Learning-based Localization with Monocular Camera for Light-rail System
-
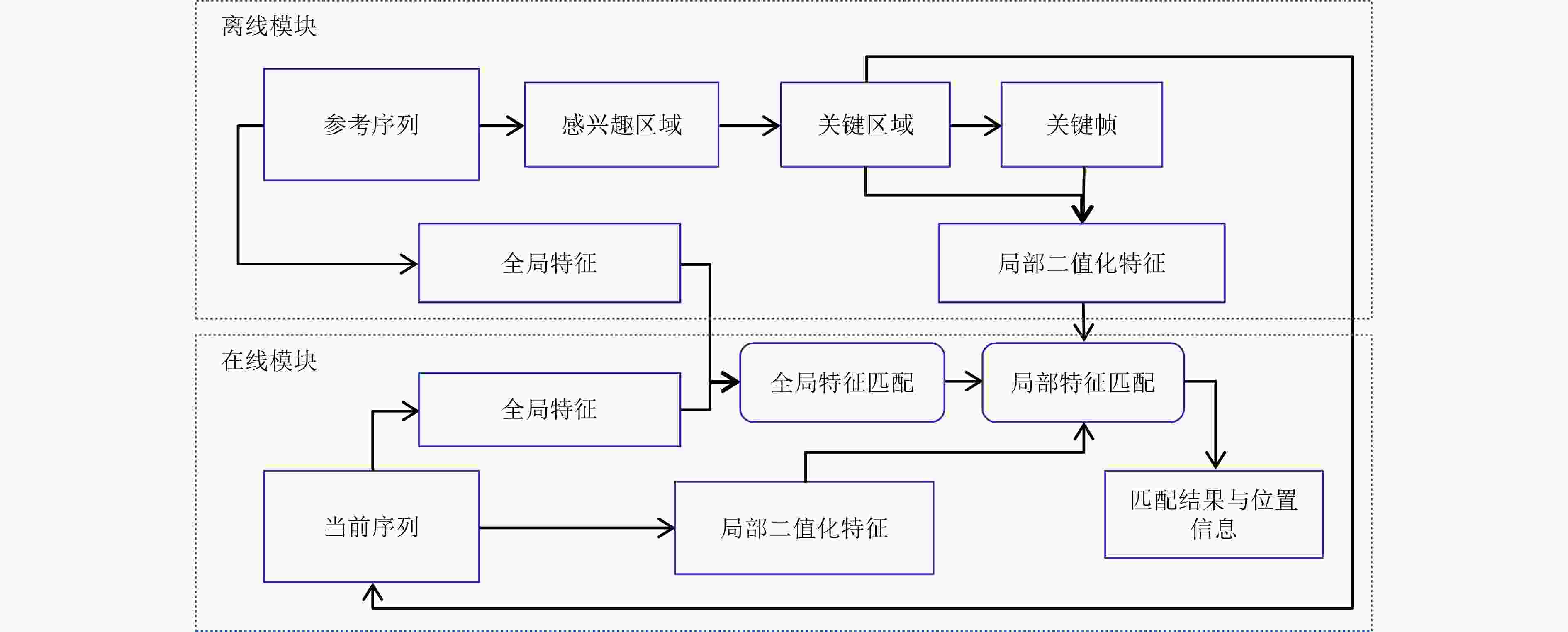
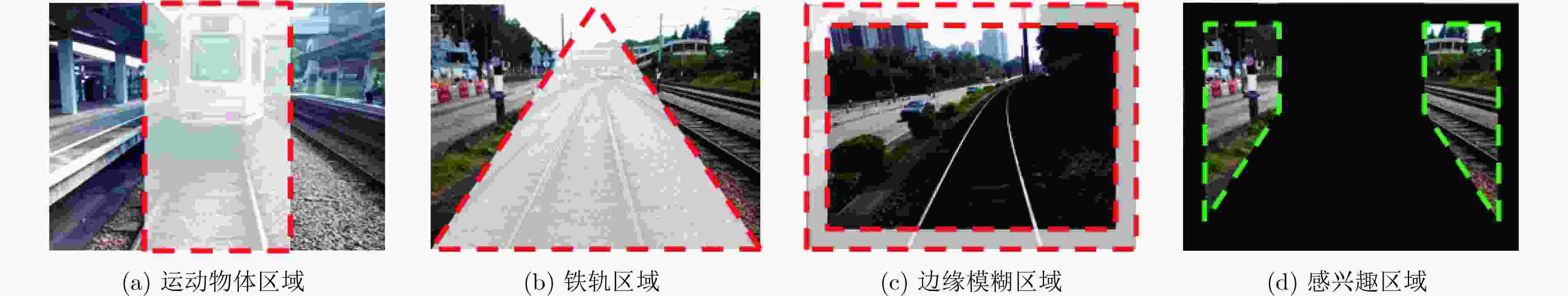
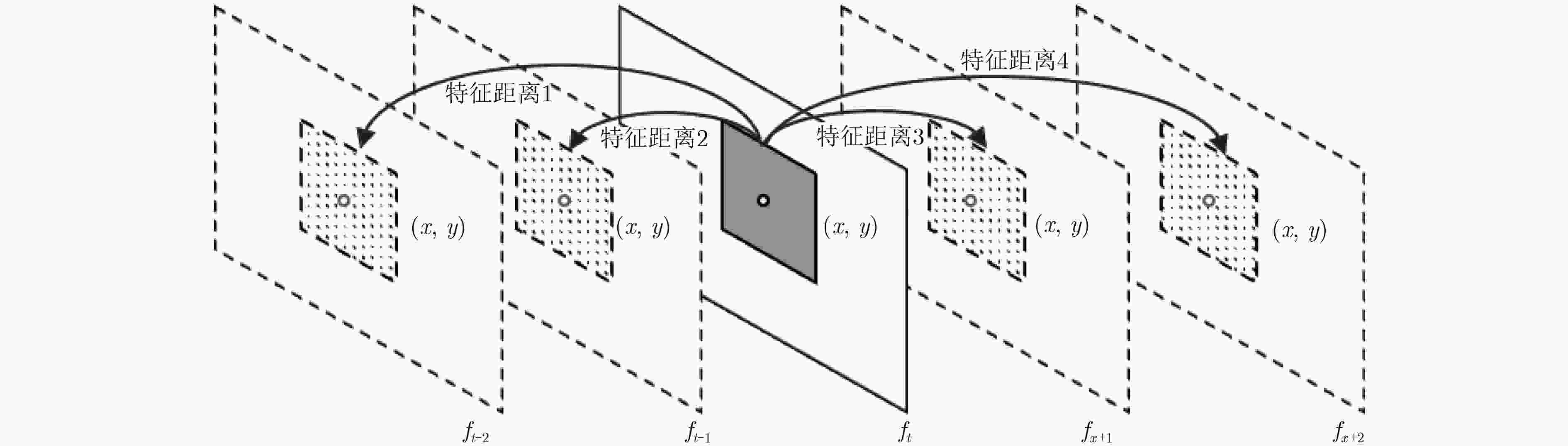
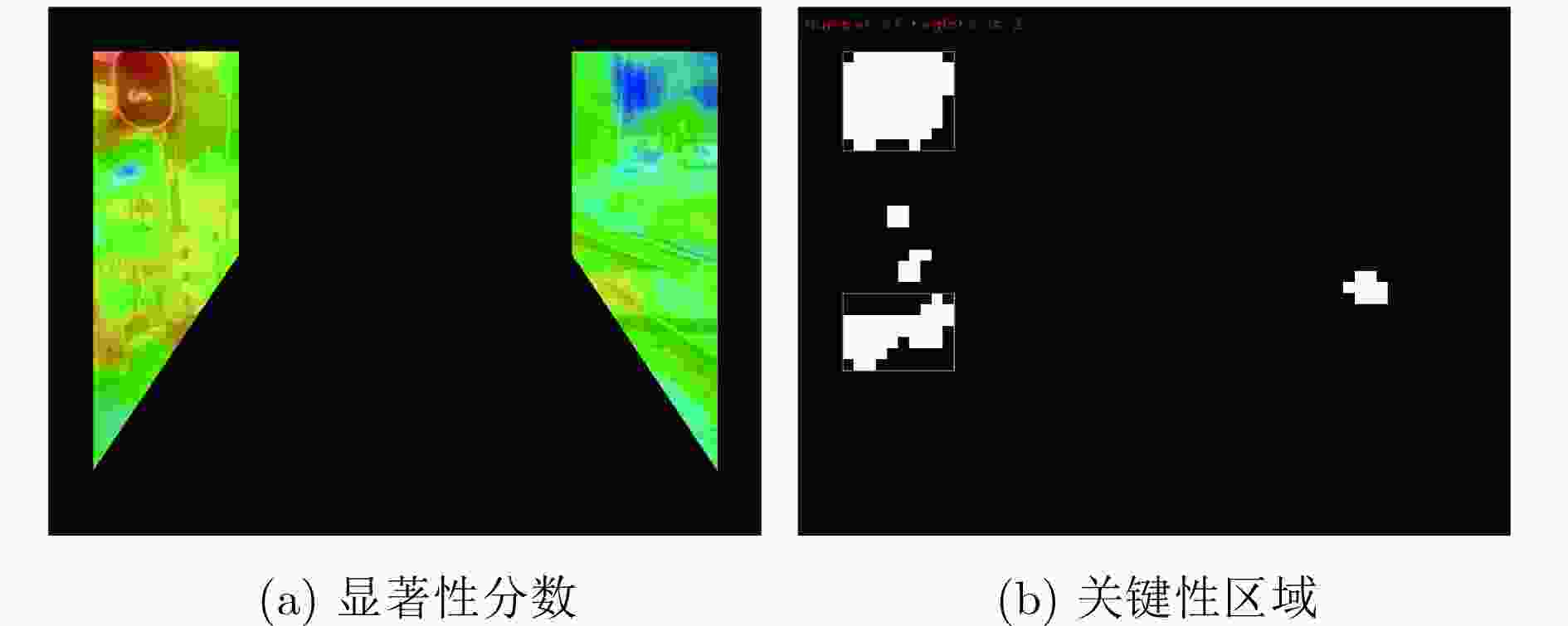
摘要: 基于视觉信息的场景识别定位模块被广泛应用于车辆安全系统。针对目前场景逐帧匹配算法训练数据量大、匹配处理计算复杂度高以及跟踪精度低导致难以实际应用的问题,该文提出一种新的基于局部关键区域与关键帧的场景识别方法,在保证匹配精度的同时满足系统实时性的要求。首先,该方法仅使用单目摄像机捕获的单一序列作为参考序列,采用无监督方式提取序列的显著性区域作为关键区域,并计算关键区域中低相关性的二值化特征,提高了场景匹配的精确度并大幅减少了实时场景匹配过程中特征生成与匹配的计算复杂度。其次,该方法以显著性分数为依据提取参考序列中的关键帧,缩小了跟踪模块的检索范围并提高了检索效率。该文使用香港轻轨系统数据集以及公开测试数据集进行方法测试。实验结果表明,该文方法在实现快速匹配的同时,其匹配正确率较基于全局特征匹配方法SeqSLAM提高了9.8%。Abstract: The visual-based scene recognition and localization module is widely used in vehicle safety system. This paper proposes a new method of scene recognition based on local key region and key frame, which is based on the problem of large amount of training data, large matching complexity and low tracking precision. The proposed method meets the real-time requirements with high accuracy. First, the method uses the unsupervised method to extract the significant regions of the single reference sequence captured by the monocular camera as the key regions. The binary features with low correlation in key regions are also extracted to improve the scene matching accuracy and reduce the computational complexity of feature generation and matching. Secondly, key frames in the reference sequence are extracted based on the discrimination score to reduce the retrieval range of the tracking module and improve the efficiency. Practical field tests are done on real data of the light railway system in Hong Kong and the open test data set in Nordland. The experimental results show that the proposed method achieves fast matching and the precision is 9.8% higher than SeqSLAM which is based on global feature.
-
Key words:
- Visual-based localization /
- Key region /
- Key frame /
- Binary feature
-
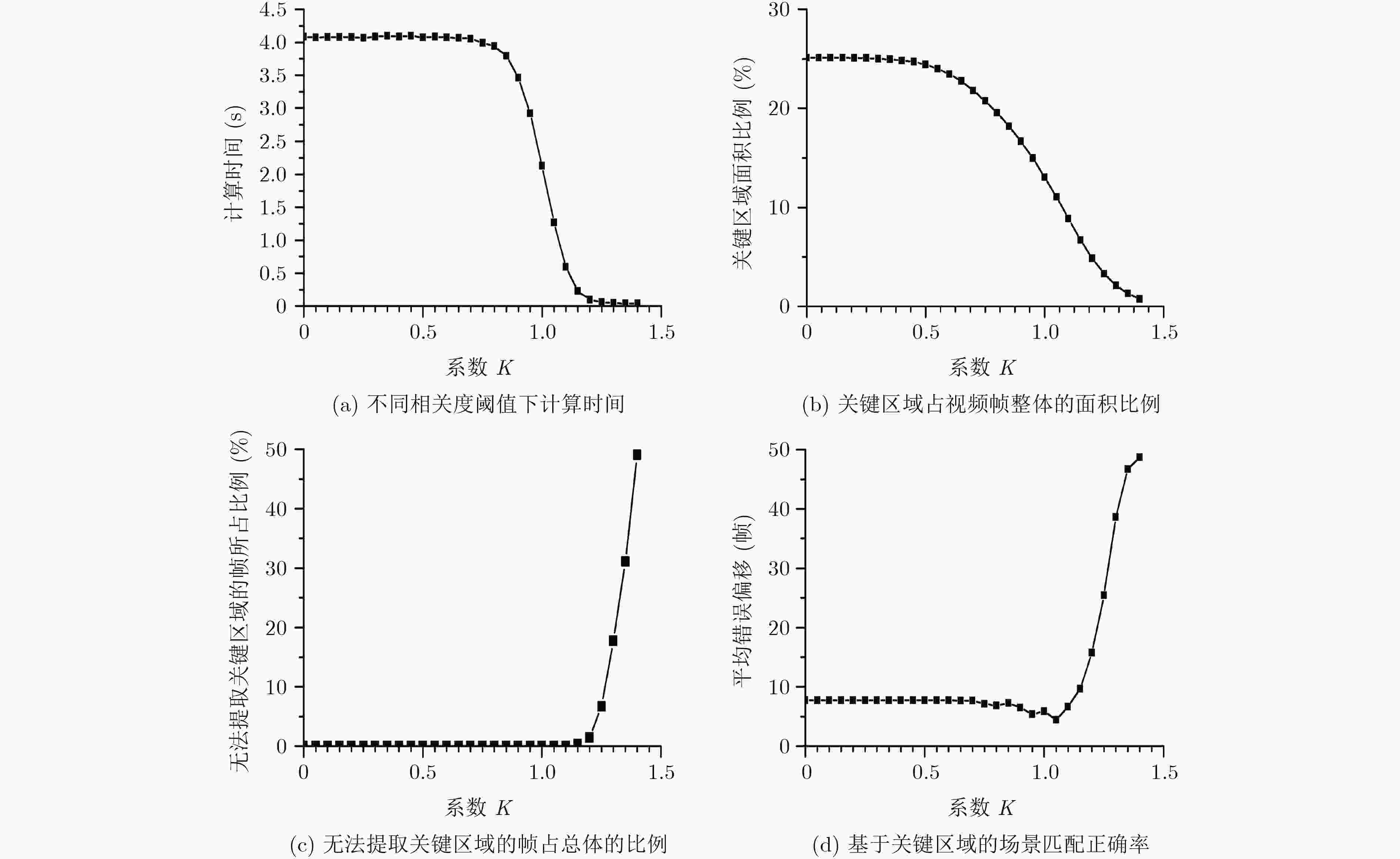
表 1 时间复杂度与算法平均错误偏移
对比方法 平均错误偏移(帧) 时间(s) 全局HOG特征 15.24 0.0593 基于宏块HOG特征 2.10 62.4205 基于感兴趣区域内宏块HOG特征 2.26 13.5960 本文基于关键区域HOG特征 1.44 3.6058 表 2 场景跟踪准确率、匹配偏移及匹配时间
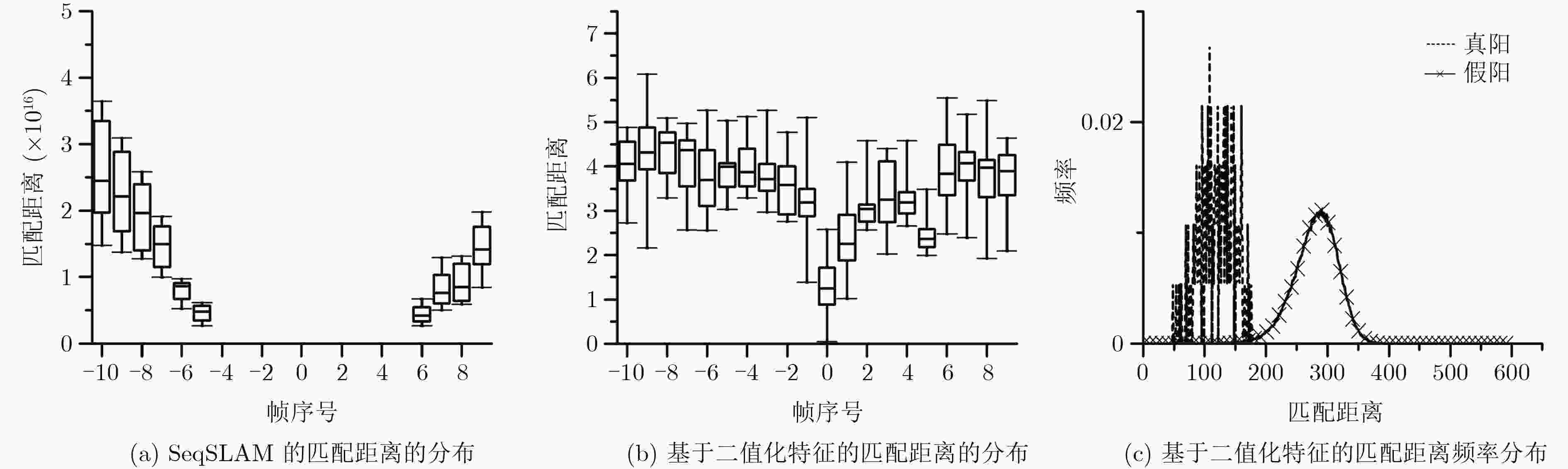
SeqSLAM 本文基于二值化特征的
场景跟踪方法△(%) 准确率(%) 89.56 99.36 +9.80 匹配偏移(帧) 1.3652 0.8728 –36.07 匹配时间(ms) 53.23 54.82 +2.99 -
LOWRY S, SUNDERHAUF N, NEWMAN P, et al. Visual place recognition: a survey[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2016, 32(1): 1–19 doi: 10.1109/TRO.2015.2496823 DAYOUB F, MORRIS T, BEN U, et al. Vision-only autonomous navigation using topometric maps[C]. IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Tokyo, Japan, 2013: 1923–1929. MURILLO A C, SINGH G, KOSECKÁ J, et al. Localization in urban environments using a panoramic gist descriptor[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2013, 29(1): 146–160 doi: 10.1109/TRO.2012.2220211 MADDERN W and VIDAS S. Towards robust night and day place recognition using visible and thermal imaging[OL]. https://eprints.qut.edu.au/52646/. MCMANUS C, FURGALE P, and BARFOOT T D. Towards lighting-invariant visual navigation: An appearance-based approach using scanning laser-rangefinders[J]. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 2013, 61(8): 836–852 doi: 10.1016/j.robot.2013.04.008 LINEGAR C, CHURCHILL W, and NEWMAN P. Made to measure: Bespoke landmarks for 24-hour, all-weather localisation with a camera[C]. 2016 IEEE International Conference on. Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Stockholm, Sweden, 2016:787–794. LOWE D G. Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2004, 60(2): 91–110 doi: 10.1023/B:VISI.0000029664.99615.94 BAY H, ESS A, TUYTELAARS T, et al. Speeded-up robust features (SURF)[J]. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 2008, 110(3): 346–359 doi: 10.1007/11744023_32 ROSTEN E, PORTER R, and DRUMMOND T. Faster and better: A machine learning approach to corner detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2010, 32(1): 105–119 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2008.275 CALONDER M, LEPETIT V, STRECHA C, et al. BRIEF: Binary robust independent elementary features[C]. Proceedings of the 11th European Conference on Computer Vision, Crete, Greece, 2010: 778–792. RUBLEE E, RABAUD V, KONOLIGE K, et al. ORB: An efficient alternative to SIFT or SURF[C]. Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Computer Vision, Barcelona, Spain, 2011: 2564–2571. MCMANUS C, UPCROFT B, and NEWMANN P. Scene signatures: Localised and point-less features for localisation[C]. Robotics:Science and Systems, Berkeley, USA, 2014: 1–9. HAN Fei, YANG Xue, DENG Yiming, et al. SRAL: Shared representative appearance learning for long-term visual place recognition[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2017, 2(2): 1172–1179 doi: 10.1109/LRA.2017.2662061 CARLEVARIS-BIANCO N and EUSTICE R M. Learning visual feature descriptors for dynamic lighting conditions[C]. IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Chicago, USA, 2014: 2769–2776. KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, and HINTON G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[C]. Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, USA, 2012: 1097–1105. SÜNDERHAUF N, SHIRAZI S, JACOBSON A, et al. Place recognition with ConvNet landmarks: Viewpoint-robust, condition-robust, training-free[C]. Proceedings of Robotics: Science and Systems XII, Rome, Italy, 2015: 296–296. ZITNICK C L and DOLLÁR P. Edge boxes: Locating object proposals from edges[C]. Proceedings of the 13th European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 2014: 391–405. ARROYO R, ALCANTARILLA P F, BERGASA L M, et al. Fusion and binarization of CNN features for robust topological localization across seasons[C]. IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Daejeon, South Korea, 2016: 4656–4663. LINEGAR C, CHURCHILL W, and NEWMAN P. Made to measure: Bespoke landmarks for 24-hour, all-weather localisation with a camera[C]. IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Stockholm, Sweden, 2016: 787–794. DALAL N and TRIGGS B. Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection[C]. IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Diego, USA, 2005: 886–893. MILFORD M J and WYETH G F. SeqSLAM: Visual route-based navigation for sunny summer days and stormy winter nights[C]. IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Saint Paul, USA, 2012: 1643–1649. BRESSON G, ALSAYED Z, LI Yu, et al. Simultaneous localization and mapping: A survey of current trends in autonomous driving[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Vehicles, 2017, 2(3): 194–220 doi: 10.1109/TIV.2017.2749181 KIM P, COLTIN B, ALEXANDROV O, et al. Robust visual localization in changing lighting conditions[C]. IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Singapore, 2017: 5447–5452. BAI Dongdong, WANG Chaoqun, ZHANG Bo, et al. Sequence searching with CNN features for robust and fast visual place recognition[J]. Computers and Graphics, 2018, 70: 270–280 doi: 10.1016/j.cag.2017.07.019 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
