Researches on Pseudo-range Biases of BeiDou Navigation Satellite System B1 Signals
-
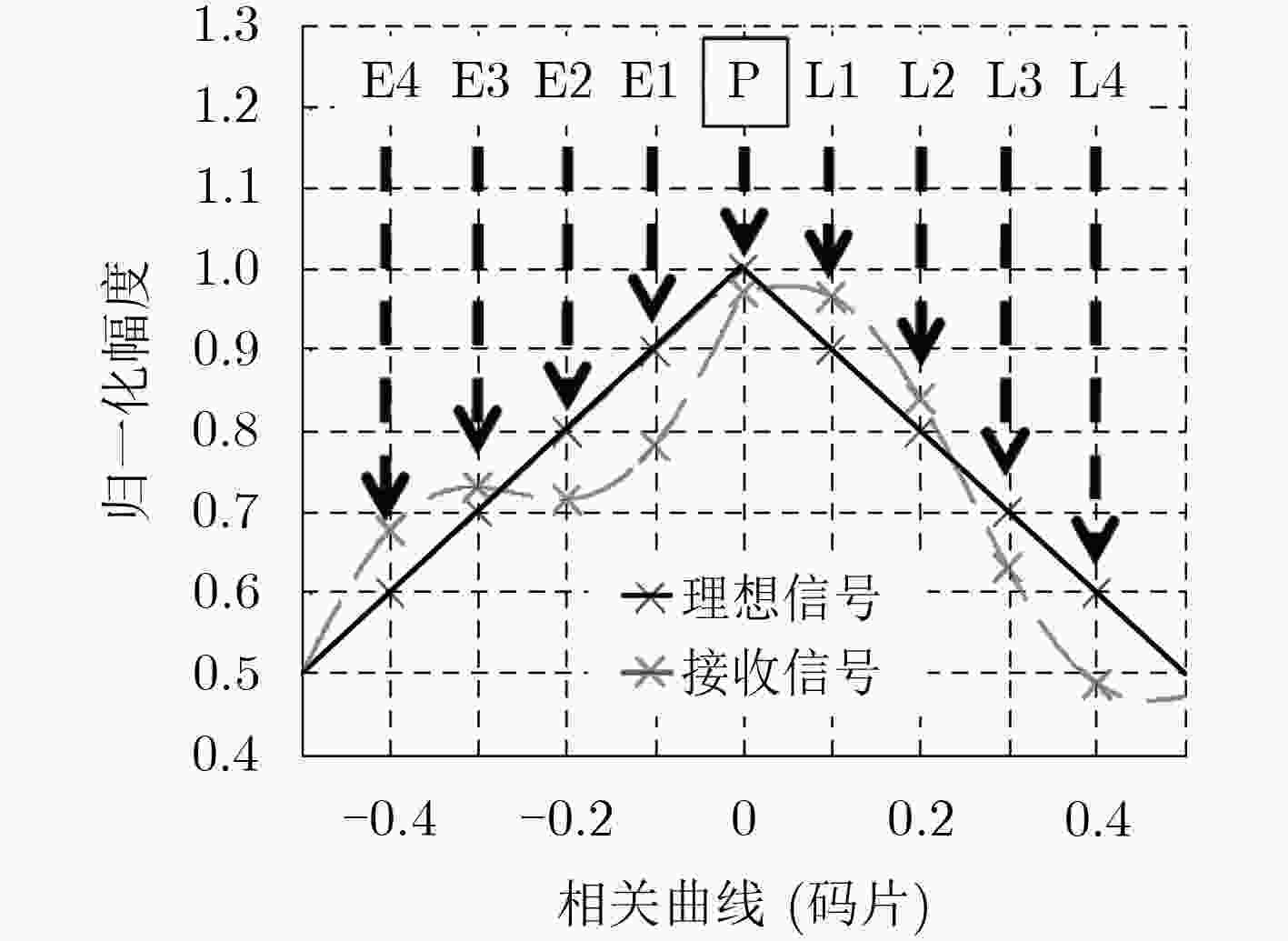
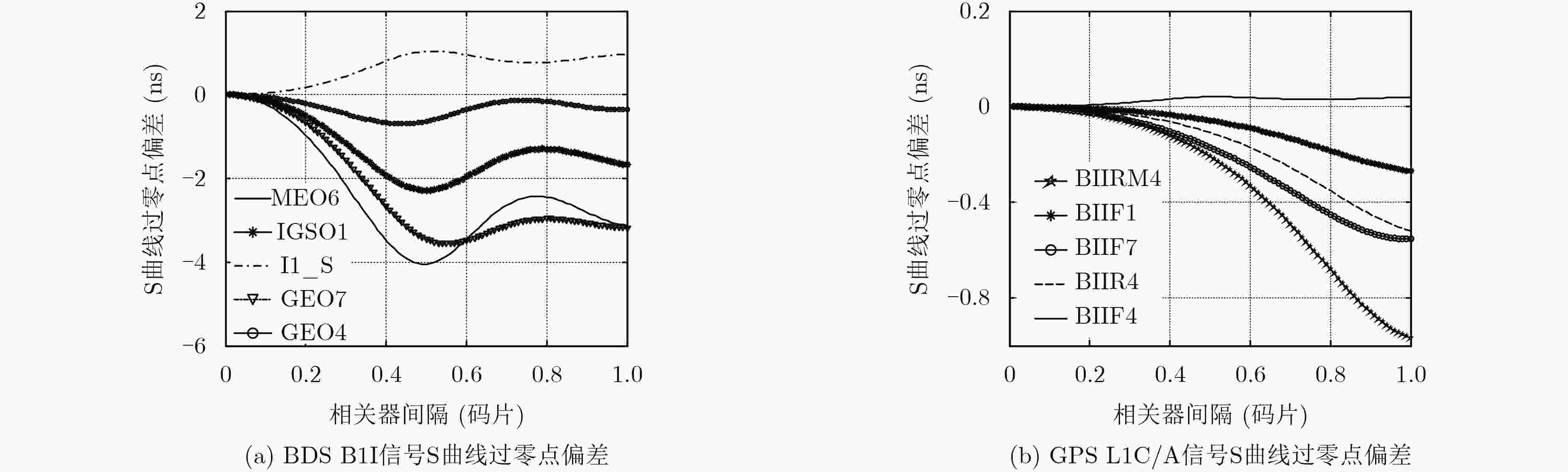
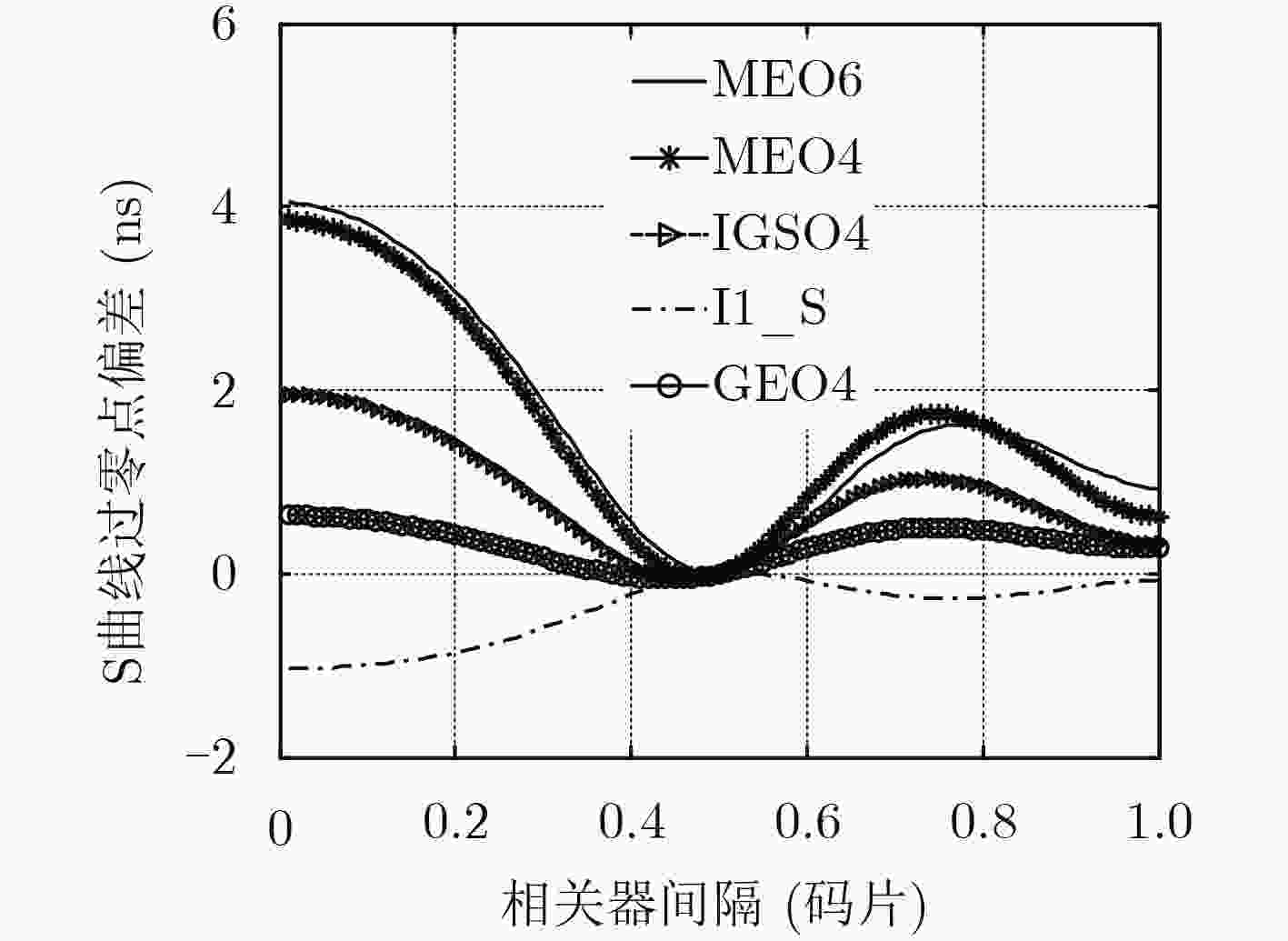
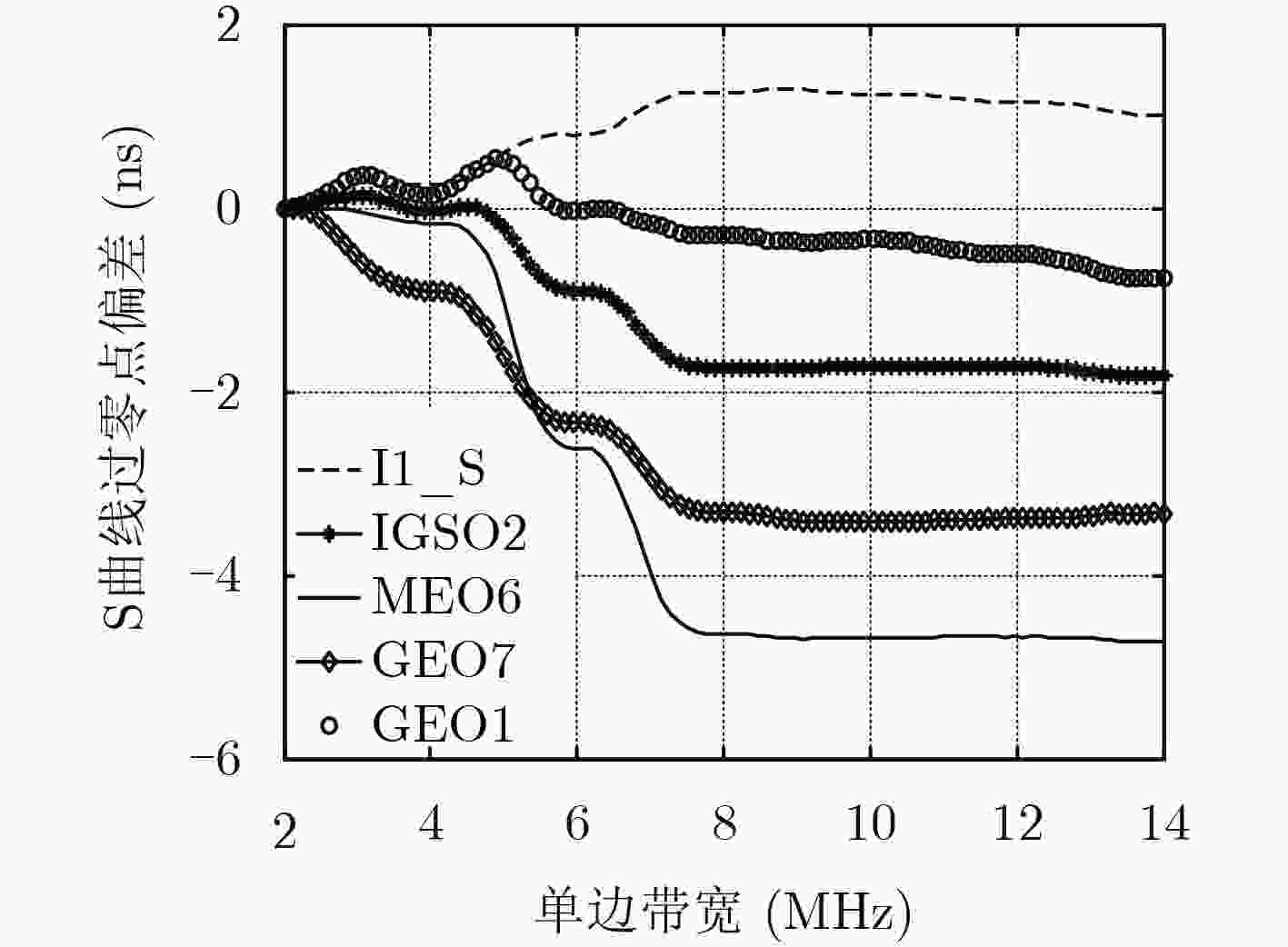
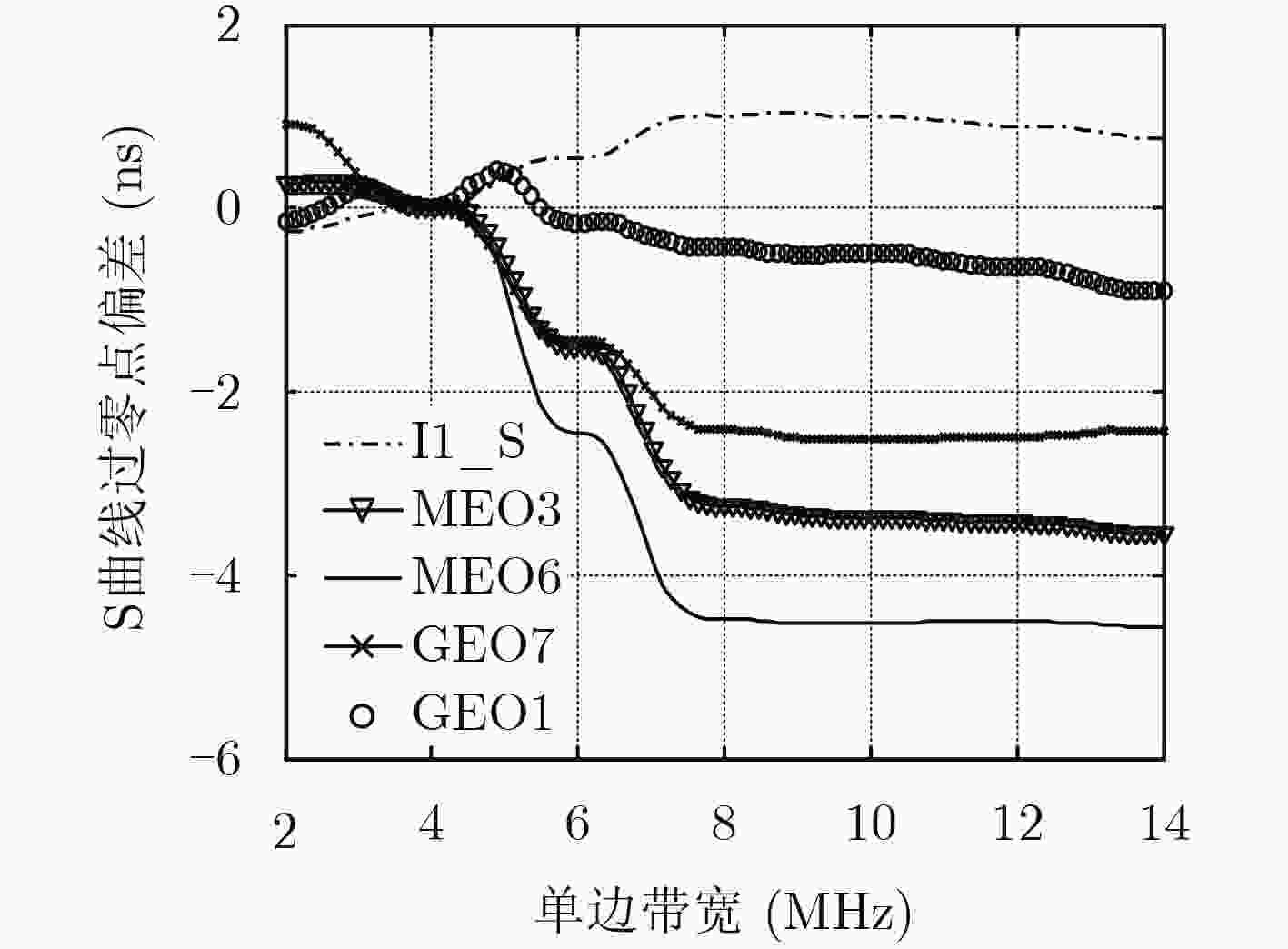
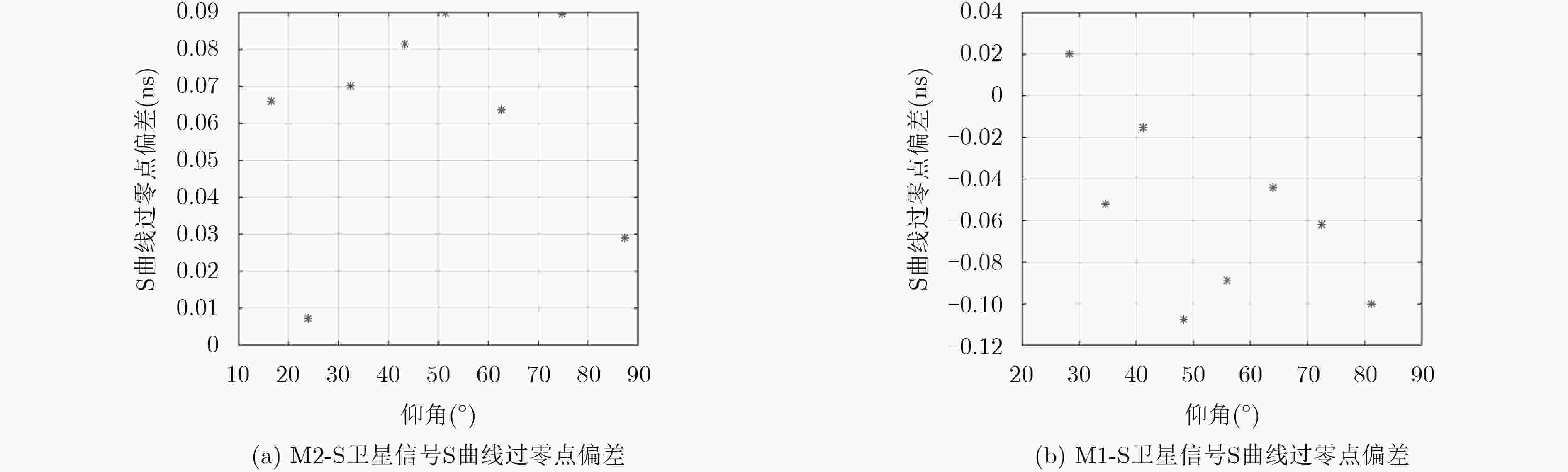
摘要: 目前各大卫星导航系统均存在伪距偏差问题,该现象不但不能通过差分的方式进行抵消,在进行双频电离层误差修正时还会被进一步放大,对卫星导航系统服务精度的提高已构成严重危害。然而目前国内对北斗系统伪距偏差产生机理研究甚少,为了最大程度降低伪距偏差对我国北斗卫星导航系统影响,该文首先深入并详细研究了伪距偏差产生机理及特点,在此基础上设计了试验验证方案,利用国内昊平观测站40 m大口径天线,准确测试并评估了所有北斗卫星导航系统(BDS)在轨可视卫星伪距偏差结果。最后根据试验测试结果,提出针对北斗卫星导航系统的接收机主要参数设置建议,从而能够最大程度上减小伪距偏差问题带来的测距误差和定位误差。该文的研究成果可为GNSS信号设计及实现、GNSS监测评估及用户终端参数设置提供有价值的参考依据。Abstract: Due to the distortions of the broadcasted satellite signals and the inconsistencies of parameter settings for different receivers, the single difference or double difference of pseudo-ranges between two receivers are different for two pair of different receivers. Bias inconsistencies will lead to adverse effects for pseudo-range-based positioning applications. Pseudo-range biases can also hinder carrier-phase ambiguity resolution. However, fewer articles deal with pseudo-range biases for BeiDou navigation satellite System (BDS). In order to mitigate the impact of biases on BDS to the greatest extent, the generation mechanisms and characteristics of pseudo-range biases are studied in detail firstly. Then based on this, experimental verification methods are designed using Haoping Radio Observatory (HRO) of Chinese Academy of Sciences to observe BDS signals. Pseudo-range biases of all visible BDS satellites are measured and evaluated with high accuracy, using the 40 meters dish antenna and modern equipment of HRO. Finally, some important parameters of BDS receivers, such as the correlator spacing and front-end bandwidth, are suggested to mitigate the ranging errors and positioning errors result from pseudo-range biases. The achievements of this paper can provide a worthy reference for GNSS signal designers, GNSS monitoring and assessment and GNSS receiver designers.
-
表 1 北斗二号卫星B1I信号伪距偏差(m)
接收机 卫星 C02 C03 C04 C05 C06 C07 C08 C09 C10 C11 C12 C14 1号–4号 0.10 0.40 0.02 – 0.23 –0.01 0.31 0.24 0.65 0.37 – 0.49 2号–4号 –0.05 0.27 0.10 0.34 0.16 –0.10 0.14 0.17 0.40 0.18 0.57 0.22 3号–4号 0.00 0.42 0.22 0.53 0.08 0.08 0.18 0.20 0.77 0.67 0.72 0.48 -
陈西宏, 刘赞, 刘继业, 等. 低仰角下对流层散射斜延迟估计方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(2): 408–412 doi: 10.11999/JEIT160776CHEN Xihong, LIU Zan, LIU Jiye, et al. Estimating tropospheric slant scatter delay at low elevation[J]. Journal of Electronics&Information Technology, 2016, 38(2): 408–412 doi: 10.11999/JEIT160776 WONG G, PHELTS R E, WALTER T, et al. Bounding errors caused by nominal GNSS signal deformations[C]. Proceedings of the 24th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation, Portland, USA, 2011: 1–9. COCO D S, COKER C, DAHLKE S R, et al. Variability of GPS satellite differential group delay biases[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1991, 27(6): 931–938. SARDON E and ZARRAOA N. Estimation of total electron content using GPS data: How stable are the differential satellite and receiver instrumental biases?[J]. Radio Science, 1997, 32(5): 1899–1910. HAUSCHILD A and MONTENBRUCK O. A study on the dependency of GNSS pseudorange biases on correlator spacing[J]. GPS Solutions, 2016, 20(2): 159–171 doi: 10.1007/s10291-014-0426-0 HAUSCHILD A and MONTENBRUCK O. The effect of correlator and front‐end design on GNSS pseudorange biases for geodetic receivers[J]. Navigation, 2016, 63(4): 443–453 doi: 10.1002/navi.165 JEFFERSON D C, HEFLIN M B, and MUELLERSCHOEN R J. Examining the C1-P1 pseudorange bias[J]. GPS Solutions, 2001, 4(4): 25–30. WONG G, CHEN Yuhsuan, PHELTS R E, et al. Measuring code-phase differences due to inter-satellite hardware differences[C]. Proceedings of the 25th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation, Nashville, USA, 2012: 1–12. 贺成艳, GNSS空间信号质量评估方法研究及测距性能影响分析[D]. [博士论文], 中国科学院大学(国家授时中心), 2013.HE Chengyan, Research on evaluation methods of GNSS signal quality and the influence of GNSS signal on ranging performance[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2013. HE Chengyan, GUO Ji, LU Xiaochun, et al. A new evil waveforms evaluating method for new BDS navigation signals[J]. GPS Solutions, 2018, 22(2): 37–49 doi: 10.1007/s10291-018-0698-x 廉昕, 王元钦, 侯孝民, 等. 一种脉冲超宽带测控信号捕获方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(8): 2000–2006 doi: 10.11999/JEIT161213LIAN Xin, WANG Yuanqin, HOU Xiaomin, et al. Acquisition scheme for impulse radio UWB TT&C signal[J].Journal of Electronics&Information Technology, 2017, 39(8): 2000–2006 doi: 10.11999/JEIT161213 刘晓明, 张鹤, 吴皓威, 等. 高动态环境下长码扩频信号快捕算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(6): 1398–1405 doi: 10.11999/JEIT150860LIU Xiaoming, ZHANG He, WU Haowei, et al. Rapid DSSS signal acquisition algorithm under high dynamic environment[J]. Journal of Electronics&Information Technology, 2016, 38(6): 1398–1405 doi: 10.11999/JEIT150860 WONG G, PHELTS R E,WALTER T, et al. Alternative characterization of analog signal deformation for GNSS-GPS satellites[C]. Proceedings of the 2011 International Technical Meeting of the Institute of Navigation, San Diego, CA, USA, 2011: 497–507. 高洪兴, 杨东凯, 张波, 等. 基于GNSS卫星反射信号的海冰厚度探测[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(5): 1096–1100 doi: 10.11999/JEIT160765GAO Hongxing, YANG Dongkai, ZHANG Bo, et al. Remote sensing of sea ice thickness with GNSS reflected signal[J]. Journal of Electronics&Information Technology, 2017, 39(5): 1096–1100 doi: 10.11999/JEIT160765 王燕, 李晴, 付进, 等. 超短基线定位系统融合分类解模糊技术研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(6): 1348–1354 doi: 10.11999/JEIT160825WANG Yan, LI Qing, FU Jin, et al. Resolving ambiguity using fusion classification for ultra-short baseline positioning systems[J]. Journal of Electronics&Information Technology, 2017, 39(6): 1348–1354 doi: 10.11999/JEIT160825 陈昌川, 周杨, 张天骐. TDDM-BOC信号组合码序列及信息序列盲估计[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(11): 2760–2766 doi: 10.11999/JEIT160042CHEN Changchuan, ZHOU Yang, and ZHANG Tianqi. Blind estimation of the combination code Sequence and information sequence for TDDM-BOC signal[J]. Journal of Electronics&Information Technology, 2016, 38(11): 2760–2766 doi: 10.11999/JEIT160042 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
