370106 QIN Xianbo, YAN Zhiting, and HE Guanghui. A near-optimal detection scheme based on joint steepest descent and jacobi method for uplink massive MIMO systems[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2016, 20(2): 276–279 doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2015.2504506 GAO Xinyu, DAI Linglong, HU Yuting, et al. Matrix inversion-less signal detection using SOR method for uplink large-scale MIMO systems[C]. Global Communications Conference, Austin, USA, 2014: 3291–3295. YIN B, WU M, CAVALLARO J R, et al. Conjugate gradient-based soft-output detection and precoding in massive MIMO systems[C]. Global Communications Conference, Austin, USA, 2014: 3696–3701. XUE Ye, ZHANG Chuan, ZHANG Shunqing, et al. Steepest descent method based soft-output detection for massive MIMO uplink[C]. IEEE International Workshop on Signal Processing Systems, Dallas, USA, 2016: 273–278. FOSCHINI G J. Layered space-time architecture for wireless communication in a fading environment when using multi-element antennas[J]. Bell Labs Technical Journal, 1996, 1(2): 41–59 doi: 10.1002/bltj.2015 FA R and LAMARE R C D. Multi-branch successive interference cancellation for MIMO spatial multiplexing systems: Design, analysis and adaptive implementation[J]. IET Communications, 2011, 5(4): 484–494 doi: 10.1049/iet-com.2009.0843 LI P, LAMARE R C D, and FA R. Multiple feedback successive interference cancellation detection for multiuser MIMO systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2011, 10(8): 2432–2439 doi: 10.1109/TWC.2011.060811.101962 MANDLOI M, HUSSAIN M A, and BHATIA V. Improved multiple feedback successive interference cancellation algorithms for near-optimal MIMO detection[J]. IET Communications, 2017, 11(1): 150–159 doi: 10.1049/iet-com.2016.0333 MANDLOI M and BHATIA V. Low-complexity near-optimal iterative sequential detection for uplink massive MIMO systems[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2017, 21(3): 568–571 doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2016.2637366 倪兴, 王晓湘, 杜娟. 一种新的基于噪声预测的部分判决反馈MIMO接收算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2008, 30(1): 52–54NI Xing, WANG Xiaoxiang, and DU Juan. A noise-predictive partial decision-feedback detection for MIMO systems[J]. Journal of Electronics&Information Technology, 2008, 30(1): 52–54 WATERS D W and BARRY J R. Noise-predictive decision-feedback detection for multiple-input multiple-output channels[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2005, 53(5): 1852–1859 doi: 10.1109/TSP.2005.845474 -








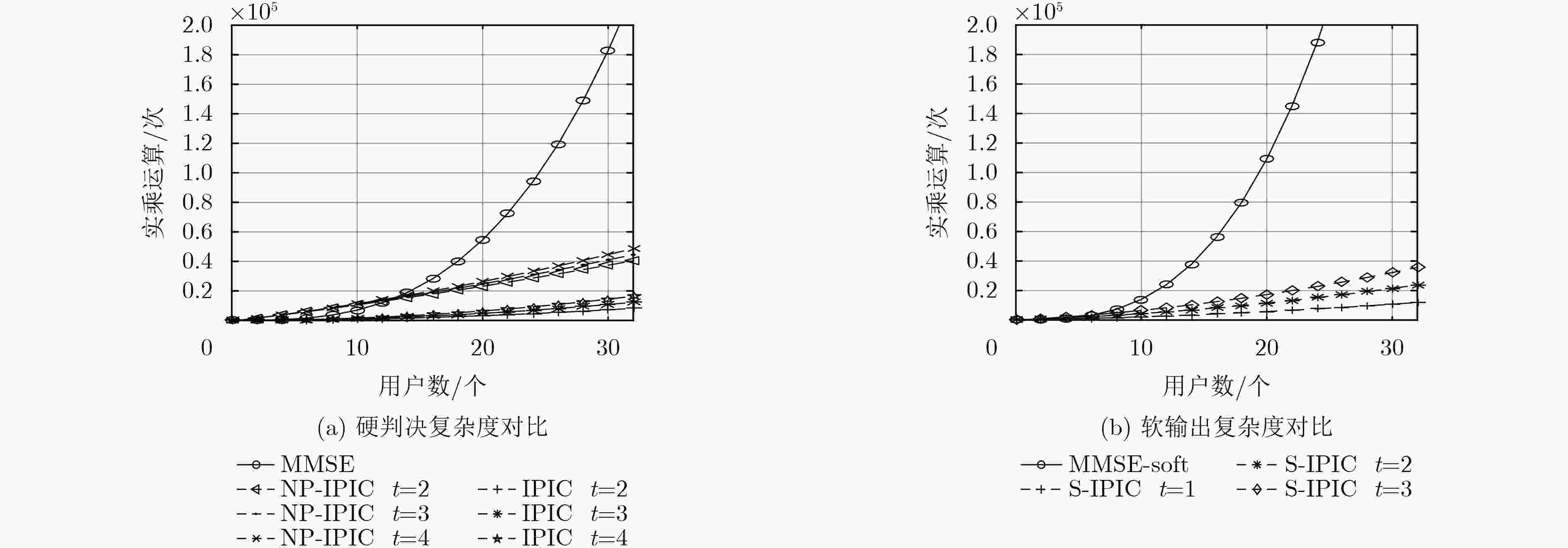
 下载:
下载:
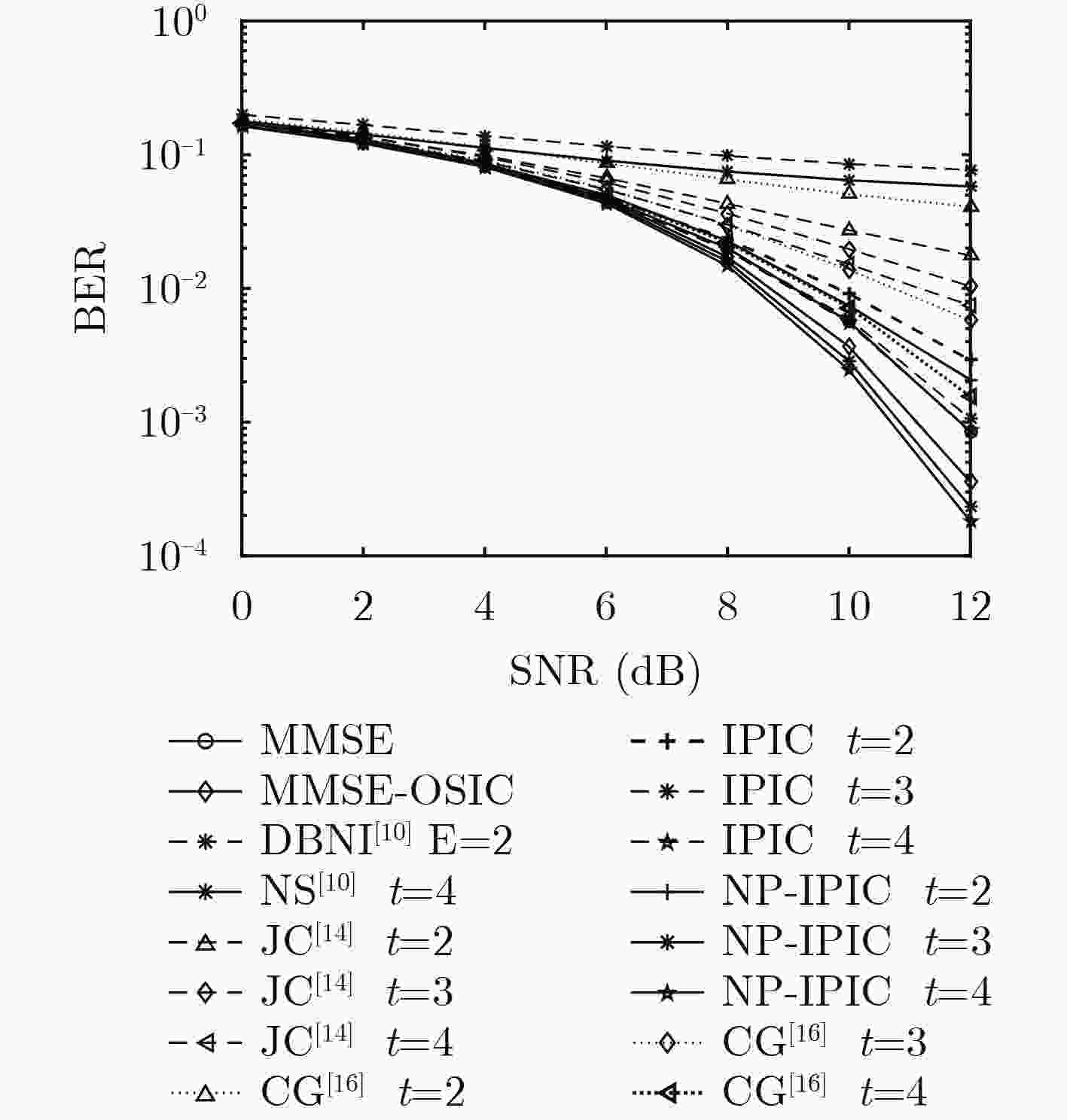

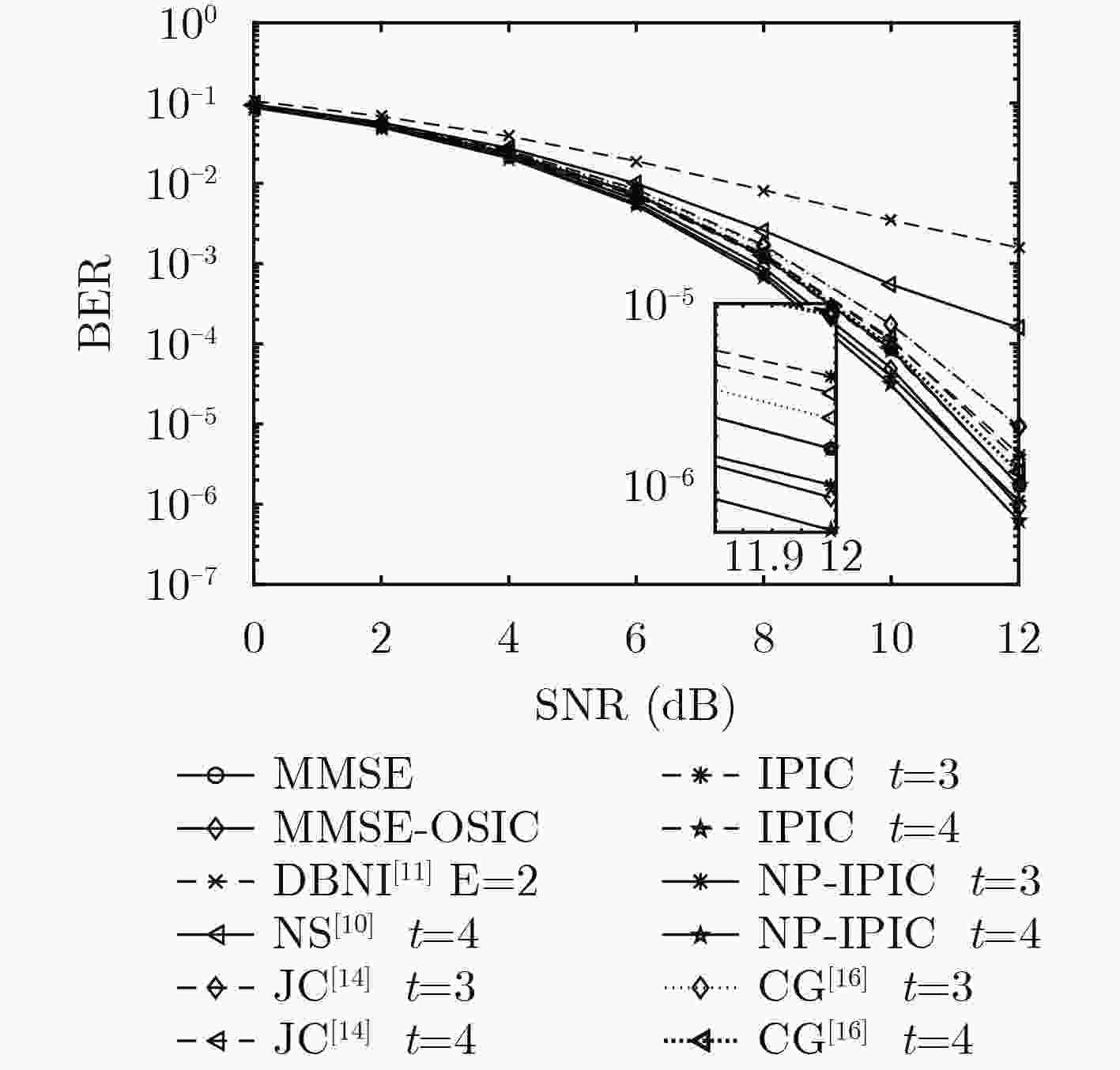

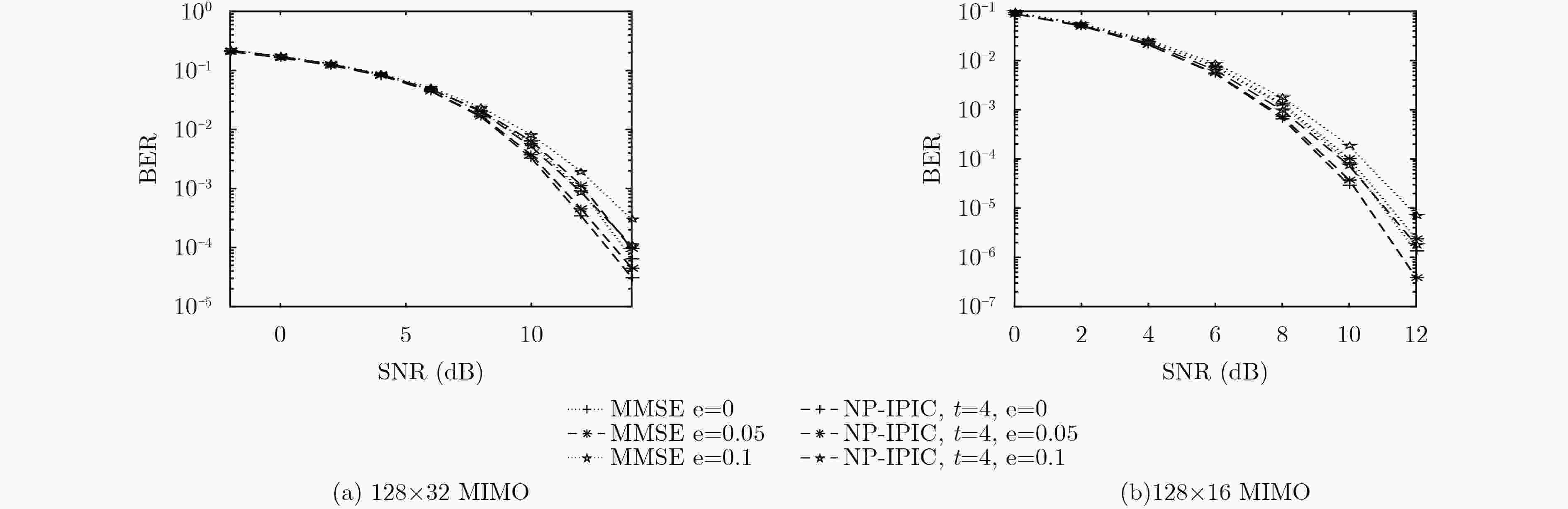




 下载:
下载:
