Sensor Search Based on Sensor Similarity Computing in the Internet of Things
-
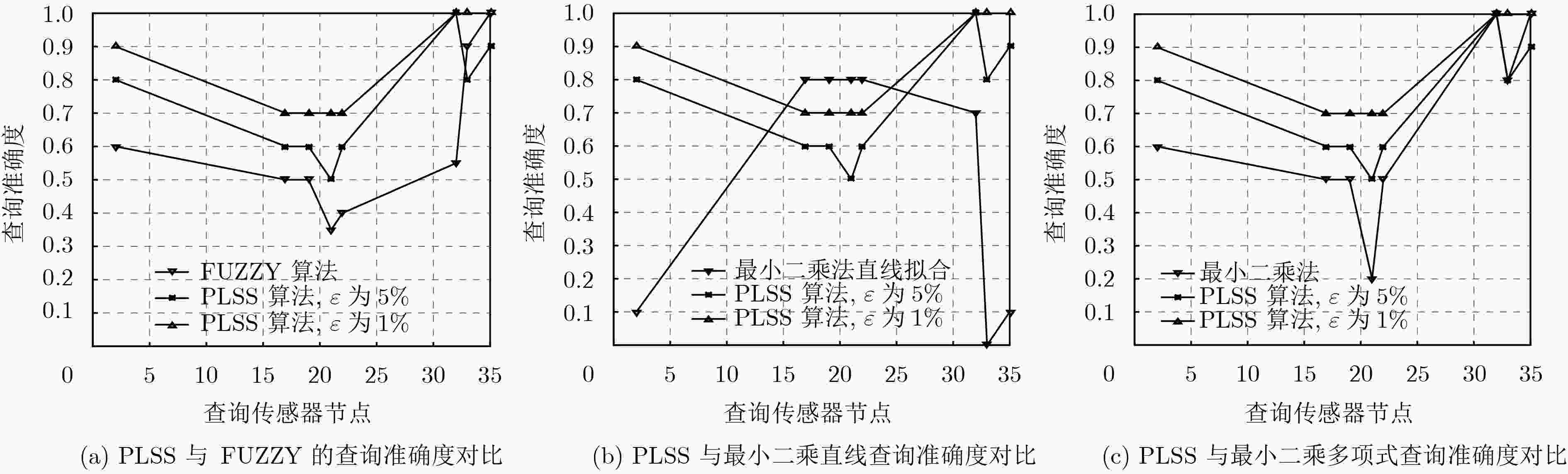
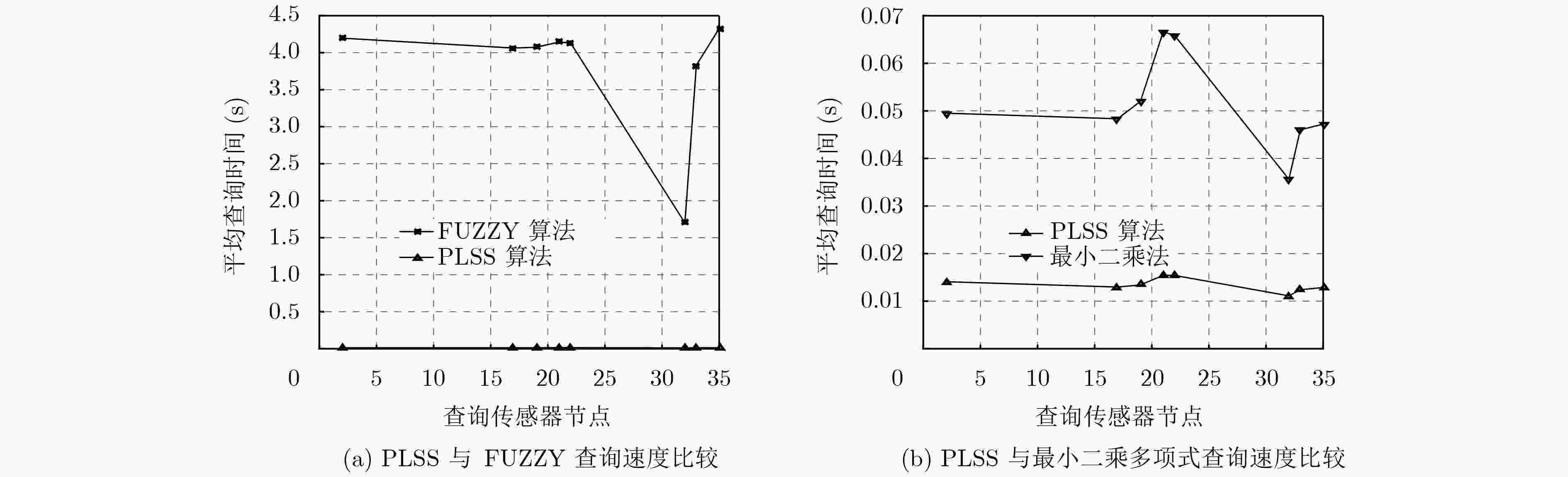
摘要: 物联网逐渐成为学术界研究的热点领域,无处不在的传感器设备促进了传感器搜索服务的产生。物联网中搜索的强时空性、海量数据的异构性与传感器节点的资源受限性,给物联网搜索引擎高效地查询传感器提出了挑战。该文提出基于传感器定量数值的线性分段拟合相似性(PLSS)搜索算法。PLSS算法通过分段和线性拟合的方法,构建传感器定量数值的相似性计算模型,从而计算传感器的相似度,根据相似度查找最相似的传感器集群。与模糊集(FUZZY)算法和最小二乘法相比,PLSS算法平均查询精度和查询效率较高。与原数据相比,PLSS算法的存储开销至少降低了两个数量级。Abstract: The Internet of Things (IoT) is becoming a hot research area, and tens of billions of devices are being connected to the Internet which are advancing on the sensor search service. IoT features (searches are strong spatiotemporal variability, limited resources of the sensor, and mass heterogeneous dynamic data) raise a challenge to the search engines for efficiently and effectively searching and selecting the sensors. In this paper, Piecewise-Linear fitting Sensor Similarity (PLSS) search method is proposed. Based on the content values, PLSS calculates the sensor similarity models to search most similarity sensors. PLSS improves the accuracy and efficiency of search compared with FUZZY set algorithm (FUZZY) and least squares method. PLSS storage costs are at least two order of magnitude less than raw data.
-
表 1 数据存储开销分析
传感器1 传感器20 数据个数统计 原数据
(时间,传感器值)1317×2 2059×2 6.752×103 FUZZY算法
(传感器平均数据密度函数)16×4×10 20×4×10 2.400×103 FUZZY算法
(传感器平均数据斜率密度函数)10×4×10 14×4×10 最小二乘多项式拟合算法
(传感器函数系数)9 9 1.800×10 PLSS算法
(传感器函数系数)16 25 4.100×10 -
BELLO O and ZEADALLY S. Intelligent device-to-device communication in the internet of things[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2016, 10(3): 1172–1182 doi: 10.1109/JSYST.2014.2298837 EVANS D. The Internet of things: How the next evolution of the internet is changing everything[C]. Cisco Internet Business Solutions Group, San Francisco, USA, 2011. RIBEIRO M, GROLINGER K, and CAPRETZ M A M. MLaaS: Machine learning as a service[C]. 2015 IEEE 14th International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications., Miami, USA, 2015: 896–902. LI Shancang, LI Daxu, and ZHAO Shanshan. The internet of things: A survey[J]. Information Systems Frontiers, 2015, 17(2): 243–259 doi: 10.1007/s10796-014-9492-7 张普宁. 面向物联网搜索服务的实体状态匹配估计方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 北京邮电大学, 2017.ZHANG Puning. Research on entity state matching estimation method towards search service in the internet of things[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2017. 于海宁, 张宏莉, 方滨兴, 等. 物联网中物理实体搜索服务的研究[J]. 电信科学, 2012, 28(10): 111–119 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0801.2012.10.019YU Haining, ZHANG Hongli, FANG Binxing, et al. Research on search service for physical entities in the internet of things[J]. Telecommunications Science, 2012, 28(10): 111–119 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0801.2012.10.019 WU Dapeng, HE Jing, WANG Hongguang, et al. A hierarchical packet forwarding mechanism for energy harvesting wireless sensor networks[J]. IEEE Communication Magazine, 2015, 53(8): 92–98 doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2015.7180514 LI Dongsheng, ZHANG Wanxin, SHEN Siqi, et al. SES-LSH: Shuffle-efficient locality sensitive hashing for distributed similarity search[C]. 2017 IEEE 24th International Conference on Web Services, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 822–827. ZHAO Xujun, ZHANG Jifu, and QIN Xiao. kNN-DP: Handling data skewness in kNN joins using mapreduce[J].IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2017, 29(3): 600–613 doi: 10.1109/TPDS.2017.2767596 蒋翠清, 疏得友, 段锐. 基于用户时空相似性的位置推荐算法[J]. 计算机工程, 2018, 44(7): 177–182 doi: 10.19678/j.issn.1000-3428.0047996JIANG Cuiqing, SHU Deyou, and DUAN Rui. Location recommendation algorithm based on spatial-temporal similarity of user[J]. Computer Engineering, 2018, 44(7): 177–182 doi: 10.19678/j.issn.1000-3428.0047996 张普宁, 刘元安, 吴帆, 等. 物联网中适用于内容搜索的实体状态匹配预测方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2015, 37(12): 2815–2820 doi: 10.11999/JEIT150191ZHANG Puning, LIU Yuanan, WU Fan, et al. An entity state matching prediction method for content-based search in the internet of things[J]. Journal of Electronics&Information Technology, 2015, 37(12): 2815–2820 doi: 10.11999/JEIT150191 ELAHI B M, ROMER K, OSTERMAIER B, et al. Sensor ranking: A primitive for efficient content-based sensor search[C]. International Conference on Information Processing in Sensor Networks, San Francisco, USA, 2009: 217–228. ROMER K, OSTERMAIER B, OSTERMAIER F, et al. Real-time search for real-world entities: A survey[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2010, 98(11): 1887–1902 doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2010.2062470 ZHANG Puning, LIU Yanan, WU Fan, et al. Low-overhead and high-precision prediction model for content-based sensor search in the internet of things[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2016, 20(4): 720–723 doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2016.2521735 EBRAHIMI M, SHAFIEIBAVANI E, WONG R K, et al. An adaptive meta-heuristic search for the internet of things[J]. Future Generation Computer Systems, 2017, 76(11): 486–494. TRUONG C, ROMER K, and CHEN K. Fuzzy-based sensor search in the web of things[C]. 2012 3rd International Conference on the Internet of Things, Wuxi, China, 2012: 127–134. ZHUKOV V and KOMAROV M. Semantic control method of the internet of things based on linked open data[C]. 2017 IEEE 19th Conference on Business Informatics, Thessaloniki, Greece, 2017: 1–4. Intel Berkeley Research lab. Intel berkeley research lab sensors data[OL]. http://db.csail.mit.edu/labdata/labdata.html. 2004.10. DIAS G M, BELLALTA B, and OECHSNER S. A survey about prediction-based data reduction in wireless sensor networks[J]. ACM Computing Surveys, 2016, 49(3): 58. -





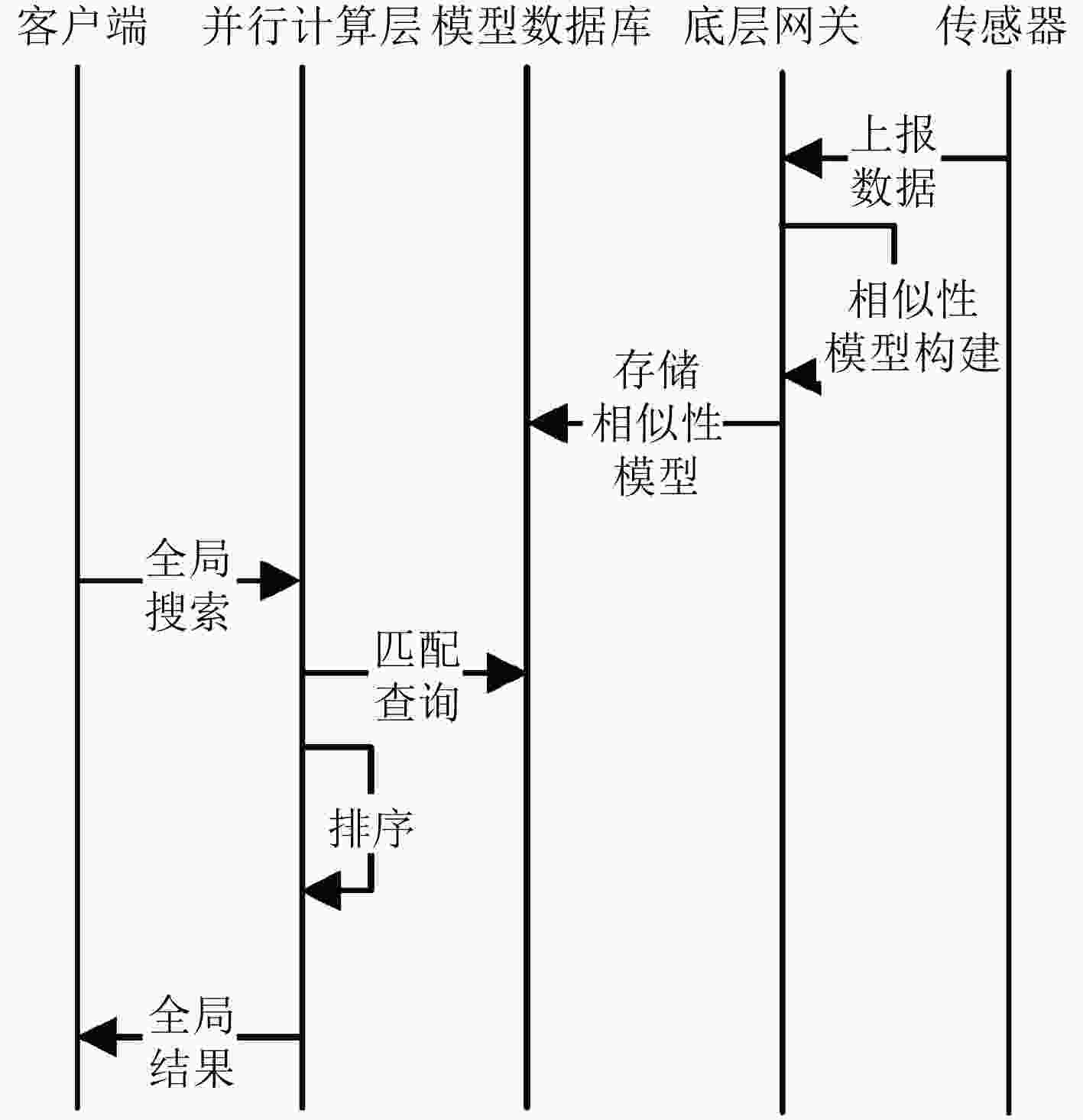
 下载:
下载:
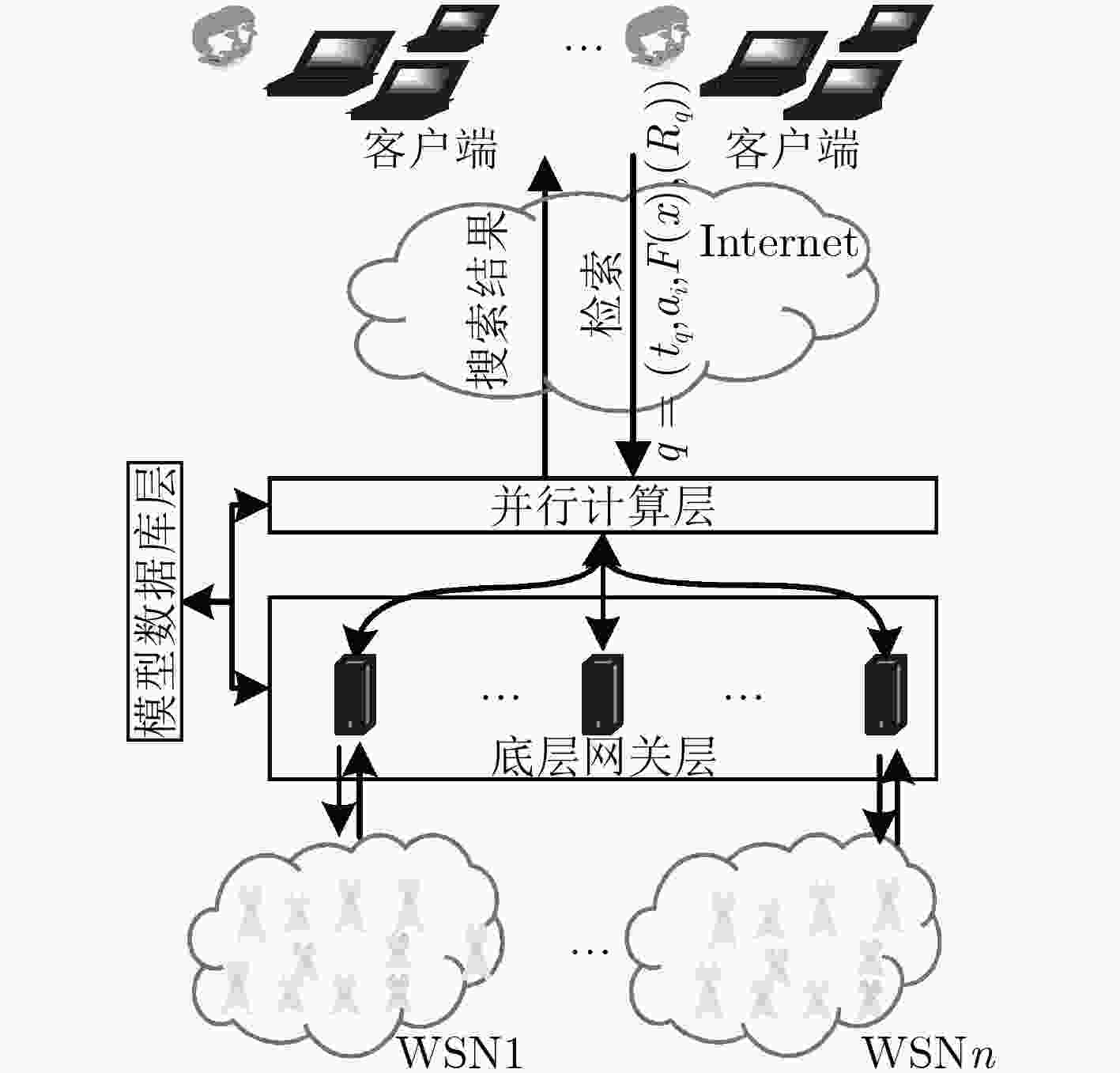
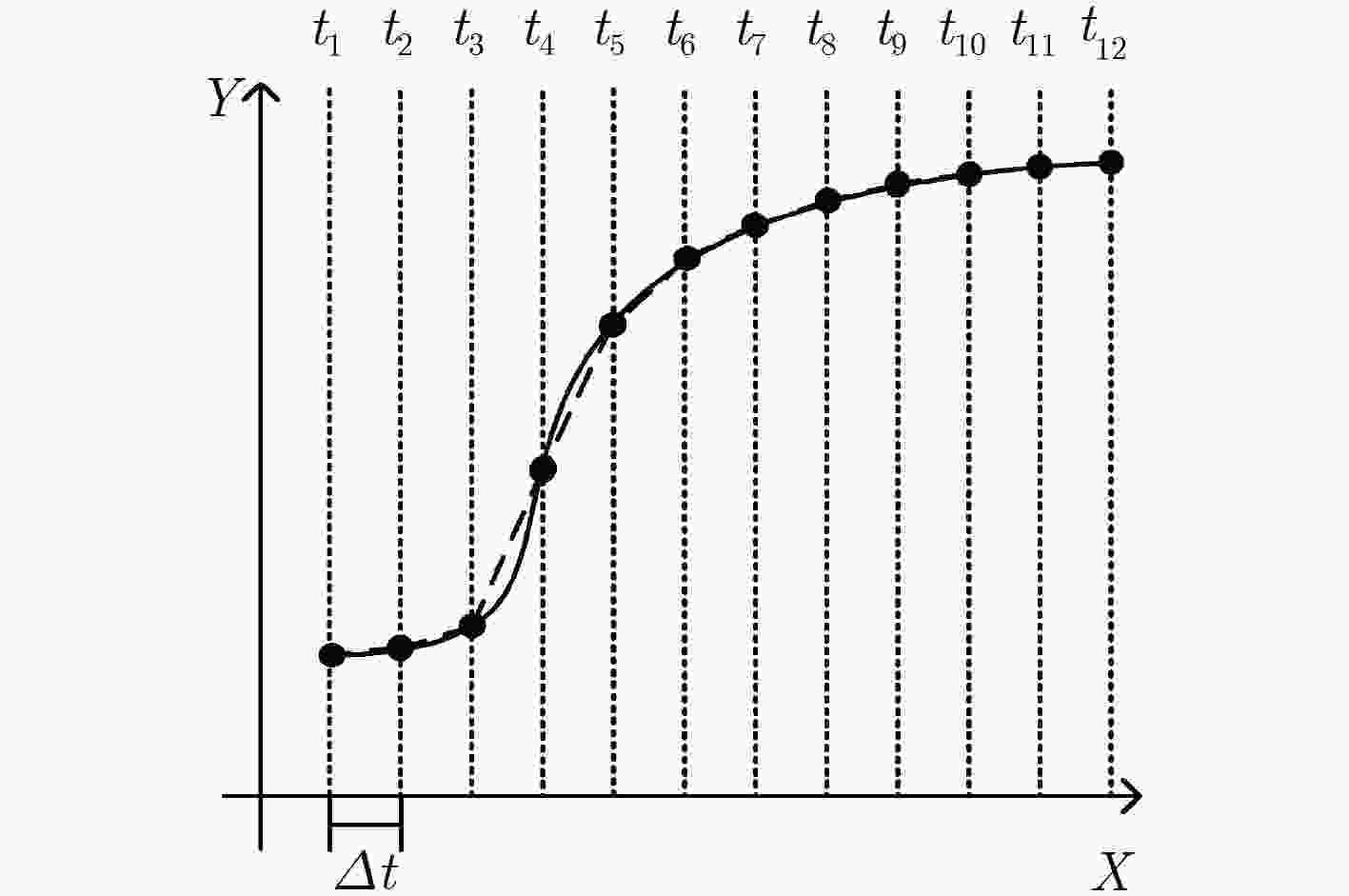
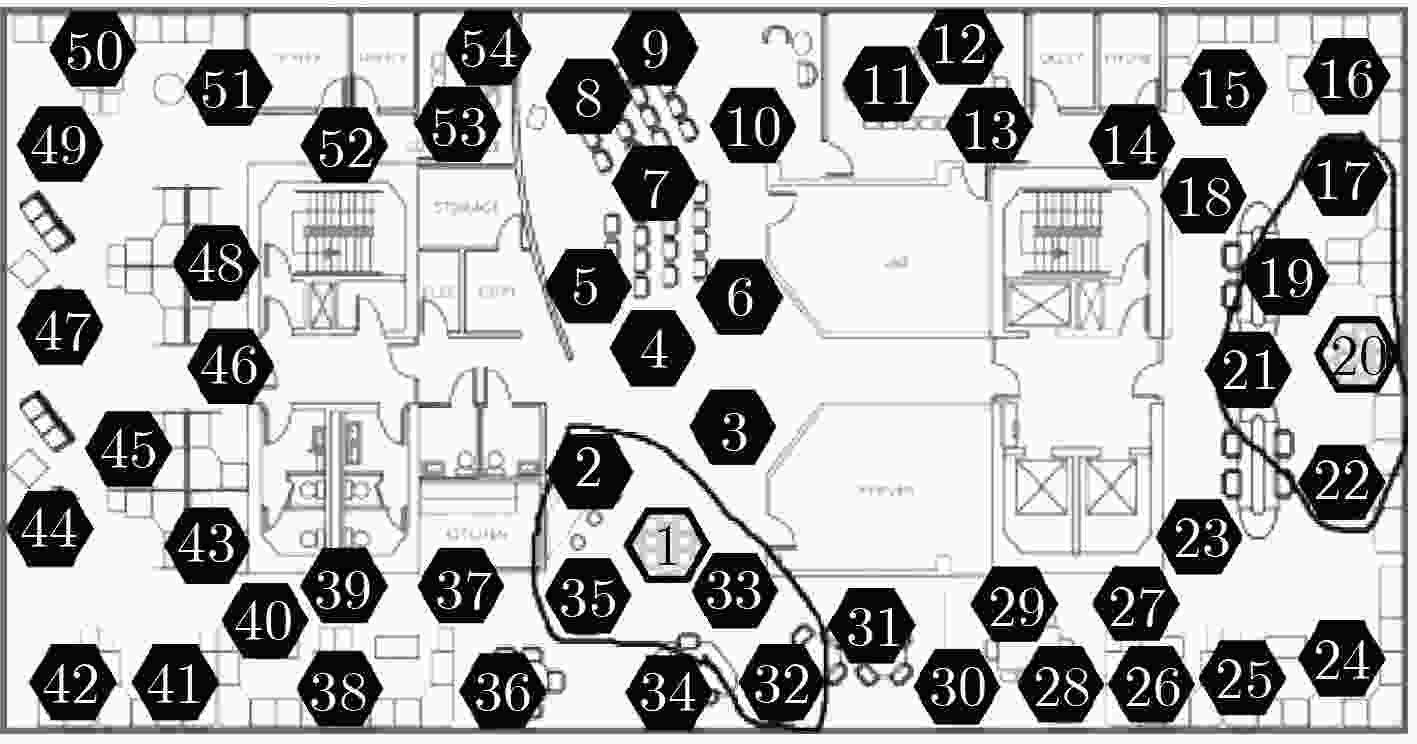


 下载:
下载:
