Non-invasive Wireless and Passive MEMS Intraocular Pressure Sensor
-
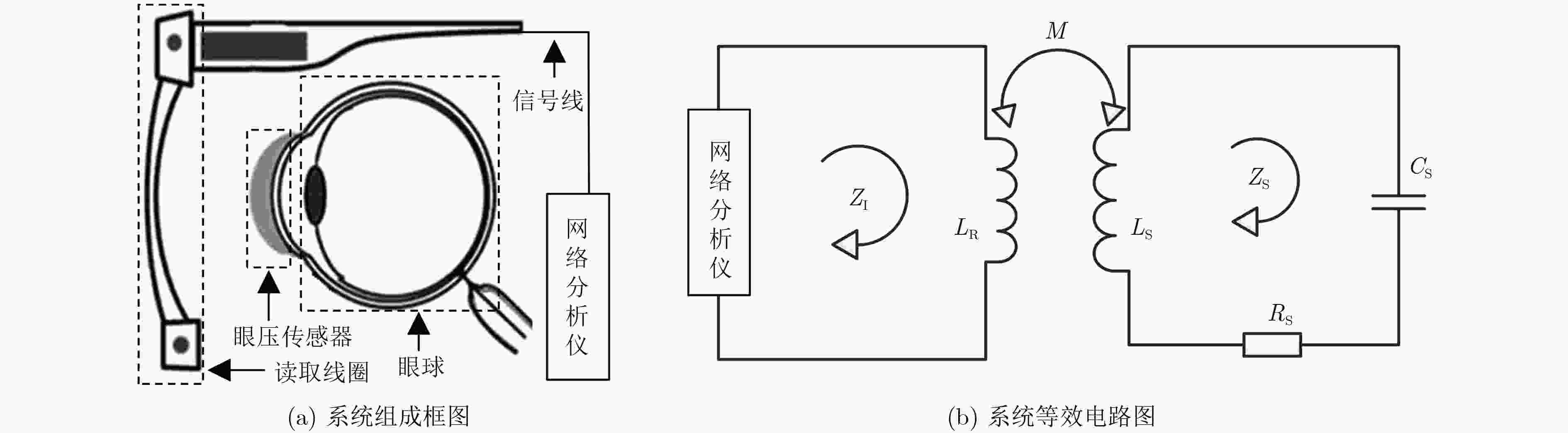
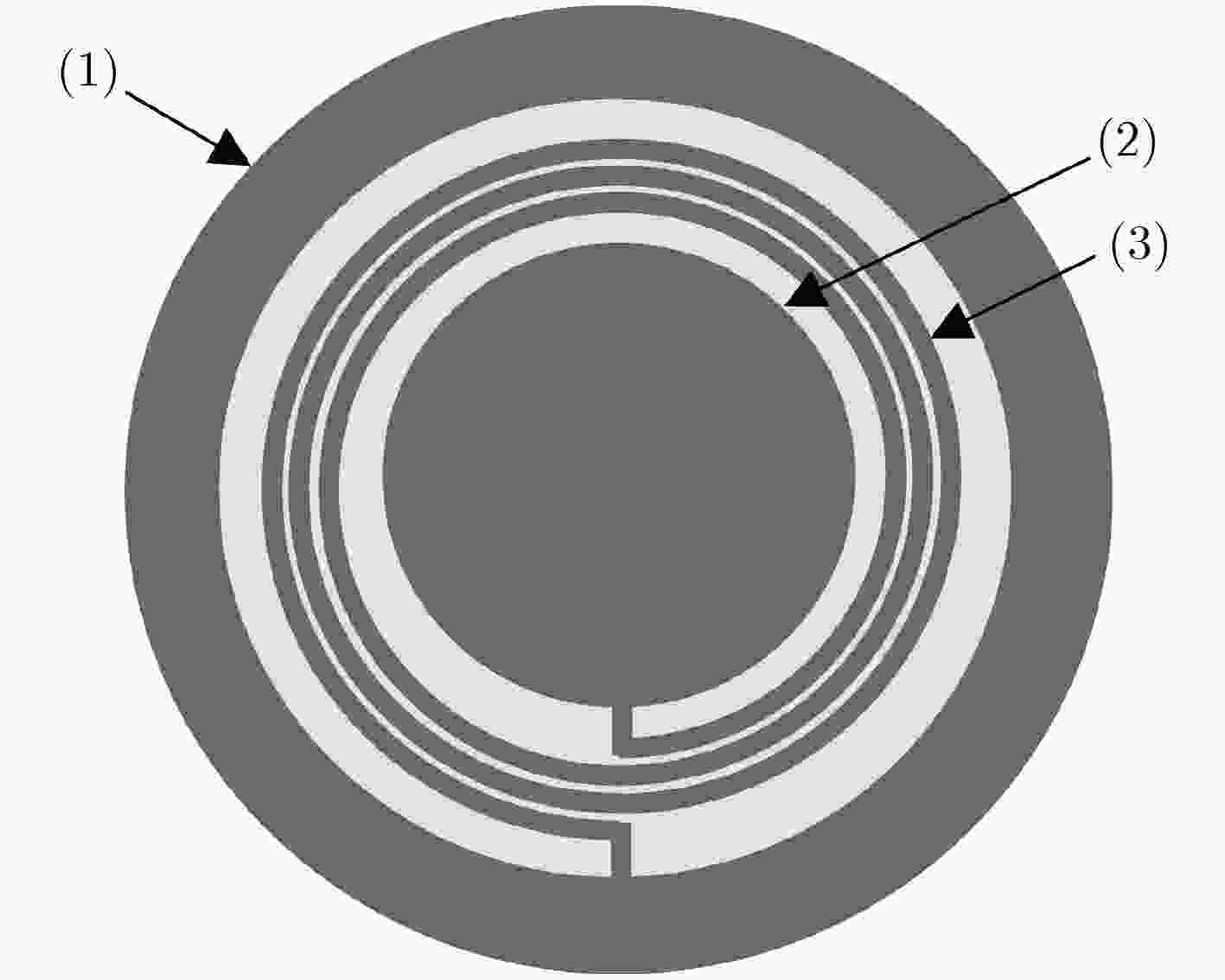
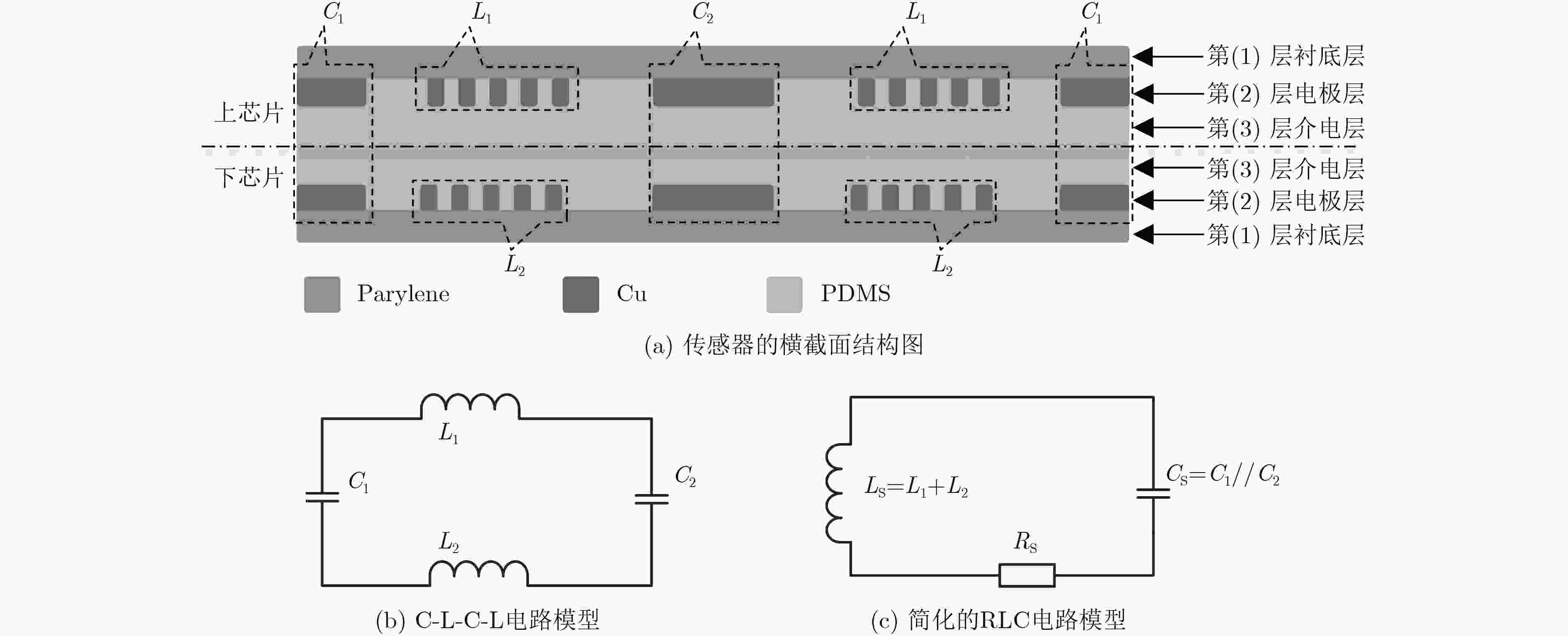
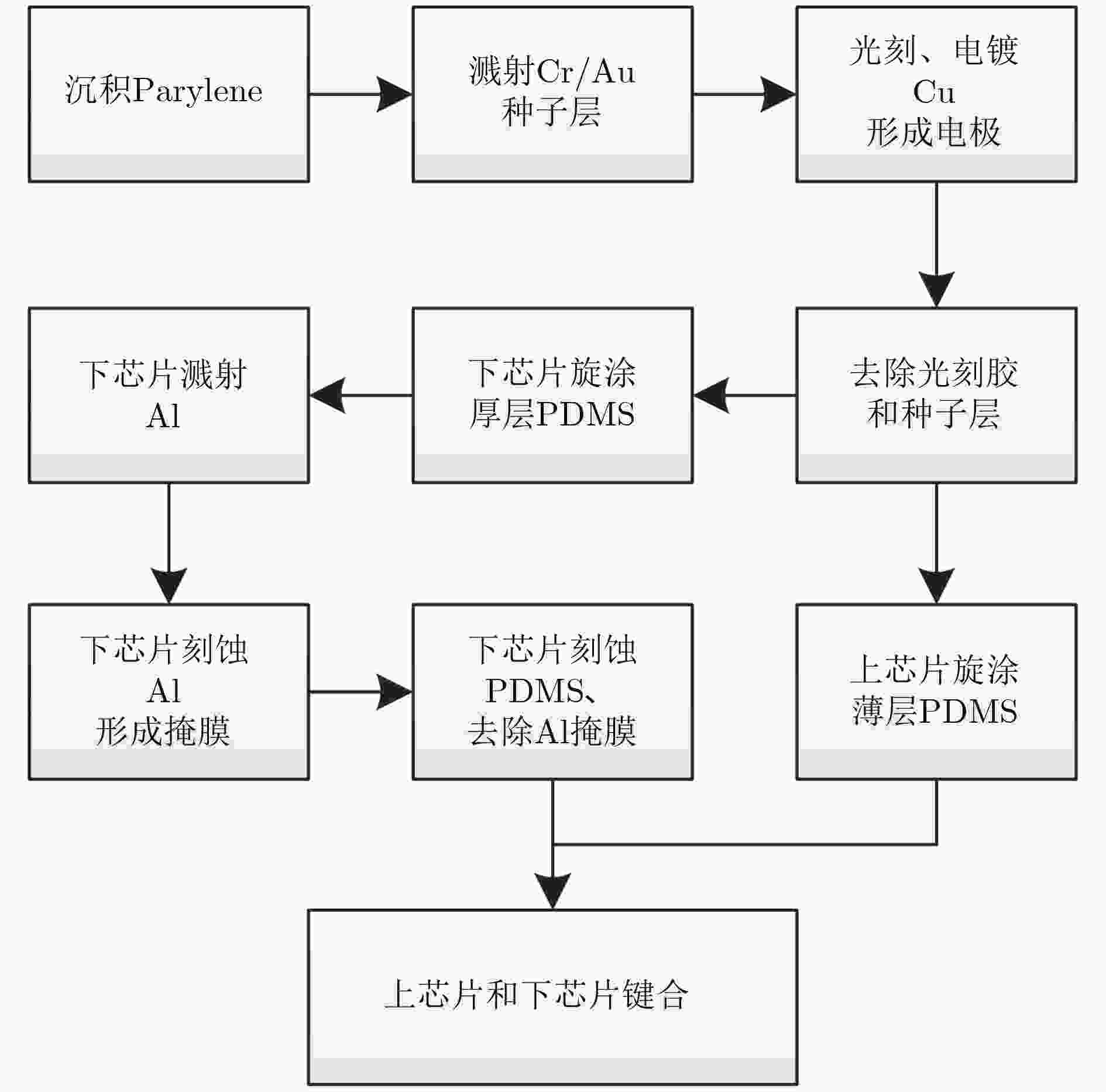
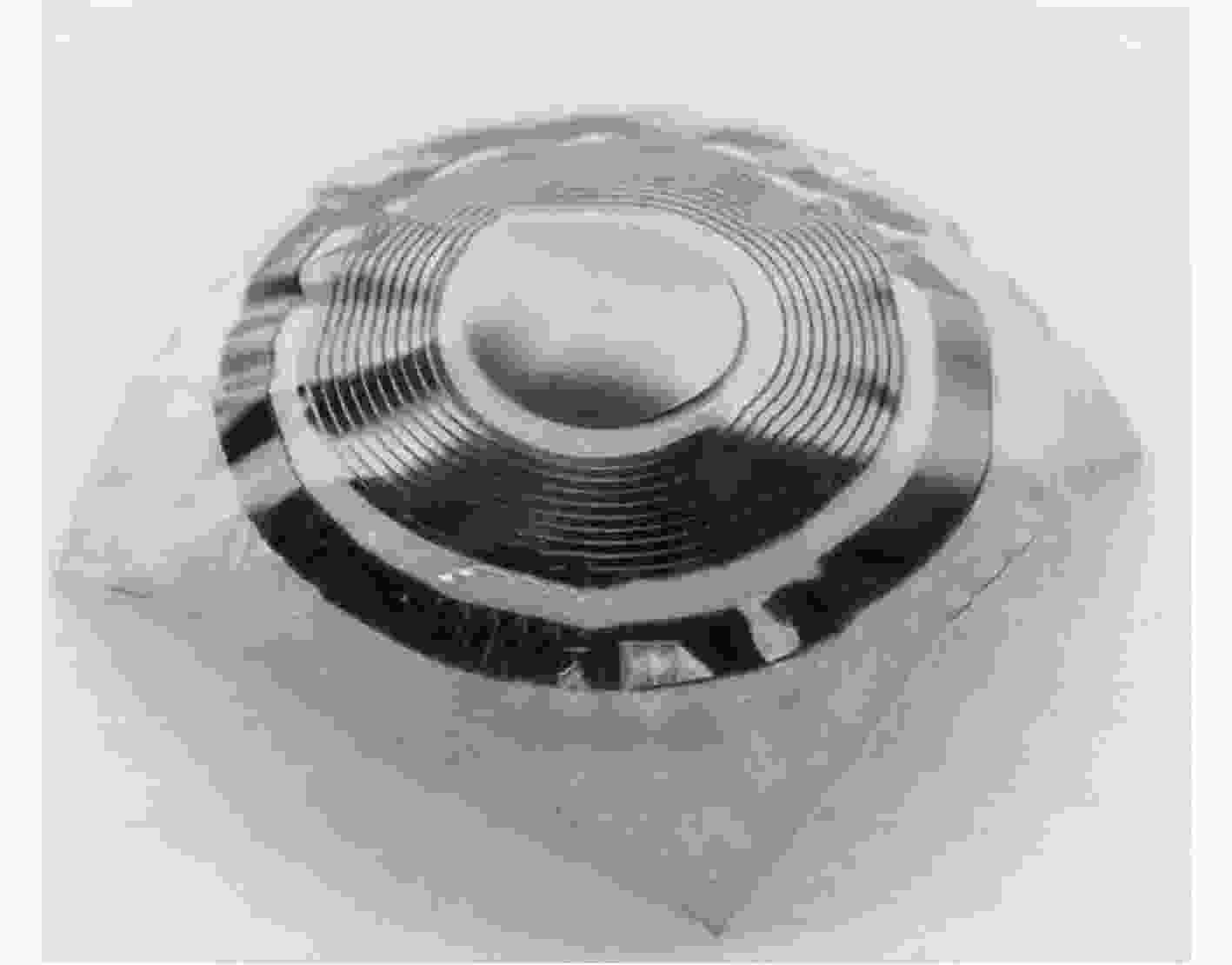
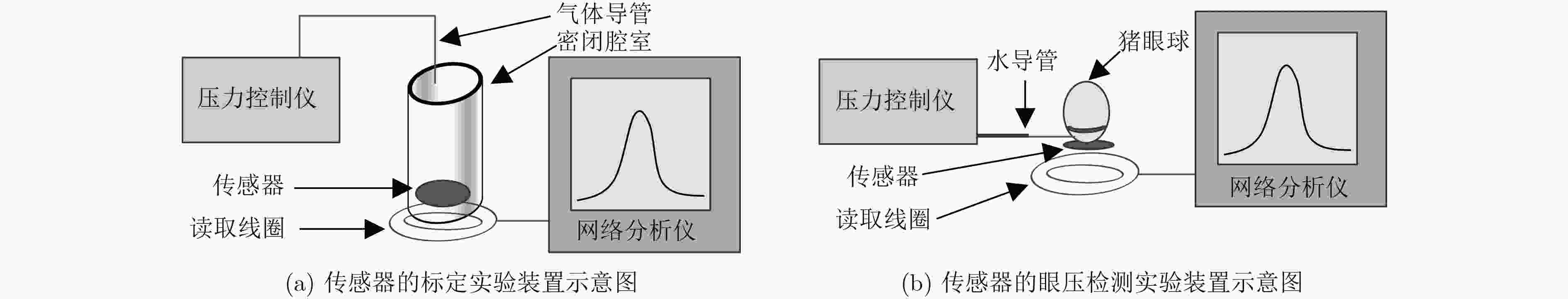
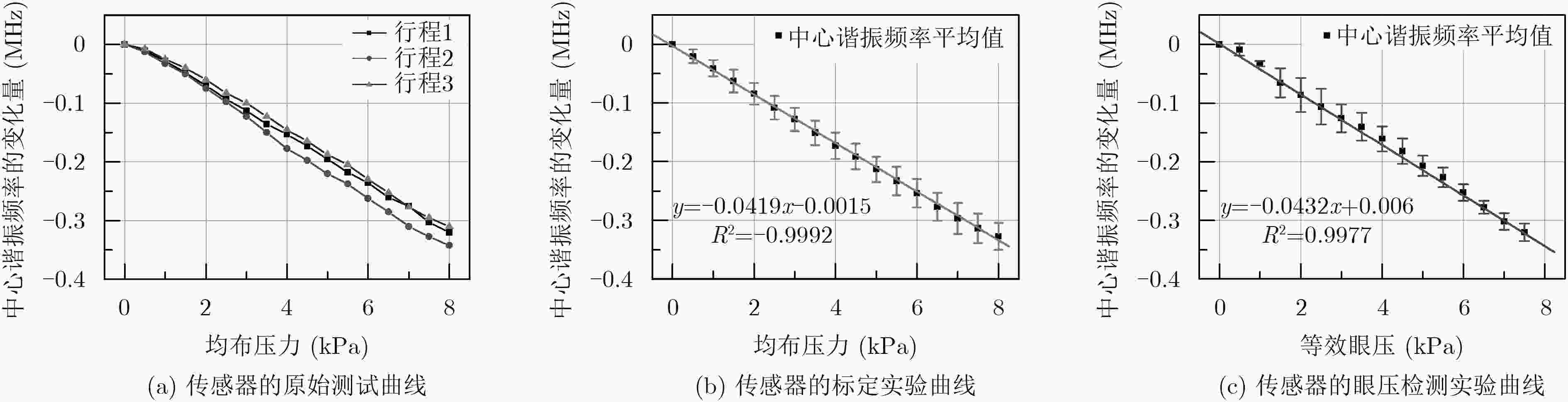
摘要: 连续监测眼压对于辅助诊断与治疗青光眼疾病具有重要作用,现有的眼压传感器存在相对灵敏度较低、中心谐振频率较高、制作工艺难度大等问题。为了解决上述问题,该文提出一种基于MEMS的非侵入式无线无源型眼压传感器。该传感器为5层堆叠结构,采用Parylene作为柔性衬底层、铜作为电极层、PDMS作为介电层,其中电极层和介电层构成两个电感和两个电容,形成C-L-C-L串联谐振电路。通过MEMS平面工艺和热塑形方法制作成能够与眼球紧密贴合的曲面形状,这种设计方案能有效地解决传感器的制作工艺难度大等问题。实验结果表明:该眼压传感器的中心谐振频率降低到了40 MHz,相对灵敏度达到1028.57 ppm/kPa,能够分辨出最小50 Pa(0.375 mmHg)的眼压值变化,为实现长期、连续性地监测眼压提供了技术支持。Abstract: Continuous monitoring of IntraOcular Pressure (IOP) plays an important role in the diagnosis and treatment of the glaucoma. Existing IOP sensors have some problems, such as low sensitivities, high central resonant frequencies and difficult fabrication. In order to solve the aforementioned problems, this paper presents a wireless, passive and non-invasive IOP sensor based on MEMS technology. The sensor contains five stacked layers, where Parylene, copper and PDMS are adopted as the functional materials within two flexible substrate layers, two electrode layers, and a dielectric layer, respectively. The electrode layers and the dielectric layer consist of two inductors and two capacitors to form a resonant circuit in C-L-C-L series. In the term of fabrication, a MEMS planar process followed by thermally shaping is proposed to fit curved surfaces of the eyeballs, and then this design scheme can effectively solve such issues as the difficulty in making the sensor and so on. Experimental results show that the central resonant frequency is decreased to 40 MHz, relative sensitivity is quantified as 1028.57 ppm/kPa, and resolution reached up to 50 Pa (0.375 mmHg). This study can be used for long-term, continuous monitoring of IOP.
-
Key words:
- MEMS /
- IntraOcular Pressure (IOP) sensor /
- Wireless and passive /
- Parylene /
- PolyDiMethylSiloxane (PDMS)
-
表 1 传感器的中心谐振频率相对变化与芯片间距的关系
芯片初始间距
(μm)中心频率降低(%)
(理论值)中心频率降低(%)
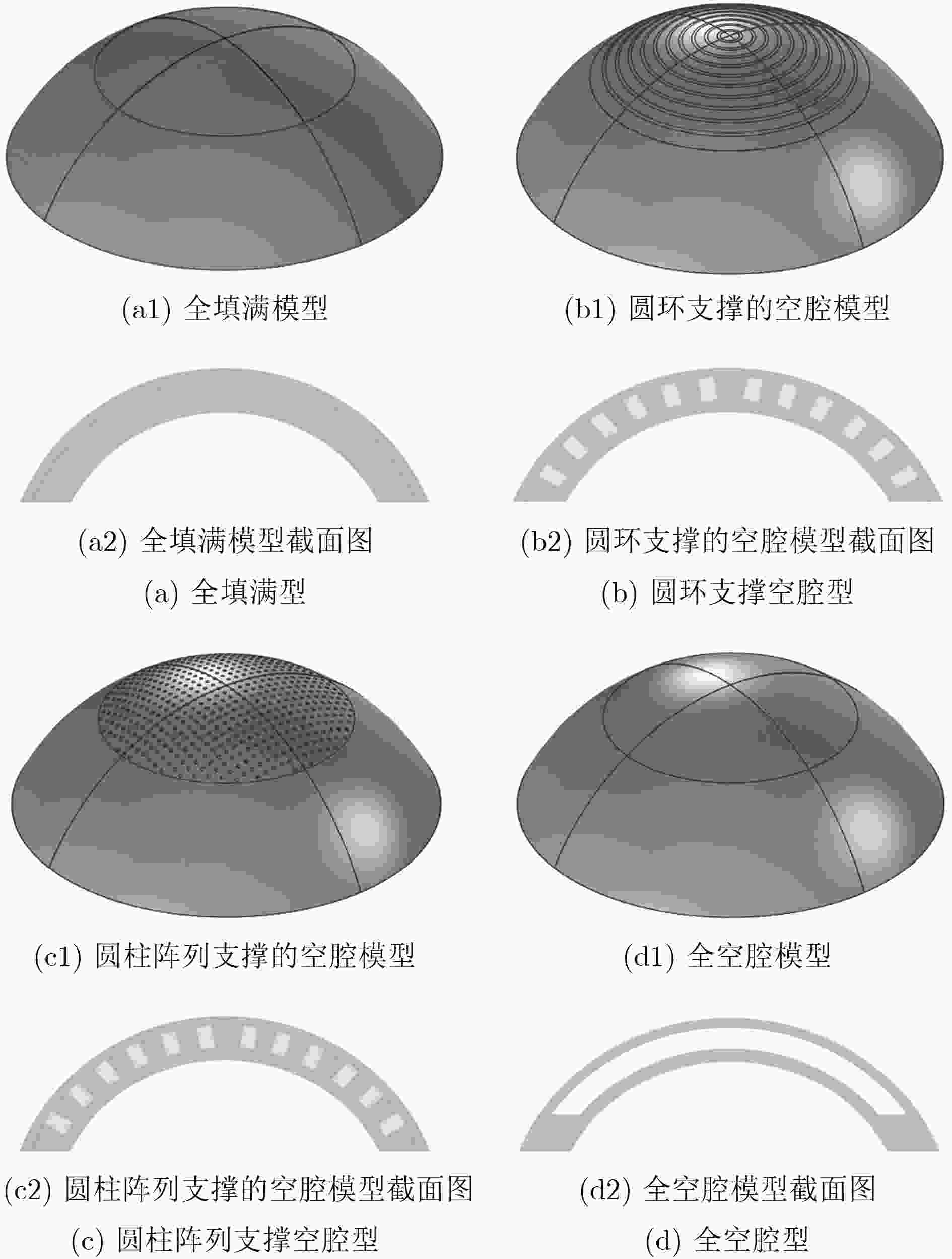
(仿真值)误差(%) 20 29.29 29.14 0.51 30 13.40 13.31 0.68 40 0 0 0 表 2 传感器灵敏度提高与PDMS结构关系
PDMS结
构类型相对灵敏度
(ppm)相对灵敏
度倍数PDMS
填充率填充率倒数 全填满型 70.62 1.00 1.00 1.00 圆环型 311.30 4.41 0.27 3.72 圆柱阵列型 1160.11 16.43 0.09 11.74 全空腔型 3064.18 43.39 NAN NAN -
汪俊, 崔巍. 我国原发性青光眼流行病学研究进展[J]. 国际眼科杂志, 2012, 12(4): 667–670 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5123.2012.04.20WANG Jun and CUI Wei. Progress in epidemiological studies of primary glaucoma in China[J]. International Journal of Ophthalmology, 2012, 12(4): 667–670 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5123.2012.04.20 PUERS R, VANDEVOORDE G, and DE BRUYKER D. Electrodeposited copper inductors for intraocular pressure telemetry[J]. Journal of Micromechanics and Microengineering, 2000, 10(2): 124–129 doi: 10.1088/0960-1317/10/2/305 ITTOOP S M, SOOHOO J R, SEIBOLD L K, et al. Systematic review of current devices for 24-h intraocular pressure monitoring[J]. Advances in Therapy, 2016, 33(10): 1679–1690 doi: 10.1007/s12325-016-0388-4 MCMONNIES C W. The importance of and potential for continuous monitoring of intraocular pressure[J]. Clinical and Experimental Optometry, 2017, 100(3): 203–207 doi: 10.1111/cxo.12497 KATURI K C, ASRANI S, and RAMASUBRAMANIAN M K. Intraocular pressure monitoring sensors[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2008, 8(1): 12–19 doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2007.912539 刘德盟, 吴淼, 梅年松, 等. 无线植入式连续眼内压检测微系统发展与展望[J]. 微纳电子技术, 2013, 50(1): 57–63 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4776.2013.01.011LIU Demeng, WU Miao, MEI Niansong, et al. Development and outlook of wireless implantable continuously intraocular pressure detection microsystems[J]. Micronanoelectronic Technology, 2013, 50(1): 57–63 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4776.2013.01.011 COLLINS C C. Miniature passive pressure transensor for implanting in the eye[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 1967, BME-14(2): 74–83 doi: 10.1109/TBME.1967.4502474 CHEN P J, SAATI S, VARMA R, et al. Wireless intraocular pressure sensing using microfabricated minimally invasive flexible-coiled LC sensor implant[J]. Journal of Microelectromechanical Systems, 2010, 19(4): 721–734 doi: 10.1109/JMEMS.2010.2049825 XUE N, CHANG S P, and LEE J B. A SU-8-based microfabricated implantable inductively coupled passive RF wireless intraocular pressure sensor[J]. Journal of Microelectromechanical Systems, 2012, 21(6): 1338–1346 doi: 10.1109/JMEMS.2012.2206072 BELLO S A and PASSAGLIA C L. A wireless pressure sensor for continuous monitoring of intraocular pressure in conscious animals[J]. Annals of Biomedical Engineering, 2017, 45(11): 2592–2604 doi: 10.1007/s10439-017-1896-3 NAZAROV A, KNYAZER B, LIFSHITZ T, et al. Assessment of intraocular pressure sensing using an implanted reflective flexible membrane[J]. Journal of Biomedical Optics, 2017, 22(4): 047001 doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.22.4.047001 ROSENGREN L, BACKLUND Y, SJOSTROM T, et al. A system for wireless intra-ocular pressure measurements using a silicon micromachined sensor[J]. Journal of Micromechanics and Microengineering, 1992, 2(3): 202–204 doi: 10.1088/0960-1317/2/3/021 LEE J O, PARK H, DU J, et al. A microscale optical implant for continuous in vivo monitoring of intraocular pressure[J]. Microsystems&Nanoengineering, 2017, 3: 17057 doi: 10.1038/micronano.2017.57 CHOW E Y, CHLEBOWSKI A L, and IRAZOQUI P P. A miniature-implantable RF-wireless active glaucoma intraocular pressure monitor[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Circuits and Systems, 2010, 4(6): 340–349 doi: 10.1109/TBCAS.2010.2081364 CHEN G Z, CHAN I S, and LAM D C C. Capacitive contact lens sensor for continuous non-invasive intraocular pressure monitoring[J]. Sensors and Actuators A:Physical, 2013, 203(63): 112–118 doi: 10.1016/j.sna.2013.08.029 JANG C I, SHIN1 K S, KIM M J, et al. Effects of inner materials on the sensitivity and phase depth of wireless inductive pressure sensors for monitoring intraocular pressure[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2016, 108(10): 103701 doi: 10.1063/1.4943136 KOUHANI M H M, WEBER A, and LI W. Wireless intraocular pressure sensor using stretchable variable inductor[C]. 2017 IEEE 30th International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS), Las Vegas, USA, 2017: 557–560. LIU Lijuan, WANG Junbo, CHEN Deyong, et al. Non-invasive wireless and passive mems intraocular pressure sensor based on flexible substrate[J]. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2015, 748: 115–127 doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.748.115 NOPPER R, NIEKRAWIETZ R, and REINDL L. Wireless readout of passive LC sensors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2010, 59(9): 2450–2457 doi: 10.1109/TIM.2009.2032966 MATEEN F, MAEDLER C, ERRAMILLI S, et al. Wireless actuation of micromechanical resonators[J]. Microsystems&Nanoengineering, 2016, 2: 16036 doi: 10.1038/micronano.2016.36 XIANG Zhuolin, LIU Jingquan, and LEE Chengkuo. A flexible three-dimensional electrode mesh: an enabling technology for wireless brain-computer interface prostheses[J]. Microsystems&Nanoengineering, 2016, 2: 16012 doi: 10.1038/micronano.2016.12 JELLALI R, BERTRAND V, ALEXANDRE M, et al. Photoreversibility and biocompatibility of polydimethylsiloxane-coumarin as adjustable intraocular lens material[J]. Macromolecular Bioscience, 2017, 17(7): 1600495 doi: 10.1002/mabi.201600495 BALDWIN A and MENG E. A kirigami-based Parylene C stretch sensor[C]. 2017 IEEE 30th International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS), Las Vegas, USA, 2017: 227–230. HUANG Xian, LIU Yuhao, KONG Gilwoo, et al. Epidermal radio frequency electronics for wireless power transfer[J]. Microsystems&Nanoengineering, 2016, 2: 16052 doi: 10.1038/micronano.2016.52 MCDONALD J C, METALLO S J, and WHITESIDES G M. Fabrication of a configurable, single-use microfluidic device[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2001, 73(23): 5645–5650 doi: 10.1021/ac010631r -





 下载:
下载:
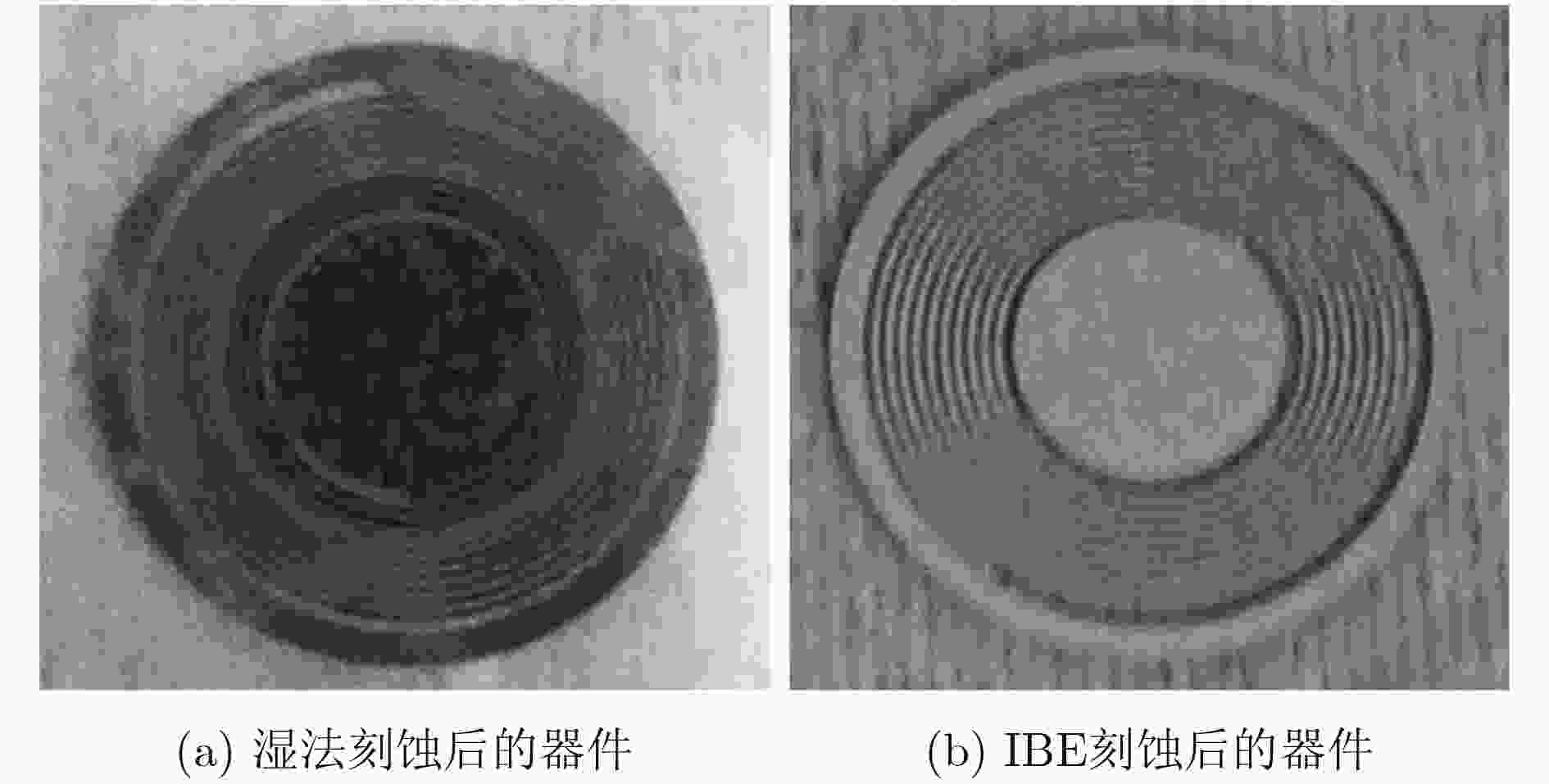
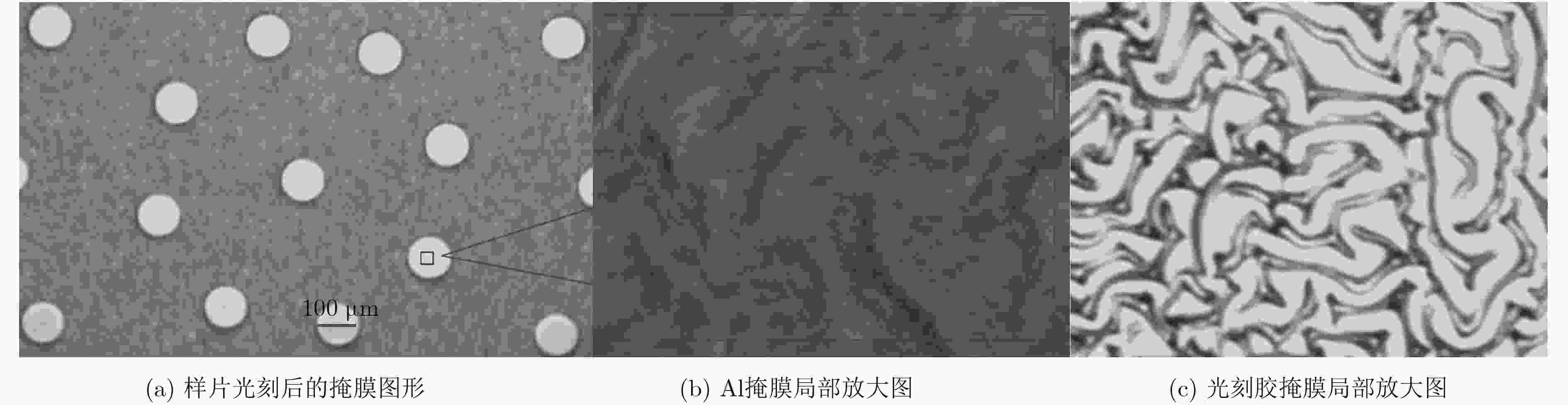


 下载:
下载:
