Flow Caching in Protocol Oblivious Forwarding Switches
-
摘要: 协议无感知转发支持任意协议的解析和处理,增强了软件定义网络的可编程能力。为提高转发性能,该文提出一种应用于协议无感知转发交换机的流缓存方法,通过识别匹配和动作的依赖关系,得到匹配字段的绝对位置,用以预先解析报文。为确保流缓存的加速效果,根据匹配类型与表项数量选择应用流缓存的流表。此外,该文对比了单流表缓存与多流表缓存对转发性能的提升,并提出了根据网络流量实际情况的自适应切换策略。通过扩展POFSwitch实现所提方法,并用实际规则与骨干网流量进行验证,应用流缓存后,交换机报文转发速率提升了220%。流缓存可以为可编程数据平面提供更高的转发性能。Abstract: Protocol Oblivious Forwarding (POF) supports the arbitrary protocol processing, enhancing the programmability of Software Defined Networking (SDN). In order to improve the forwarding performance, a flow caching method is proposed. To parse the packet in advance, absolute positions of matching fields are obtained by identifying the dependency of matching and actions. To guarantee the acceleration effect of flow caching, flow tables are selected according to their matching types and number of entries. In addition, the single-flow table cache and multi-flow table cache are compared and an adaptive switching strategy is proposed based on the actual situation of network traffic. The POFSwitch is extended to implement the proposed method and it is validated under the real rules and backbone traces. The switch packet forwarding rate is increased by 220% after applying flow caching. Flow caching can provide higher forwarding performance for programmable data planes.
-
表 1 依赖关系识别算法
算法1 依赖关系识别算法 $\operatorname{Dep} (e,F)$ (1) for each action $a$ in entry $e$ in reverse order (2) if $a\cdot g(F) \ne \varnothing$ (3) $\quad F = a\cdot g(F)$ (4) $\quad F = F + \{ {\rm{input \; fields \; of }}\; a\} $ (5) return $F$ 表 2 几种典型的匹配算法
匹配类型 LM EM LPM MM 匹配算法 线性 哈希 PartitionSort 类S-Trie $f\left( n \right)$ $O\left( 1 \right)$ $O\left( 1 \right)$ $O\left( {p \cdot \left( {d + \lg n} \right)} \right)$ $O\left( {d \cdot \lg n} \right)$ 表 3 流表选择算法
算法2 流表选择算法 $\operatorname{Select} (X)$ (1) label flow table $X$ as discovered (2) delete type (3) actions and merge duplicate entries (3) if $X$ is LPM or MM (4) if entry number of $X$ ${\rm{ > Thr}}$ (5) label $X$ as worth caching (6) for each entry $e$ in $X$ (7) let $Y\;$ as the table which $e$ leads (8) if $Y\;$ is not discovered (9) let $F'(Y\;) = {Φ} $ (10) recursively call $\operatorname{Select} (Y\;)$ (11) if $X$ is worth caching and $Y\;$ is worth caching (12) $F'(Y\;) = F'(Y\;) + \operatorname{Dep} (e,F(Y\;))$ (13) if $X$ is worth caching (14) let $F(X) = $match fields of $X$ (15) for each child table $Y\;$ worth caching (16) $F(X) = F(X) + F'(Y\;)$ -
MCKEOWN N, ANDERSON T, BALAKRISHNAN H, et al. OpenFlow: Enabling innovation in campus networks[J]. ACM SIGCOMM Computer Communication Review, 2008, 38(2): 69–74 doi: 10.1145/1355734.1355746 SONG Haoyu. Protocol-oblivious forwarding: Unleash the power of SDN through a future-proof forwarding plane[C]. Proceedings of the Second ACM SIGCOMM Workshop on Hot Topics in Software Defined Networking, New York, USA, 2013: 127–132. 李平, 王雷. 融合SDN的信息中心网络研究综述[J]. 网络新媒体技术, 2017, 6(6): 11–18LI Ping and WANG Lei. A survey of information-centric networking fusing SDN[J]. Journal of Network New Media, 2017, 6(6): 11–18 RYGIELSKI P, SELIUCHENKO M, KOUNEV S, et al. Performance analysis of SDN switches with hardware and software flow tables[C]. Proceedings of the 10th EAI International Conference on Performance Evaluation Methodologies and Tools on 10th EAI International Conference on Performance Evaluation Methodologies and Tools, Brussels, Belgium, 2017: 80–87. YINGCHAREONTHAWORNCHAI S, DALY J, LIU A X, et al. A sorted partitioning approach to high-speed and fast-update OpenFlow classification[C]. 2016 IEEE 24th International Conference on Network Protocols (ICNP), Singapore, 2016: 1–10. KATTA N, ALIPOURFARD O, REXFORD J, et al. CacheFlow: Dependency-aware rule-caching for software-defined networks[C]. Proceedings of the Symposium on SDN Research, New York, USA, 2016: 6: 1–6: 12. PFAFF B, PETTIT J, KOPONEN T, et al. The design and implementation of Open vSwitch[C]. 12th USENIX Symposium on Networked Systems Design and Implementation (NSDI 15), Oakland, USA, 2015: 117–130. CLAFFY K C. Internet traffic characterization[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], University of California, 1994: 90–91. JACKSON E J, WALLS M, PANDA A, et al. Softflow: A middlebox architecture for Open vSwitch[C]. 2016 Usenix Annual Technical Conference (USENIX ATC 16), Santa Clara, USA, 2016: 15–28. SHAHBAZ M, CHOI S, PFAFF B, et al. PISCES: A programmable, protocol-independent software switch[C]. Proceedings of the 2016 Conference on ACM SIGCOMM 2016 Conference, New York, USA, 2016: 525–538. SUN Quanying, XUE Yuhan, LI Shengru, et al. Design and demonstration of high-throughput protocol oblivious packet forwarding to support software-defined vehicular networks[J]. IEEE Access, 2017, 5: 24004–24011 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2767640 USTC-INFINITELAB. POFSwitch: The original protocol-oblivious forwarding (POF) switch by Huawei[OL]. https://github.com/USTC-INFINITELAB/POFSwitch, 2016. FLETCHER R. Practical Methods of Optimization[M]. John Wiley & Sons, 2000: 213–219. BAR-YOSSEF Z, JAYRAM T, KUMAR R, et al. Counting distinct elements in a data stream[C]. International Workshop on Randomization and Approximation Techniques in Computer Science, Cambridge, USA, 2002: 1–10. USTC-INFINITELAB. PCTRL: A POF controller extending from POX[OL]. https://github.com/USTC-INFINITELAB/PCTRL, 2017. CAIDA. The CAIDA anonymized Internet traces 2016 dataset[OL]. http://www.caida.org/data/passive/passive_2016_dataset.xml, 2018. UNIVERSITY OF OREGON. Route Views Project[OL]. http://www.routeviews.org/chicago.html, 2018. TAYLOR D E and TURNER J S. Classbench: A packet classification benchmark[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking(TON) , 2007, 15(3): 499–511 doi: 10.1109/TNET.2007.893156 -





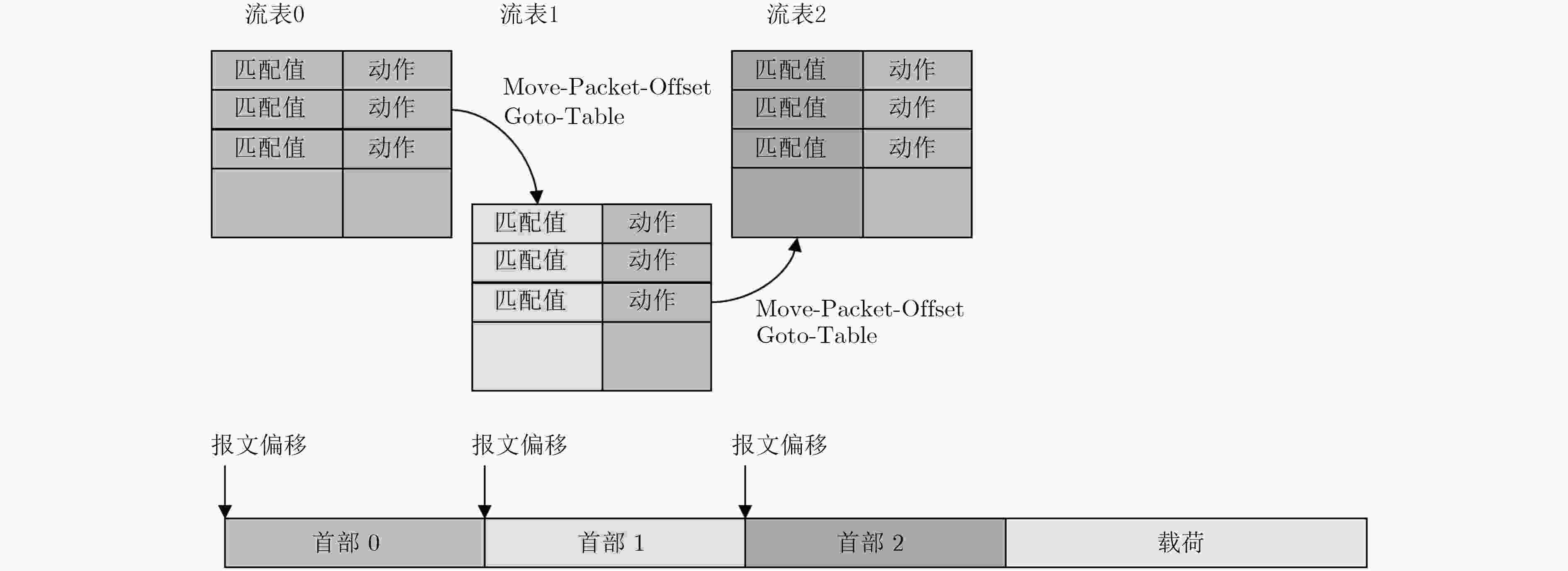
 下载:
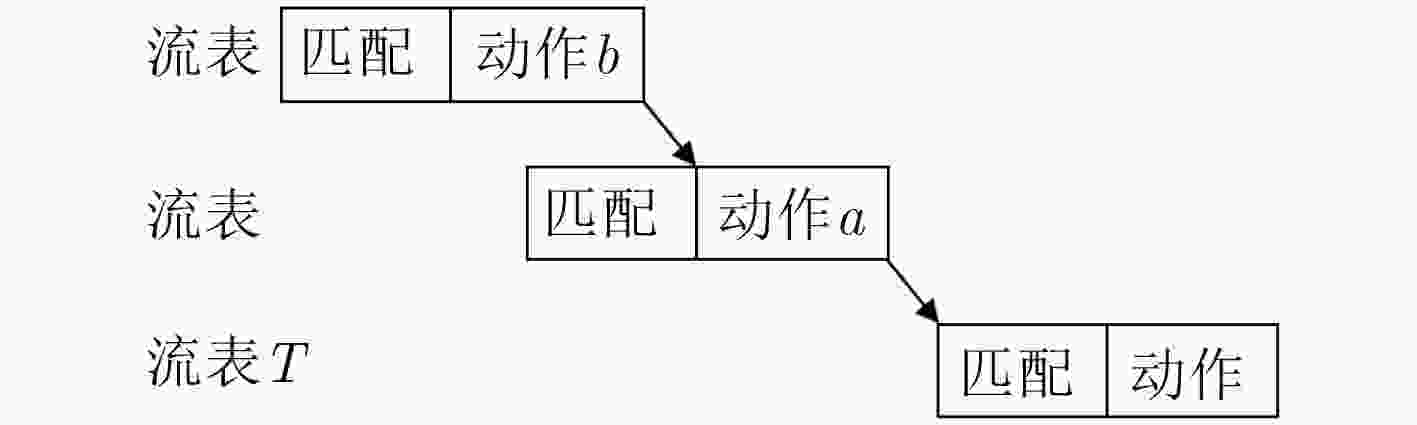
下载:
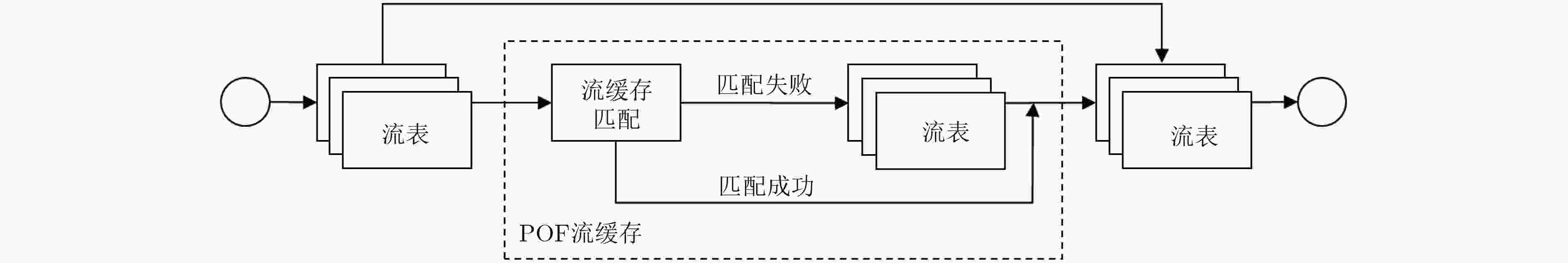
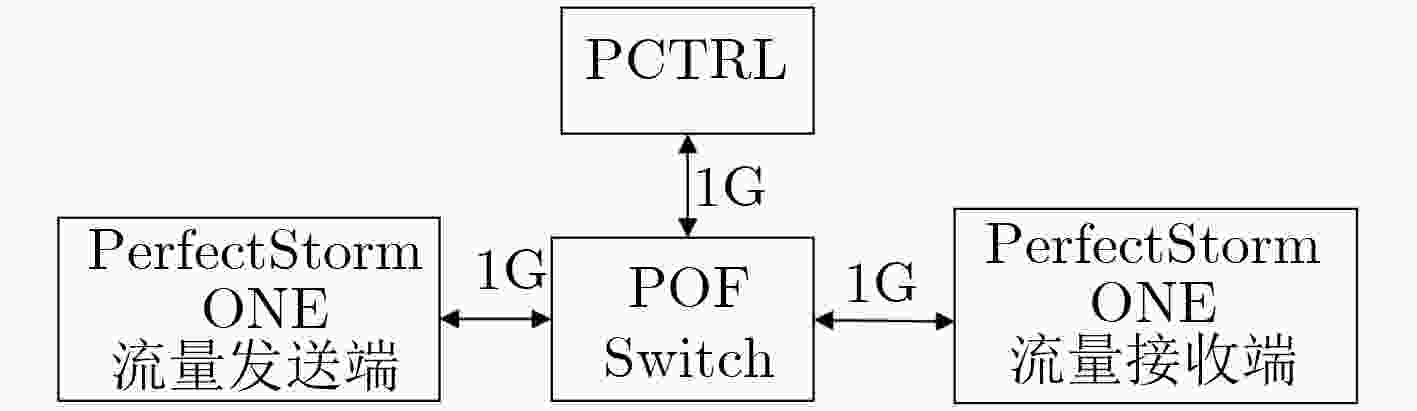
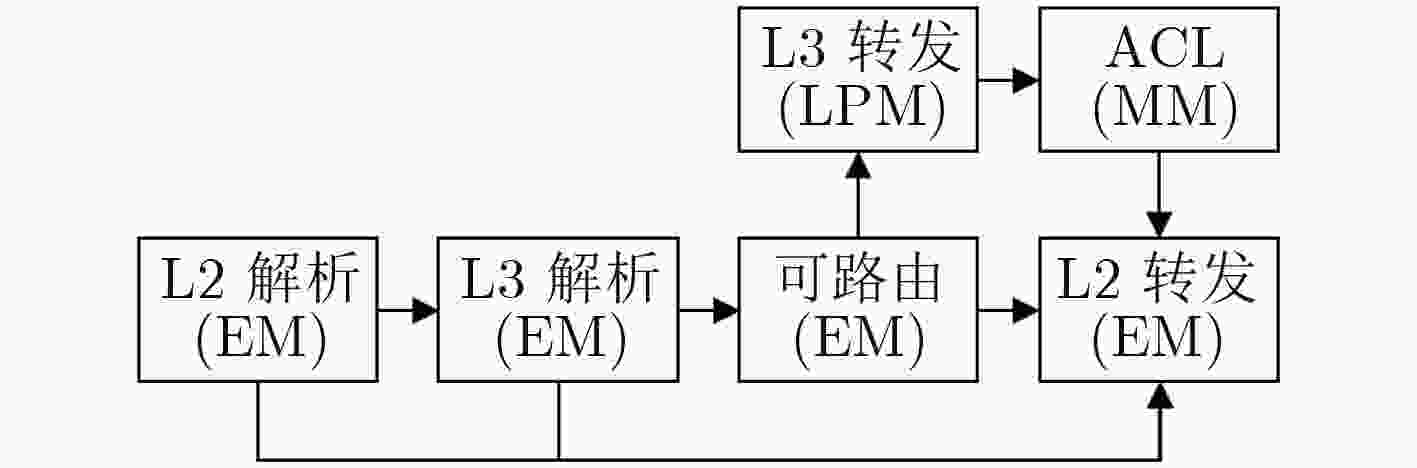
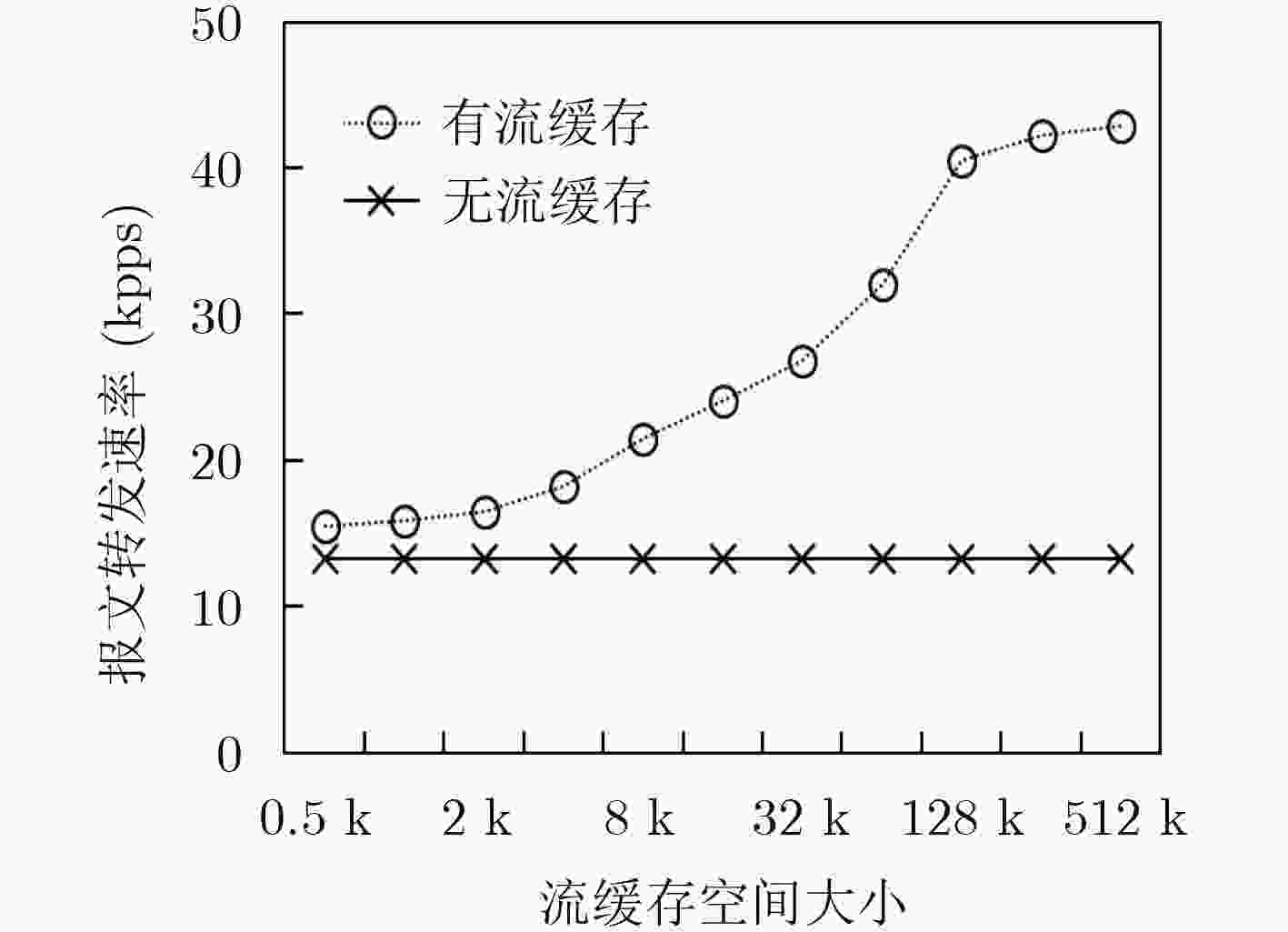
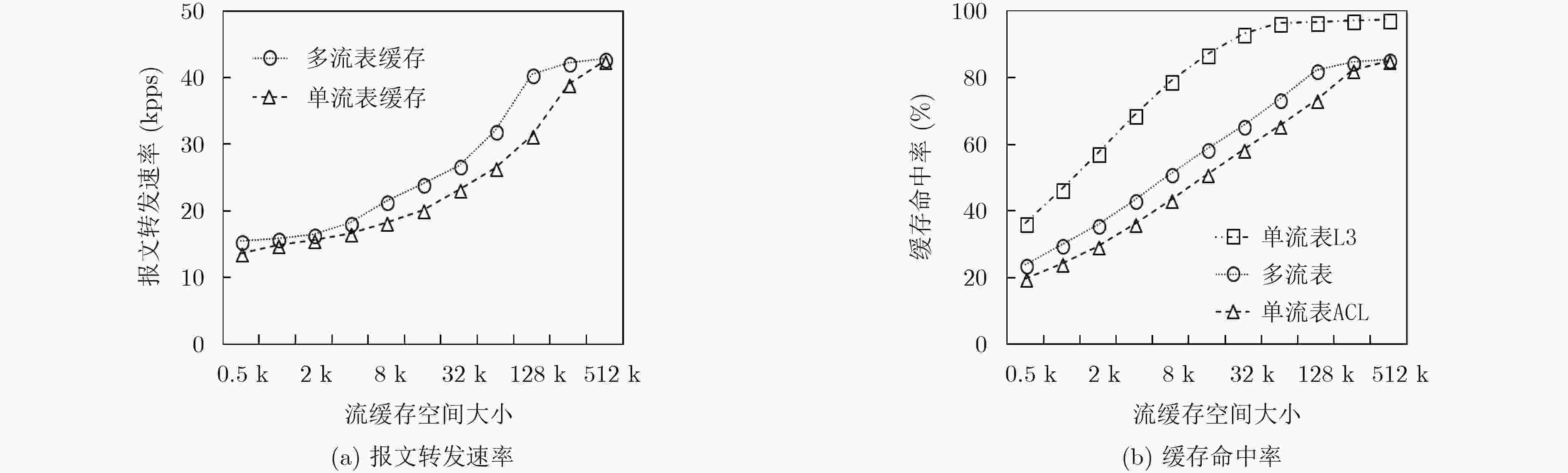


 下载:
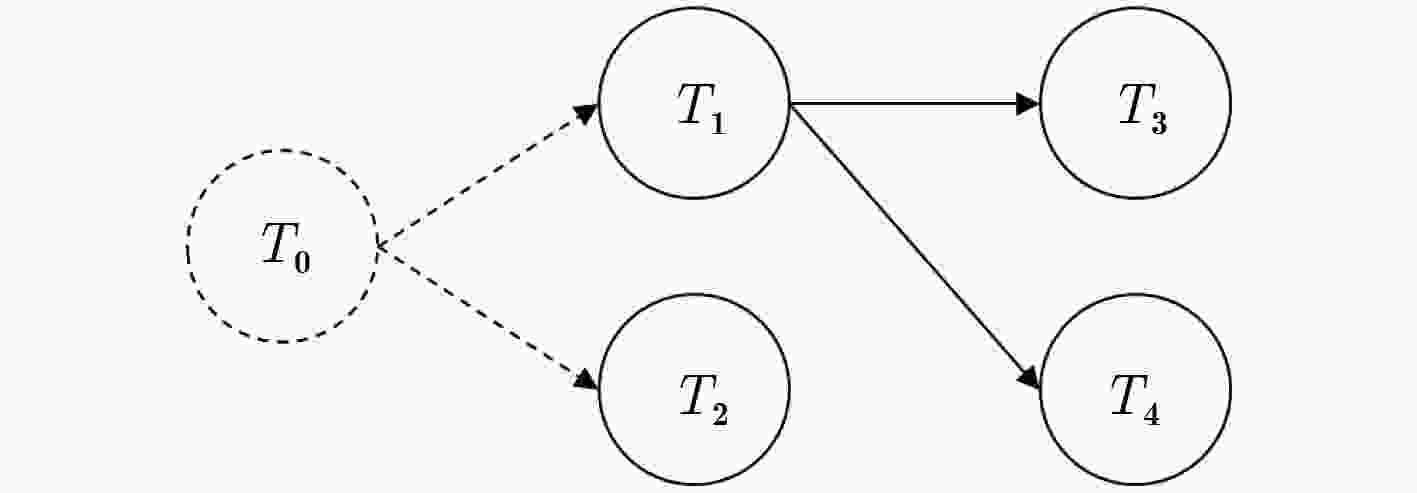
下载:
