A Robust Optical Flow Calculation Method Based on Wavelet
-
摘要: 针对系统误差导致光流计算稳健性较差及精度较低的问题,该文提出一种基于小波多分辨理论的稳健光流计算方法。所提算法基于小波多尺度分辨率特性,将光照条件变化及传感器噪声引起的系统误差包含进光流计算中以改善光流计算的稳健性及估计精度,并通过总体最小二乘法求解超定小波光流方程组以获得光流矢量。仿真结果表明,与传统的Lucas-Kanade算法、Horn-Schunck算法及基于小波的全向图像光流估计方法相比,所提算法可显著改善光流估计精度及稳健性。Abstract: Focusing on the issue that the systematic errors lead to poor robustness and low accuracy of optical flow calculation, a robust optical flow calculation method is proposed in this paper, which is based on the wavelet multi-resolution theory. With the multi-resolution characteristics of wavelet, the system error caused by variation of illumination conditions and sensor noise is incorporated into the calculation of optical flow to improve the robustness and estimation accuracy. In what follows, the total least square method is used to solve the over-determined wavelet optical flow equations to obtain the optical flow vector. As compared to the traditional Lucas-Kanade approach, Horn-Schunck method and optical flow estimation in omnidirectional images using wavelet approach, simulation results show that the proposed algorithm can significantly improve the accuracy of optical flow estimation and the robustness of the optical flow field.
-
Key words:
- Optical flow calculation /
- Wavelet multi-resolution /
- System error /
- Total least squares
-
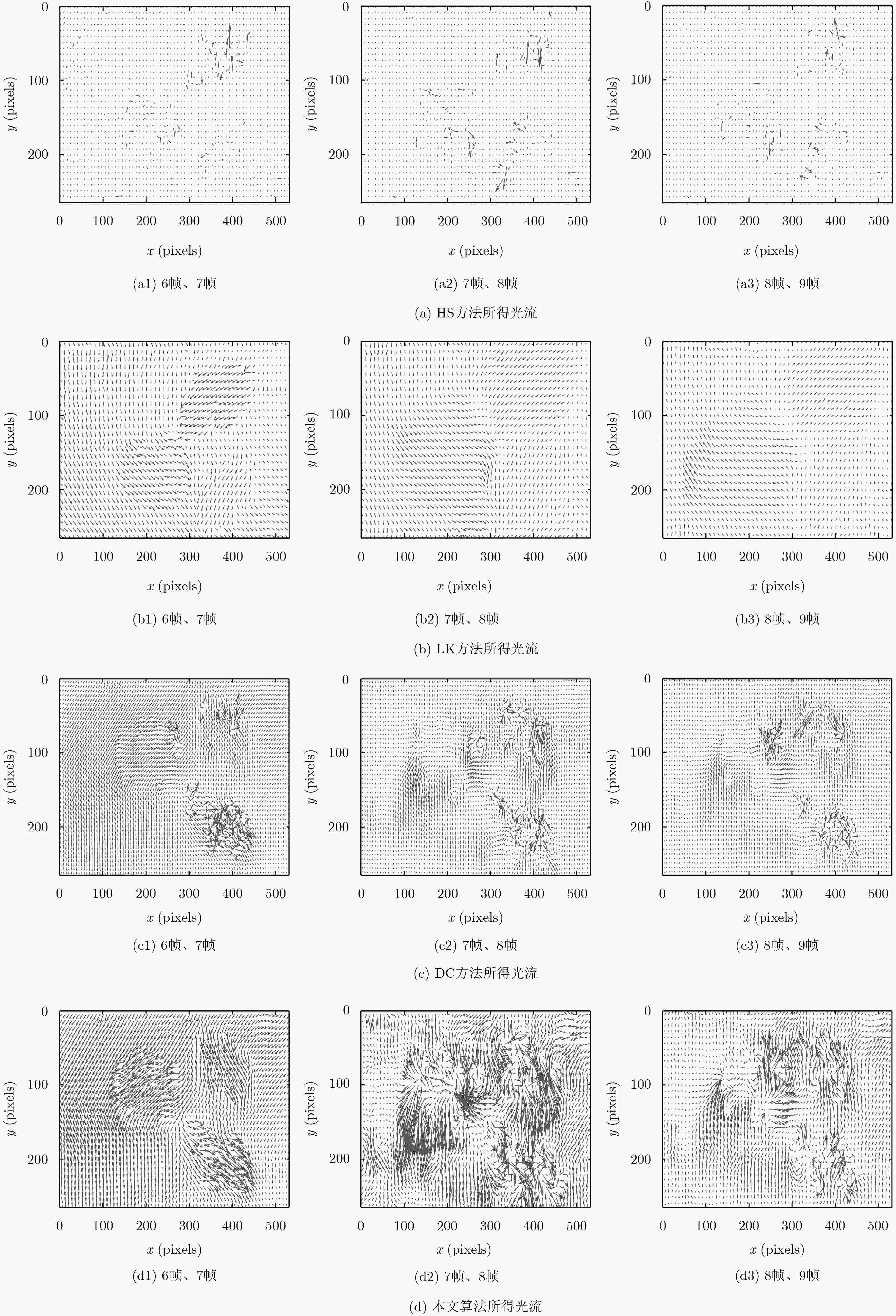
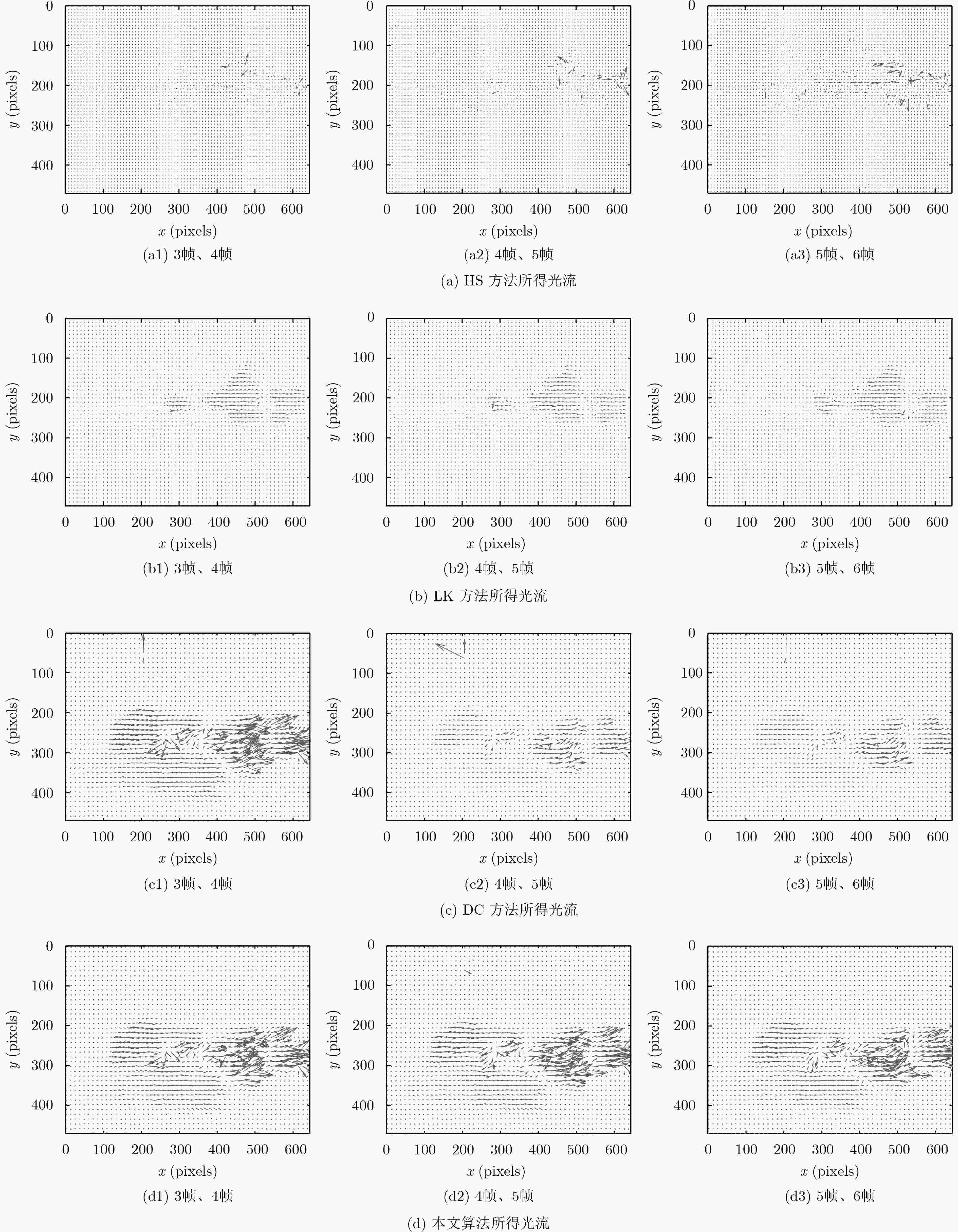
表 2 快速运动下光流性能参数
算法类型 E F H 3帧、4帧 4帧、5帧 5帧、6帧 3帧、4帧 4帧、5帧 5帧、6帧 3帧、4帧 4帧、5帧 5帧、6帧 HS 12.23 12.20 12.27 12.59 12.54 12.57 0.91 0.93 0.90 LK 8.76 8.75 8.78 9.12 9.08 9.10 0.78 0.76 0.77 DC 4.89 4.78 4.82 4.35 4.33 4.36 0.34 0.36 0.35 本文算法 2.08 2.11 2.13 2.47 2.46 2.41 0.26 0.23 0.25 表 1 慢速运动下光流性能参数
算法类型 E F H 6帧、7帧 7帧、8帧 8帧、9帧 6帧、7帧 7帧、8帧 8帧、9帧 6帧、7帧 7帧、8帧 8帧、9帧 HS 11.56 11.48 11.51 12.07 11.98 12.05 0.79 0.76 0.80 LK 7.64 7.57 7.60 8.39 8.36 8.38 0.68 0.64 0.67 DC 3.21 3.19 3.34 3.45 3.42 3.47 0.34 0.36 0.32 本文算法 1.95 1.89 1.94 2.26 2.23 2.25 0.18 0.16 0.17 表 3 求解光流所需时间(s)
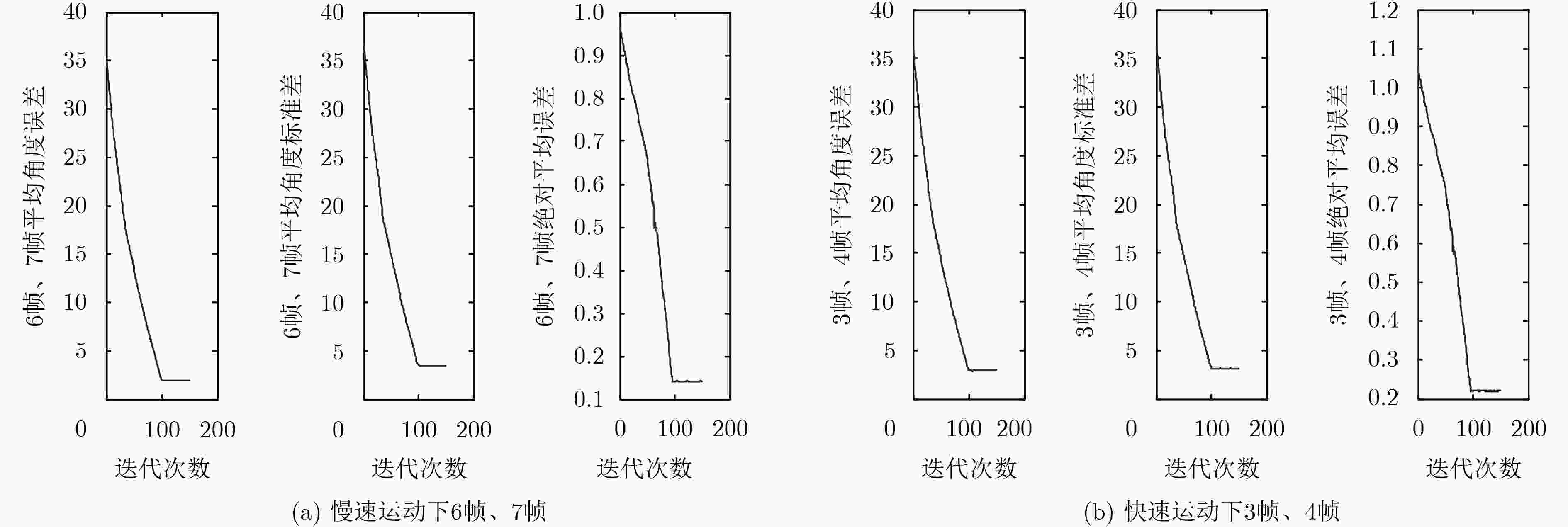
算法类型 慢速运动耗时 快速运动耗时 6帧、7帧 7帧、8帧 8帧、9帧 3帧、4帧 4帧、5帧 5帧、6帧 HS光流法 4.42 4.38 4.45 5.58 5.39 5.45 LK光流法 4.14 4.03 4.18 4.67 4.31 4.46 DC光流法 3.23 3.19 3.42 3.53 3.42 3.47 本文算法 2.26 2.24 2.31 2.50 2.46 2.41 -
BLESER G and HENDEBY G. Using optical flow as lightweight SLAM alternative[C]. International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality, Orlando, USA, 2009, 175–176. doi: 10.1109/ISMAR.2009.5336475. ZHANG Congxuan, Ge Liyue, CHEN Zhen, et al. Guided filtering: Toward edge-preserving for optical flow[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 26958–26970 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2831920 GOPPERT J, YANTEK S, and HWANG I. Invariant Kalman filter application to optical flow based visual odometry for UAVs[C]. IEEE Ninth International Conference on Ubiquitous and Future Networks, Milan, Italy, 2017: 99–104. doi: 10.1109/ICUFN.2017.7993755. PASTOR-MORENO D, SHIN H S, and WALDOCK A. Optical flow localisation and appearance mapping (OFLAAM) for long-term navigation[C]. IEEE International Conference on Unmanned Aircraft Systems, Colorado, USA, 2015: 980–988. doi: 10.1109/ICUAS.2015.7152387. CHAMORRO-MARTINEZ J and FERNANDEZ-VALDIVIA J. A new approach to motion pattern recognition and its application to optical flow estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems Man&Cybernetics Part C, 2006, 37(1): 39–51 doi: 10.1109/TSMCC.2006.876044 HORN B K P and SCHUNCK B G. Determining optical flow[J]. Artificial Intelligence, 1981, 17(1/3): 185–203 doi: 10.1016/0004-3702(81)90024-2 LUCAS B D and KANADE T. An iterative image registration technique with an application to stereo vision[C]. International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vancouver, Canada, 1981: 674–679. DRULEA M and NEDEVSCHI S. Total variation regularization of local-global optical flow[C]. IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems, Washington, DC, USA, 2011: 318–323. doi: 10.1109/ITSC.2011.6082986. NIU Yan, XU Zhiwen, CHE Xiangjiu, et al. Dynamically removing false features in pyramidal lucas-kanade registration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2014, 23(8): 3535–3544 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2014.2331140 田天, 周兵, 李波, 等. 基于解析小波的光流计算方法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2003, 29(6): 548–551 doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2003.06.019TIAN Tian, ZHOU Bing, LI Bo, et al. Optical flow computation based on analytic wavelet[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2003, 29(6): 548–551 doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2003.06.019 MAGAREY J and KINGSBURY N. Motion estimation using a complex-valued wavelet transform[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2002, 46(4): 1069–1084 doi: 10.1109/78.668557 WU Yute, KANADE T, COHN J, et al. Optical flow estimation using wavelet motion model[C]. IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Bombay, India, 1998: 992–998. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.1998.710837. 项学智, 赵春晖. 形态梯度恒常的复值小波光流求解[J]. 哈尔滨工程大学学报, 2008, 29(8): 872–876 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7043.2008.08.020XIANG Xuezhi and ZHAO Chunhui. An estimation of complex wavelet optical flow with invariant morphological gradient[J]. Journal of Harbin Engineering University, 2008, 29(8): 872–876 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7043.2008.08.020 DEMONCEAUX C and KACHI-AKKOUCHE D. Optical flow estimation in omnidirectional images using wavelet approach[C]. IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Madison, USA, 2003: 71–76. doi: 10.1109/CVPRW.2003.10080. SCHAFFRIN B and FELUS Y A. On the multivariate total least-squares approach to empirical coordinate transformations. Three algorithms[J]. Journal of Geodesy, 2008, 82(6): 373–383 doi: 10.1007/s00190-007-0186-5 NIAZ M T, IMDAD F, KIM S, et al. Total least-square-based receiver for asymmetrically clipped optical-orthogonal frequency divisional multiplexing visible light communication system[J]. IET Optoelectronics, 2017, 11(4): 129–133 doi: 10.1049/iet-opt.2015.0133 ARTYUSHENKO V M and VOLOVACH V I. The effect of multiplicative noise on probability density function of signal and additive noise[C]. IEEE Workshop on Electronic and Networking Technologies, Moscow, Russia, 2018: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/MWENT.2018.8337270. DATESMAN A. Shot noise in radiobiological systems[J]. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 2016, 164: 365–368 doi: 10.1016/j.jenvrad.2016.06.017 CELLA G. Thermal noise correlations and subtraction[J]. Physics Letters A, 2017, 382: 2269–2274 doi: 10.1016/j.physleta.2017.06.026 SHOU Guofa, XIA Ling, JIANG Mingfeng, et al. Truncated total least squares: A new regularization method for the solution of ECG inverse problems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Bio-medical Engineering, 2008, 55(4): 1327–1335 doi: 10.1109/TBME.2007.912404 曲付勇, 孟祥伟. 基于约束总体最小二乘方法的到达时差到达频差无源定位算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2014, 36(5): 1075–1081 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.01019QU Fuyong and MENG Xiangwei. Source localization using TDOA and FDOA measurements based on constrained total least squares algorithm[J]. Journal of Electronics&Information Technology, 2014, 36(5): 1075–1081 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.01019 BARRON J L, FLEET D J, and CHEMIN S. Performance of optical flow techniques[C]. IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Champaign, USA, 2002: 236–242. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.1992.223269. -





 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:
