A Deep Metric Learning Based Video Classification Method
-
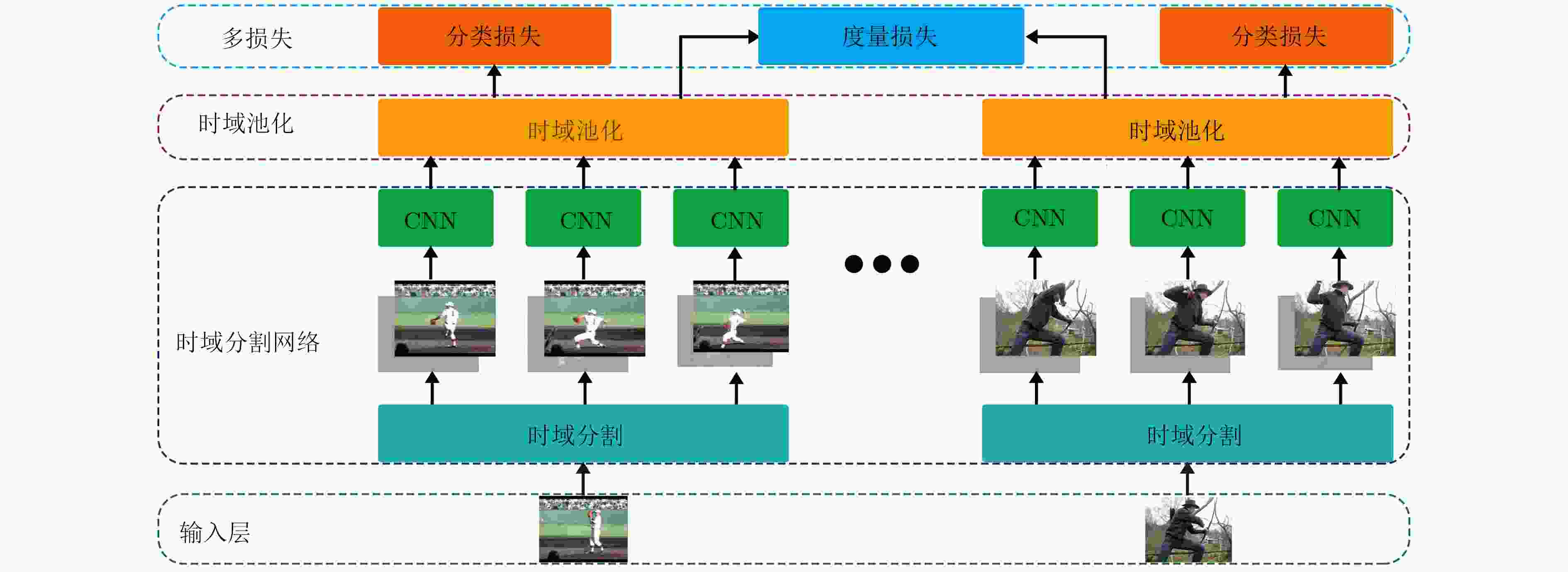
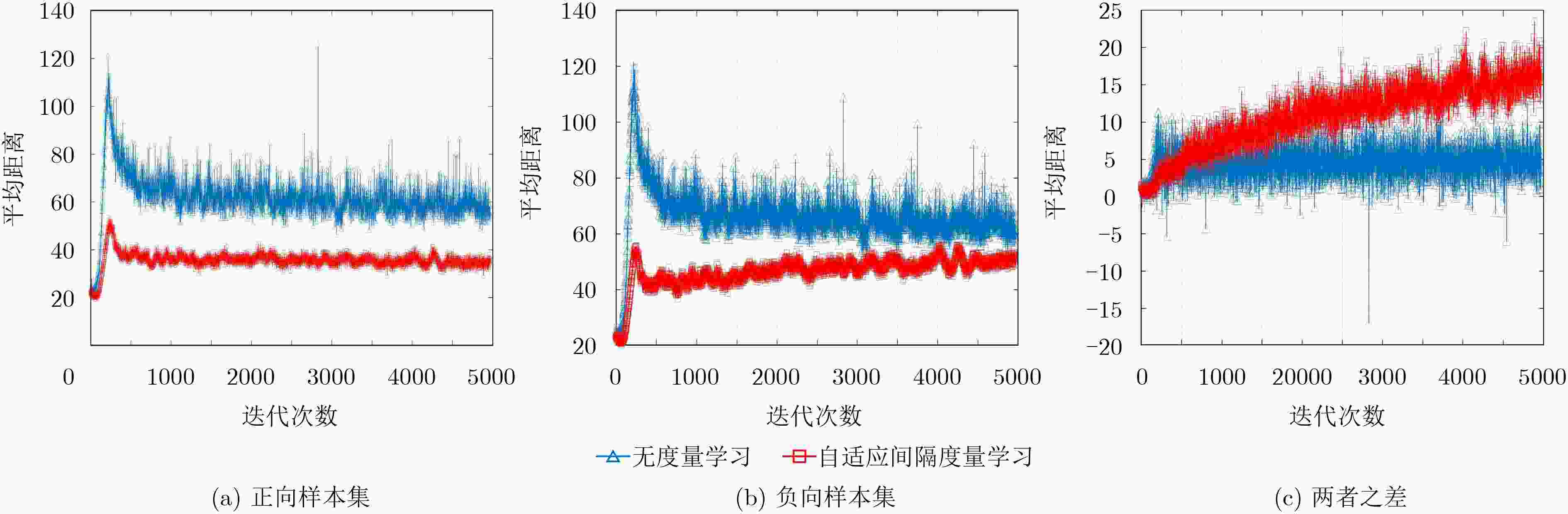
摘要: 针对视频分类中普遍面临的类内离散度和类间相似性较大而制约分类性能的问题,该文提出一种基于深度度量学习的视频分类方法。该方法设计了一种深度网络,网络包含特征学习、基于深度度量学习的相似性度量,以及分类3个部分。其中相似性度量的工作原理为:首先,计算特征间的欧式距离作为样本之间的语义距离;其次,设计一个间隔分配函数,根据语义距离动态分配语义间隔;最后,根据样本语义间隔计算误差并反向传播,使网络能够学习到样本间语义距离的差异,自动聚焦于难分样本,以充分学习难分样本的特征。该网络在训练过程中采用多任务学习的方法,同时学习相似性度量和分类任务,以达到整体最优。在UCF101和HMDB51上的实验结果表明,与已有方法相比,提出的方法能有效提高视频分类精度。Abstract: To solve the common problem of classification performance restriction caused by big intra-class variations and inter-class similarities in video classification domain, this paper proposes a deep metric learning based video classification method. The proposed method designs a deep network which contains three parts: feature learning, deep metric learning based similarity measure as well as classification. The principle of similarity measure is: Firstly, the Euclidean distance between features is calculated as the semantic distance between samples. Secondly, a margin distributing function is designed to dynamically allocate margin in the basis of the semantic distances. Finally, the difference of the sample semantic distance can be learned by calculating the loss and propagating it backwards so as to the network can automatically focus on the hard negative samples and more fully learn the characteristic of them. With a multi-task learning training method in the training stage, the similarity measure and classification can be learned jointly. Experimental results on UCF101 and HMDB51 show that the proposed method can effectively improve the classification precision.
-
Key words:
- Video classification /
- Deep learning /
- Adaptive margin /
- Deep metric learning /
- Multi-task learning
-
表 1 UCF101上时域池化的影响(%)
原始TSN TSN+时域池化 RGB 82.31) 83.2 Optical Flow 83.61) 82.9 RGB + Optical Flow 92.51) 92.8 注:1)比原论文中的分类精度低。也许是因为批量大小较小等原因,本文未能复现原论文的实验结果。 表 2 当
${{λ} _1}$ 固定为1时,${{λ} _2}$ 在数据集UCF101上的影响(%)${\lambda _2}$ 0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 mAP 92.7 93.1 93.8 不收敛 不收敛 表 3 不同间隔分配函数在UCF101上的性能(%)
函数 ${\alpha _{\rm{r}}}$ ${\alpha _{\lg }}$ ${\alpha _{\exp }}$ mAP 92.9 91.9 93.8 表 4 NFMML子结构在数据集UCF101上对分类性能的影响(%)
子结构 原始TSN TSN+时域池化 TSN+时域池化+度量学习 mAP 92.5 92.8 93.8 -
BRANSON S, VAN HORN G, PERONA P, et al. Improved bird species recognition using pose normalized deep convolutional nets[C]. Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference, Nottingham, British, 2014: 197–211. doi: 10.5244/C.28.87. ZHANG Ning, DONAHUE J, GIRSHICK R, et al. Part-based R-CNNs for fine-grained category detection[C]. European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 2014, 8689: 834–849. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-10590-1_54. KRAUSE J, JIN Hailin, YANG Jianchao, et al. Fine-grained recognition without part annotations[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA, 2015: 5546–5555. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2015.7299194. LIN Tsungyu, ROYCHOWDHURY A, and MAJI S. Bilinear CNN models for fine-grained visual recognition[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 1449–1457. CUI Yin, ZHOU Feng, LIN Yuanqing, et al. Fine-grained categorization and dataset bootstrapping using deep metric learning with humans in the loop[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 1153–1162. JI Shuiwang, XU Wei, YANG Ming, et al. 3D convolutional neural networks for human action recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis&Machine Intelligence, 2013, 35(1): 221–231 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2012.59 SIMONYAN K and ZISSERMAN A. Two-stream convolutional networks for action recognition in videos[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2014, 1(4): 568–576. MA Chihyao, CHEN Minhung, KIRA Z, et al. TS-LSTM and temporal-inception: exploiting spatiotemporal dynamics for activity recognition[OL]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1703.10667, 2017. IOFFE S and SZEGEDY C. Batch normalization: accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift[OL]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1502. 03167, 2015. WANG Limin, XIONG Yuanjun, WANG Zhe, et al. Temporal segment networks: Towards good practices for deep action recognition[J]. ACM Transactions on Information Systems, 2016, 22(1): 20–36 doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-46484-8_2 SONG Hyunoh, XIANG Yu, JEGELKA S, et al. Deep metric learning via lifted structured feature embedding[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 4004–4012. doi: 10.1109/cvpr.2016.434. YI Dong, LEI Zhen, LIAO Shengcai, et al. Deep metric learning for person re-identification[C]. International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Stockholm, Sweden, 2014: 34–39. CHEN Xingyu, LAN Xuguang, LIANG Guoqiang, et al. Pose-and-illumination-invariant face representation via a triplet-loss trained deep reconstruction model[J]. Multimedia Tools&Applications, 2017(7): 1–16 doi: 10.1007/s11042-017-4782-y BELL S and BALA K. Learning visual similarity for product design with convolutional neural networks[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2015, 34(4): 98–99 doi: 10.1145/2766959 SCHROFF F, KALENICHENKO D, and PHILBIN J. FaceNet: A unified embedding for face recognition and clustering[C]. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA, 2015: 815–823. NG Y H, HAUSKNECHT M, VIJAYANARASIMHAN S, et al. Beyond short snippets: Deep networks for video classification[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA, 2015: 4694–4702. doi: 10.1109/cvpr.2015.7299101. MCLAUGHLIN N, RINCON J M D, and MILLER P. Recurrent convolutional network for video-based person re-identification[C]. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 1325–1334. JIA Yangqing, SHELHAMER E, DONAHUE J, et al. Caffe: Convolutional architecture for fast feature embedding[C]. ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Orlando, USA, 2014: 675–678. SOOMRO K, ZAMIR A R, and SHAH M. UCF101: A dataset of 101 human actions classes from videos in the wild[OL]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1212. 0402, 2012. KUEHNE H, JHUANG H, STIEFELHAGEN R, et al. HMDB51: A Large Video Database for Human Motion Recognition[M]. Heidelberg, Berlin: Springer, 2013: 2556–2563. BRADSKI G. The opencv library[J]. Doctor Dobbs Journal, 2000, 25(11): 384–386. ZACH C, POCK T, and BISCHOF H. A Duality Based Approach for Realtime TV-L1 Optical Flow[M]. Heidelberg, Berlin: Springer, 2007: 214–223. DENG Jia, DONG Wei, SOCHER R, et al. ImageNet: A large-scale hierarchical image database[C]. Proceedings of Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, USA, 2009: 248–255. EVERINGHAM M, GOOL LV, WILLIAMS CKI, et al. The pascal visual object classes (VOC) challenge[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2010, 88(2): 303–338 doi: 10.1007/s11263-009-0275-4 CAI Zhuowei, WANG Limin, PENG Xiaojiang, et al. Multi-view super vector for action recognition[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, USA, 2014: 596–603. PENG Xiaojiang, WANG Limin, WANG Xingxing, et al. Bag of visual words and fusion methods for action recognition: Comprehensive study and good practice[J]. Computer Vision&Image Understanding, 2016, 150(C): 109–125 doi: 10.1016/j.cviu.2016.03.013 WANG Heng and SCHMID C. Lear-inria submission for the thumos workshop[C]. ICCV Workshop on Action Recognition with a Large Number of Classes, Sydney, Australia, 2013: 39–47. WANG Limin, QIAO Yu, and TANG Xiaoou. MoFAP: A multi-level representation for action recognition[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2016, 119(3): 254–271 doi: 10.1007/s11263-015-0859-0 SUN Lin, JIA Kui, YEUNG D Y, et al. Human action recognition using factorized spatio-temporal convolutional networks[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 4597–4605. WANG Limin, QIAO Yu, and TANG Xiaoou. Action recognition with trajectory-pooled deep-convolutional descriptors[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 4305–4314. VAROL G, LAPTEV I, and SCHMID C. Long-term temporal convolutions for action recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2018, 40(6): 1510–1517 doi: 10.1109/tpami.2017.2712608 -





 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:
