Ship Detection in SAR images Based on Generative Adversarial Network and Online Hard Examples Mining
-
摘要:
基于深度学习的SAR图像舰船目标检测算法对图像的数量和质量有很高的要求,而收集大体量的舰船SAR图像并制作相应的标签需要消耗大量的人力物力和财力。该文在现有SAR图像舰船目标检测数据集(SSDD)的基础上,针对目前检测算法对数据集利用不充分的问题,提出基于生成对抗网络(GAN)和线上难例挖掘(OHEM)的SAR图像舰船目标检测方法。利用空间变换网络在特征图上进行变换,生成不同尺寸和旋转角度的舰船样本的特征图,从而提高检测器对不同尺寸、旋转角度的舰船目标的适应性。利用OHEM在后向传播过程中发掘并充分利用难例样本,去掉检测算法中对样本正负比例的限制,提高对样本的利用率。通过在SSDD数据集上的实验证明以上两点改进对检测算法性能分别提升了1.3%和1.0%,二者结合提高了2.1%。以上两种方法不依赖于具体的检测算法,且只在训练时增加步骤,在测试时候不增加计算量,具有很强的通用性和实用性。
Abstract:Deep learning based ship detection method has a strict demand for the quantity and quality of the SAR image. It takes a lot of manpower and financial resources to collect the large volume of the image and make the corresponding label. In this paper, based on the existing SAR Ship Detection Dataset (SSDD), the problem of insufficient utilization of the dataset is solved. The algorithm is based on Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) and Online Hard Examples Mining (OHEM). The spatial transformation network is used to transform the feature map to generate the feature map of the ship samples with different sizes and rotation angles. This can improve the adaptability of the detector. OHEM is used to discover and make full use of the difficult sample in the process of backward propagation. The limit of positive and negative proportion of sample in the detection algorithm is removed, and the utilization ratio of the sample is improved. Experiments on the SSDD dataset prove that the above two improvements improve the performance of the detection algorithm by 1.3% and 1.0% respectively, and the combination of the two increases by 2.1%. The above two methods do not rely on the specific detection algorithm, only increase the time in training, and do not increase the amount of calculation in the test. It has very strong generality and practicability.
-
表 1 4种方法检测性能
方法 mAP
(%)训练时间
(s)测试时间
(s)标准的 Fast R-CNN 68.0 0.610 0.328 标准的 Fast R-CNN+ GAN 69.4 0.823 0.326 标准的 Fast R-CNN+OHEM 69.1 1.152 0.321 标准的 Fast R-CNN+GAN
+OHEM70.2 2.109 0.330 -
KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I and HINTON G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[C]. International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Nevada, USA, 2012: 1097–1105. GIRSHICK, DONAHUE J, DARRELL T, et al. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation[C]. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, USA, 2014: 580–587. REN Shaoqing, HE Kaiming, GIRSHICK R, et al. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis & Machine Intelligence, 2015, 39(6): 1137–1149. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2577031 REDMON J, DIVVALA S, GIRSHICK R, et al. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection[C]. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 779–788. LIU Wei, ANGUELOV D, ERHAN D, et al. SSD: Single shot multiBox detector[C]. IEEE European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2016: 21–37. 王思雨, 高鑫, 孙皓, 等. 基于卷积神经网络的高分辨率SAR图像飞机目标检测方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(2): 195–203. doi: 10.12000/JR17009Wang Siyu, Gao Xin, Sun Hao, et al. An aircraft detection method based on convolutional neural networks in high-resolution SAR images[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(2): 195–203. doi: 10.12000/JR17009 徐丰, 王海鹏, 金亚秋. 深度学习在SAR目标识别与地物分类中的应用[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(2): 136–148. doi: 10.12000/JR16130Xu Feng, Wang Haipeng, and Jin Yaqiu. Deep learning as applied in SAR target recognition and terrain classification[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(2): 136–148. doi: 10.12000/JR16130 刘泽宇, 柳彬, 郭炜炜, 等. 高分三号NSC模式SAR图像舰船目标检测初探[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(5): 473–482. doi: 10.12000/JR17059Liu Zeyu, Liu Bin, Guo Weiwei et al. Ship detection in GF-3 NSC mode SAR images[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(5): 473–482. doi: 10.12000/JR17059 HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770–778. HUANG Gao, LIU Zhuang, WEINBERGER K Q, et al. Densely connected convolutional networks[C]. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Hawaii, USA, 2017: 4700–4708. SUNG K K and POGGIO T. Example-based learning for view-based human face detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis & Machine Intelligence, 2002, 20(1): 39–51. doi: 10.1109/34.655648 SHRIVASTAVA A, GUPTA A, and GIRSHICK R. Training region-based object detectors with online hard example mining[C]. IEEE Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 761–769. UIJLINGS J R R, SANDE K, GEVES T, et al. Selective search for object recognition[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2013, 104(2): 154–171. doi: 10.1007/s11263-013-0620-5 WANG Xiaolong, SHRIVASTAVA A, and GUPTA A. A-Fast-RCNN: Hard positive generation via adversary for object detection[C]. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Hawaii, USA, 2017. JADERBERG M, KAREN S, and ANDREW Z. Spatial transformer networks[C]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, Canada, 2015: 2017–2025. GOODFELLOW I J, POUGET-ABADIE J, MIRZA M, et al. Generative adversarial nets[C]. International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, Canada, 2014: 2672–2680. -





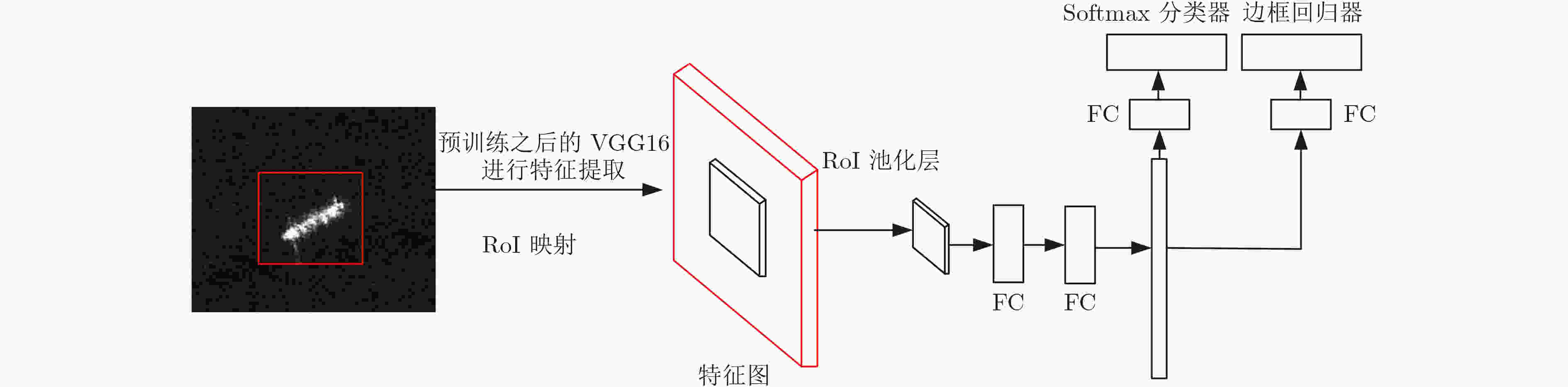
 下载:
下载:
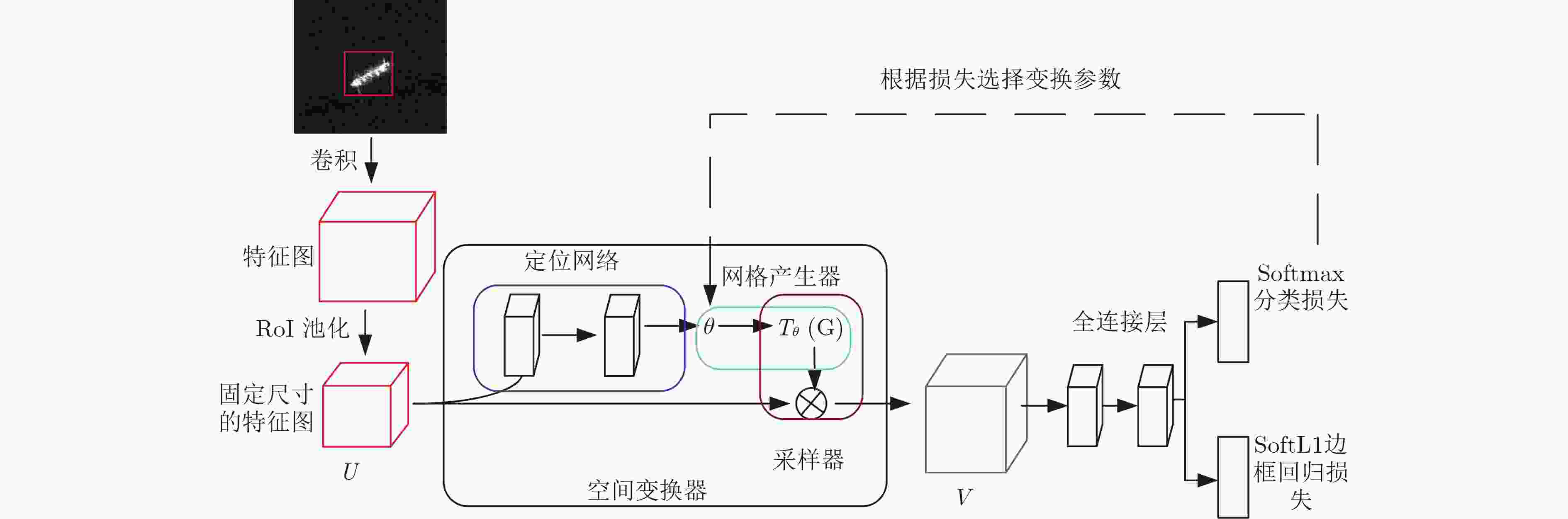
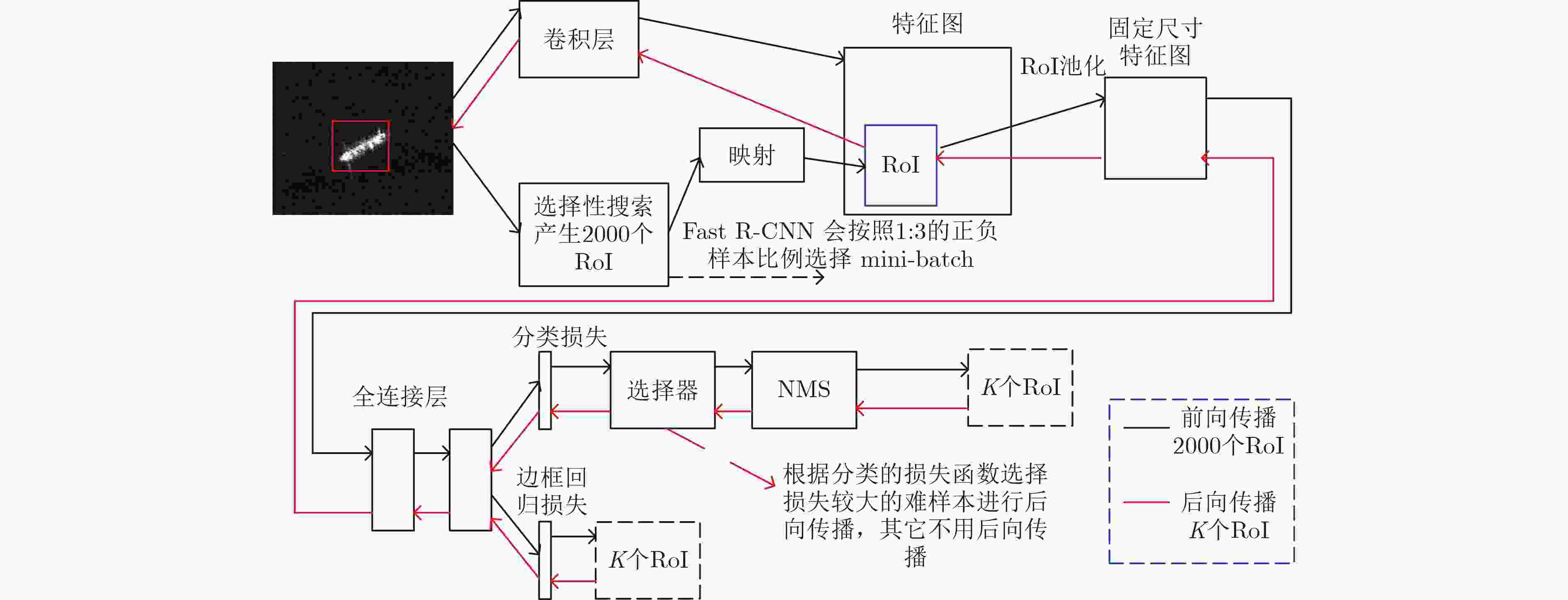
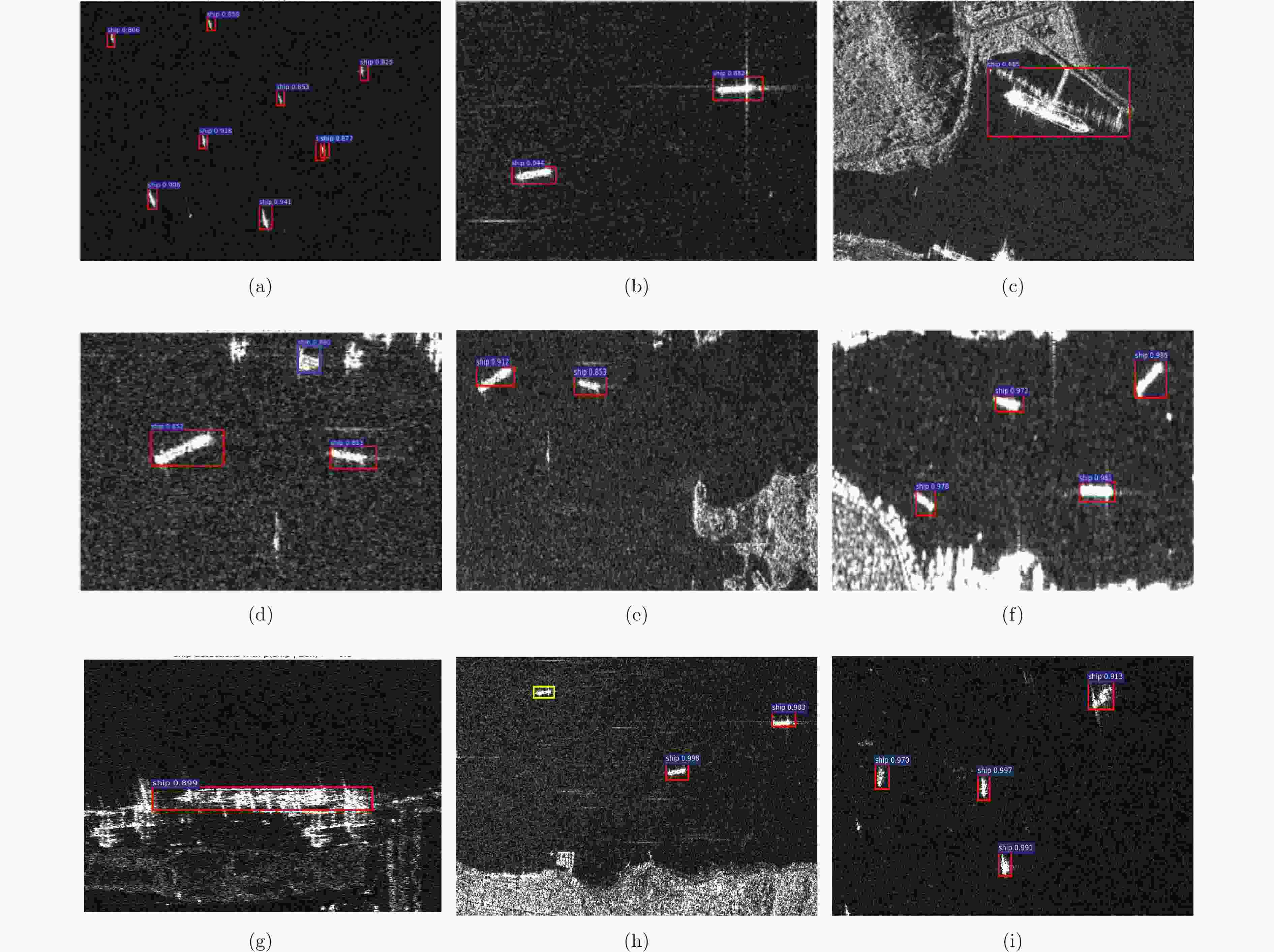


 下载:
下载:
