Investigation on PRI Variation for High Squint Spaceborn Spotlight SAR
-
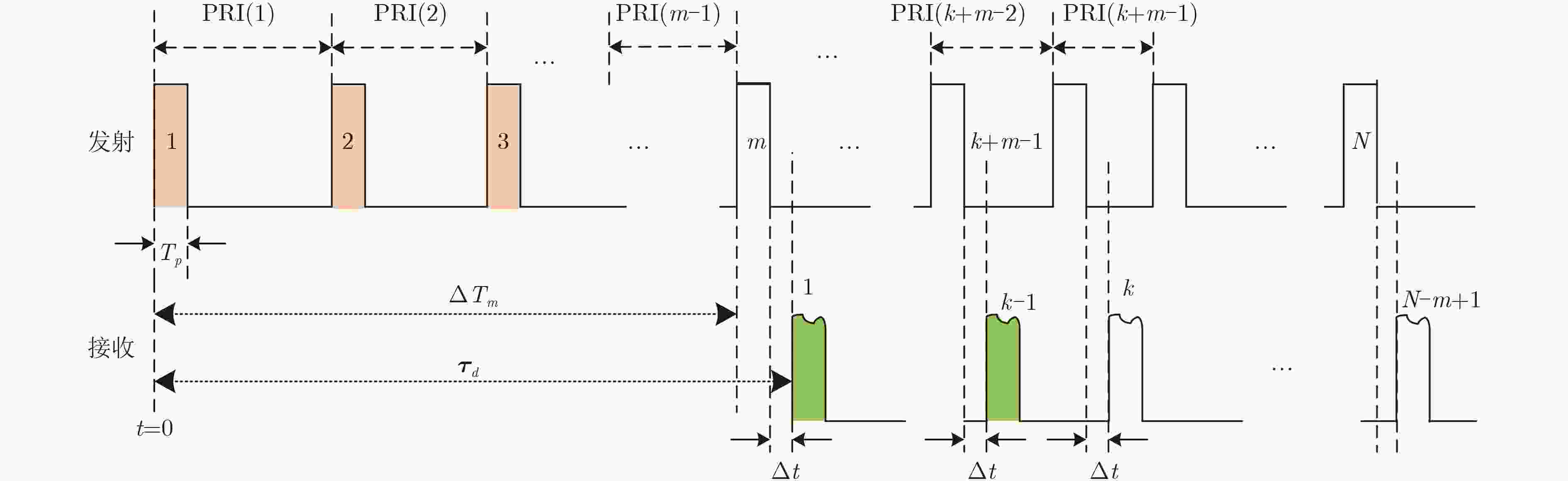
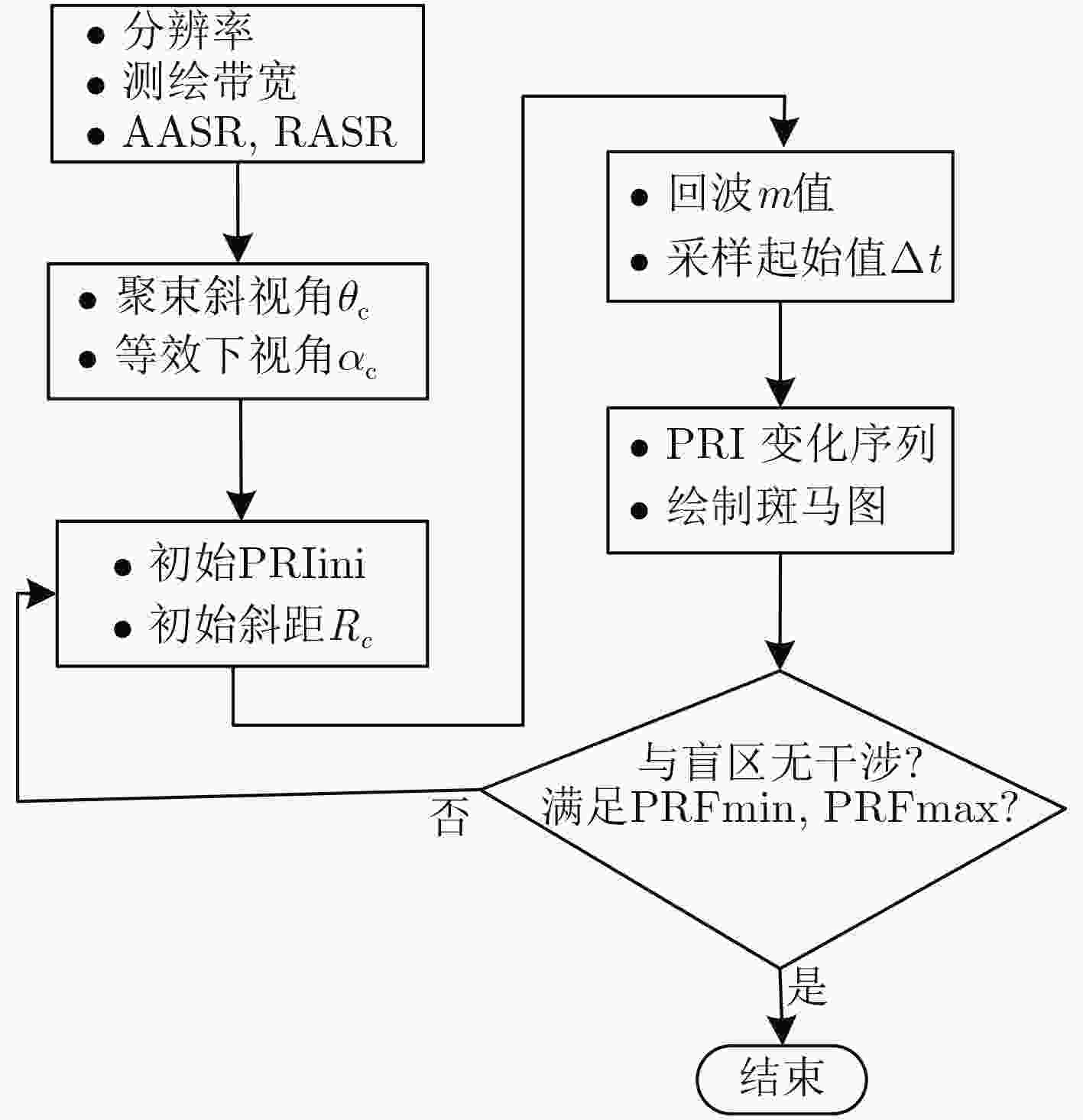
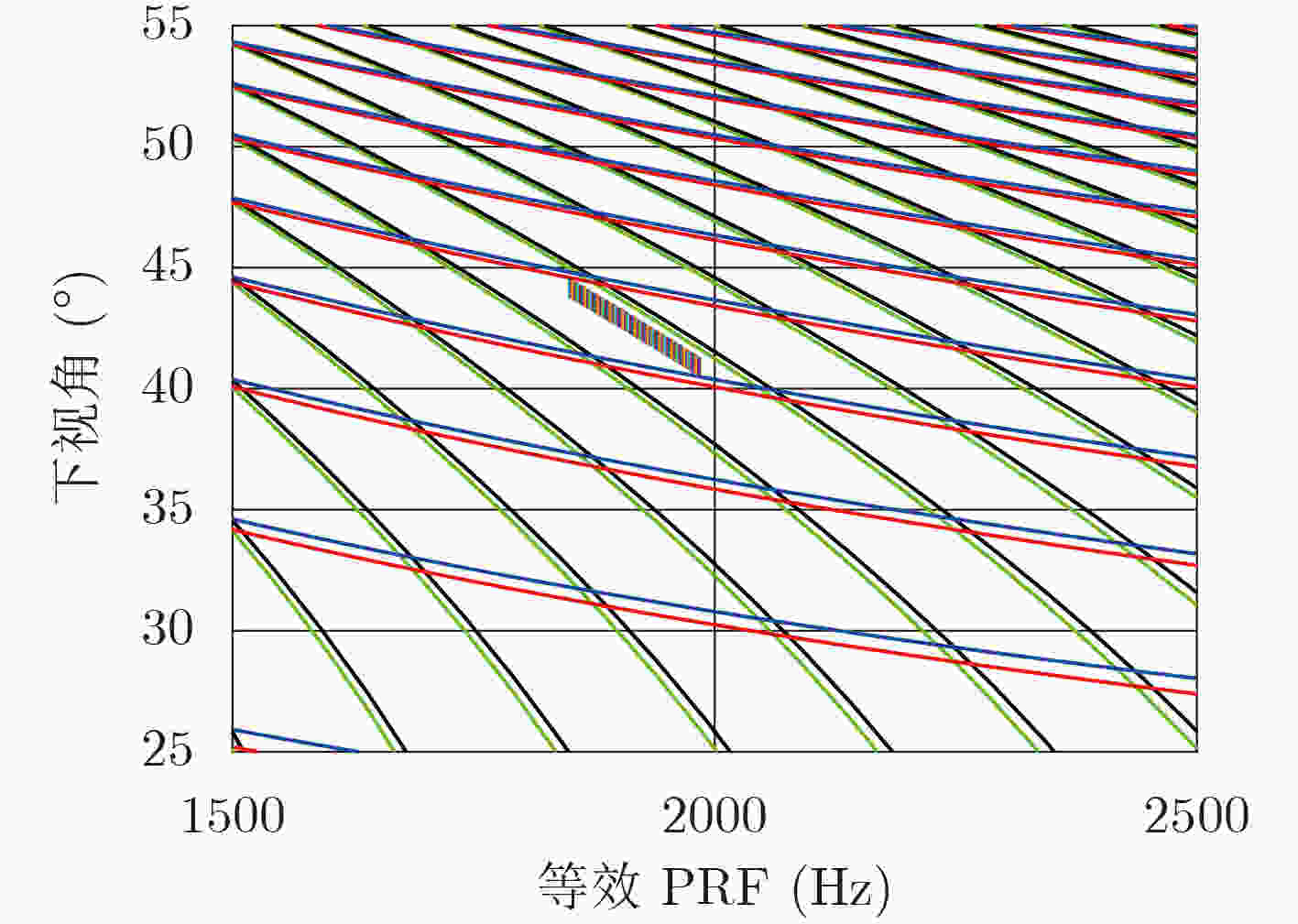
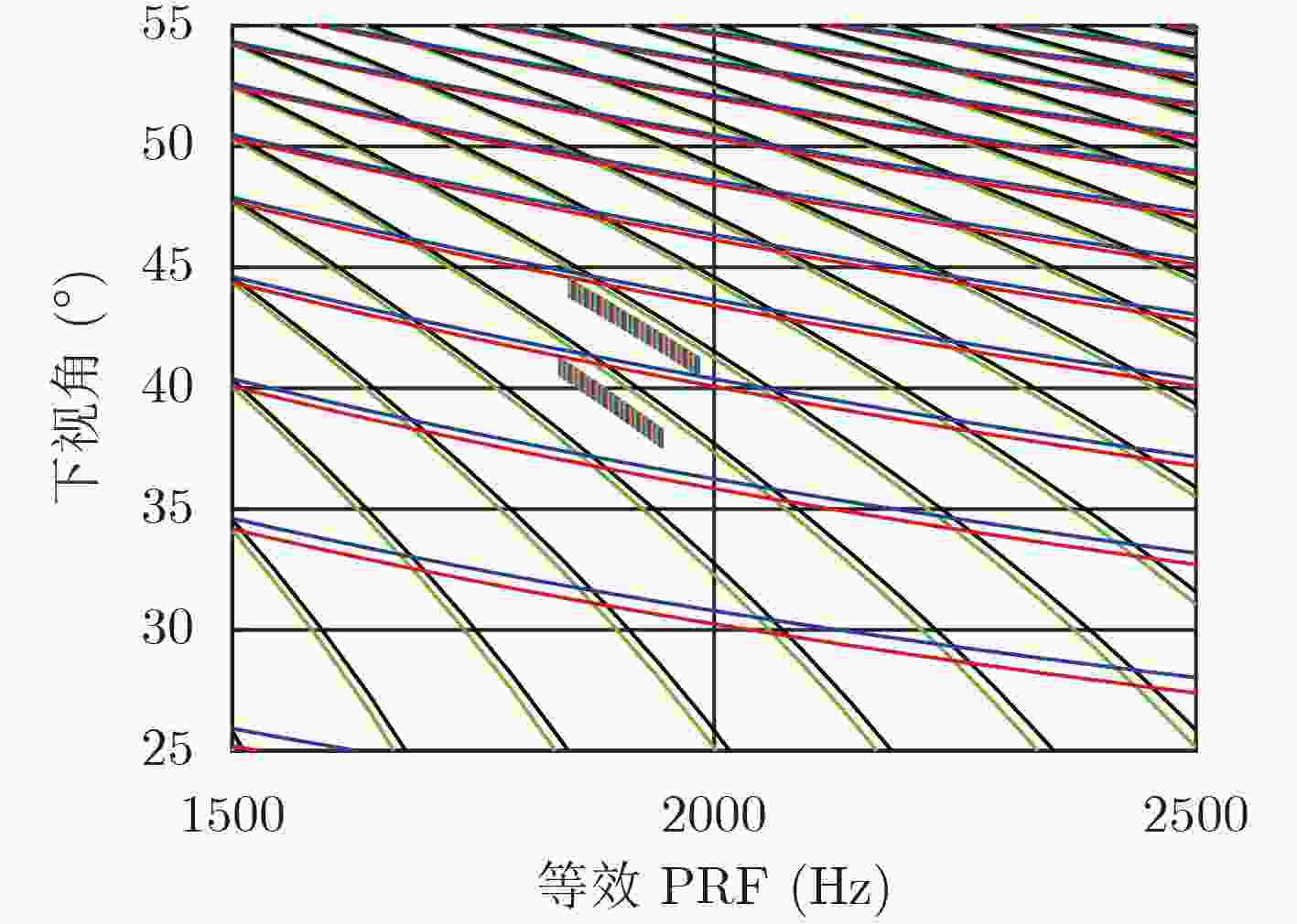
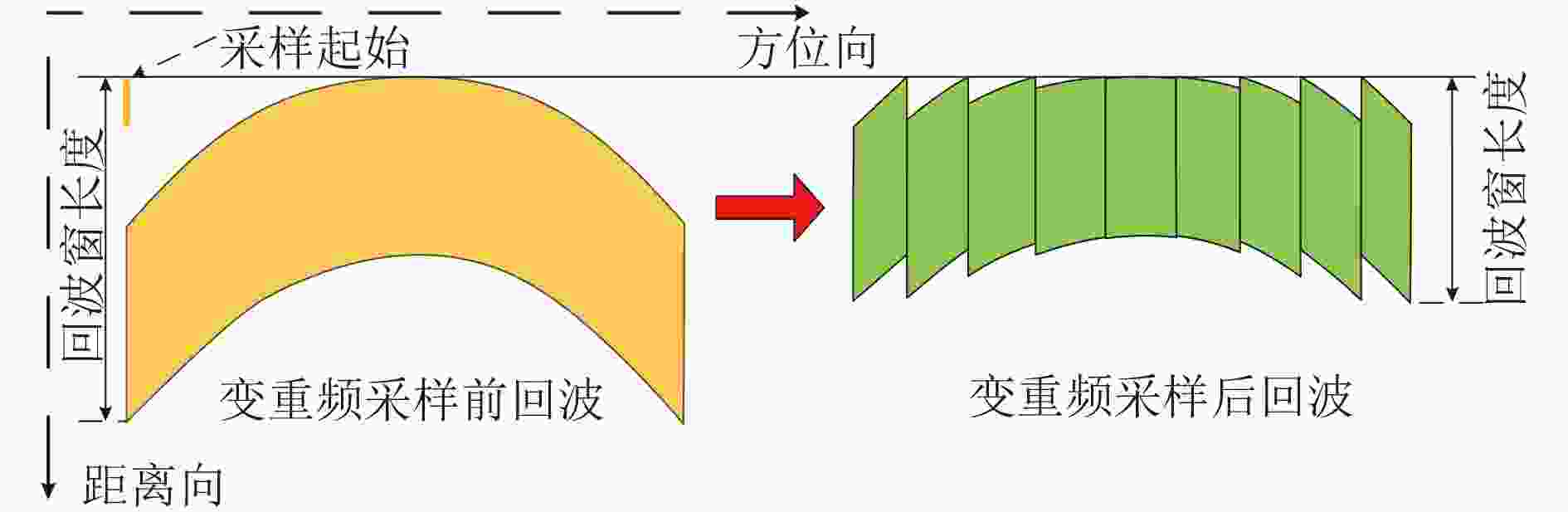
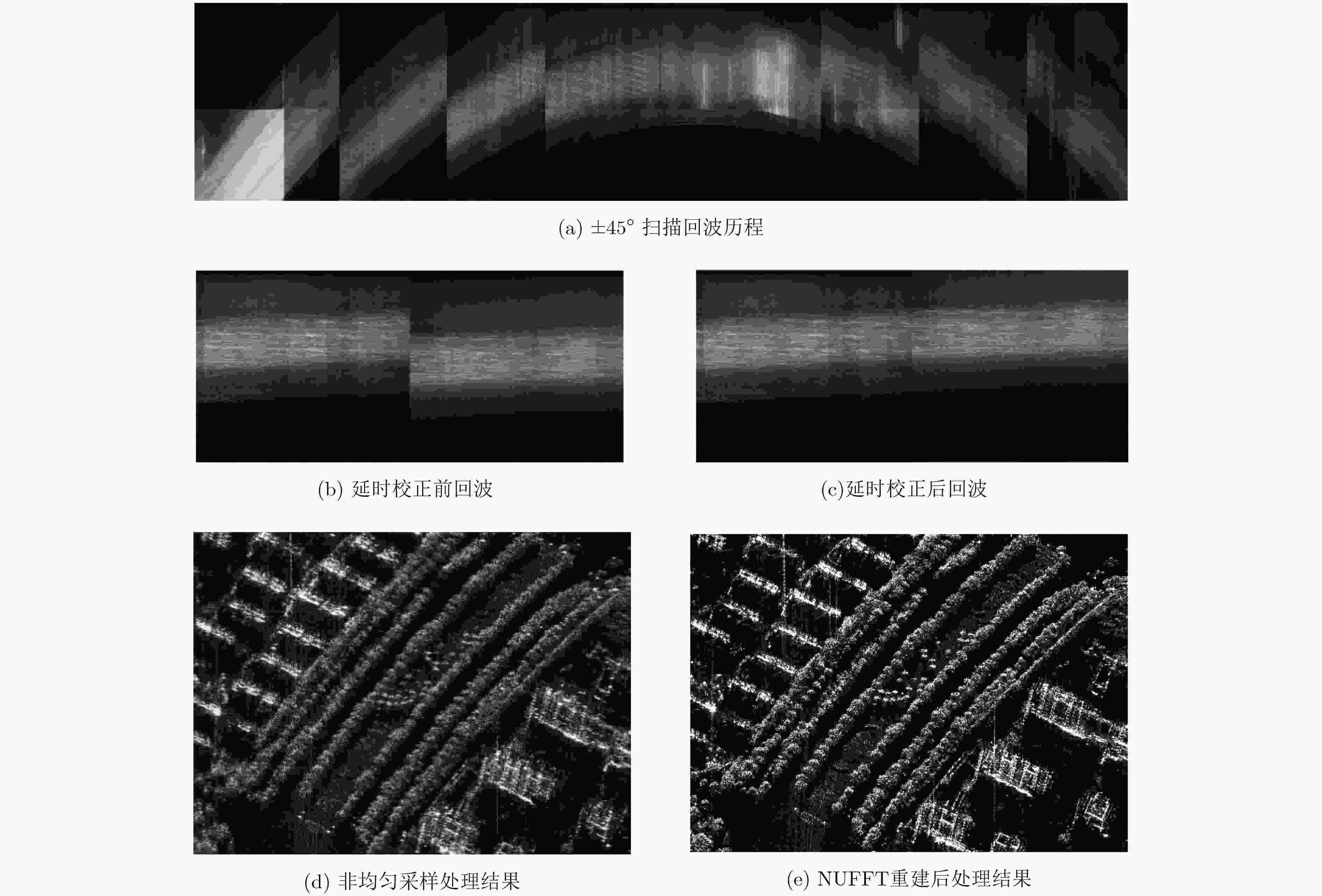
摘要: 星载SAR大斜视聚束可以实现高分辨率宽覆盖成像和目标多方位信息获取,但斜视情况下大距离徙动会造成回波数据获取效率下降、波位选择困难等问题。变PRI技术可以跟踪聚束成像过程中目标斜距变化,提高数据获取效率、降低波位选择难度。该文对星载大斜视聚束SAR的变PRI工作机理进行了研究,提出了一种PRI变化序列迭代设计方法和波位选择策略,研究了样条插值和NUFFT两种非周期非均匀采样重建方法,并首次通过机载飞行试验对所提出的变PRI的SAR系统工作体制进行了验证。Abstract: High squint spotlight mode of spaceborne SAR can be used to achieve high resolution and wide swath, and also can be used to acquire information of target from multi-azimuth. However, the considerable range migration can result in efficiency decreasing in data acquisition, and dilemma in system design. This problem can be solved by the technology named PRI (Pulse Repetition Interval) variation which can track the slant range variation of the target during data acquisition. In this paper, the principle of PRI variation is studied, and methods of PRI sequence iterative design and system parameter selection are proposed. Two approaches to reconstruct the nonequal spaced and nonperiod data in azimuth sampling are compared. Finally, the first results of PRI variation mode of airborne SAR experiment with high slant spotlight mode are presented.
-
Key words:
- SAR /
- Pulse Repetition Interval (PRI) variation /
- High squint spotlight /
- Spaceborne /
- Airborne
-
表 1 星载SAR仿真参数
参数名称 符号 取值 中心频率 ${f_c}$ 9600 MHz 卫星高度 $H$ 800 km 卫星速度 ${V_s}$ 7486 m/s 雷达下视角 ${\alpha _0}$ 30° 发射脉宽 ${T_p}$ 20 μs 天线长度 ${L_a}$ 10 m 天线高度 ${L_r}$ 2 m 表 2 两种重建方法性能比较
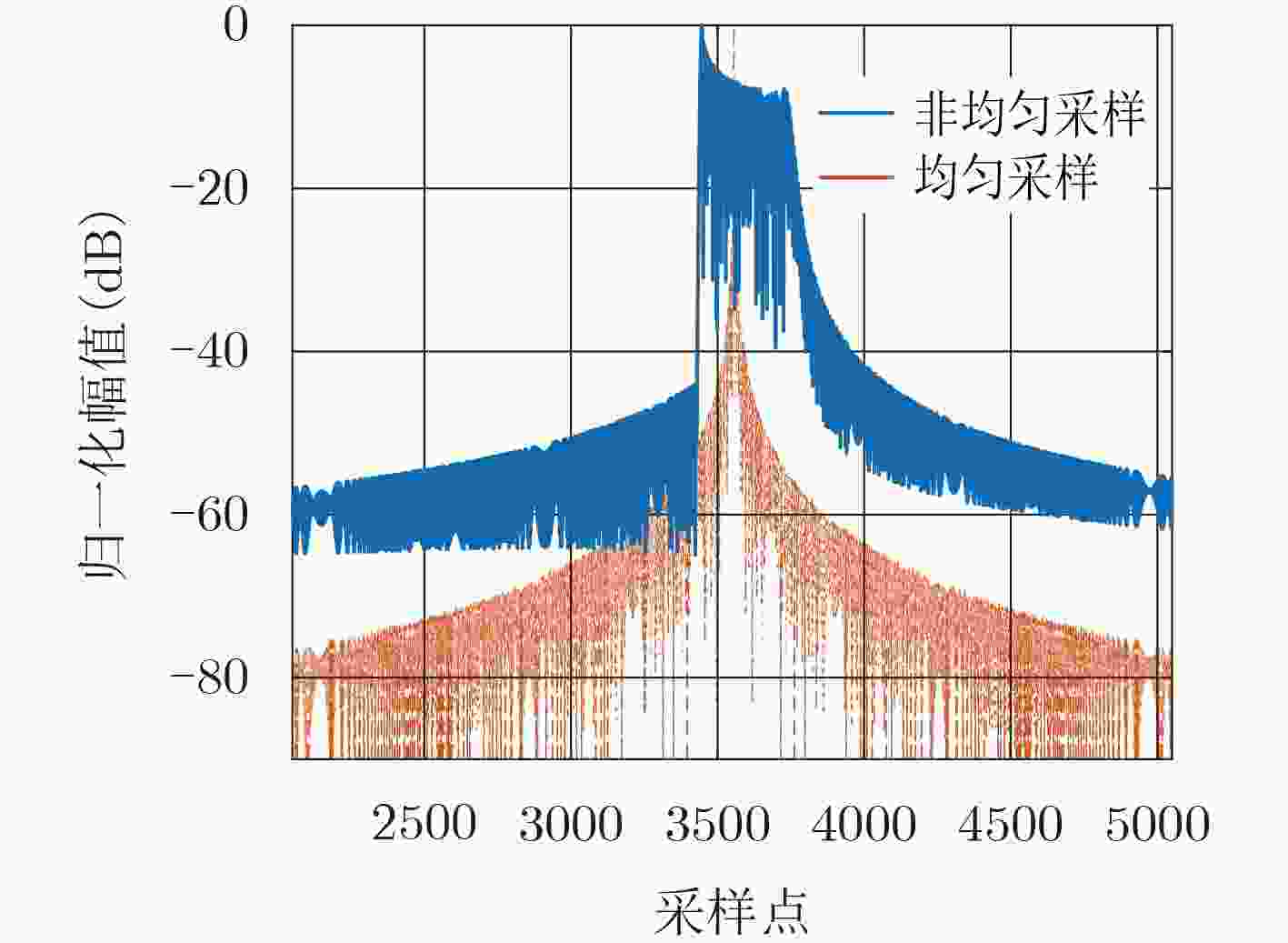
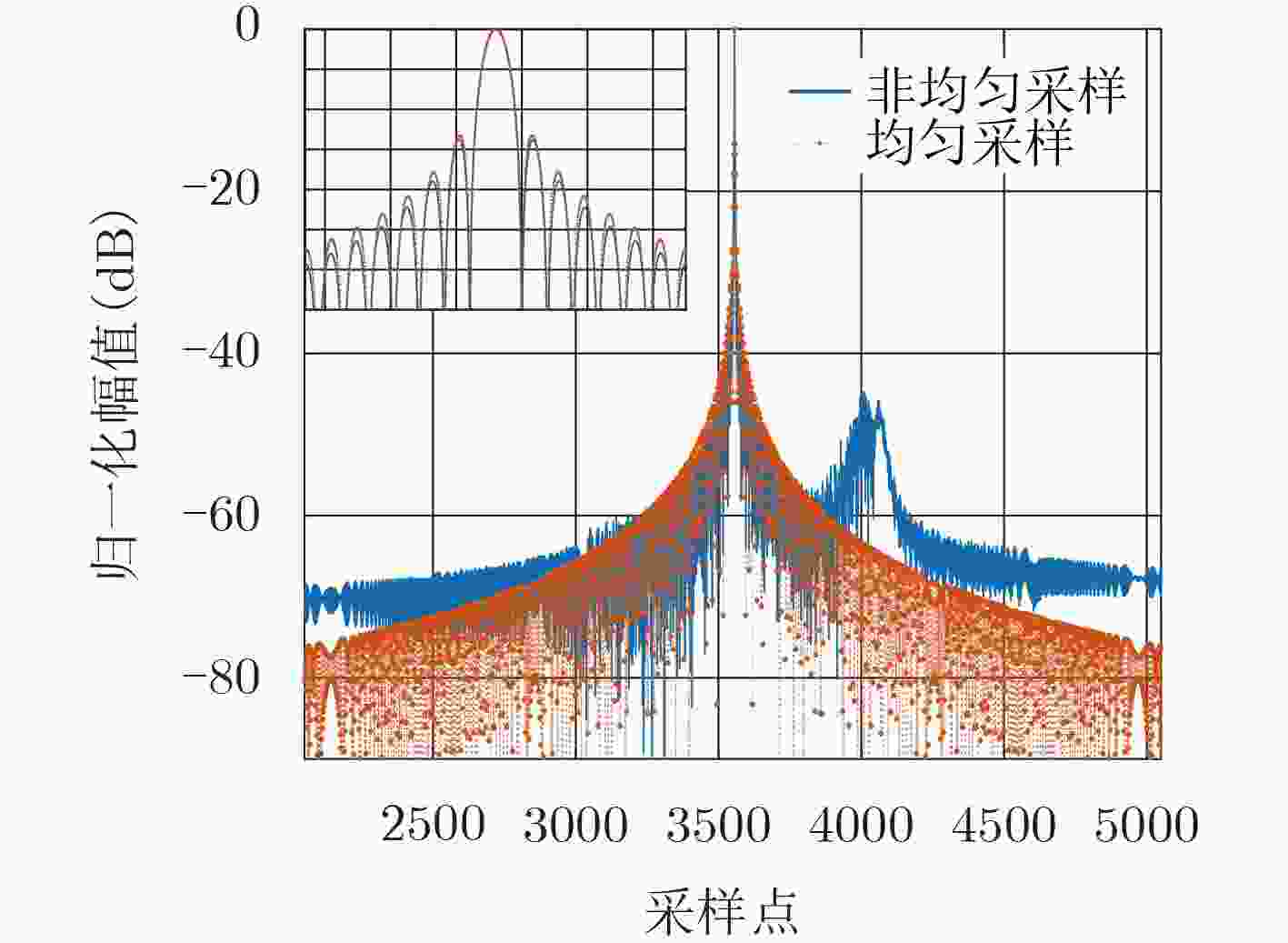
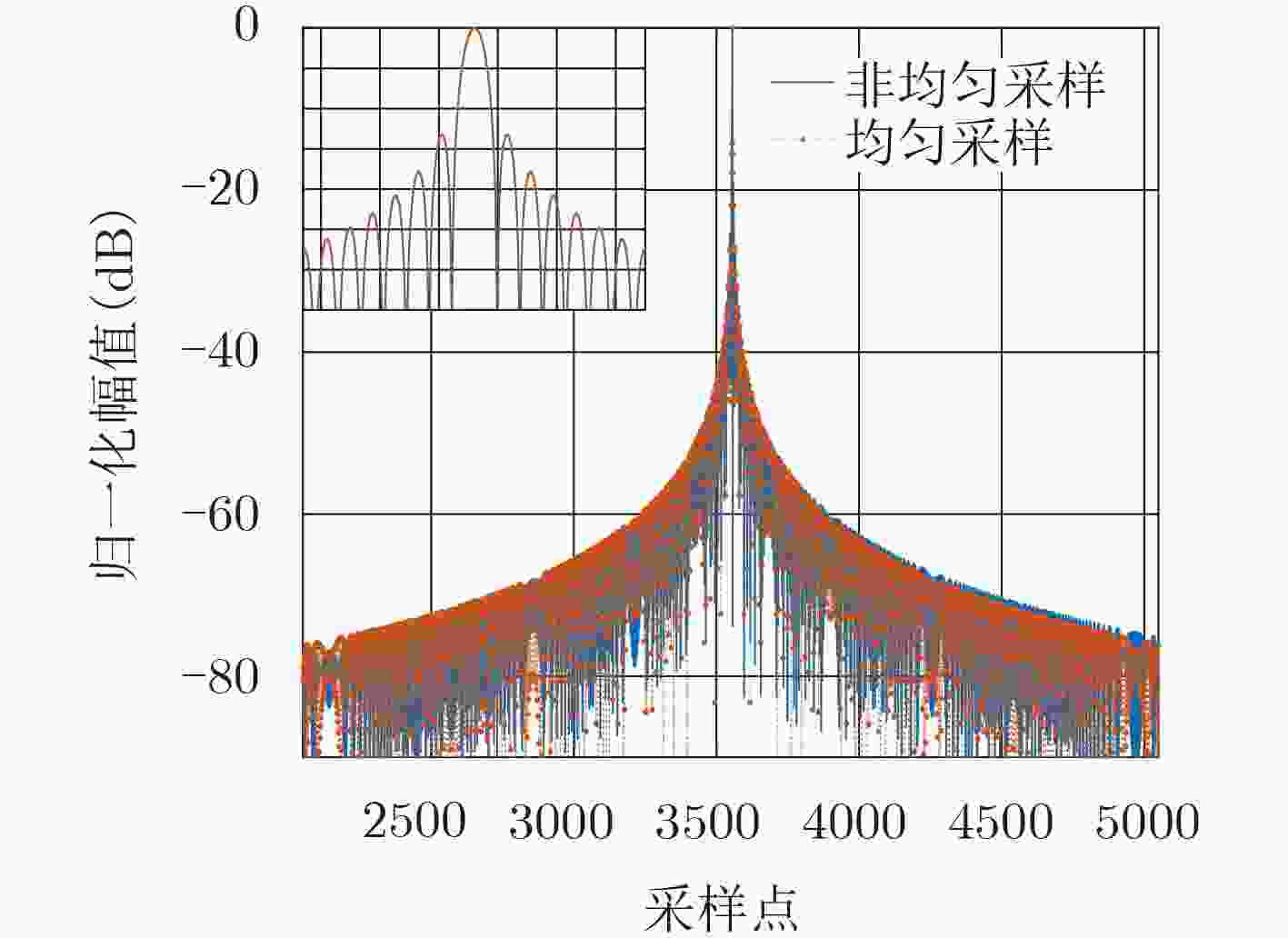
均匀采样 样条插值重建 NUFFT重建 主瓣展宽比ML 1.00 1.01 1.00 峰值旁瓣比PSLR (dB) –13.27 –13.82 –13.26 积分旁瓣比ISLR (dB) –9.72 –10.67 –9.72 均方误差(%) 0.00 0.26 0.0119 -
袁孝康. 星载合成孔径雷达导论[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2003: 157–163.YUAN Xiaokang. Introduce to the Spaceborne Synthetic Aperture Radar[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2003: 157–163. 邓云凯, 赵凤军, 王宇. 星载SAR技术的发展趋势及应用浅 析[J]. 雷达学报, 2012, 1(1): 1–10 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.20015DENG Yunkai, ZHAO Fengjun, and WANG Yu. Brief analysis on the development and application of spaceborne SAR[J]. Journal of Radars, 2012, 1(1): 1–10 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.20015 李春升, 王伟杰, 王鹏波, 等. 星载SAR技术的现状与发展趋 势[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(1): 229–240 doi: 10.11999/JEITl51116LI Chunsheng, WANG Weijie, WANG Pengbo, et al. Current situation and development trends of spaeeborne SAR technology[J]. Journal of Electronics and Information Technology, 2016, 38(1): 229–240 doi: 10.11999/JEITl51116 CARRARA W G, GOODMAN R S, and MAJEWSKI R M. Spotlight synthetic aperture radar: Signal processing Algorithms[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Solar-Terrestrial physics, 1995, 59(5): 597–598. WANG Pengbo, LIU Wei, CHEN Jie, et al. A raster scan SAR system for ultra-wide swath imaging[J]. Remote Sensing Letters, 2014, 5(9): 833–842 doi: 10.1080/2150704X.2014.971904 NAFTALY U and NATHANSOHN R L. Overview of the TECSAR satellite hardware and Mosaic mode[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2008, 5(3): 423–426 doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2008.915926 罗绣莲, 徐伟, 郭磊. 捷变PRF 技术在斜视聚束SAR 中的应 用[J]. 雷达学报, 2015, 4(1): 70–77 doi: 10.12000/JR14149LUO Xiulian, XU Wei, and GUO Lei. The application of PRF variation to squint spotlight SAR[J]. Journal of Radars, 2015, 4(1): 70–77 doi: 10.12000/JR14149 GEBERT N and KRIEGER G. Ultra-wide swath SAR imaging with continuous PRF variation[C]. European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar (EUSAR), Aachen, Germany, 2010: 966–969. ALMEIDA F, YOUNIS M, KRIEGER G, et al. Multichannel staggered SAR azimuth processing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 5(56): 2772–2788 doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2783444 VILLANO M, KRIEGER G, and MOREIRA A. Staggered-SAR: A new concept for high-resolution wide-swath imaging[C]. IEEE Gold Remote Sensing Conference, Rome, Italy, 2012: 1–3. VILLANO M, KRIEGER G, and MOREIRA A. Staggered-SAR for high resolution wide-swath imaging[C]. IET International Conference on Radar Systems, Glasgow, UK, 2012: 1–6. VILLANO M, KRIEGER G, and MOREIRA A. Staggered SAR: Highresolution wide-swath imaging by continuous PRI variation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(7): 4462–4479 doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2282192 ZENG H, CHEN Jie, YANG Wei, et al. Image formation algorithm for highly-squint strip-map SAR onboard high-speed platform using continuous PRF variation[C]. IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Quebec City, Canada, 2014: 1117–1120. 高祥武. 星载聚束模式合成孔径雷达系统研究[D]. [博士论文], 中国科学院电子学研究所, 2004: 13–18, 26–30.GAO Xiangwu. Study on spaceborne spotlight synthetic aperture radar system[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Institute of Electronics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2004: 13–18, 26–30. 齐伟孔. 基于数字波束形成和多发多收的星载合成孔径雷达系统及其信号处理研究[D]. [博士论文], 中国科学院电子学研究所, 2010: 77–83.QI Weikong. Study on spaceborne synthetic aperture radar system and signal processing based on digital beamforming and multiple-input multiple-output[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Institute of Electronics Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2010: 77–83. 连剑. 非均匀采样信号重构技术及应用研究[D]. [硕士论文], 哈尔滨工业大学, 2011: 28–37.LIAN Jian. Research on reconstruction and application of nonuniformly sampled signals[D]. [Master dissertation], Harbin Institute of Technology, 2011: 28–37. GREENGARD L and LEE J. Accelerating the nonuniform fast fourier transform[J]. Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, 2004, 46(3): 443–454. SUBIZA B, GIMENO-NIEVES E, and LOPEZ-SANCHEZ J M. An approach to SAR imaging by means of non-uniform FFT’s[C]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Toulouse, France, 2003: 4089–4091. HWANG J, CHO S, MOON J, et al. Nonuniform DFT based on nonequispaced sampling[C]. Wseas International Conference on Signal, Corfu, Greece, 2005: 11–16. FESSLER JA and SUTTON BP. Nonuniform fast fourier transforms using min-max interpolation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2003, 51(2): 560–574 doi: 10.1109/TSP.2002.807005 SOUMEKH M. Band-limited interpolation from unevenly spaced sampled data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics Speech and Signal Processing, 1988, 36(1): 110–122 doi: 10.1109/29.1497 -





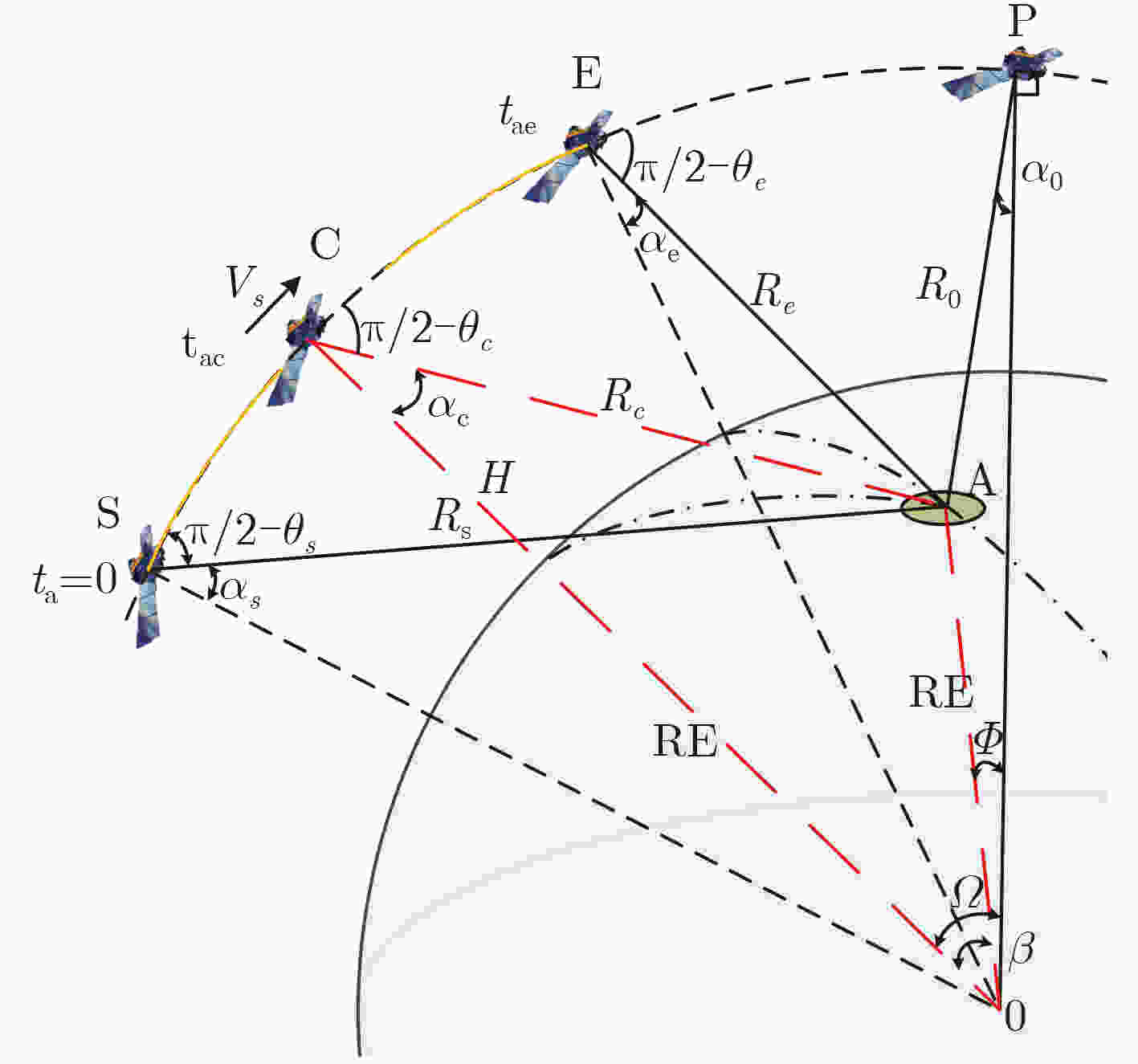
 下载:
下载:
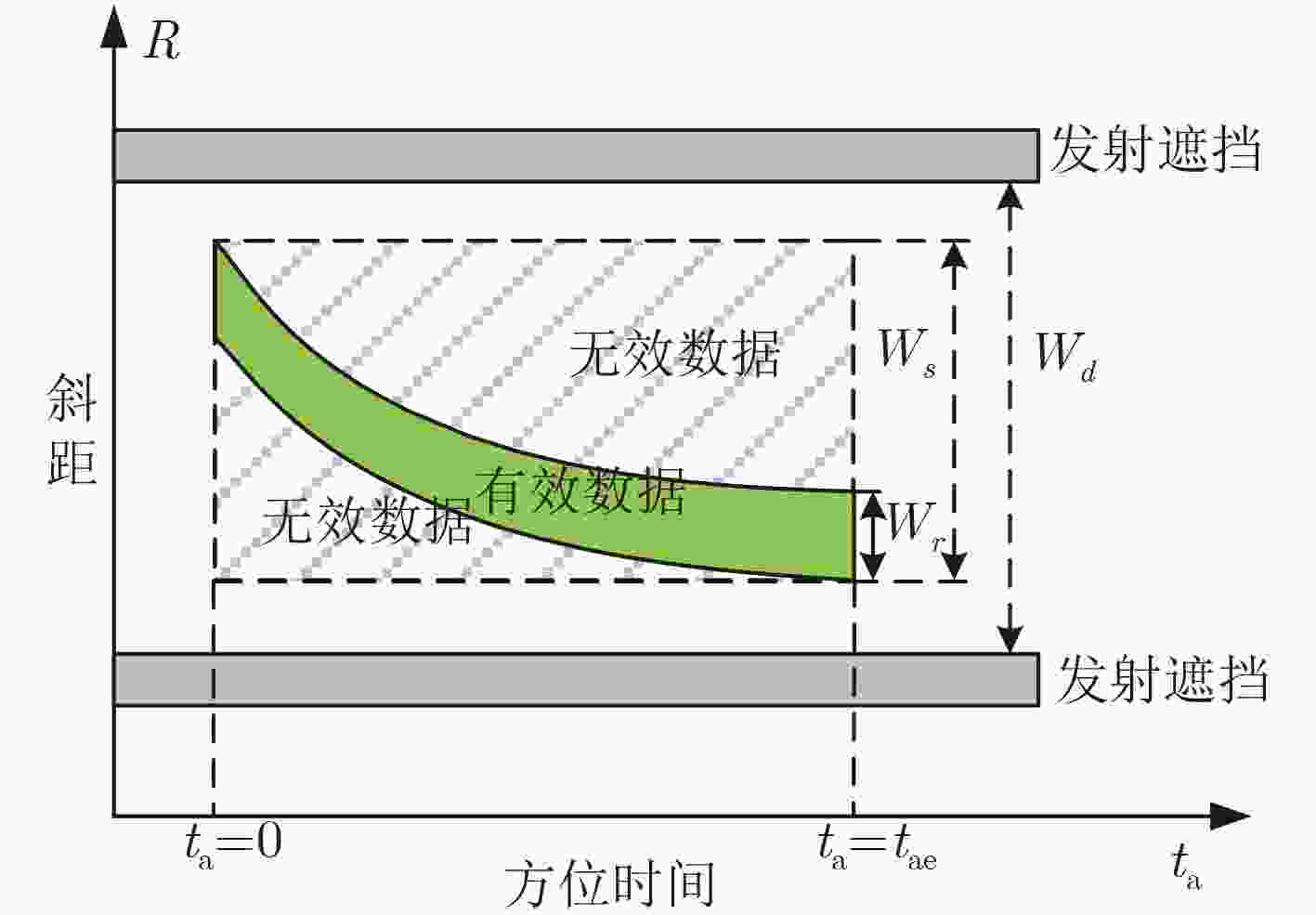
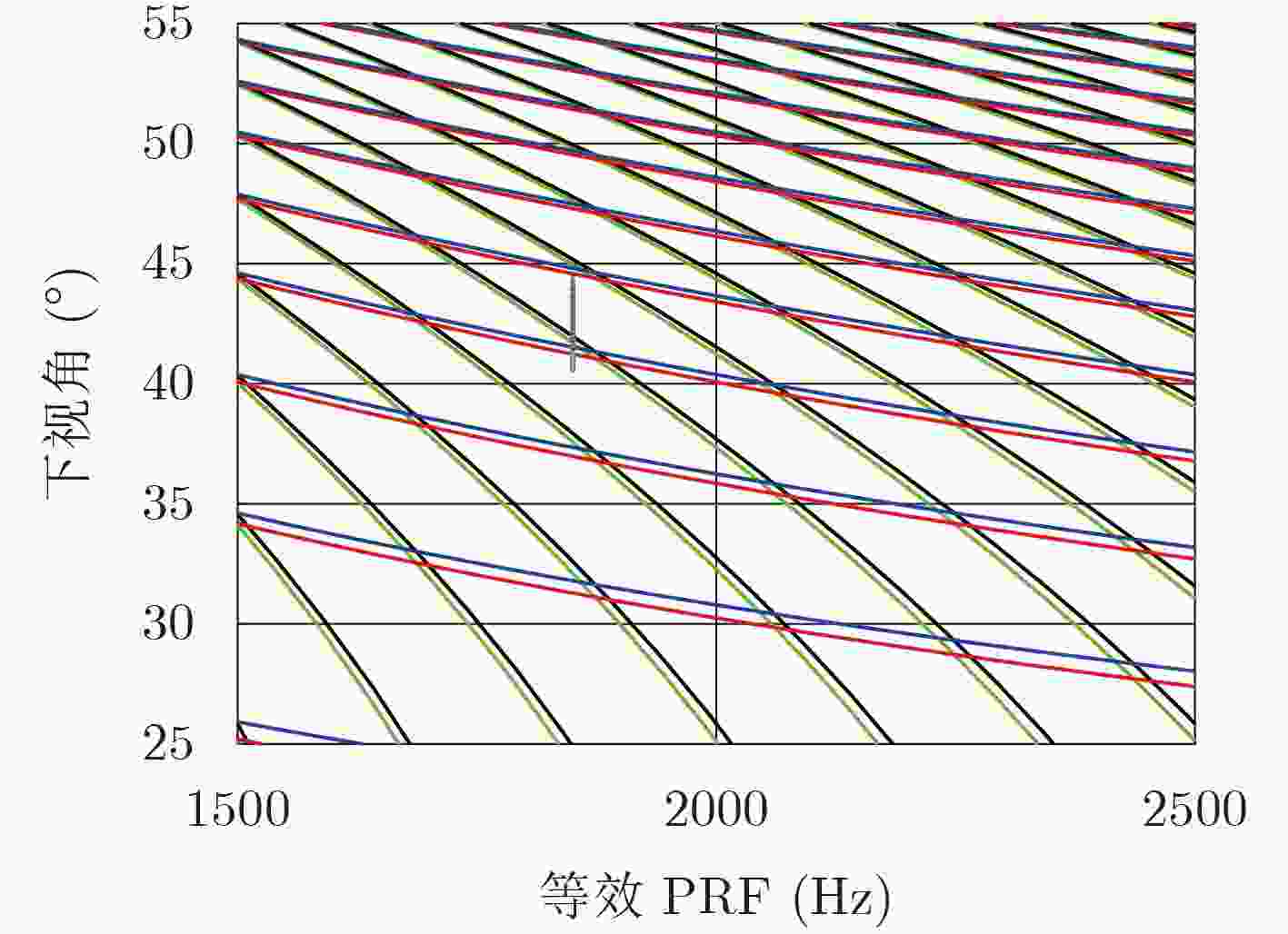
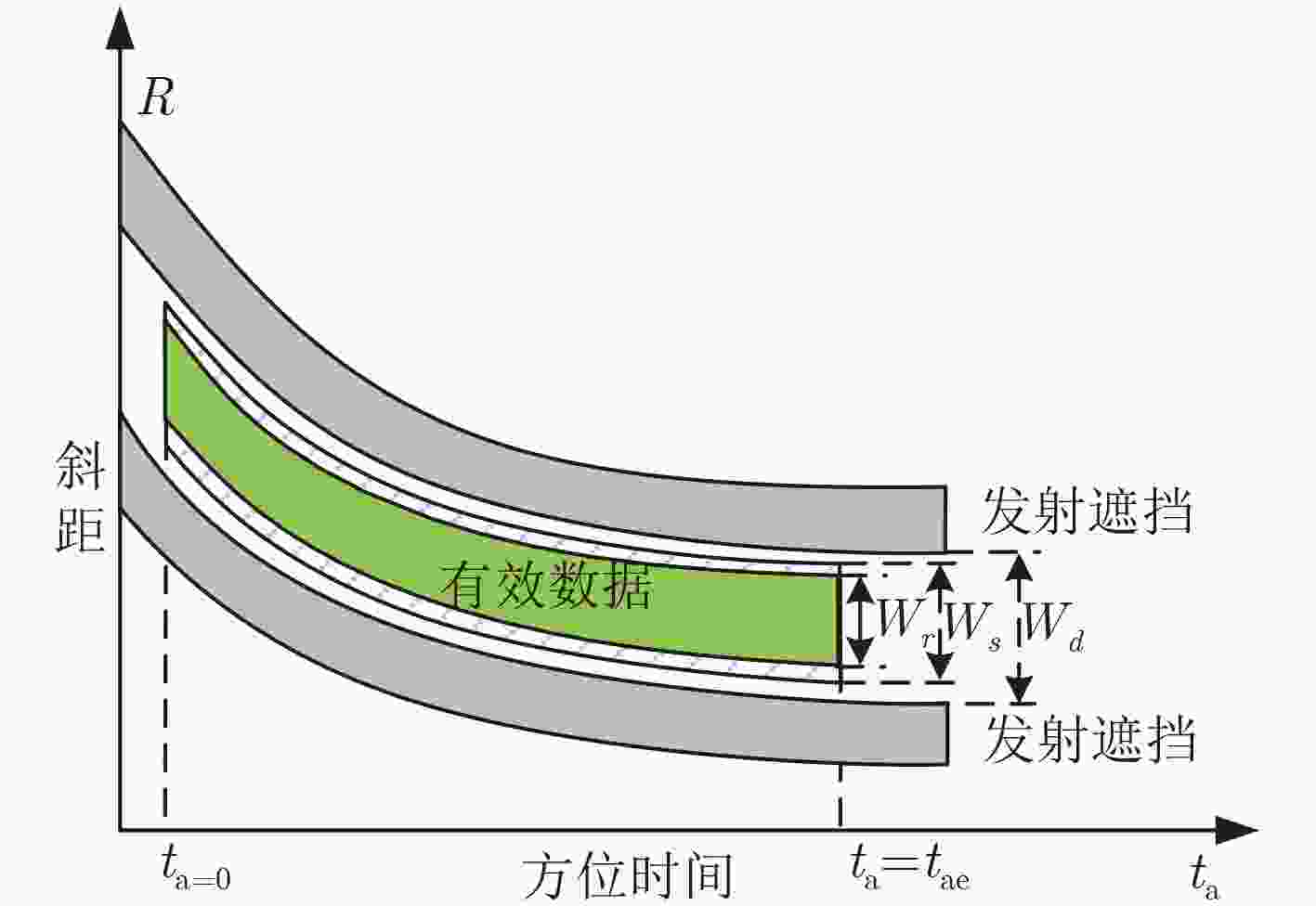


 下载:
下载:
