A Non-stationary 3D Spatial Channel Model Based on Stochastic Scattering Cluster
-
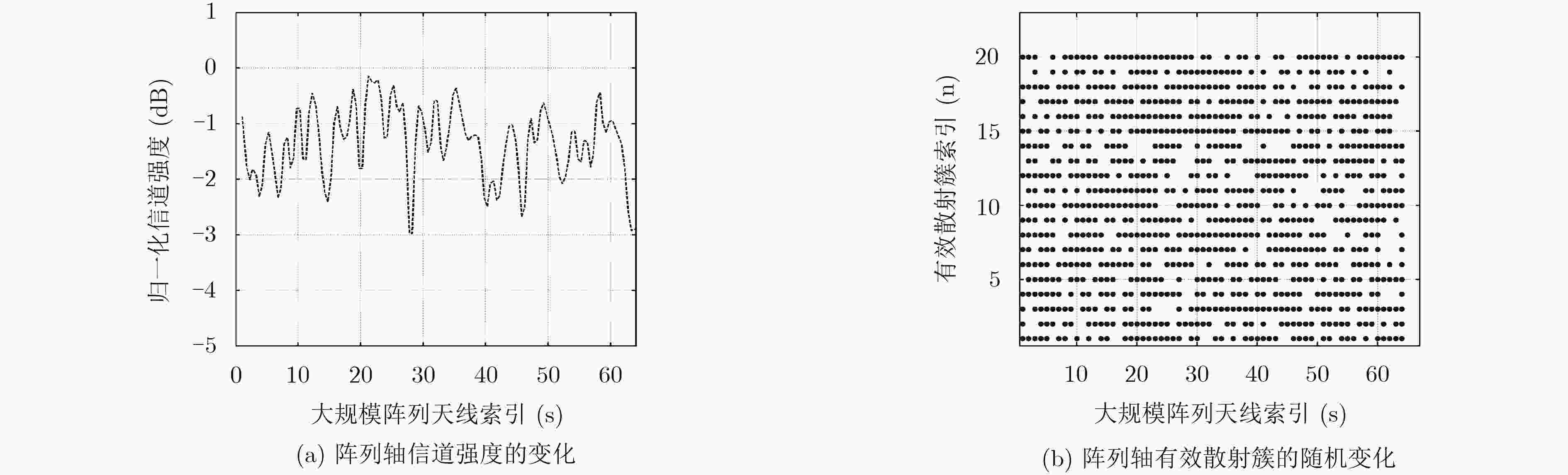
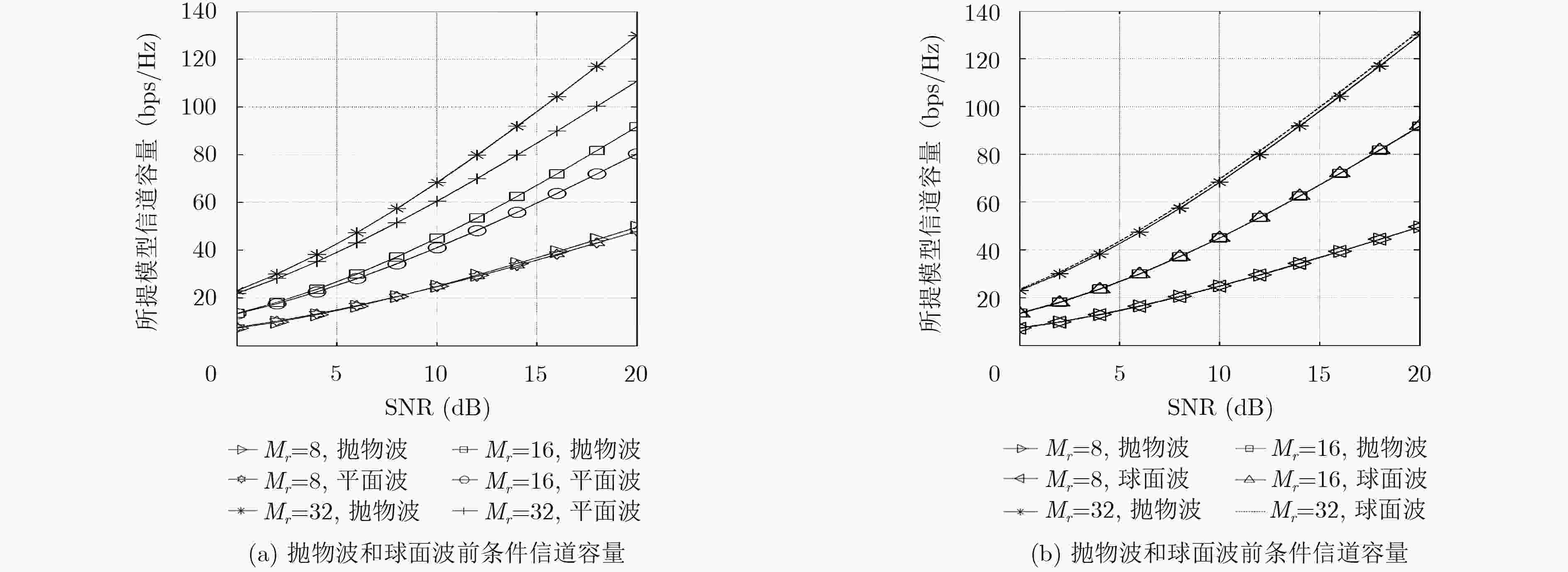
摘要: 针对大规模MIMO信道的近场效应和非平稳特性,该文提出适用大规模MIMO信道的一种基于随机散射簇的非平稳3D空间信道模型。采用抛物波前代替球面波前建模近场效应,并分析抛物波前条件下该模型的信道容量。对于大规模MIMO信道的非平稳特性,提出基于散射簇的有效概率确定收发天线阵元的有效散射簇集合,从而建模散射簇沿天线阵列轴的随机演变来合理描述散射簇的出现和消失。仿真结果表明,用抛物波前和有效散射簇的随机演变来建模大规模MIMO信道特征是很好的候选方法。Abstract: To describe the near field effect and the non-stationary characteristic of the Massive MIMO channel, a non-stationary 3D spatial channel model based on stochastic scattering clusters for Massive MIMO systems is proposed. The parabolic wave instead of the spherical wave is used to model the near field effect, and the channel capacity of the model is analyzed under parabolic wavefront condition. For non-stationary properties of massive MIMO channel, the effective scattering clusters set of transmitting and receiving antenna elements is determined based on the effective probability of scattering clusters, and the stochastic evolution of scattering clusters along the antenna array axis is modeled to describe properly the appearance and disappearance of scattering clusters. Simulation results demonstrate that parabolic wavefront and the stochastic evolution of effective scattering clusters are good candidates to model Massive MIMO channel characteristics.
-
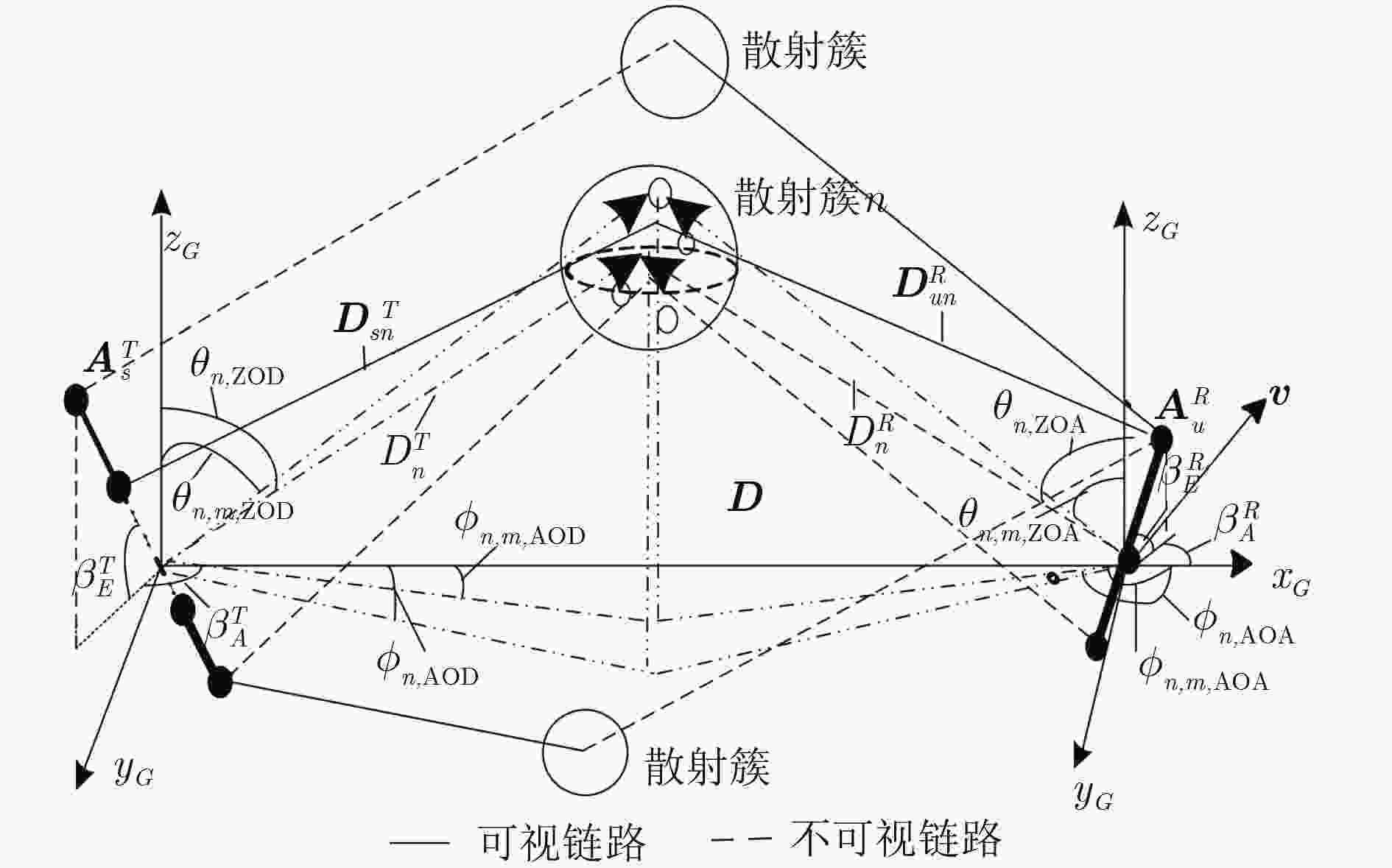
表 1 非平稳3D空间信道模型的主要几何参数定义
参数 定义 $\beta _E^R$ ,

$\beta _E^T$ 

接收天线和发送天线的俯仰角 $\beta _A^R$ ,

$\beta _A^T$ 

接收天线和发送天线的方位角 ${\theta _{n,\rm{ZOA}}}$ ,

${\phi _{n,\rm{AOA}}}$ 

散射簇 $n$ 的俯仰和方位到达角

${\theta _{n,\rm{ZOD}}}$ ,

${\phi _{n,\rm{AOD}}}$ 

散射簇 $n$ 的俯仰和方位离开角

${\theta _{n,m,\rm{ZOA}}}$ ,

${\phi _{n,m,\rm{AOA}}}$ 

散射簇 $n$ 经第

$m$ 散射子径的俯仰和方位到达角

$\theta _{n,m,\rm{ZOD}}^{}$ ,

$\phi _{n,m,\rm{AOD}}^{}$ 

散射簇 $n$ 经第

$m$ 散射子径的俯仰和方位离开角

${{{D}}}_n^R$ ,

${{{D}}}_n^T$ 

散射簇 $n$ 和接收(发送)天线阵列轴中心的距离矢量

${{{A}}}_u^R$ ,

${{{A}}}_s^T$ 

接收天线阵元 $u$ 和发送天线阵元

$s$ 的位置矢量

${{{D}}}_{un}^R$ ,

${{{D}}}_{sn}^T$ 

散射簇 $n$ 和接收天线阵元

$u$ (发送天线阵元

$s$ )的距离矢量

${{{D}}}_{un,m}^R$ ,

${{{D}}}_{sn,m}^T$ 

散射簇 $n$ 和接收天线阵元

$u$ (发送天线阵元

$s$ )经第

$m$ 子径的距离矢量

$f_{un,m}^{}$ 

散射簇 $n$ 和接收天线阵元

$u$ 之间经第

$m$ 子径的多普勒频率

${{v}}$ 

接收天线阵列的速度矢量 -
DONG Lei, ZHAO Hongyi, CHEN Yan, et al. Introduction on IMT-2020 5G trials in China[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2017, 35(8): 1849–1866 doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2017.2710678 WANG Chengxiang, WU Shangbin, BAI Lu, et al. Recent advances and future challenges on massive MIMO channel measurements and models[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2016, 59(2): 21301–21302 doi: 10.1007/s11432-015-5517-1 刘留, 陶成, 卢艳萍, 等. 大规模多天线无线信道及容量特性研究[J]. 北京交通大学学报, 2015, 39(2): 69–79 doi: 10.11860/j.issn.1673-0291LIU Liu, TAO Cheng, LU Yanping, et al. Research on the propagation condition and channel capacity for Massive MIMO[J]. Journal of Beijing Jiaotong University, 2015, 39(2): 69–79 doi: 10.11860/j.issn.1673-0291 GAO Xiang, TUFVESSON F, and EDFORS O. Measured propagation characteristics for very-large MIMO at 2.6 GHz[C]. Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers (ACSSC), Pacific Grove, USA, 2012: 295–299. GAO Xiang, TUFVESSON F, and EDFORS O. Massive MIMO channels-measurements and models models[C]. Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers(ACSSC), Pacific Grove, USA, 2013: 280–284. ZHANG Ping, CHEN Jianqiao, and TANG Tian. An overview of non-stationary property for massive MIMO channel modeling[J]. ZTE Communications, 2017, 15(1): 3–7 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5188.2017.01.001 WU Shangbin, WANG Chengxiang, AGGOUNE M, et al. A non-stationary wideband channel model for massive MIMO communication systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2015, 14(3): 1434–1446 doi: 10.1109/TWC.2014.2366153 WU Shangbin, WANG Chengxiang, AGGOUNE M, et al. A non-stationary 3-D wideband twin-cluster model for 5G massive MIMO channels[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2014, 32(6): 1207–1218 doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2014.2328131 LI X, ZHOU S, BJORNSON E, et al. Capacity analysis for spatially non-wide sense stationary uplink massive MIMO systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2015, 14(12): 7044–7056 doi: 10.1109/TWC.2015.2464219 ADEMAJ F, TARANETZ M, and RUPP M. 3GPP 3D MIMO channel model: A holistic implementation guideline for open source simulation tools[J]. Eurasip Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking, 2016, 2016(1): 55–67 doi: 10.1186/s13638-016-0549-9 LOPEZ F, WANG Chengxiang, and FENG Rui. A novel 2D non-stationary wideband massive MIMO channel model[C]. Computer Aided Modelling and Design of Communication Links and Networks (CAMAD), Toronto, Canada, 2016: 2378–2382. ABDI A and KAVEH M. A versatile spatio-temporal correlation function for mobile fading channels with non-isotropic scattering[C]. Proceedings of the Tenth IEEE Workshop on Statistical Signal Array Processing, Pocono Manor, USA, 2000: 58–62. PATZOLD M. Mobile Radio Channels[M]. West Sussex: John Wiley & Sons, 2012: 369–375. MAMMASIS K, STEWART W R, PFANN E, et al. Three-dimensional channel modelling using spherical statistics for multiple-input multiple-output systems[J]. IET Communications, 2008, 3(1): 48–56 doi: 10.1049/iet-com:20070518 LIU Liu, MATOLAK D W, TAO Cheng, et al. Channel capacity investigation of a linear massive MIMO system using spherical wave model in LOS scenarios[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2016, 59(2): 1–15 doi: 10.1007/s11432-015-5512-6 -





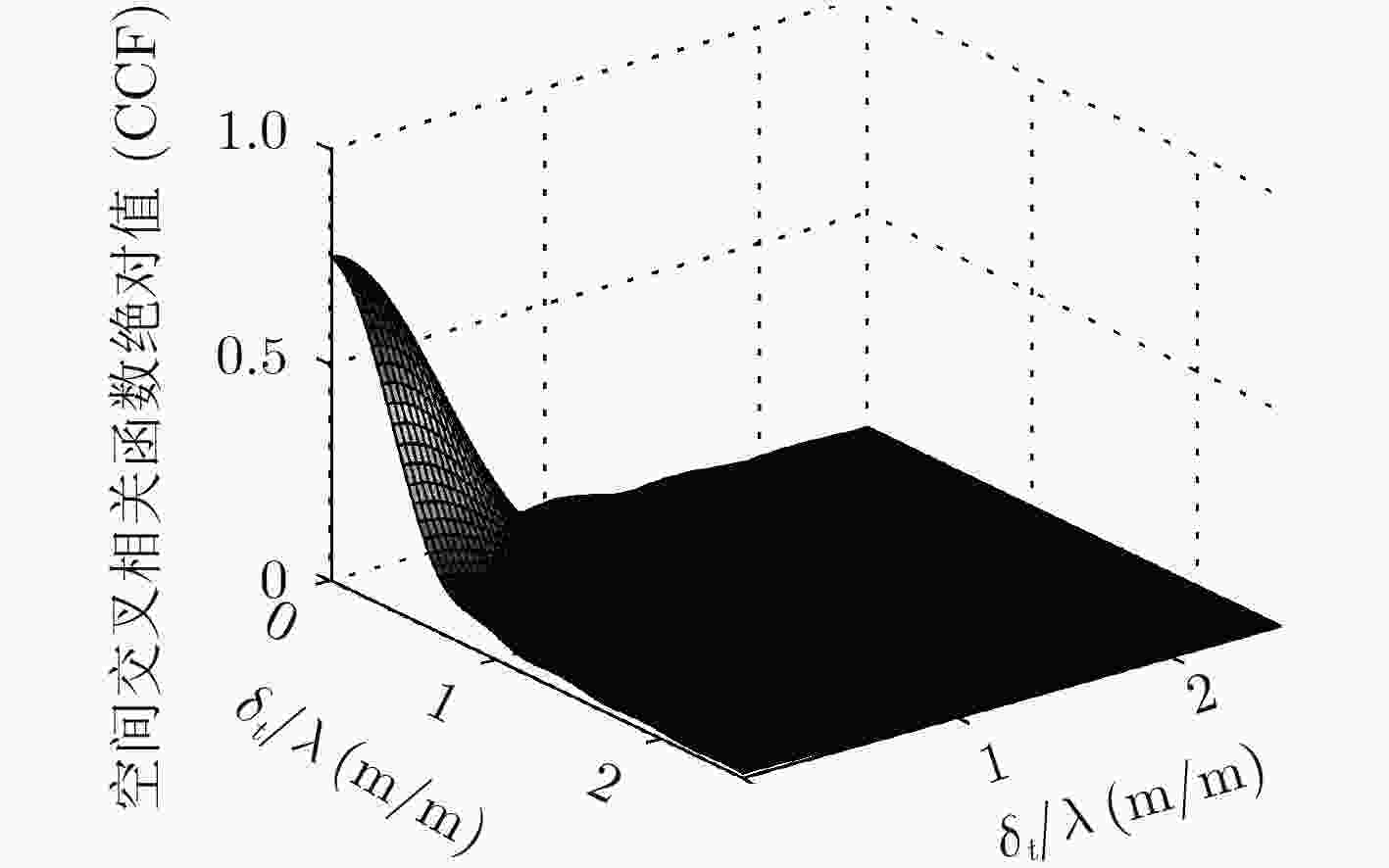
 下载:
下载:
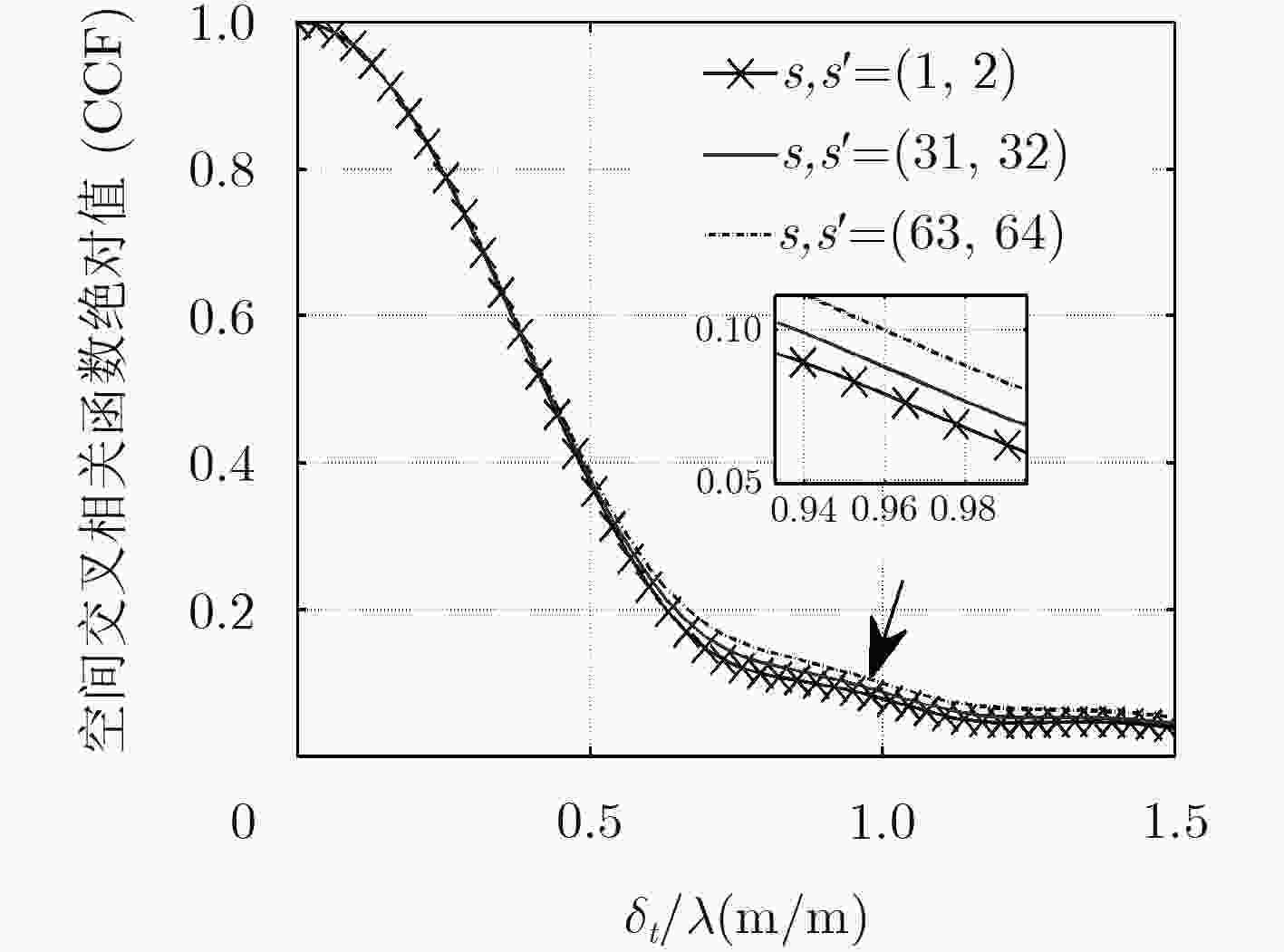
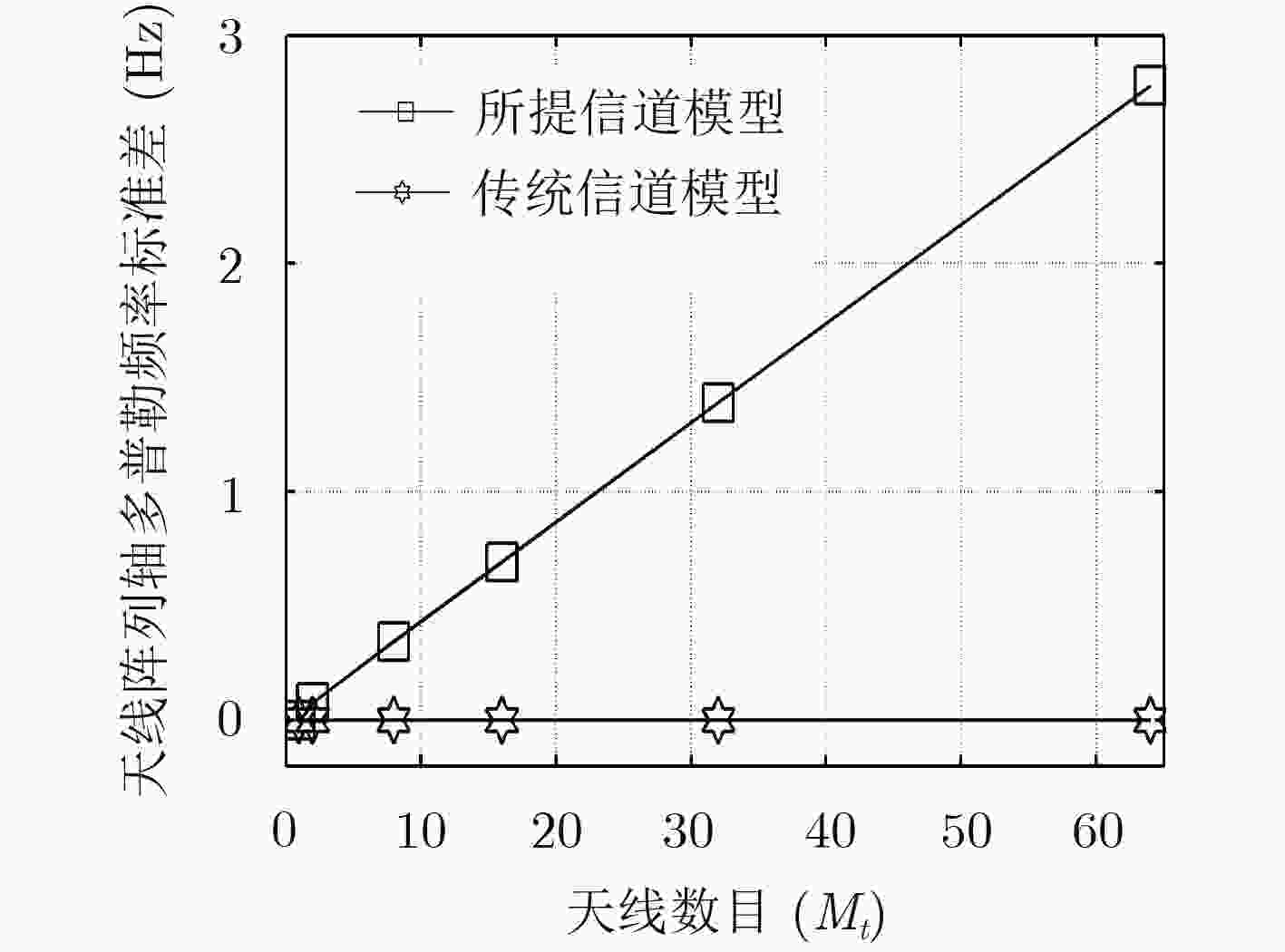


 下载:
下载:
