Cognitive Radio Network Downlink Power Allocation and Beamforming Method with Imperfect Channel State Information
-
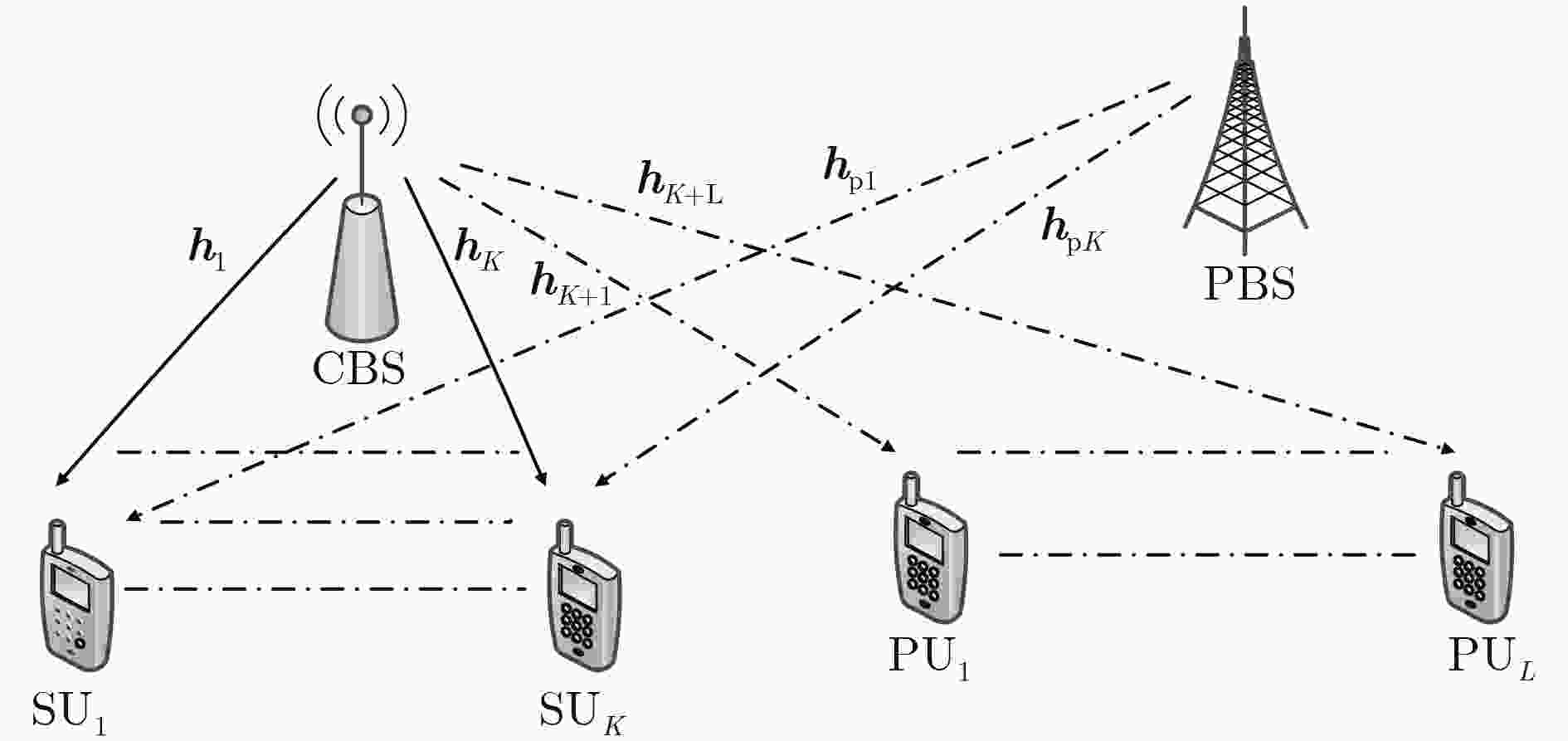
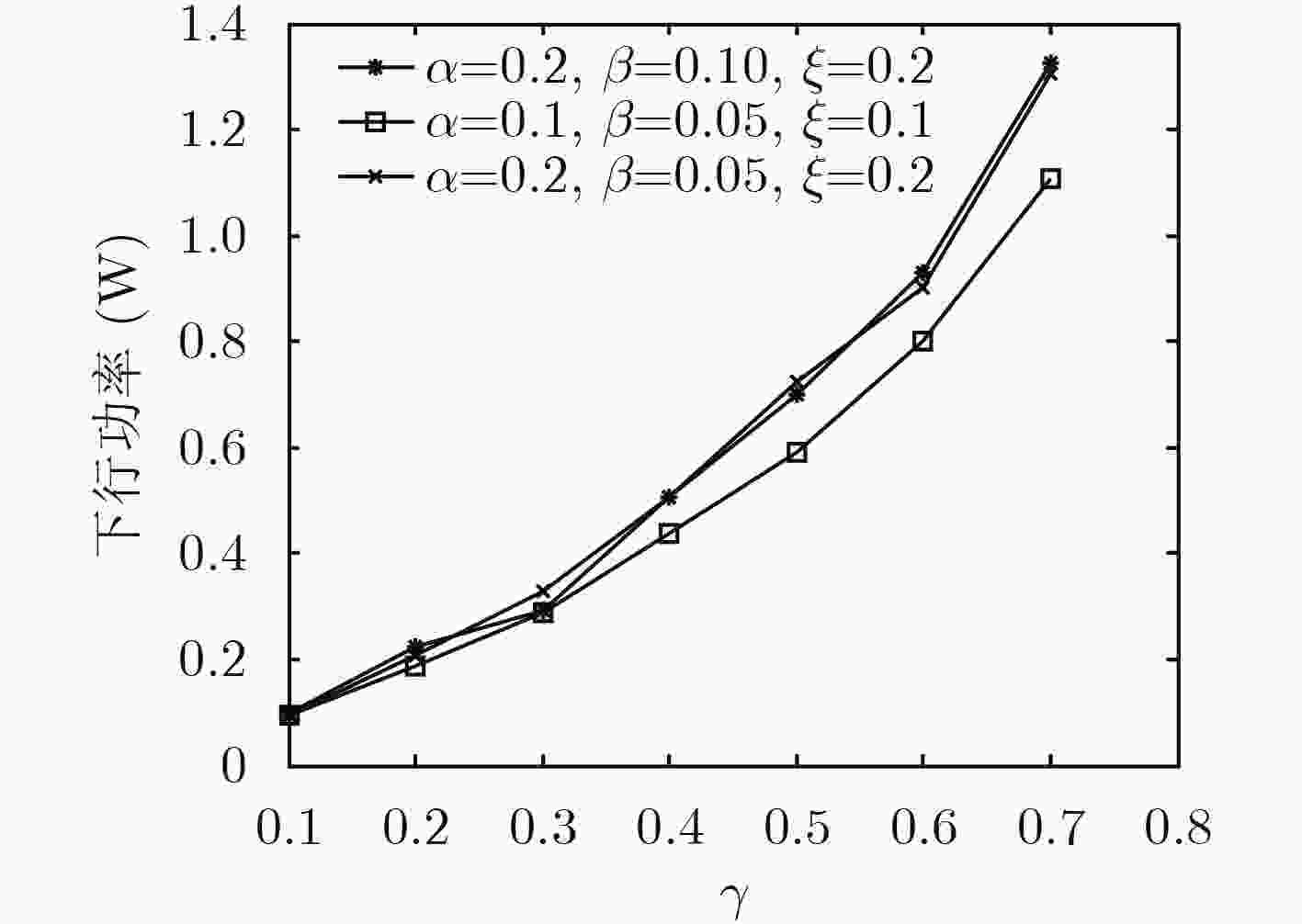
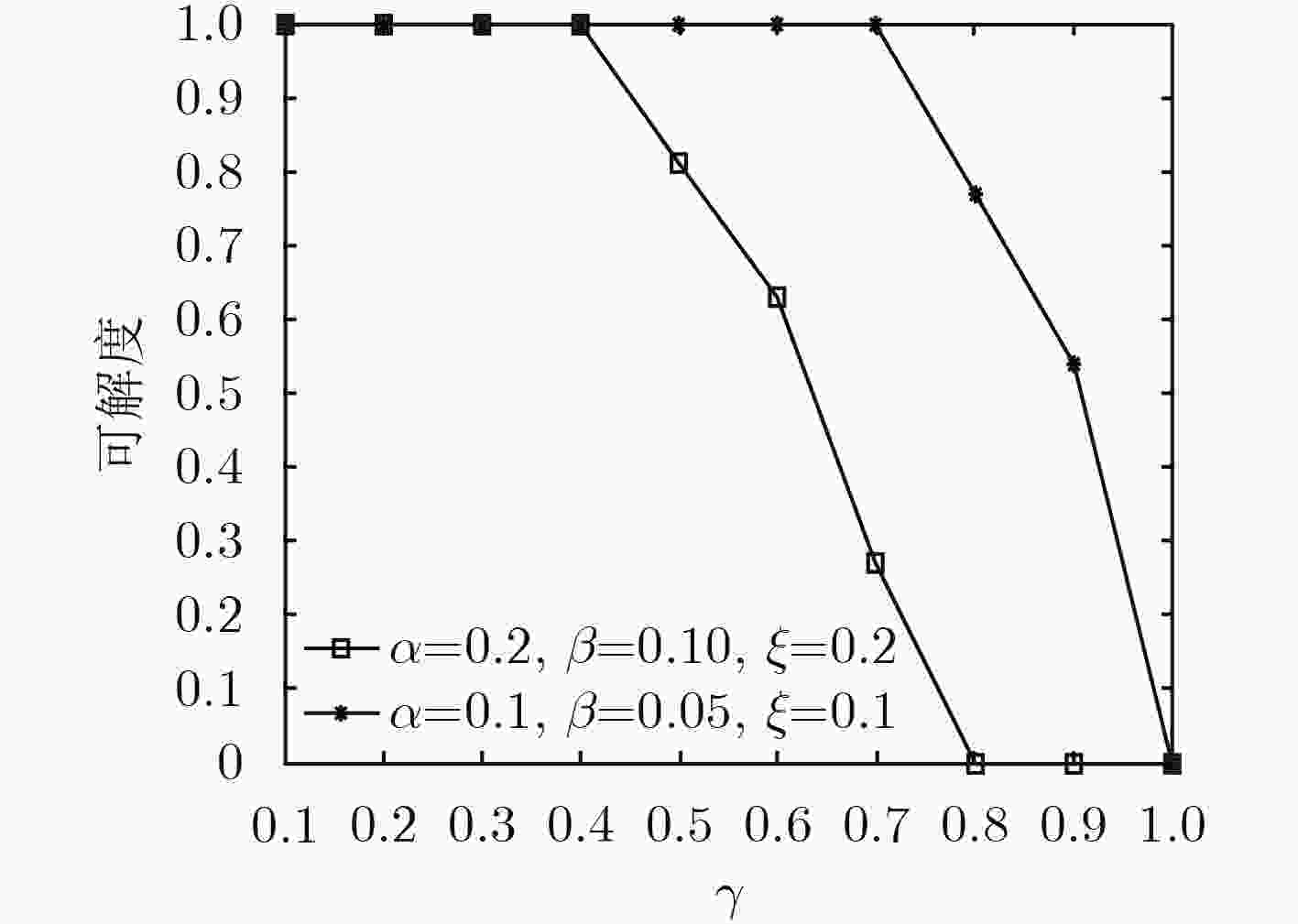
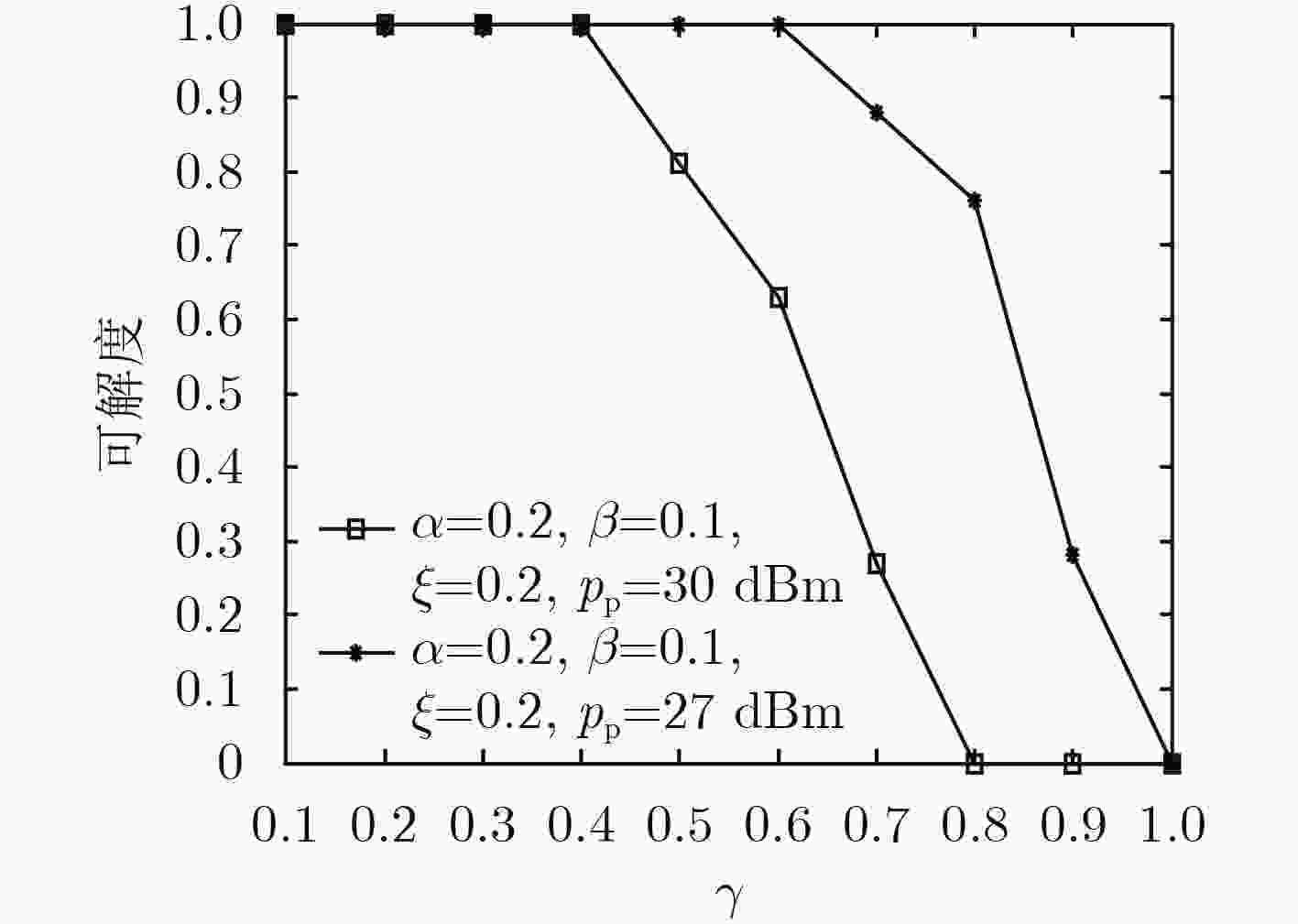
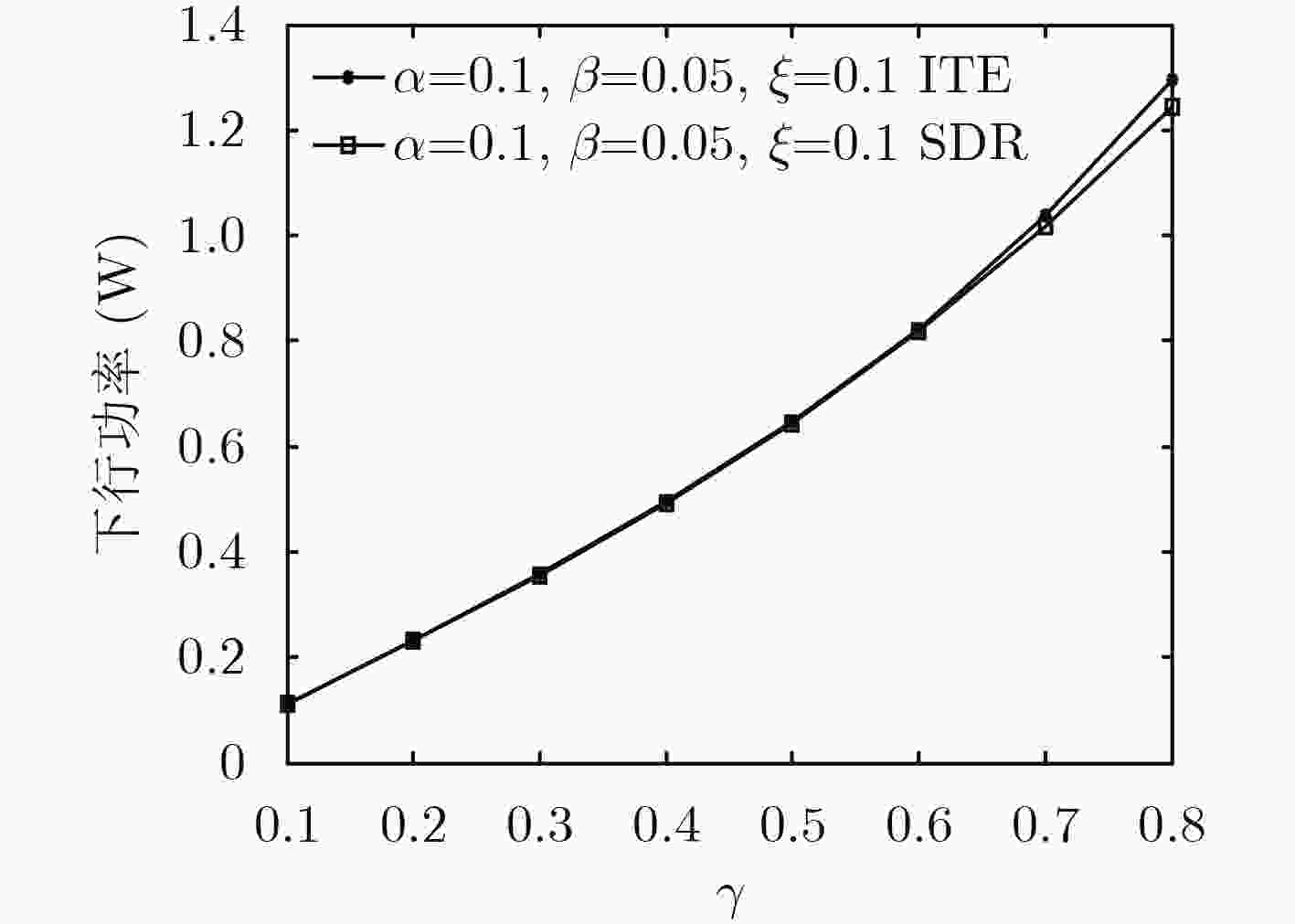
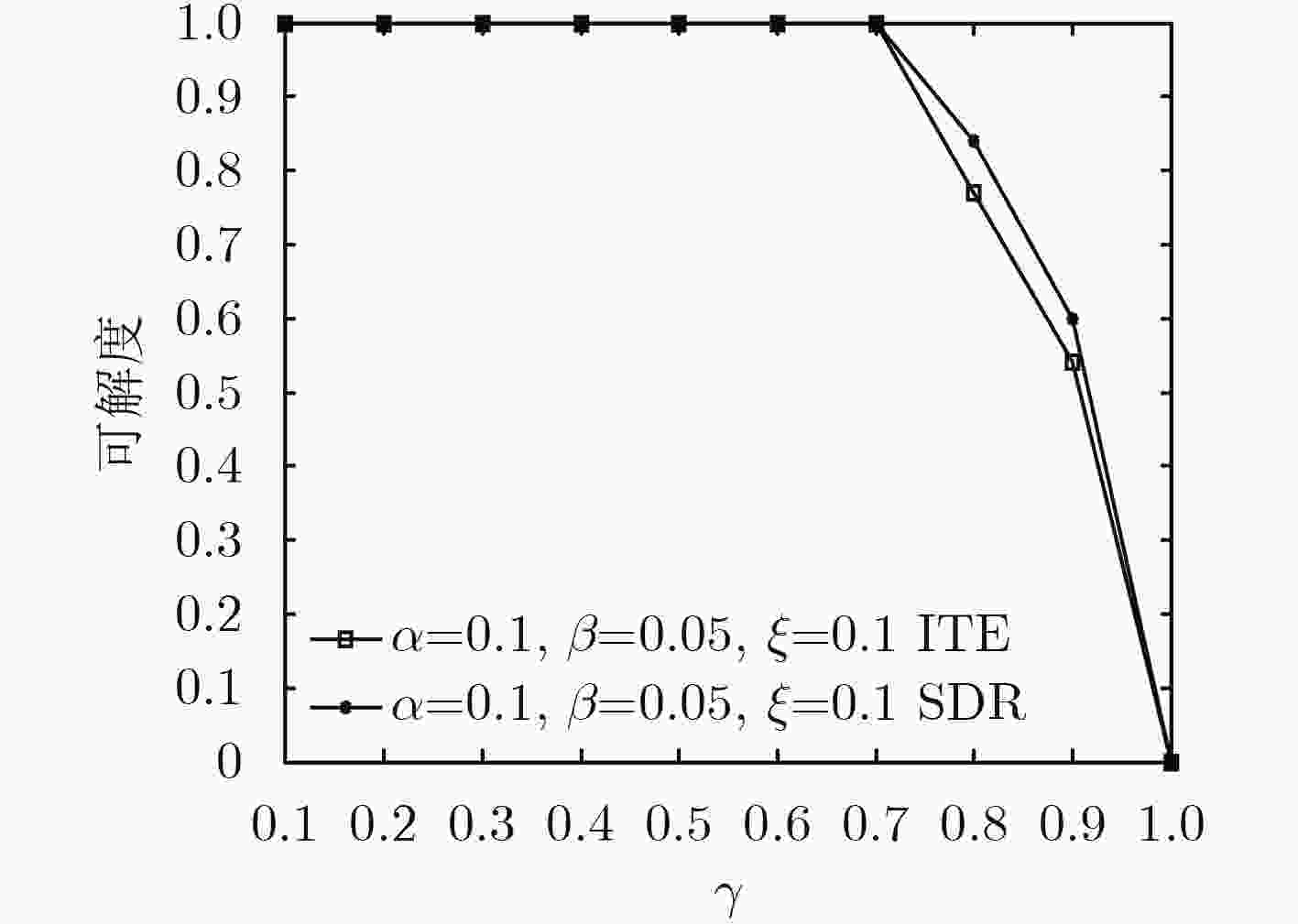
摘要: 针对非理想信道状态信息(CSI)条件下工作于underlay模式的认知无线网络(CRN)多用户下行功率分配和波束赋形研究中普遍存在的问题,包括忽略主网络(PN)对认知用户(SU)的干扰、传统的凸优化SDR方法对约束条件的近似要求以及实现算法复杂、实用性受限等,首先建立CRN模型,增添PN对SU的干扰项,而后在非理想CSI的最差条件下形成优化问题。再通过Lagrange对偶对问题的约束条件进行变换,并基于变换后的问题形式,利用上行和下行的对偶特性,引入虚拟功率,将优化问题转换为上行功率分配和波束赋形问题,进一步得到简便、快速和实用的迭代算法。数值仿真显示,算法收敛很快。并且发现非理想CSI引起的误差不仅对下行功率影响明显而且还改变优化问题的可行解区域;PN基站(PBS)的发送功率的变化对可行解区域有显著的影响。Abstract: Some problems of multi-user downlink power allocation and beamforming in a underlay Cognitive Radio Network (CRN) with imperfect Channel State Information (CSI) are addressed. They include ignoring the interferences of the Primary Network (PN) to the Secondary Users (SU), conventional SDR algorithm of convex optimization needing the constraint approximation, the high complexity of the algorithm, and implemented with difficulty, etc. Firstly the term of interference of the PN to the SU is added to the CRN model. The optimization problem is formulated with the worst-case imperfect CSI. Next the constraints of the problem are transformed by means of Lagrange duality. Then, based on the form of the problem, the simple, fast and practical iterative algorithm is obtained by utilizing the duality of uplink-downlink, introducing virtual power, and transforming the optimization problem into the problem of uplink power allocation and beamforming. Numerical simulation results show that it converges faster. It is also found that the errors of the imperfect CSI not only influence the downlink power but also change the feasibility region. The variation of transmitting power of the PN Base Station (PBS) could affect the feasibility region notably.
-
表 1 不同收敛门限下的迭代次数
序号 1 2 3 4 5 收敛门限 $\delta $ 10–3 10–4 10–5 10–6 10–7 迭代次数 $N$ 11 17 25 47 67 -
DENKOVSKI D, RAKOVIC V, ATANASOVSKI V, et al. Generic multiuser coordinated beamforming for underlay spectrum sharing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2016, 64(6): 2285–2298 doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2016.2561272 ZHANG Yu, DALLANESE E, and GIANNAKIS G B. Distributed optimal beamformers for cognitive radios robust to channel uncertainties[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2012, 60(12): 6495–6508 doi: 10.1109/TSP.2012.2218240 WAJID I, PESAVENTO M, ELDAR Y C, et al. Robust downlink beamforming with partial channel state information for conventional and cognitive radio networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2013, 61(14): 3656–3670 doi: 10.1109/TSP.2013.2265682 JEONG Y, QUEK T Q S, and SHIN H. Downlink beamforming optimization for cognitive underlay networks[C]. International Symposium On Information Theory & Its Applications, Taichung, 2010: 934–939. doi: 10.1109/ISITA.2010.5649545. MA Shuai and SUN Dechun. Chance constrained robust beamforming in cognitive radio networks[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2013, 17(1): 67–70 doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2012.112812.121829 HUANG Yongwei and PALOMAR D P. Rank-constrained separable semidefinite programming with applications to optimal beamforming[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2010, 58(2): 664–678 doi: 10.1109/TSP.2009.2031732 NOH J H and OH S J. Beamforming in a multi-user cognitive radio system with partial channel state information[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2013, 12(2): 616–625 doi: 10.1109/TWC.2012.121812.111897 TSAKMALIS A, CHATZINOTAS S, and OTTERSTEN B. Centralized power control in cognitive radio networks using modulation and coding classification feedback[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 2016, 2(3): 223–237 doi: 10.1109/TCCN.2016.2613562 XU Lei, WANG Ping, LI Qianmu, et al. Call admission control with inter-network cooperation for cognitive heterogeneous networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2017, 16(3): 1963–1973 doi: 10.1109/TWC.2017.2657757 TSAKMALIS A, CHATZINOTAS S, and OTTERSTEN B. Interference constraint active learning with uncertain feedback for cognitive radio networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2017, 16(7): 4654–4668 doi: 10.1109/TWC.2017.2701361 XU Yongjun, ZHAO Xiaohui, and LIANG Y C. Robust power control and beamforming in cognitive radio networks: a survey[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys&Tutorials, 2015, 17(4): 1834–1857 doi: 10.1109/COMST.2015.2452414 DHIFALLAH O, DAHROUJ H, AL-NAFFOURI T, et al. Decentralized SINR balancing in cognitive radio networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2017, 66(4): 3491–3496 doi: 10.1109/TVT.2016.2587753 TONG Xue, DONG Xiaodai, and SHI Yi. Resource allocation strategy for multi-user cognitive radio systems: Iocation-aware spectrum access[J].IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2017, 66(1): 884–889 doi: 10.1109/TVT.2016.2531738 PESAVENTO M, CIOCHINA D, and GERSHMAN A B. Iterative dual downlink beamforming for cognitive radio networks[C]. Fifth International Conference on Cognitive Radio Oriented Wireless Networks & Communications, Cannes, France, 2010: 1–5. doi: 10.4108/ICST.CROWNCOM2010.9247. BOYD S and VANDENBERGHE L. Convex Optimization [M]. New York, USA: Cambridge University Press, 2004: 136–138, 234–236. doi: 10.1017/CBO9780511804441. 张贤达. 矩阵分析与应用[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2004: 491–492.ZHANG Xianda. Matrix Analysis and Applications[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2004: 491–492. GRANT M, BOYD S, and YE Y. CVX: MATLAB software for disciplined convex programming[OL]. http://www.stanford.edu/boyd/cvx/V.1.0RC3, 2009. 曹杰, 廖勇, 沈轩帆. 基于QoS的多小区下行TDD大规模MIMO系统顽健波束成形[J]. 通信学报, 2017, 38(11): 44–53 doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2017218CAO Jie, LIAO Yong, and SHENG Xuanfan. Robust beamforming for multicell downlink TDD massive MIMO system based on QoS[J]. Journal on Communications, 2017, 38(11): 44–53 doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2017218 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
