Fast High-resolution Imaging Method for Wideband Spinning Targets under Sub-Nyquist Sampling
-
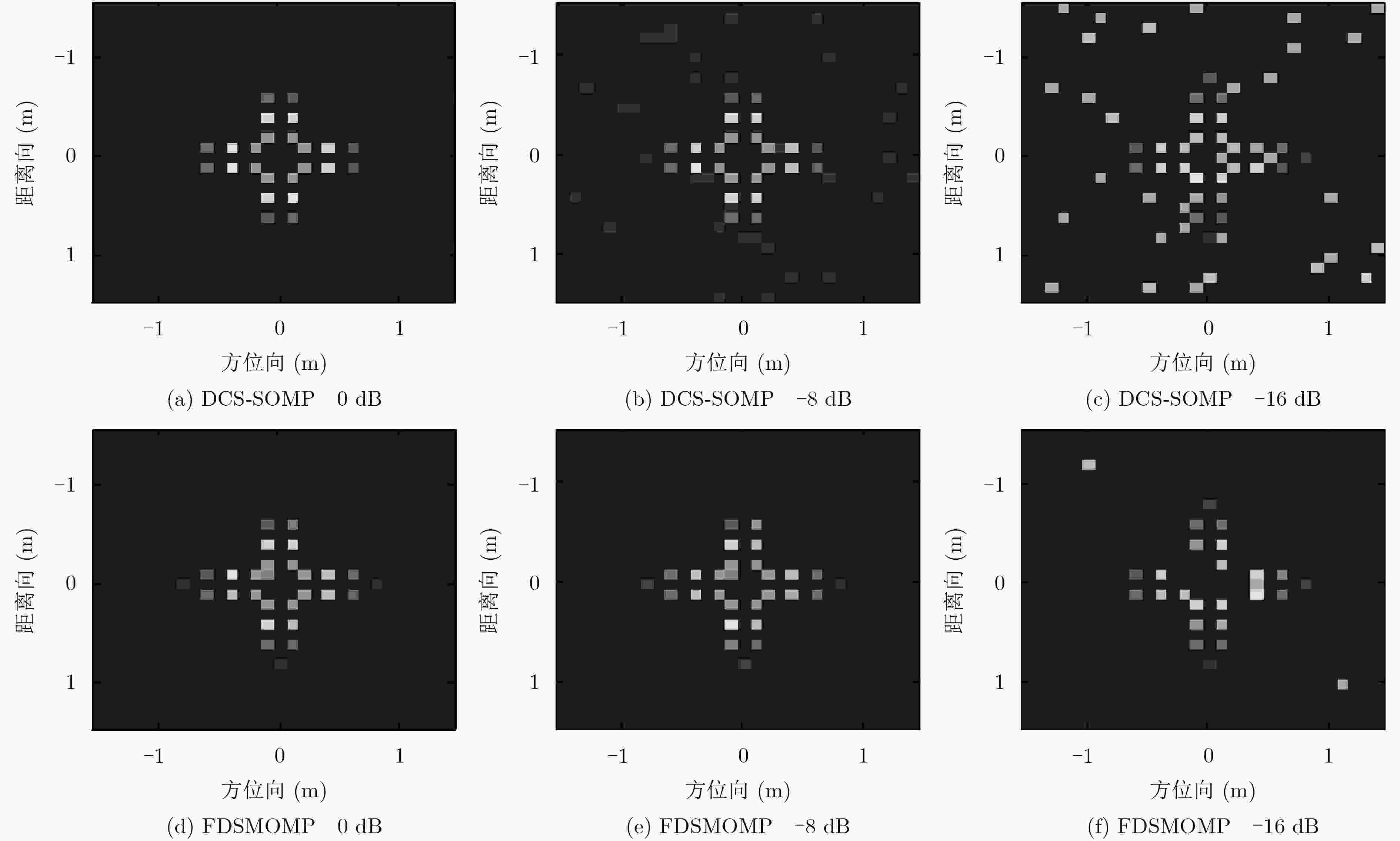
摘要: 逆合成孔径雷达(ISAR)观测自旋目标时,自旋目标回波的距离-多普勒时变性会导致传统成像方法失效。针对此问题,该文提出一种基于分布式匹配稀疏表示模型的宽带自旋目标快速高分辨成像方法。首先,通过自旋目标回波在距离频域表征出的稀疏性,构建分布式匹配稀疏表示模型;其次,研究快速分布式同步多正交匹配追踪算法,并通过减少算法总的迭代次数和每次迭代运算量来提高算法的重构效率,同时设计相关阈值抑制虚假重构散射点,实现鲁棒成像;最后,从理论上分析该方法在欠采样及低信噪比条件下依然可获得高质量图像的机理。仿真结果证明了该方法的有效性。Abstract: When using Inverse Synthetic Aperture Radar (ISAR) to observe the spinning targets, the range-Doppler time-varying characteristics of spinning target echo would lead to the inefficiency of traditional imaging methods. To solve this problem, a fast high-resolution imaging method based on distributed matching sparse representation model is proposed for wideband spinning targets imaging. Firstly, a distributed matching sparse representation model is constructed based on the sparsity of spinning target echo. Secondly, a Fast Distributed Simultaneous Multiple Orthogonal Matching Pursuit (FDSMOMP) algorithm is proposed for achieving the fast robust imaging of the spinning parts. The proposed algorithm can significantly improve the reconstruction efficiency by reducing the iteration times and computational complexity of each iteration. Additionally, in order to enhance the robustness of FDSMOMP, a related threshold is designed to suppress the false reconstruction. Finally, the mechanism of the presented method is analyzed theoretically, and it is proved that the high quality imaging result can still be obtained under the conditions of sub-Nyquist sampling and lower (SNR Signal Noise Ratio). Simulation results show the validation of the proposed method.
-
Key words:
- High-resolution sparse imaging /
- Sparsity /
- Spinning target /
- Sub-Nyquist sampling /
- Low SNR
-
表 1 FDSMOMP算法
输入:量测数据 ${{Y}}$,感知矩阵 ${{Θ}}$,预置稀疏度 ${k_0}$,组选支撑集 $s$。 输出:重构结果 ${\tilde {{X}}_{{\rm{Finaset}}}}$。 算法初始化:初始残差 ${{{R}}^{\left( 0 \right)}} = {{Y}}$,预重构结果 $\tilde {{X}} = 0$,初始支
撑集 $\tilde {{S}} = \varnothing $。第1步 多原子识别:根据式(11)计算新原子支撑集 ${\rm{pos}}$,以此为 索引构建新的原子组; 第2步 投影计算:更新支撑集 ${\tilde S^j} = {\tilde S^{j - 1}} \cup {\rm{pos}}$,依据式(12)进 行投影值计算,得到 $\tilde {{X}}{({{{{{f}}}_p})_{\tilde S}}$; 第3步 残差更新: ${{R}}{\left( {{f_p}} \right)^{\left( j \right)}} = {{y}}\left( {{f_p}} \right) - {{Θ}}_{\tilde S}^{\left( j \right)}\tilde {{X}}{\left( {{{{f}_p}} \right)_{\tilde S}}$,判断迭代 停止条件是否满足,若满足则执行第4步,否则循环迭代 第1至第3步; 第4步 利用最小二乘估计最终结果 ${\tilde {{X}}_{{\rm{Finaset}}}}$。 表 2 不同算法的图像熵值和运算时间对比
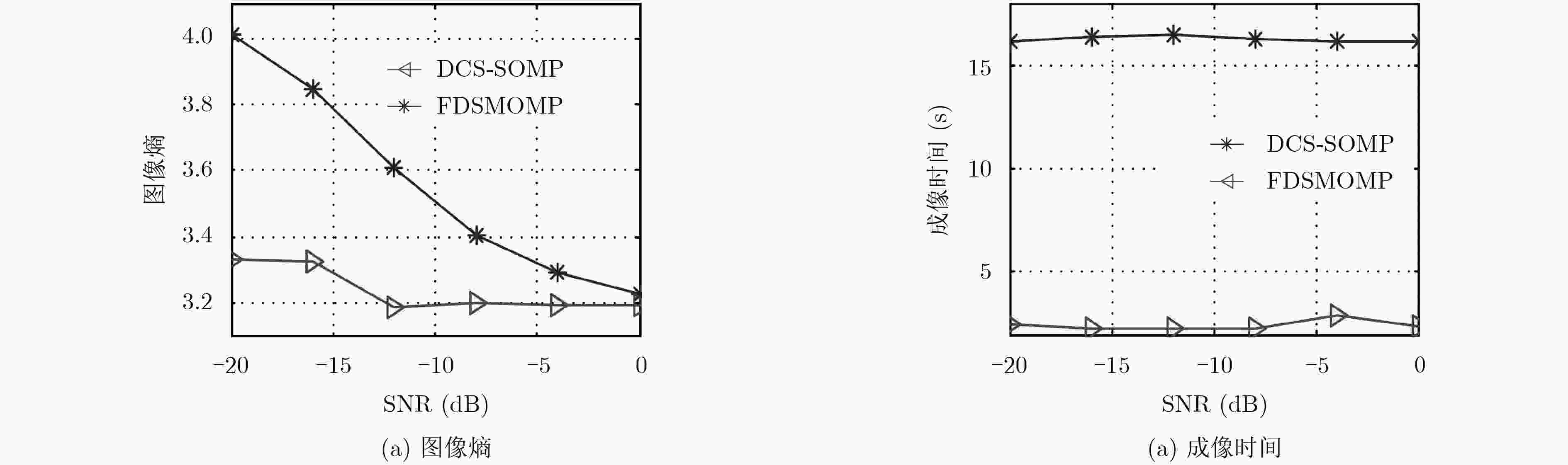
欠采样倍数 DCS-SOMP FDSMOMP 图像熵值 运算时间(s) 图像熵值 运算时间(s) $\delta = 2$ 3.162 15.287 3.151 4.202 $\delta = 4$ 3.169 8.125 3.168 2.222 $\delta = 8$ 3.189 4.995 3.182 1.740 -
张群, 何其芳, 罗迎. 基于贝塞尔函数基信号分解的微动群目标特征提取方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(12): 3056–3062 doi: 10.11999/JEIT161036ZHANG Qun, HE Qifang, and LUO Ying. Micro-Doppler feature extraction of group targets using signal decomposition based on Bessel function basis[J]. Journal of Electronics&Information Technology, 2016, 38(12): 3056–3062 doi: 10.11999/JEIT161036 TOMEI S, BACCI A, GIUSTI E, et al. Compressive sensing-based inverse synthetic radar imaging from incomplete data[J].IET Radar,Sonar and Navigation, 2016, 10(2): 386–397 doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2015.0290 THAYAPARAN T, ABROL S, RISEBOROUGH E, et al. Analysis of radar micro-Doppler signatures from experimental helicopter and human data[J]. IET Radar,Sonar and Navigation, 2007, 1(4): 289–299 doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn:20060103 BAI Xueru, XING Mengdao, ZHOU Feng, et al. Imaging of micromotion targets with rotating parts based on empirical-mode decomposition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2008, 46(11): 3514–3523 doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2008.2002322 袁斌, 徐世友, 陈曾平. 基于复数局部均值分解的含自旋目标目标微多普勒分离技术[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2012, 34(12): 2927–2933 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2012.00655YUAN Bin, XU Shiyou, and CHEN Zengping. Micro-Doppler separation from targets with rotating parts based on complex local mean decomposition[J]. Journal of Electronics&Information Technology, 2012, 34(12): 2927–2933 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2012.00655 SATO T. Shape estimation of space debris using single-range Doppler interferometry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1999, 37(2): 1000–1005 doi: 10.1109/36.752218 ZHANG Qun, YEO Tat Soon, TAN Hwee Siang, et al. Imaging of a moving target with rotating parts based on the Hough transform[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2008, 46(1): 291–299 doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2007.907105 白雪茹, 周峰, 邢孟道. 空中微动旋转目标的二维ISAR成像算法[J]. 电子学报, 2009, 37(9): 1938–1943 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.0009.09.011BAI Xueru, ZHOU Feng, and XING Mengdao. 2D ISAR imaging algorithm for air micro-motion targets[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2009, 37(9): 1938–1943 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.0009.09.011 BAI Xueru, ZHOU Feng, XING Mengdao, et al. High resolution ISAR imaging of targets with rotating parts[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2011, 47(4): 2530–2543 doi: 10.1109/TAES.2011.6034649 句彦伟, 张燕. 自旋目标高效参数化高分辨成像研究[J]. 现代雷达, 2016, 38(6): 30–33 doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2016.06.008JU Yanwei and ZHANG Yan. An effective super-resolution ISAR imaging method for spinning-target[J]. Modern Radar, 2016, 38(6): 30–33 doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2016.06.008 HONG Ling, DAI Fengzhou, and LIU Hongwei. A fused-lasso-based Doppler imaging algorithm for spinning targets with occlusion effect[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2016, 16(9): 3099–3108 doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2016.2522405 SUN Chao, WANG Baoping, FANG Yang, et al. Narrow-band radar imaging for off-grid spinning targets via compressed sensing[J]. Multidimensional Systems and Signal Processing, 2017, 28(4): 1167–1181 doi: 10.1007/s11045-016-0384-5 孙玉雪, 罗迎, 张群, 等. 空间自旋目标宽带雷达干涉三维成像方法[J]. 航空学报, 2017, 38(4): 227–239 doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2016.0286SUN Yuxue, LUO Ying, ZHANG Qun, et al. Interferometric 3D imaging for space rotating targets in wideband radar[J]. Acta Aeronautics et Astronautics Sinica, 2017, 38(4): 227–239 doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2016.0286 SUNDMAN D. Greedy algorithms for distributed compressed sensing[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], KTH Royal Institute of Technology School of Electrical Engineering, 2014: 13–91. DROR B, MICHAEL B. Distributed compressed sensing[J]. Preprint, 2005, 22(10): 2729–2732 doi: 10.1007/978-981-287-390-3 WANG J, KWON S, and SHIM B. Generalized orthogonal matching pursuit[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2012, 60(12): 6202–6216 doi: 10.1109/TSP.2012.2218810 李少东, 陈永彬, 刘润华, 等. 基于压缩感知的窄带高速自旋目标高分辨成像物理机理分析[J]. 物理学报, 2017, 66(3): 337–346 doi: 10.7498/aps.66.038401LI Shaodong, CHEN Yongbin, LIU Runhua, et al. Analysis on the compressive sensing based narrow-band radar super resolution imaging mechanism of rapidly spinning targets[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2017, 66(3): 337–346 doi: 10.7498/aps.66.038401 张磊. 高分辨SAR/ISAR成像及误差补偿技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2012.ZHANG Lei. Study on high resolution SAR/ISAR imaging and error correction[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], XiDian University, 2012. -





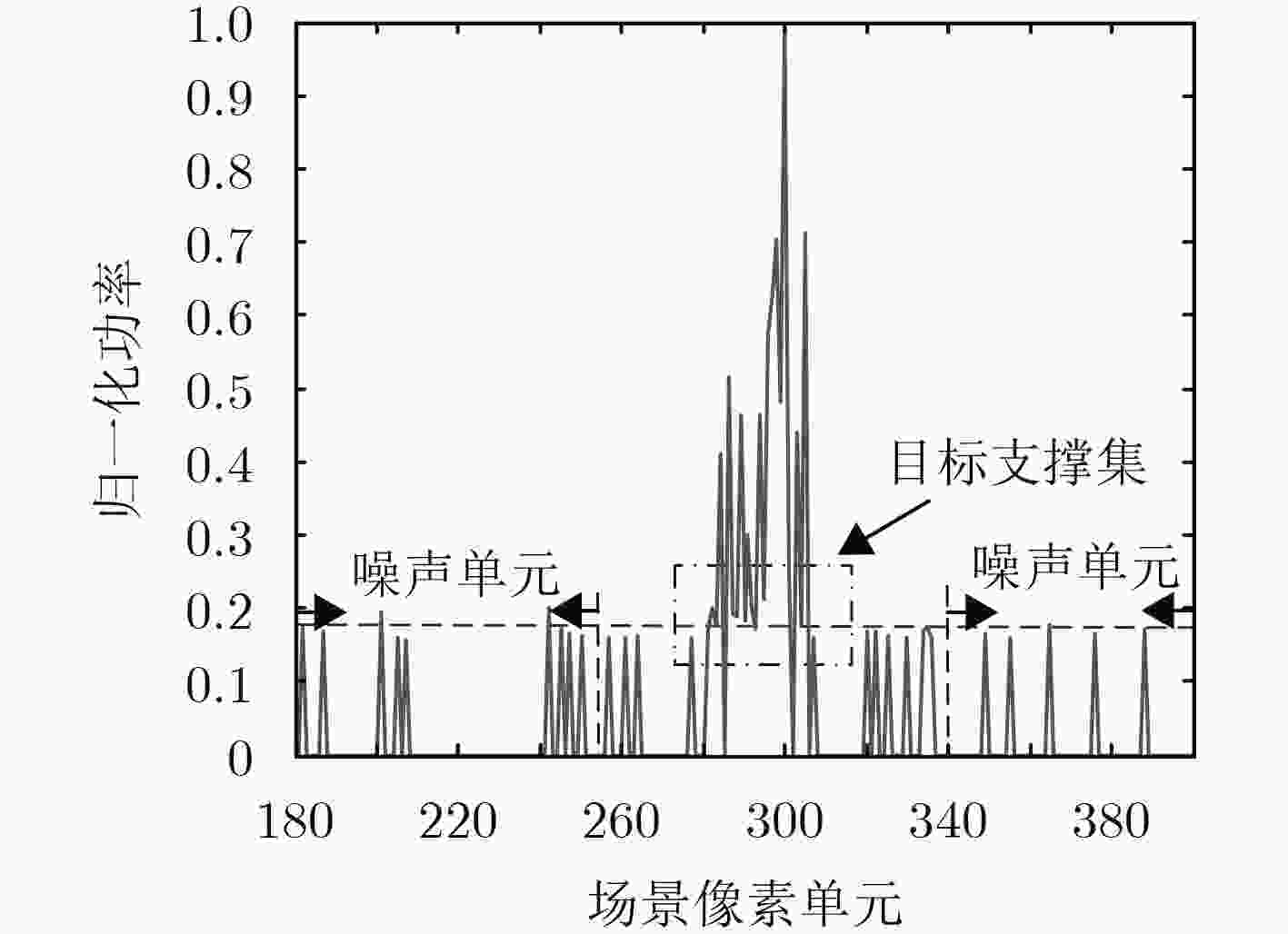
 下载:
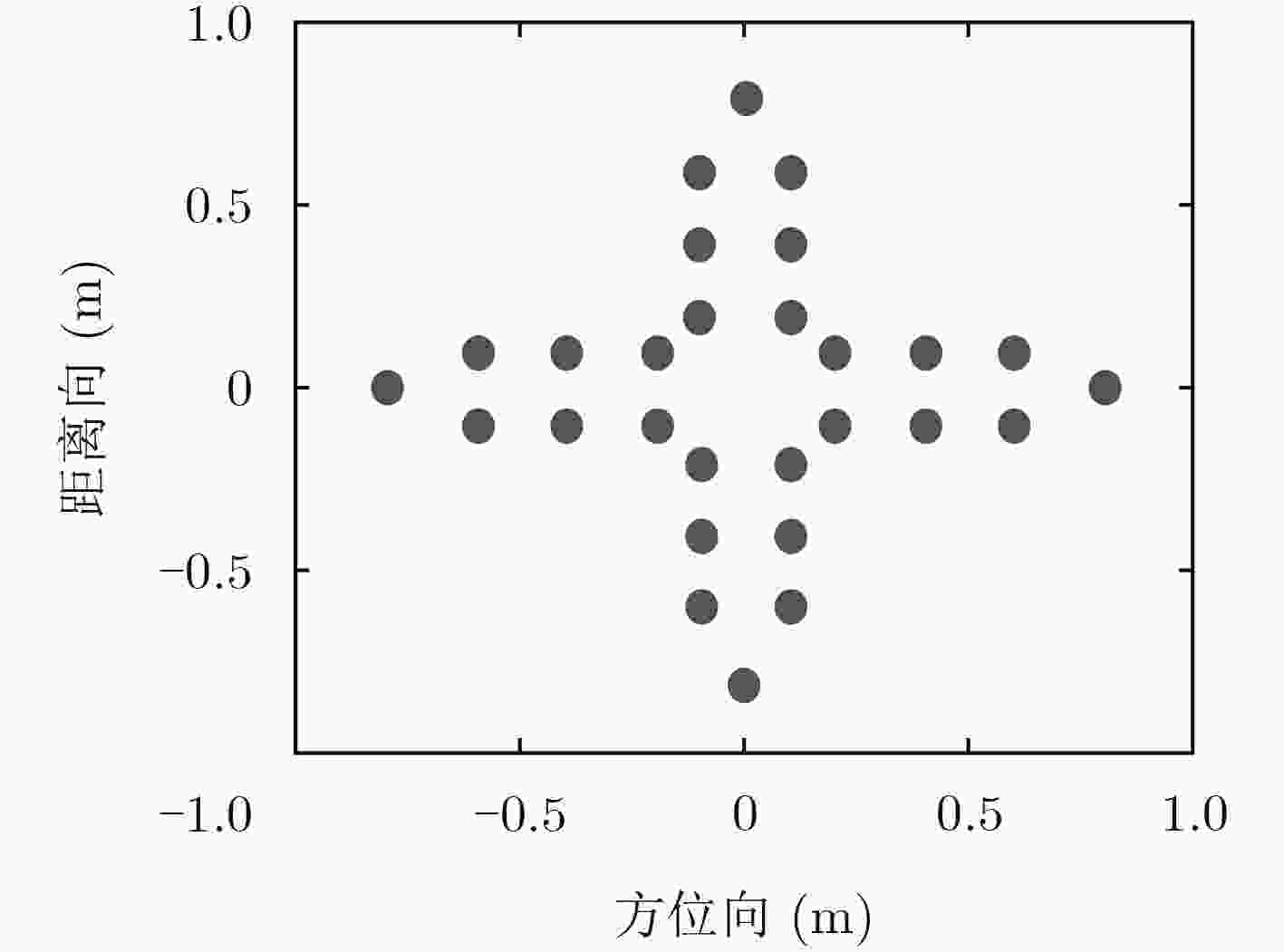
下载:
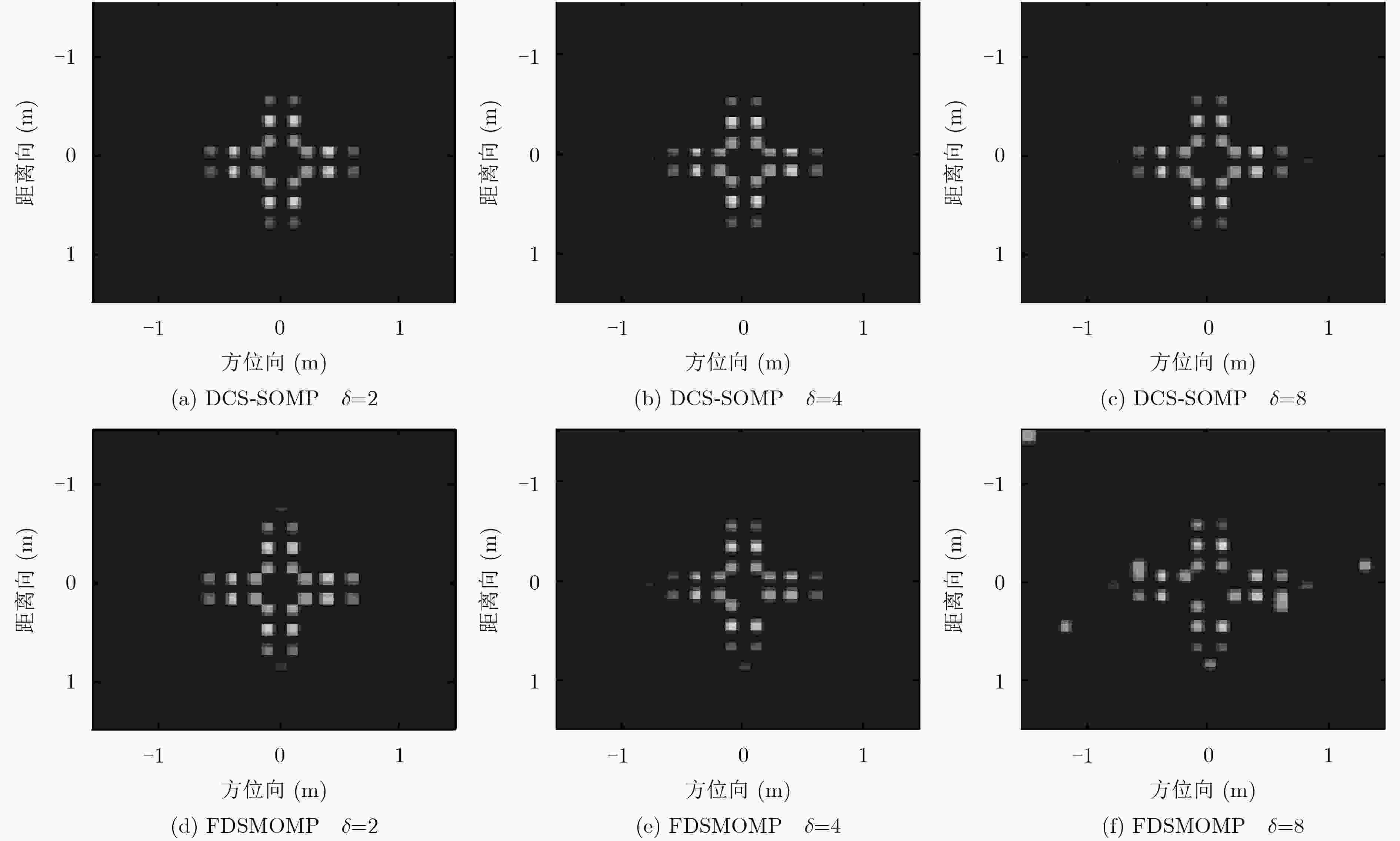


 下载:
下载:
