Visual Objects Detection Based Robust Ridge Regression Indoor Localization Method
-
摘要: 基于视觉物体识别的室内定位算法是一种新型的室内定位解决方案,算法通过物体检测、位置匹配、定位方程解算等步骤确定用户位置。然而,受到单目相机视域较小和物体检测算法精度较低的影响,根据检测物体测距信息而构成的定位方程存在严重的病态性,极大降低了算法的定位成功率和定位精度。因此,该文提出一种抗差岭估计定位解算算法,通过引入岭参数将无偏估计变为有偏估计,实现均方误差最小约束条件下的最优位置估计,并利用迭代选权降低了质量较差的观测量对定位精度的影响。实验结果表明,与OLS (Ordinary Least Square), LM (Levenberg-Marquardt)和RR (Ridge Regression)算法相比,该文提出的抗差岭估计定位解算算法能够有效提高基于视觉物体识别的室内定位方法的成功率和精度。Abstract: The indoor vision positioning algorithm based on object detection is a novel indoor positioning solution, which determines the position of the user through the process of objects detection, position matching, location equation calculation, etc. However, limited by the field-of-view of monocular camera and objects detection accuracy, the localization equation, which is constructed according to the detected objects range information, is seriously ill conditioned. Therefore, this paper proposes a novel localization method based on an improved robust ridge regression estimation, which reduces the influence of the lower accurate observations by iterative weight selection. The experimental results show that compared with Ordinary Least Square (OLS), Levenberg-Marquardt (LM) and Ridge Regression (RR) algorithms, the proposed improved robust ridge regression estimation algorithm can effectively improve the positioning success rate and positioning accuracy of the object detection based indoor navigation method.
-
Key words:
- Indoor localization /
- Ridge regression /
- Deep learning
-
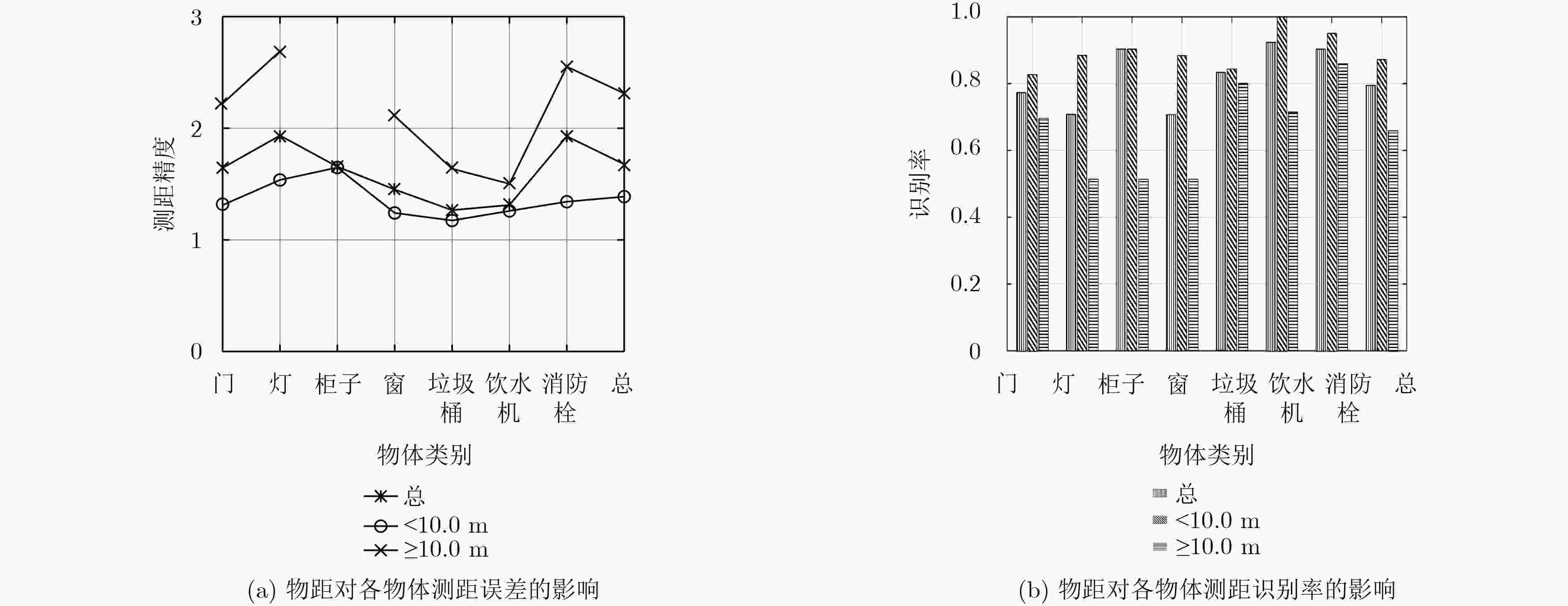
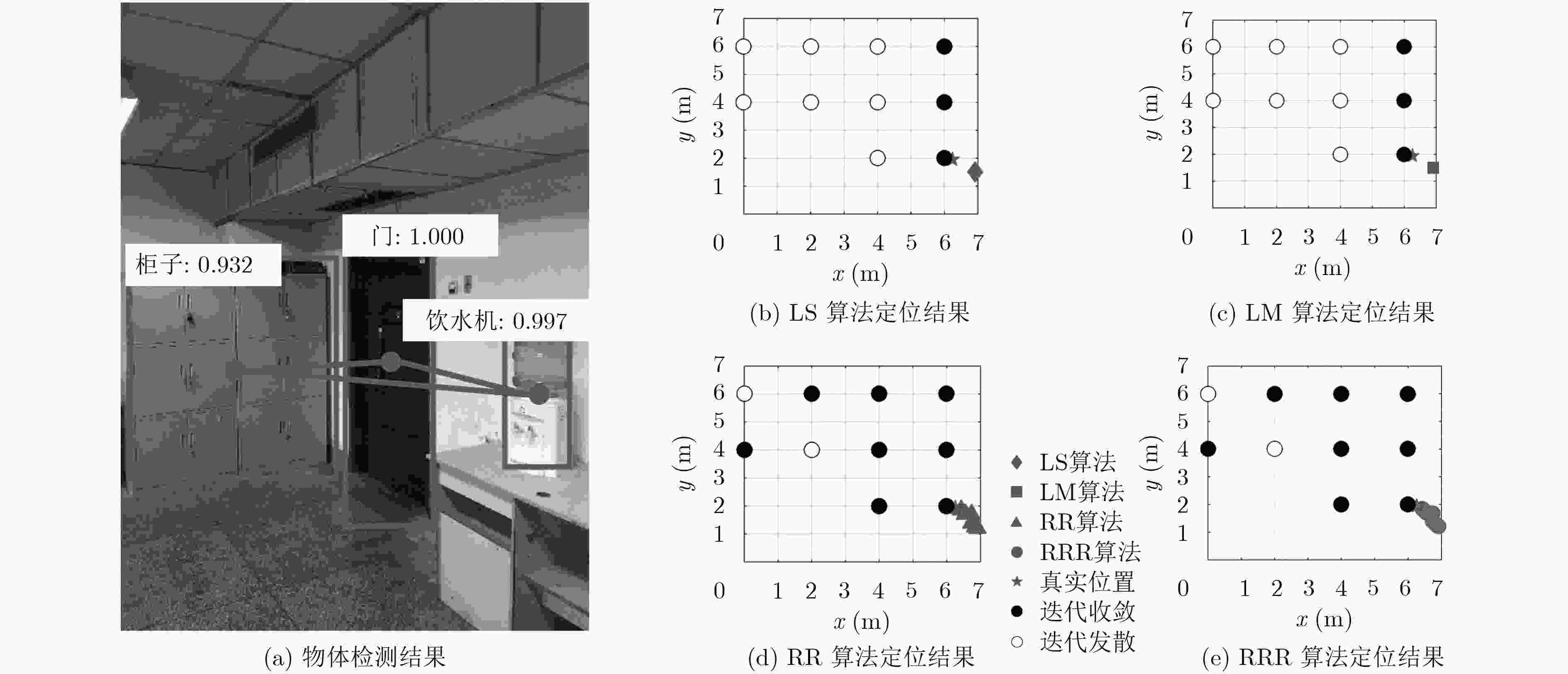
表 1 4种定位解算方法的定位结果比较
检测出物体数 3个 4个 5个 6个 7个 总 照片数 47 22 7 3 1 80 OLS算法 定位成功率(%) 61.7 50.0 42.8 0.0 0.0 53.8 定位误差(m) 1.8 2.1 2.4 – – 1.9 收敛率(%) 42.1 37.5 23.1 0.0 0.0 39.6 迭代次数 8 8 9 – – 8 LM算法 定位成功率(%) 66.0 68.2 42.8 33.0 0.0 62.5 定位误差(m) 1.6 2.0 2.0 1.2 – 1.7 收敛率(%) 45.7 42.5 34.6 9.0 0.0 43.3 迭代次数 7 7 8 6 – 7 RR算法 定位成功率(%) 70.2 63.6 71.4 66.0 0.0 67.5 定位误差(m) 1.5 1.9 1.9 1.0 – 1.6 收敛率(%) 56.0 50.9 53.8 36.4 0.0 53.7 迭代次数 7 7 9 9 – 7 RRR算法 定位成功率(%) 80.9 81.8 85.7 100.0 100.0 82.5 定位误差(m) 1.4 1.3 1.3 0.5 0.6 1.3 收敛率(%) 62.9 62.1 57.7 45.5 40.0 61.1 迭代次数 8 9 11 13 12 9 -
KOPPANYI Z and TOTH C K. Indoor ultra-wide band network adjustment using maximum likelihood estimation[J]. ISPRS Annals of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, 2014, 2(1): 31–35 doi: 10.5194/isprsannals-II-1-31-2014 陈增强, 国峰, 张青. 基于模糊神经网络建模的RFID室内定位算法[J]. 系统科学与数学, 2014, 34(12): 1438–1450CHEN Zengguo, GUO Feng, and ZHANG Qing. An RFID indoor location algorithm based on fuzzy neural network model[J]. Journal of Systems Science&Mathematical Sciences, 2014, 34(12): 1438–1450 周牧, 唐云霞, 田增山, 等. 基于流形插值数据库构建的WLAN室内定位算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(8): 1826–1834 doi: 10.11999/JEIT161269ZHOU Mu, TANG Yunxia, TIAN Zengshan, et al. WLAN indoor localization algorithm based on manifold interpolation database construction[J]. Journal of Electronics&Information Technology, 2017, 39(8): 1826–1834 doi: 10.11999/JEIT161269 CHAE H, PARK C, and SONG J B. Sliding window based landmark extraction for indoor 2D SLAM using forward-looking monocular camera[C]. Control, Automation and Systems (ICCAS), Busan, Korea, 2015: 336–341. SHIM J H and CHO Y I. A Mobile robot localization using external surveillance cameras at indoor[J]. Procedia Computer Science, 2015, 56: 502–507 doi: 10.1016/j.procs.2015.07.242 LU Guoyu, YAN Yan, SEBE N, et al. Indoor localization via multi-view images and videos[J]. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 2017, 32: 121–132 doi: 10.1016/j.cviu.2017.05.003 XU Haowei, KOPPANYI Z, TOTH C K, et al. Indoor localization using region-based convolutional neural network[C]. Proceedings of the 2017 International Technical Meeting of ION, Monterey, USA, 2017: 314–323. TOTH C K, KOPPANYI Z, XU Haowei, et al. Localization using region-based convolution neural network: A comparison study[C]. Proceedings of the 10th International Conference of Mobile Mapping Technology, Cairo, Egypt, 2017: 134–142. UEDA K and YAMASHITA N. On a global complexity bound of the Levenberg-Marquardt method[J]. Journal of Optimization Theory and Applications, 2010, 147(3): 443–453. CHEN B H, DA R, and TEKIN I. Location determination using weighted ridge regression[P]. USA, Patent, US6587692, 2003-7-1. GIRSHICK R, DONAHUE J, DARRELL T, et al. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, USA, 2014: 580–587. GIRSHICK R. Fast R-CNN[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 1440–1448. REN Shaoqing, HE Kaiming, GIRSHICK R, et al. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(6): 1137–1149 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2577031 HOERL A E and KENNARD R W. Ridge regression: Biased estimation for nonorthogonal problems[J]. Technometrics, 1970, 12(1): 55–67. MORÉ J J. The Levenberg-Marquardt Algorithm: Implementation and Theory[M]. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 1978: 105–116. KIBRIA B M G. Performance of some new ridge regression estimators[J]. Communications in Statistics-Simulation and Computation, 2003, 32(2): 419–435 doi: 10.1081/SAC-120017499 -





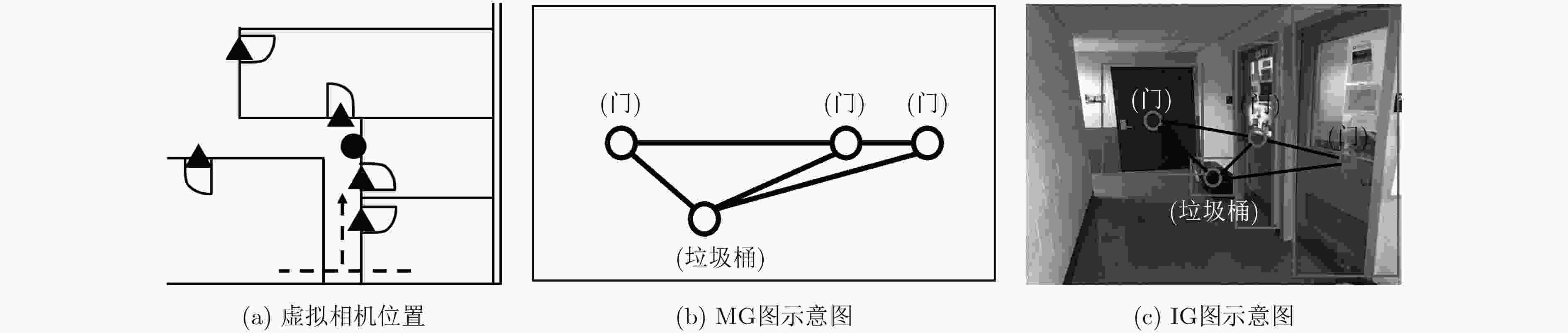
 下载:
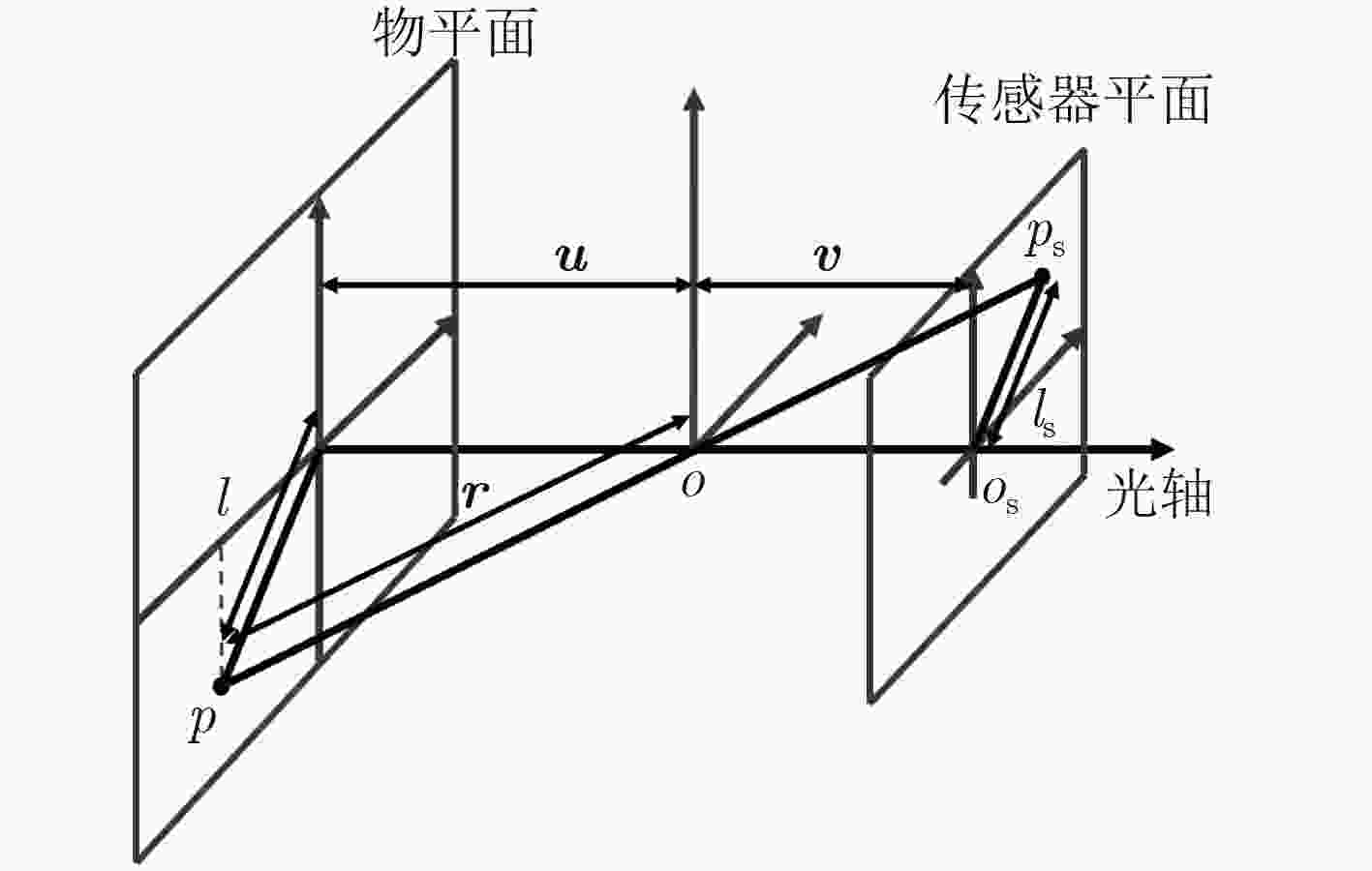
下载:
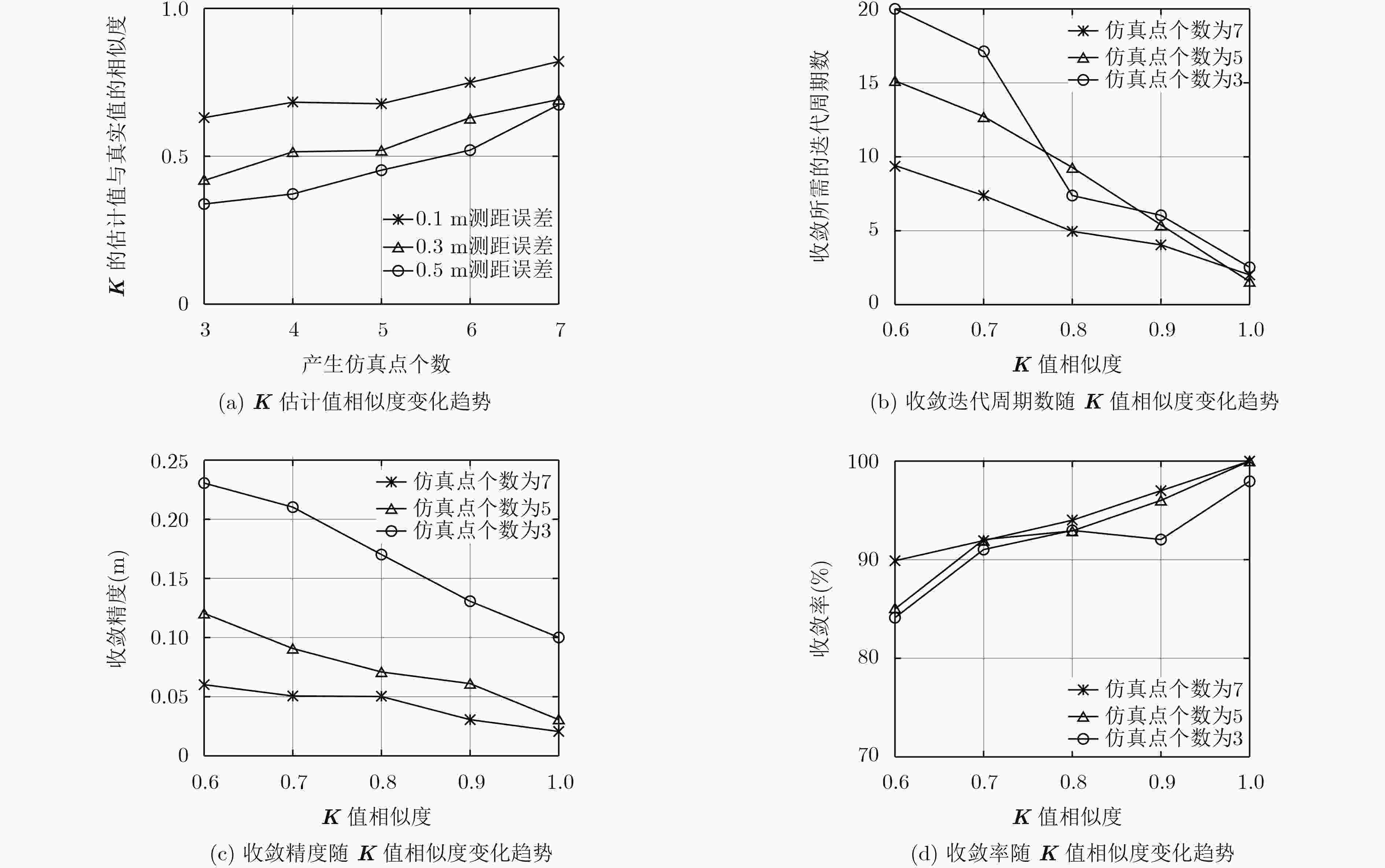


 下载:
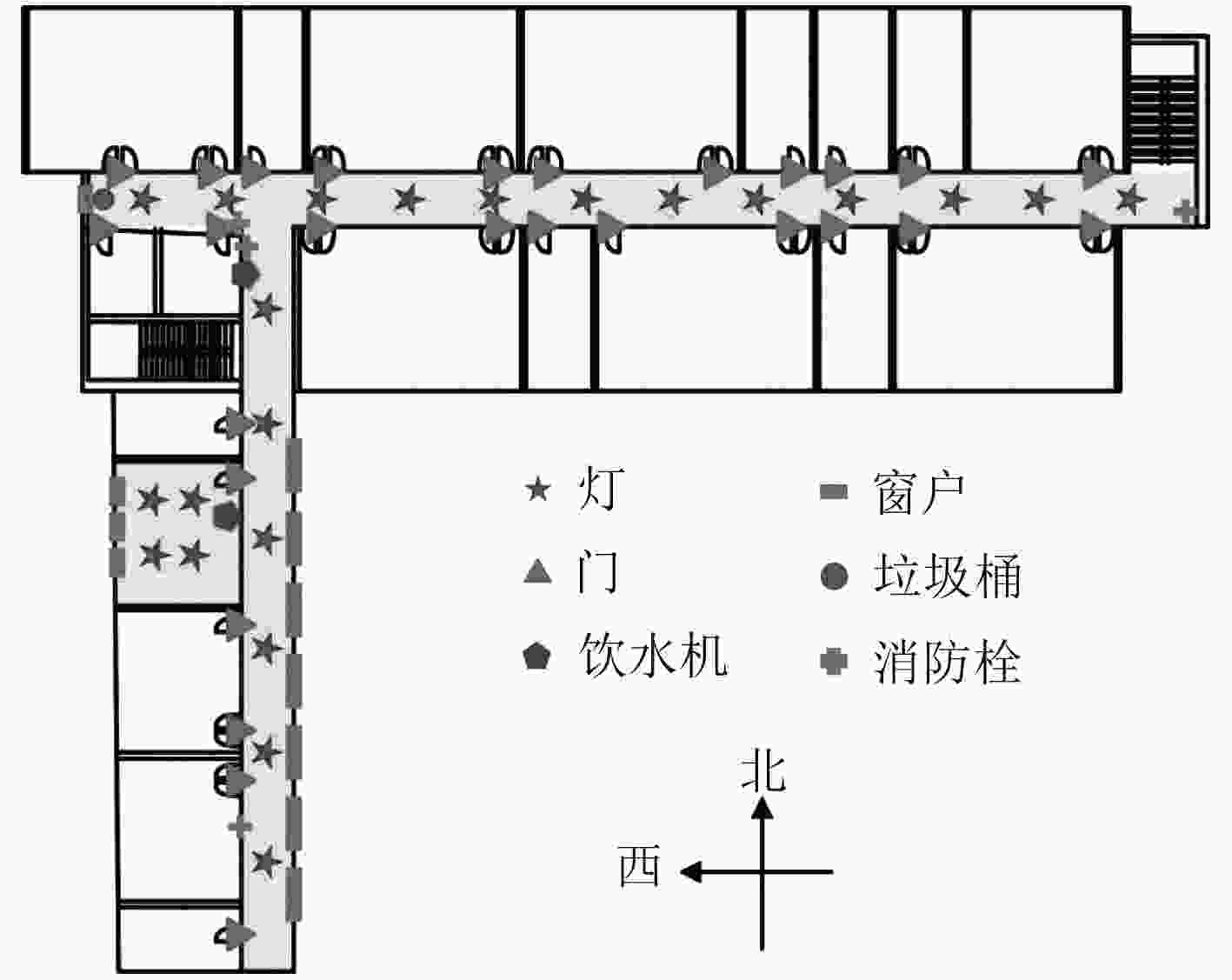
下载:
