Matrix Pencil Method Based Processing Approach for Spaceborne MEB SAR with Digital Beamforming in Elevation
-
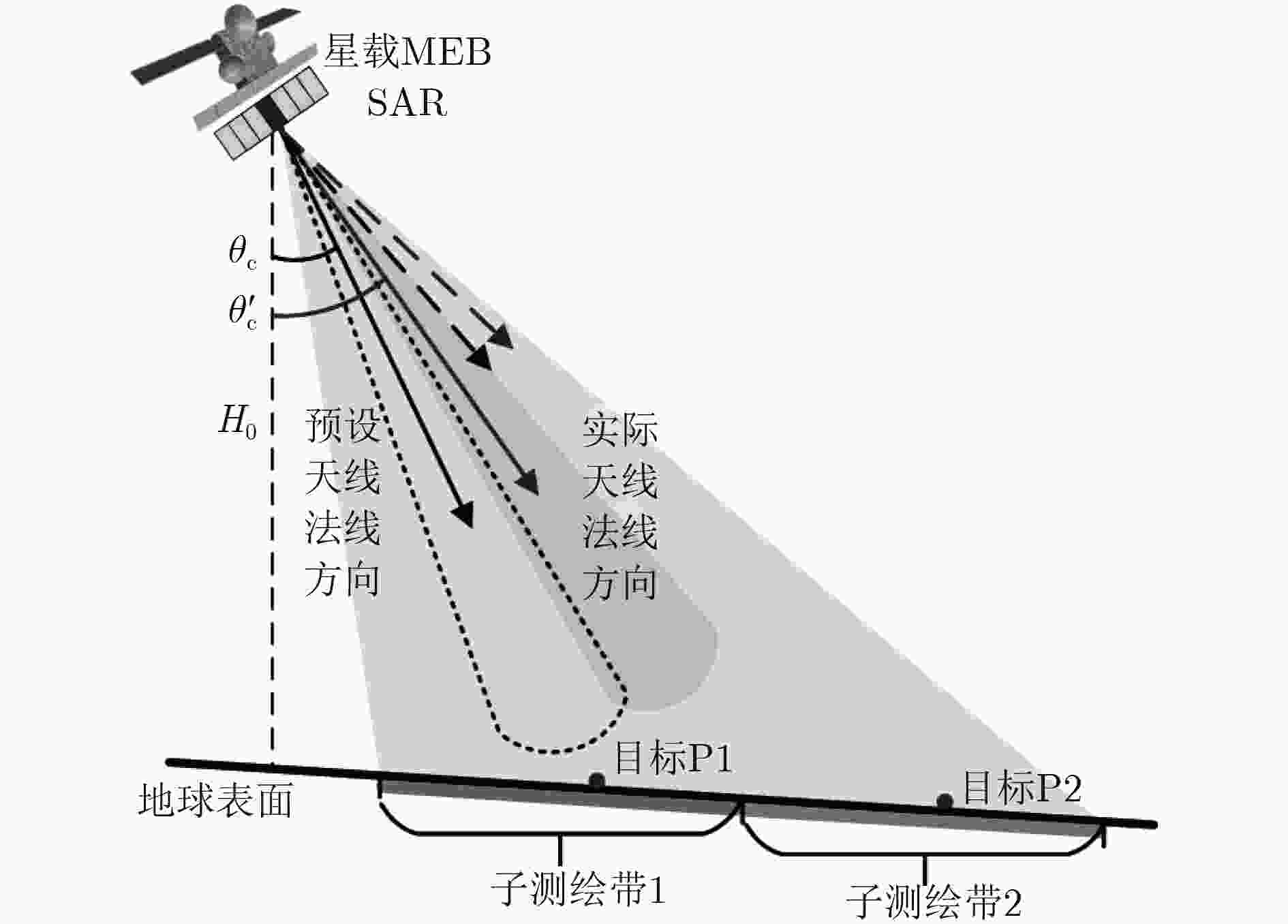
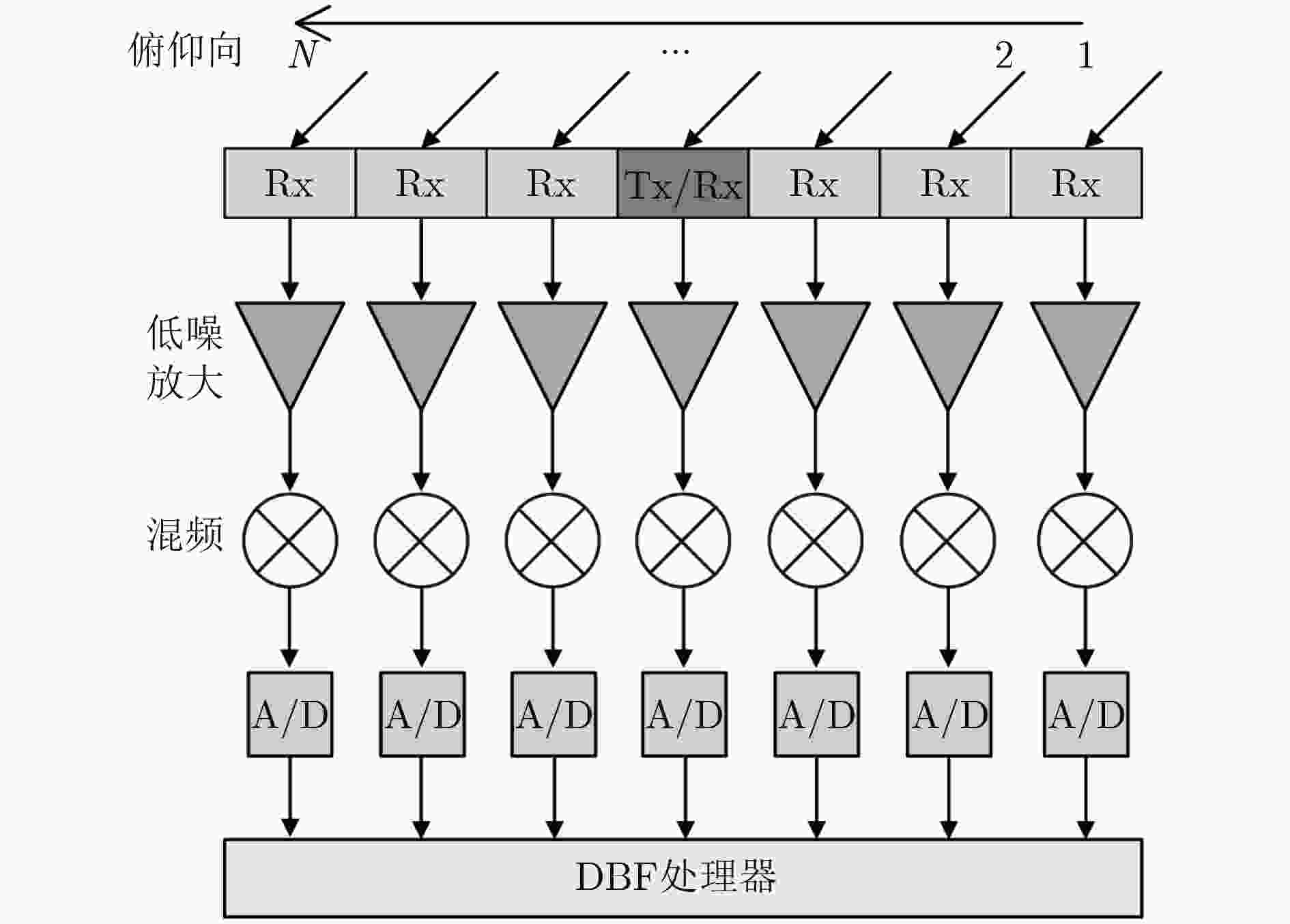
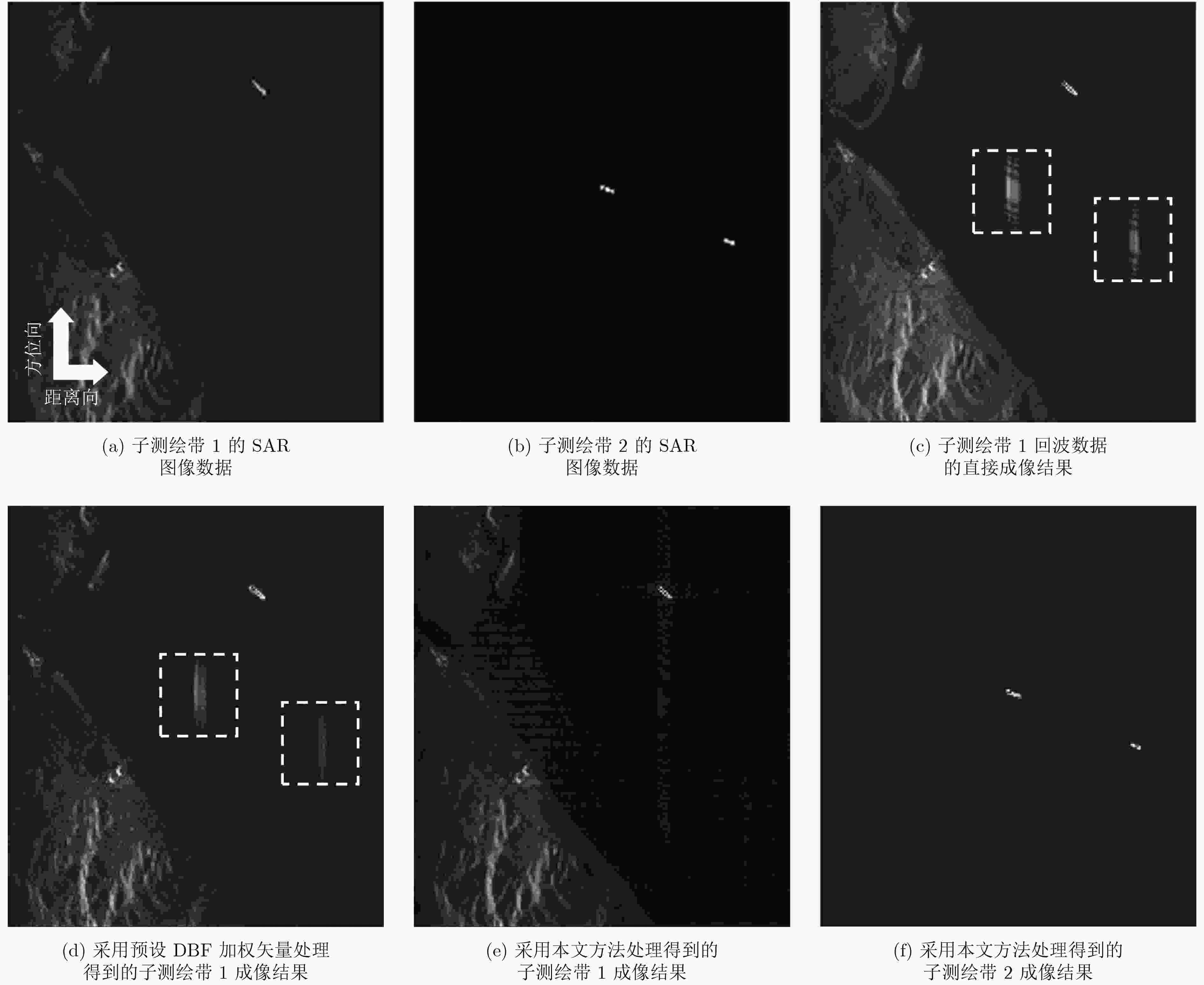
摘要: 俯仰向数字波束形成(DBF)处理是距离向多波束体制(MEB)星载合成孔径雷达(SAR)系统实现较高分辨率、超宽幅成像的关键。但是,由于存在卫星姿态误差等因素的影响,星载MEB SAR系统的DBF接收波束指向会出现偏差,这将导致在对具有强散射体的区域(如存在船舶的海面、港口等区域)进行成像时会出现鬼影目标。针对这一问题,该文提出一种基于矩阵束方法的俯仰向DBF处理方法。首先对俯仰向通道回波数据进行匹配滤波处理,并根据预设阈值寻找强散射体的峰值位置;然后利用矩阵束方法准确估计强散射体的波达角;最后利用这些信息调整俯仰向DBF加权矢量,确保DBF接收波束指向正确,从而消除鬼影目标的干扰。仿真实验验证了该方法的有效性。Abstract: Digital BeamForming (DBF) in elevation plays a crucial role for spaceborne Multiple Elevation Beam (MEB) SAR realizing the High-Resolution Wide-Swath (HRWS) imaging mode. However, due to the influence of satellite attitude error, the deviation of the DBF receiving beam direction always arises in such system. This leads to ghost targets appearing in the SAR image, when mapping the scenes (such as the seaport areas) with strong scatterers. To address the problem, a matrix pencil method based DBF processing approach in elevation is presented. Firstly, according to the given threshold, the peak position of the strong scatterer is found from the range-compressed signals. Then, the direction of arrival angle of the strong scatterer is estimated using the matrix pencil method. Finally, based on the imaging geometry model, the DBF weighting vector is adjusted to ensure the receiving beam to precisely point to the signal sources. Thereby, the interferences of ghost targets in SAR image can be eliminated effectively. The theoretical analysis is derived in detail, then it is validated by simulation experiments.
-
Key words:
- SAR /
- Multiple Elevation Beam (MEB) /
- Digital BeamForming (DBF) /
- Matrix pencil method
-
表 1 系统仿真参数
轨道高度 700 km 卫星速度 7504 m/s 载频 5.4 GHz 信号带宽 60 MHz 脉冲宽度 22 μs 天线高度 1.5 m 俯仰向子孔径数目 23 天线长度 10 m 脉冲重复频率 1800 Hz -
FREEMAN A, JOHNSON W, HUNEYCUTT B, et al. The " myth” of the minimum SAR antenna area constraint[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2000, 38(1): 320–324 doi: 10.1109/36.823926 SUESS M, GRAFMUELLER B, ZAHN R, et al. A novel high resolution, wide swath SAR system[C]. Proceedings of the International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Sydney, 2001: 1013–1015. YOUNIS M, ALMEIDA F, LOPEZ-DEKKER P, et al. Techniques and modes for multi-channel SAR instruments[C]. Preceedings of European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Hamburg, Germany, 2016: 812–817. KRIEGER G, HUBER S, VILLANO M, et al. SIMO and MIMO system architectures and modes for high-resolution ultra-wide-swath SAR imaging[C]. Preceedings of European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Hamburg, Germany, 2016: 187–192. YOUNIS M, HUBER S, PATYUCHENKO A, et al. Performance comparison of reflector- and planar- antenna based digital beam-forming SAR[J]. International Journal of Antenna and Propagation, 2009, 2009(6): 1–13 doi: 10.1155/2009/614931 RINCON R, FATOYINBO T, OSMANOGLU B, et al. Development of NASA’s next generation L-band digital beamforming synthetic aperture radar (DBSAR-2)[C]. Proceedings of European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Hamburg, Germany, 2016: 1251–1254. VILLANO M, KRIEGER G , and MOREIRA A. Advanced spaceborne SAR systems with planar antenna[C]. Radar Conference, Seattle, USA, 2017: 152–156. YAN Wei, YANG Xu, SUN Jia, et al. An airborne demonstration for high-resolution wide-swath spaceborne reflector SAR systems[C]. International Conference on Frontiers of Sensors Technologies, Shenzhen, China, 2017: 350–353. HUBER S, VILLANO M, YOUNIS M, et al. Tandem-L: design concepts for a next-generation Spaceborne SAR system[C]. Proceedings of European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Hamburg, Germany, 2016: 1237–1241. TRIDON D, BACHMANN M, ZAN F, et al. Tandem-L observation concept-contributions and challenges of systematic monitoring of earth system dynamics[C]. The 18th International Radar Symposium, Prague, Czech Republic, 2017: 1–9. MOREIRA A, KRIEGER G, HAJNSEK I, et al. Tandem-L: A highly innovative bistatic SAR mission for global observation of dynamic processes on the Earth’s surface[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine, 2015, 3(2): 8–23 doi: 10.1109/MGRS.2015.2437353 NANNINI M, MARTONE M, RIZZOLI P, et al. Spaceborne demonstration of coherent SAR tomography for future companion satellite SAR missions[C]. IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Fort Worth, USA, 2017: 129–132. VILLANO M, KRIEGER G, and MOREIRA A. Staggered SAR: High-resolution wide-swath imaging by continuous PRI variation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(7): 4462–4479 doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2282192 VILLANO M, KRIEGER G, JAGER M, et al. Staggered SAR: Performance analysis and experiments with real data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(11): 6617–6638 doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2731047 KRIEGER G, GEBERT N, and MOREIRA A. Multidimensional waveform encoding: A new digital beamforming technique for synthetic aperture radar remote sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2008, 46(1): 31–46 doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2007.905974 KRIEGER G. MIMO-SAR: Opportunities and pitfalls[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(5): 2628–2645 doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2263934 叶恺, 禹卫东, 王伟. 一种基于短偏移正交波形的MIMO SAR处理方案研究[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(4): 376–387 doi: 10.12000/JR17048YE Kai, YU Weidong, and WANG Wei. Investigation on processing scheme for MIMO SAR with STSO chirp waveforms[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(4): 376–387 doi: 10.12000/JR17048 林玉川, 张剑云, 武拥军, 等. 双基星载HRWS-SAR系统方位向信号重构的矩阵求逆算法[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(4): 388–396 doi: 10.12000/JR17060LIN Yuchuan, ZHANG Jianyun, WU Yongjun, et al. Matrix inversion method for azimuth reconstruction in bistatic spaceborne high-resolution wide-swath SAR system[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(4): 388–396 doi: 10.12000/JR17060 赵庆超, 张毅, 王宇, 等. 基于多帧超分辨率的方位向多通道星载SAR非均匀采样信号重建方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(4): 408–419ZHAO Qingchao, ZHANG Yi, WANG Yu, et al. Signal reconstruction approach for multichannel SAR in azimuth based on multiframe super resolution[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(4): 408–419 VAN T H L. Optimum Array Processing Part IV of Detection, Estimation, and Modulation Theory[M]. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 2002: 428–669. MAKHOUL V. Adaptive digital beam-forming for high-resolution wide-swath synthetic aperture radar[D]. [Master dissertation], Polytechnic University of Catalonia, 2009: 23–91. BORDONI F, YOUNIS M, MAKHOUL V, et al. Adaptive digital beamforming algorithm for high-resolution, wide-swath synthetic aperture radar[C]. International Radar Symposium, Hamburg, Germany, 2009: 1–5. KHAN M and TUFAIL M. Comparative analysis of various matrix pencil methods for direction of arrival estimation[C]. International Conference on Image Analysis and Signal Processing, Zhejiang, China, 2010: 1–6. SARKAR T and PEREIRA O. Using the matrix pencil method to estimate the parameters of a sum of complex exponentials[J]. IEEE Antennas an Propagation Magazine, 1995, 37(1): 48–55 doi: 10.1109/74.370583 HUA Y and SARKAR T. On SVD for estimating generalized eigenvalues of singular matrix pencil in noise[J]. IEEE Transaction on Signal Processing, 1991, 39(4): 892–900 doi: 10.1109/78.80911 -





 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:
