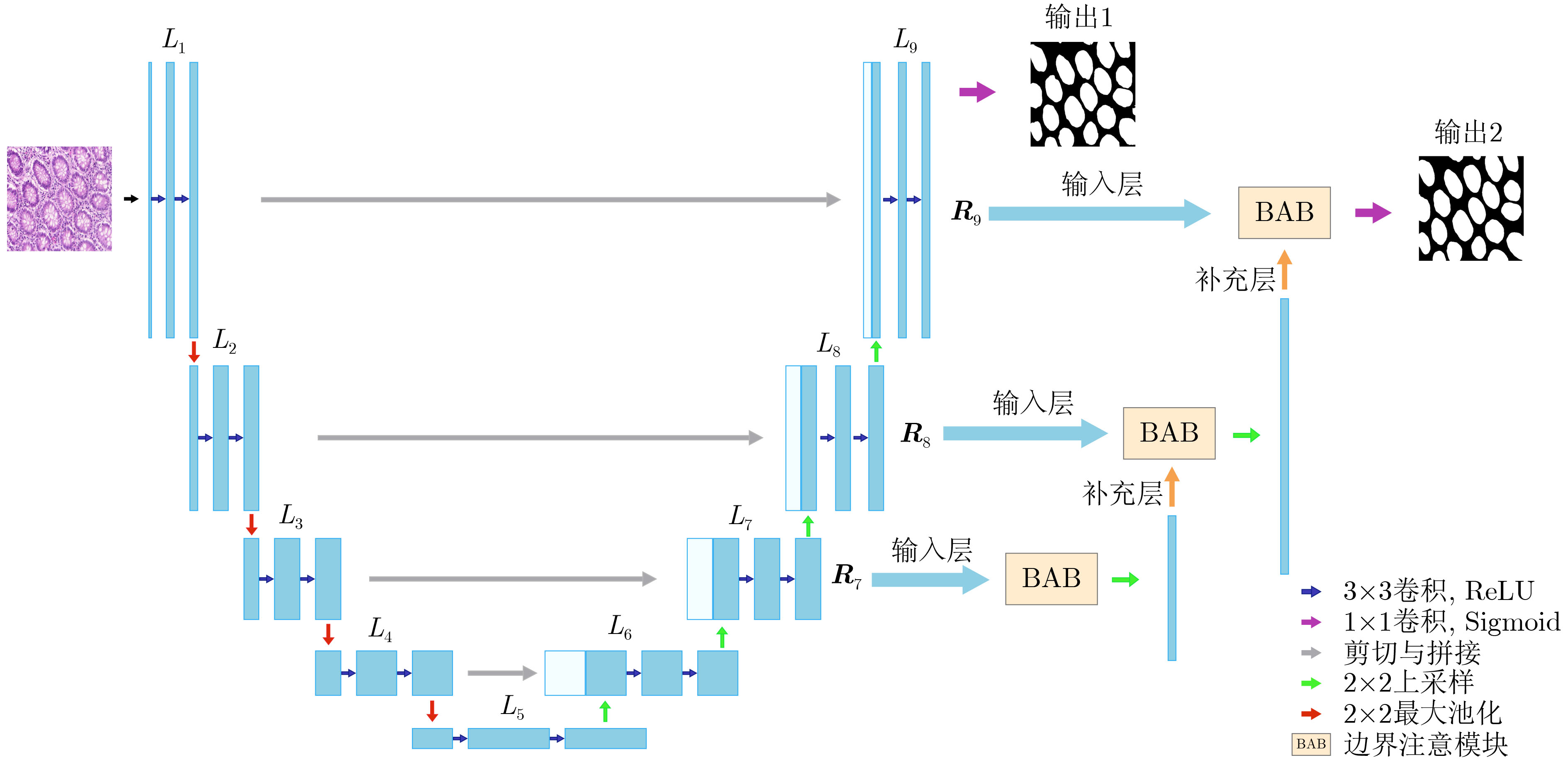
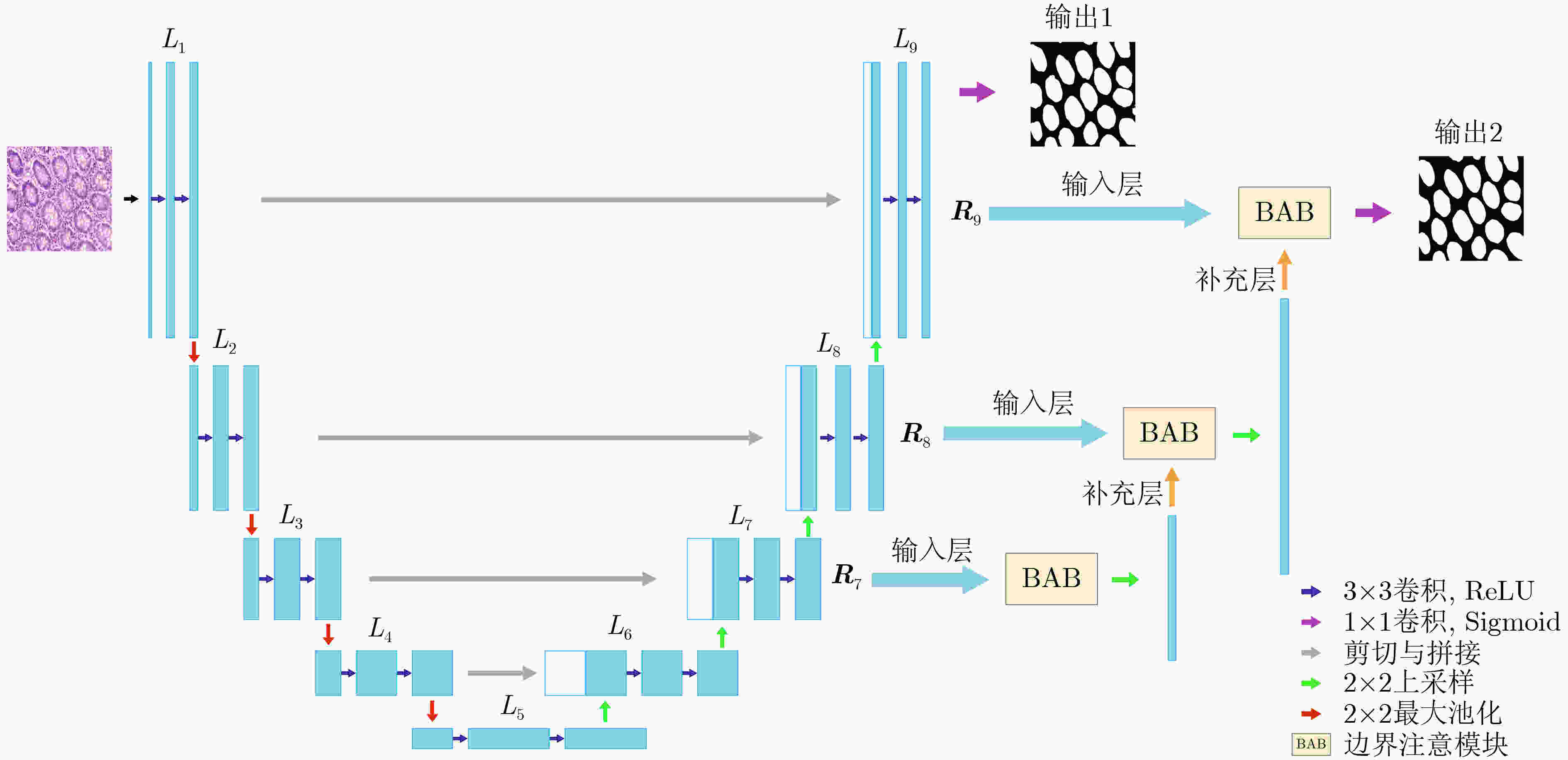
A Medical Image Segmentation Network with Boundary Enhancement
-
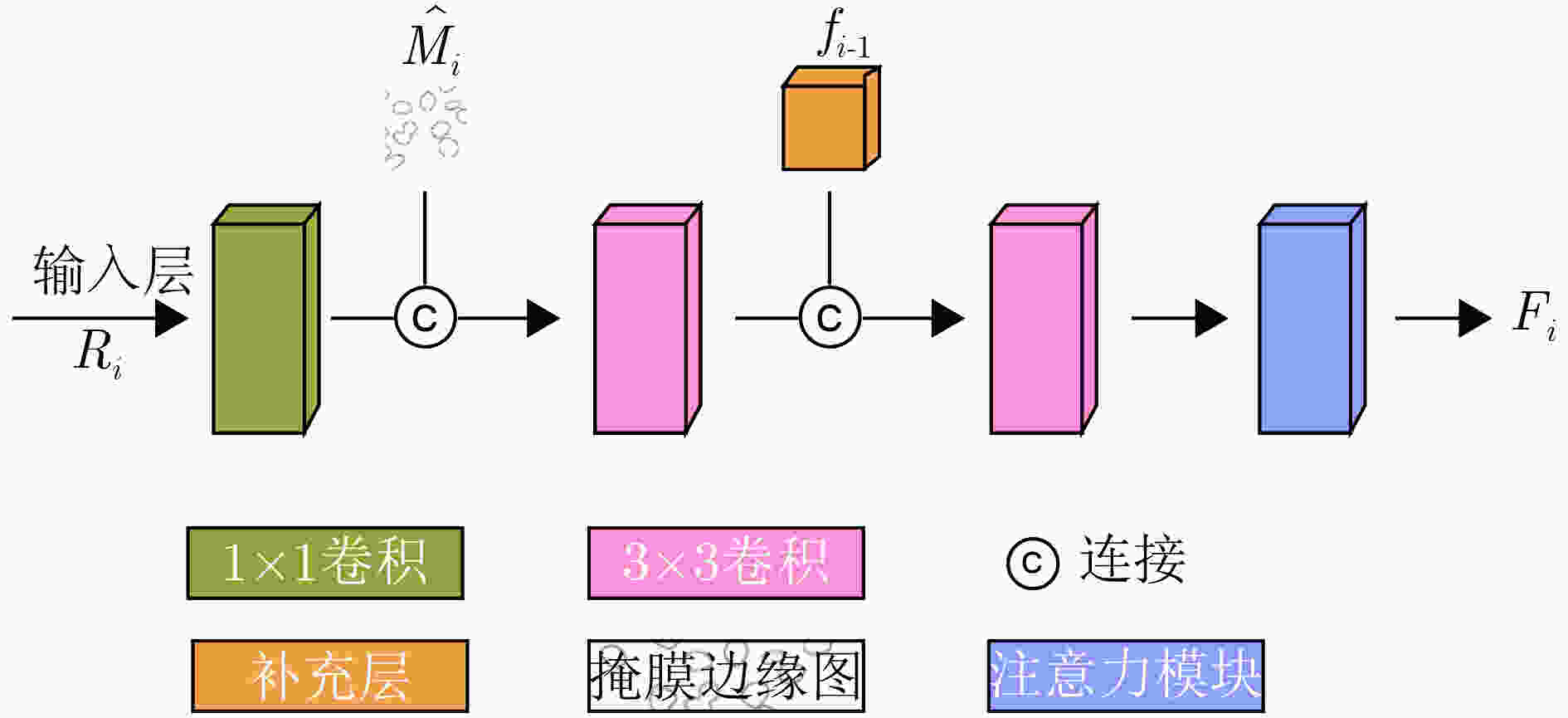
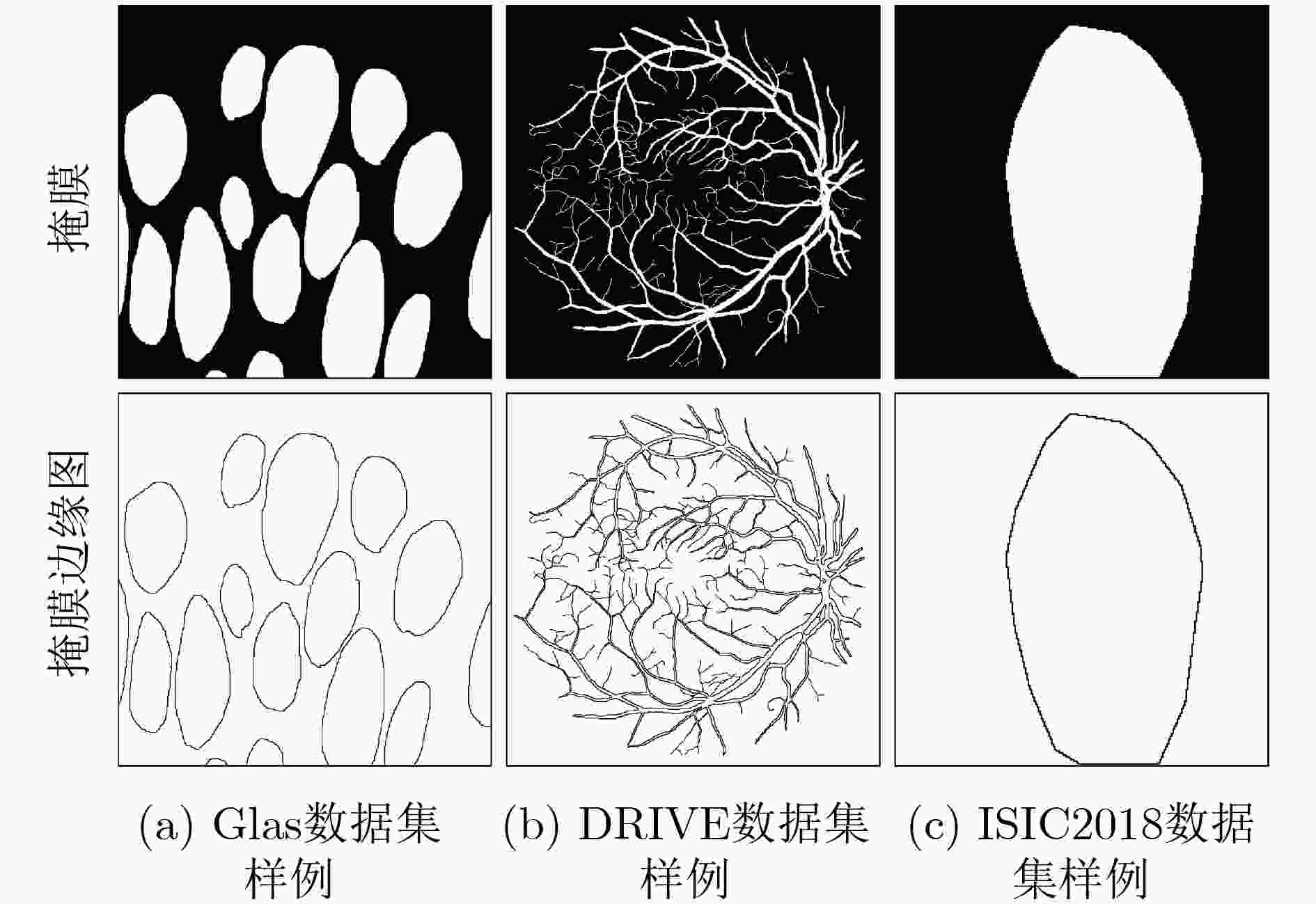
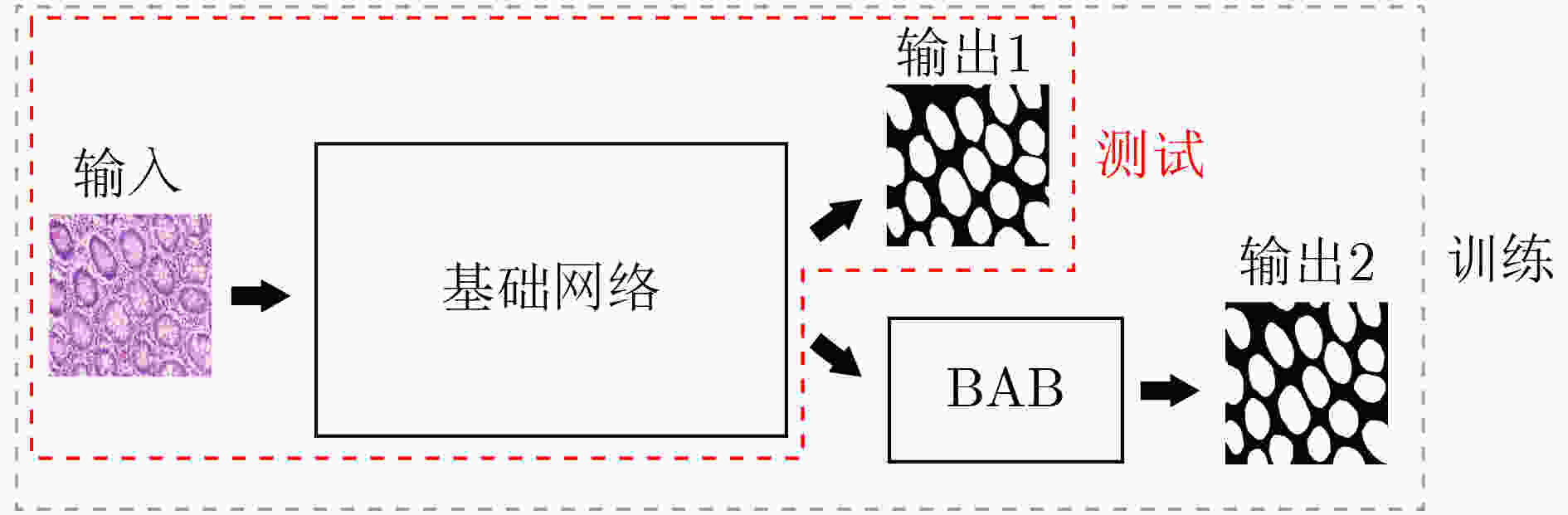
摘要: 针对传统医学图像分割网络存在边缘分割不清晰、缺失值大等问题,该文提出一种具有边缘增强特点的医学图像分割网络(AS-UNet)。利用掩膜边缘提取算法得到掩膜边缘图,在UNet扩张路径的最后3层引入结合多尺度特征图的边缘注意模块(BAB),并提出组合损失函数来提高分割精度;测试时通过舍弃BAB来减少参数。在3种不同类型的医学图像分割数据集Glas, DRIVE, ISIC2018上进行实验,与其他分割方法相比,AS-UNet分割性能较优。Abstract: A medical image segmentation network with boundary enhancement, named as the AS-UNet (Add-and-Subtract UNet), is proposed to solve the problems of traditional segmentation networks for medical images, such as unclear boundary segmentation and large missing value. The mask boundary image is obtained by using the mask boundary image extraction algorithm, and the Boundary Attention Block (BAB) with multi-scale feature maps is introduced into the last three layers of the UNet expansion path. Moreover, the combinatorial loss function is proposed to improve the segmentation accuracy. In testing, the BAB can be abandoned to reduce testing parameters. Comparisons with other segmentation methods on three different types of medical image segmentation datasets, Glas, DRIVE and ISIC2018 are provided, indicating that the segmentation performance of the AS-UNet is better.
-
表 1 不同模型在不同数据集上分割结果对比
方法 Glas DRIVE ISIC2018 参数量(M) Mean Dice F1值 Hausdorff距离 Mean Dice F1值 Hausdorff距离 Mean Dice F1值 Hausdorff距离 UNet 0.8620 0.9120 120.82 0.7403 0.8806 55.50 0.8684 0.8932 42.48 7.93 UNet++ 0.8679 0.9238 89.19 0.7545 0.8992 52.17 0.8693 0.9016 38.19 9.24 DRU-Net 0.8724 0.9131 128.09 0.7402 0.8939 95.23 0.8731 0.9050 41.22 3.57 KiU-Net 0.8668 0.9154 101.45 0.7436 0.8828 50.79 0.8667 0.9159 36.23 0.75 本文 0.8839 0.9341 89.02 0.7619 0.9070 44.61 0.8837 0.9223 34.95 7.94 表 2 消融实验
基础网络 对比
方法Glas DRIVE ISIC2018 参数量(M) Mean
DiceF1值 Hausdorff
距离Mean
DiceF1值 Hausdorff
距离Mean
DiceF1值 Hausdorff
距离UNet UNet 0.8620 0.9120 120.82 0.7403 0.8806 55.50 0.8684 0.8932 42.48 7.93 +BAB 0.8842 0.9340 90.11 0.7619 0.9071 44.90 0.8835 0.9223 34.77 8.95 +Sub 0.8839 0.9341 89.02 0.7619 0.9070 44.61 0.8837 0.9223 34.95 7.94 FCN FCN 0.7931 0.7171 135.12 0.6671 0.5863 59.12 0.8026 0.8015 50.30 9.31 +BAB 0.8175 0.7346 120.47 0.7038 0.6034 49.35 0.8294 0.8203 44.88 10.09 +Sub 0.8174 0.7346 121.33 0.7038 0.6032 49.81 0.8296 0.8201 44.95 9.31 表 3 不同注意力模块在不同数据集上的分割结果对比
BAB中注意力模块 Glas DRIVE ISIC2018 Mean
DiceF1值 Hausdorff
距离Mean
DiceF1值 Hausdorff
距离Mean
DiceF1值 Hausdorff
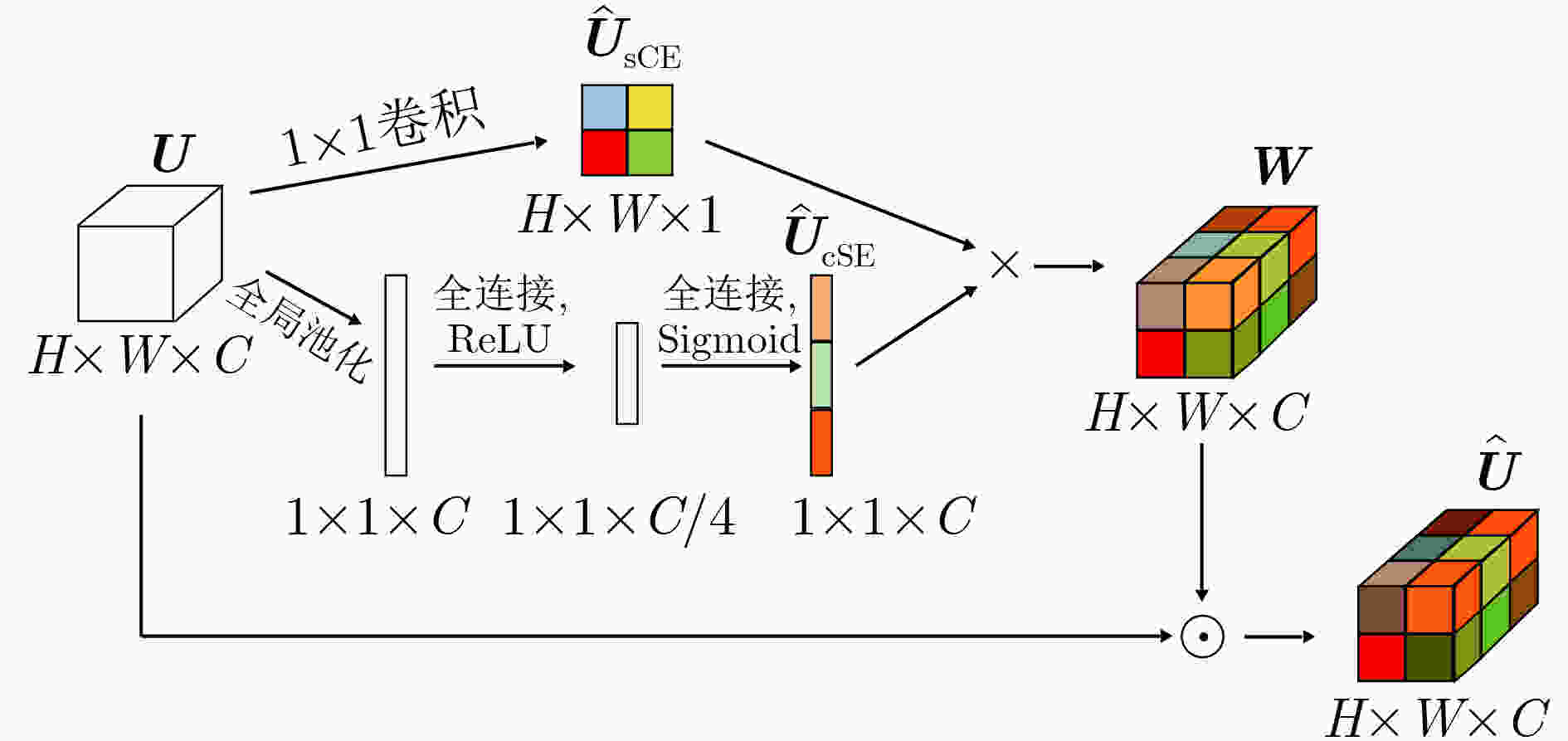
距离无 0.8768 0.8993 108.51 0.7535 0.8754 49.05 0.8799 0.9096 38.18 scSE 0.8803 0.9208 97.08 0.7595 0.8812 46.18 0.8812 0.9166 37.51 本文方法 0.8839 0.9341 89.02 0.7619 0.9070 44.61 0.8837 0.9223 34.95 表 4 不同损失函数在不同数据集上的分割结果对比
损失函数 Glas DRIVE ISIC2018 Mean
DiceF1值 Hausdorff
距离Mean
DiceF1值 Hausdorff
距离Mean
DiceF1值 Hausdorff
距离Dice 损失 0.8779 0.9250 90.19 0.7605 0.8891 45.02 0.8800 0.9195 35.30 Boundary损失 0.8648 0.9189 92.53 0.7518 0.8773 47.91 0.8777 0.9173 36.19 Dice + Boundary
损失0.8839 0.9341 89.02 0.7619 0.9070 44.61 0.8837 0.9223 34.95 -
[1] GENG Qichuan, ZHOU Zhong, and CAO Xiaochun. Survey of recent progress in semantic image segmentation with CNNs[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2018, 61(5): 051101. doi: 10.1007/s11432-017-9189-6 [2] ANWAR S M, MAJID M, QAYYUM A, et al. Medical image analysis using convolutional neural networks: A review[J]. Journal of Medical Systems, 2018, 42(11): 226. doi: 10.1007/s10916-018-1088-1 [3] 徐莹莹, 沈红斌. 基于模式识别的生物医学图像处理研究现状[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(1): 201–213. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190657XU Yingying and SHEN Hongbin. Review of research on biomedical image processing based on pattern recognition[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(1): 201–213. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190657 [4] RONNEBERGER O, FISCHER P, and BROX T. U-Net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]. The 18th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 2015: 234–241. [5] SHANKARANARAYANA S M, RAM K, MITRA K, et al. Joint optic disc and cup segmentation using fully convolutional and adversarial networks[C]. International Workshop on Ophthalmic Medical Image Analysis, Québec City, Canada, 2017: 168–176. [6] OKTAY O, SCHLEMPER J, LE FOLGOC L, et al. Attention U-Net: Learning where to look for the pancreas[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1804.03999.pdf, 2021. [7] ZHOU Zongwei, SIDDIQUEE M R, TAJBAKHSH N, et al. Unet++: Redesigning skip connections to exploit multiscale features in image segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2020, 39(6): 1856–1867. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2019.2959609 [8] JAFARI M, AUER D, FRANCIS S, et al. DRU-Net: An efficient deep convolutional neural network for medical image segmentation[C]. The 2020 IEEE 17th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging, Iowa City, USA, 2020: 1144–1148. [9] HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770–778. [10] HUANG Zehao and WANG Naiyan. Like what you like: Knowledge distill via neuron selectivity transfer[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1707.01219.pdf, 2021. [11] LI Ziqiang, PAN Hong, ZHU Yaping, et al. PGD-UNet: A position-guided deformable network for simultaneous segmentation of organs and tumors[C]. 2020 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, Glasgow, UK, 2020: 1–8. [12] KITRUNGROTSAKUL T, YUTARO I, LIN Lanfen, et al. Interactive deep refinement network for medical image segmentation[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/pdf/2006.15320.pdf, 2021. [13] ZHANG Zhijie, FU Huazhu, DAI Hang, et al. ET-Net: A Generic edge-aTtention guidance network for medical image segmentation[C]. The 22nd International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Shenzhen, China, 2019: 442–450. [14] VALANARASU J M J, SINDAGI V A, HACIHALILOGLU I, et al. KiU-Net: Towards accurate segmentation of biomedical images using over-complete representations[C]. The 23rd International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Lima, Peru, 2020: 363–373. [15] LEE H J, KIM J U, LEE S, et al. Structure boundary preserving segmentation for medical image with ambiguous boundary[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 4816–4825. [16] CHU Jiajia, CHEN Yajie, ZHOU Wei, et al. Pay more attention to discontinuity for medical image segmentation[C]. The 23rd International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Lima, Peru, 2020: 166–175. [17] BAHETI B, INNANI S, GAJRE S, et al. Eff-UNet: A novel architecture for semantic segmentation in unstructured environment[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Seattle, USA, 2020: 1473–1481. [18] TREBING K, STAǸCZYK T, and MEHRKANOON S. SmaAT-UNet: Precipitation nowcasting using a small attention-UNet architecture[J]. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2021, 145: 178–186. doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2021.01.036 [19] QAMAR S, JIN Hai, ZHENG Ran, et al. A variant form of 3D-UNet for infant brain segmentation[J]. Future Generation Computer Systems, 2020, 108: 613–623. doi: 10.1016/j.future.2019.11.021 [20] GADOSEY P K, LI Yujian, AGYEKUM E A, et al. SD-UNet: Stripping down U-Net for segmentation of biomedical images on platforms with low computational budgets[J]. Diagnostics, 2020, 10(2): 110. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics10020110 [21] SUN J, DARBEHANI F, ZAIDI M, et al. SAUNet: Shape attentive U-Net for interpretable medical image segmentation[C]. The 23rd International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Lima, Peru, 2020: 797–806. [22] TAKIKAWA T, ACUNA D, JAMPANI V, et al. Gated-SCNN: Gated shape CNNS for semantic segmentation[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea (South), 2019: 5228–5237. [23] HEIDLER K, MOU Lichao, BAUMHOER C, et al. HED-UNet: Combined segmentation and edge detection for monitoring the Antarctic coastline[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.01849v1.pdf, 2021. [24] JADON S. A survey of loss functions for semantic segmentation[C]. 2020 IEEE Conference on Computational Intelligence in Bioinformatics and Computational Biology, Via del Mar, Chile, 2020: 1–7. [25] KERVADEC H, BOUCHTIBA J, DESROSIERS C, et al. Boundary loss for highly unbalanced segmentation[J]. Medical Image Analysis, 2021, 67: 101851. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2020.101851 [26] ROY A G, NAVAB N, and WACHINGER C. Concurrent spatial and channel ‘squeeze & excitation’ in fully convolutional networks[C]. The 21st International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Granada, Spain, 2018: 421–429. [27] CODELLA N, ROTEMBERG V, TSCHANDL P, et al. Skin lesion analysis toward melanoma detection 2018: A challenge hosted by the international skin imaging collaboration (ISIC)[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1902.03368.pdf, 2021. [28] TSCHANDL P, ROSENDAHL C, and KITTLER H. The HAM10000 dataset, a large collection of multi-source dermatoscopic images of common pigmented skin lesions[J]. Scientific Data, 2018, 5: 180161. doi: 10.1038/sdata.2018.161 [29] MILLETARI F, NAVAB N, and AHMADI S A. V-Net: Fully convolutional neural networks for volumetric medical image segmentation[C]. The 2016 4th International Conference on 3D Vision, Stanford, USA, 2016: 565–571. [30] ATTOUCH H, LUCCHETTI R, and WETS R J B. The topology of the ρ-hausdorff distance[J]. Annali di Matematica Pura ed Applicata, 1991, 160(1): 303–320. doi: 10.1007/BF01764131 -





 下载:
下载: